July 07 , 2022.
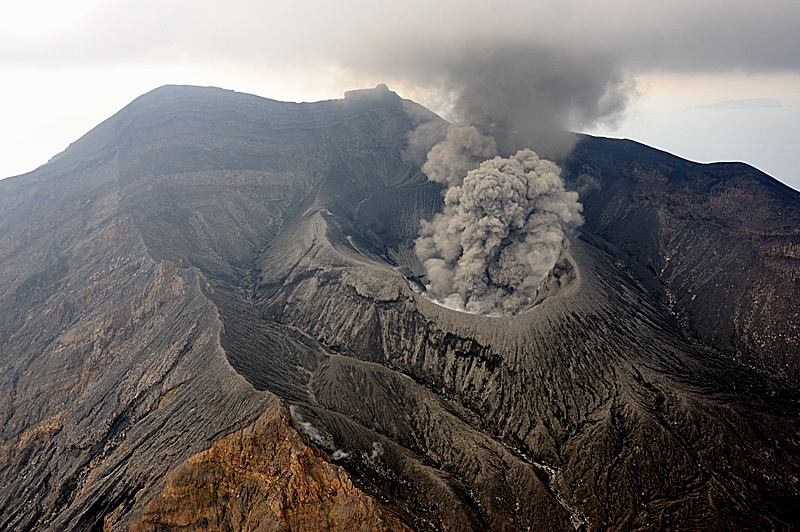
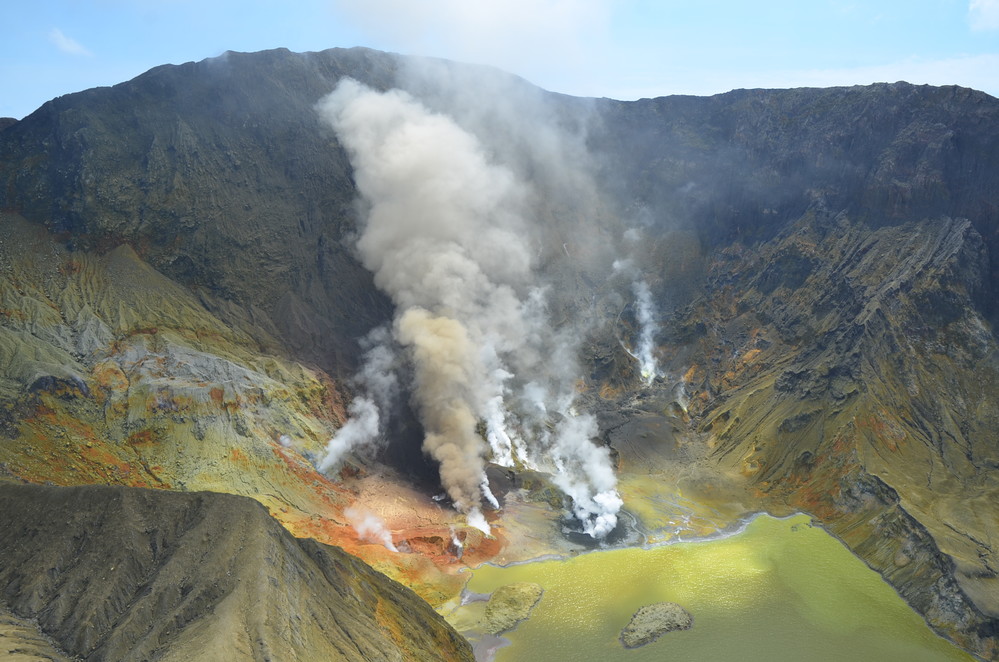
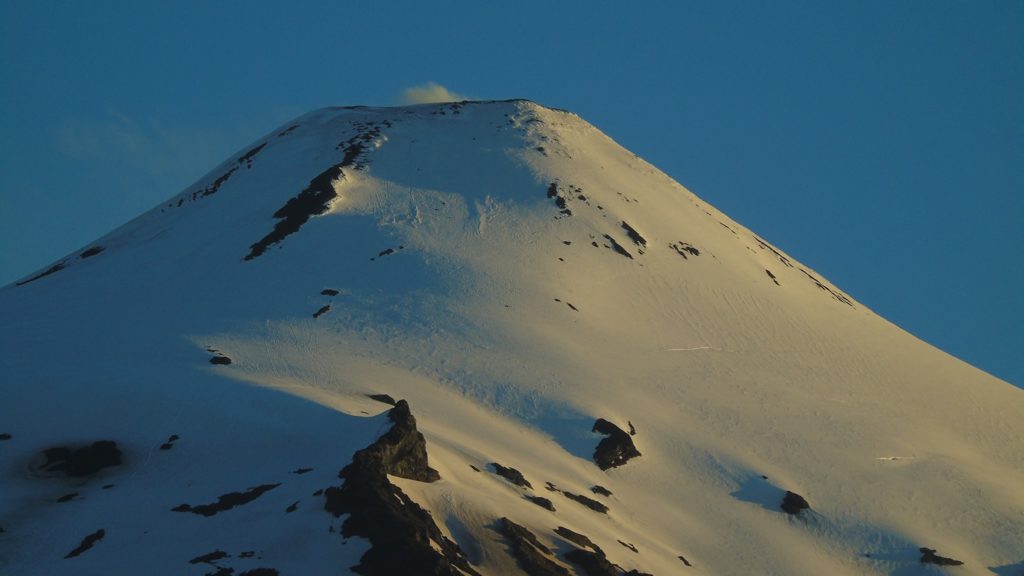
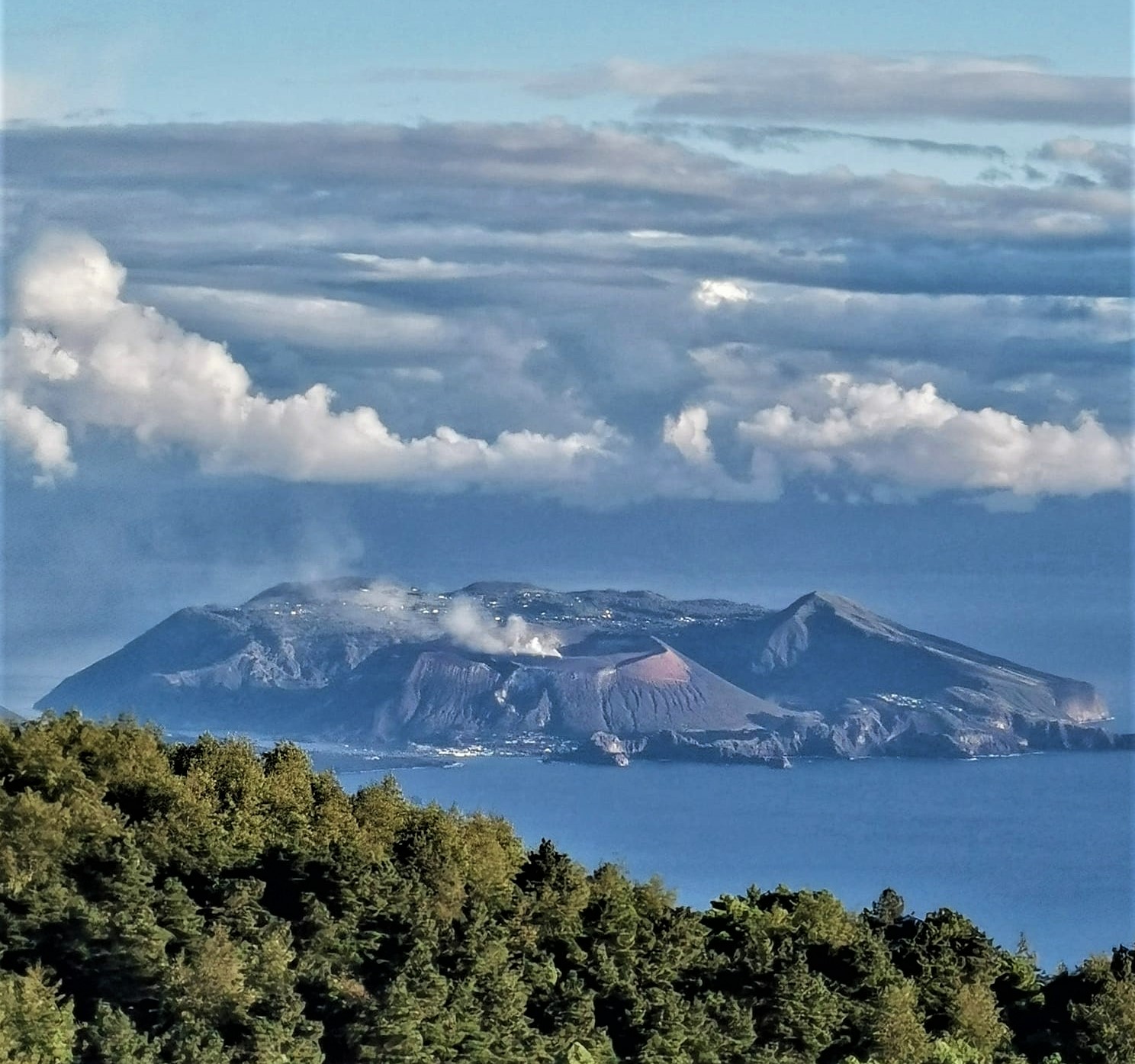
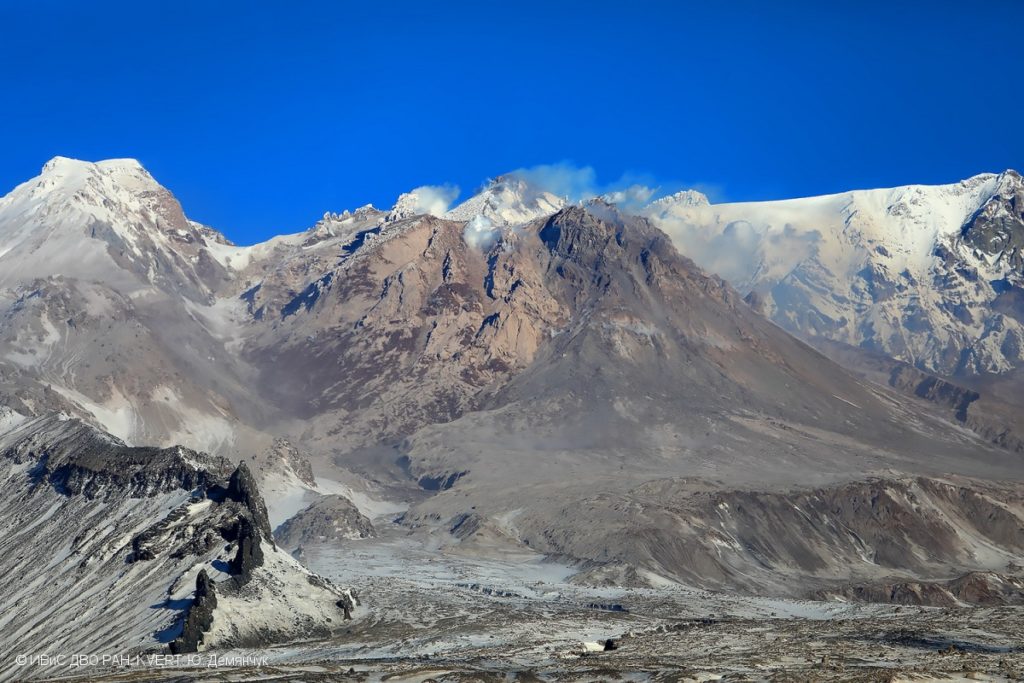
Italy , Vulcano :
WEEKLY BULLETIN, from June 27, 2022 to July 03, 2022. (issue date July 05, 2022)
ACTIVITY STATUS SUMMARY
In the light of the surveillance data, it is highlighted:
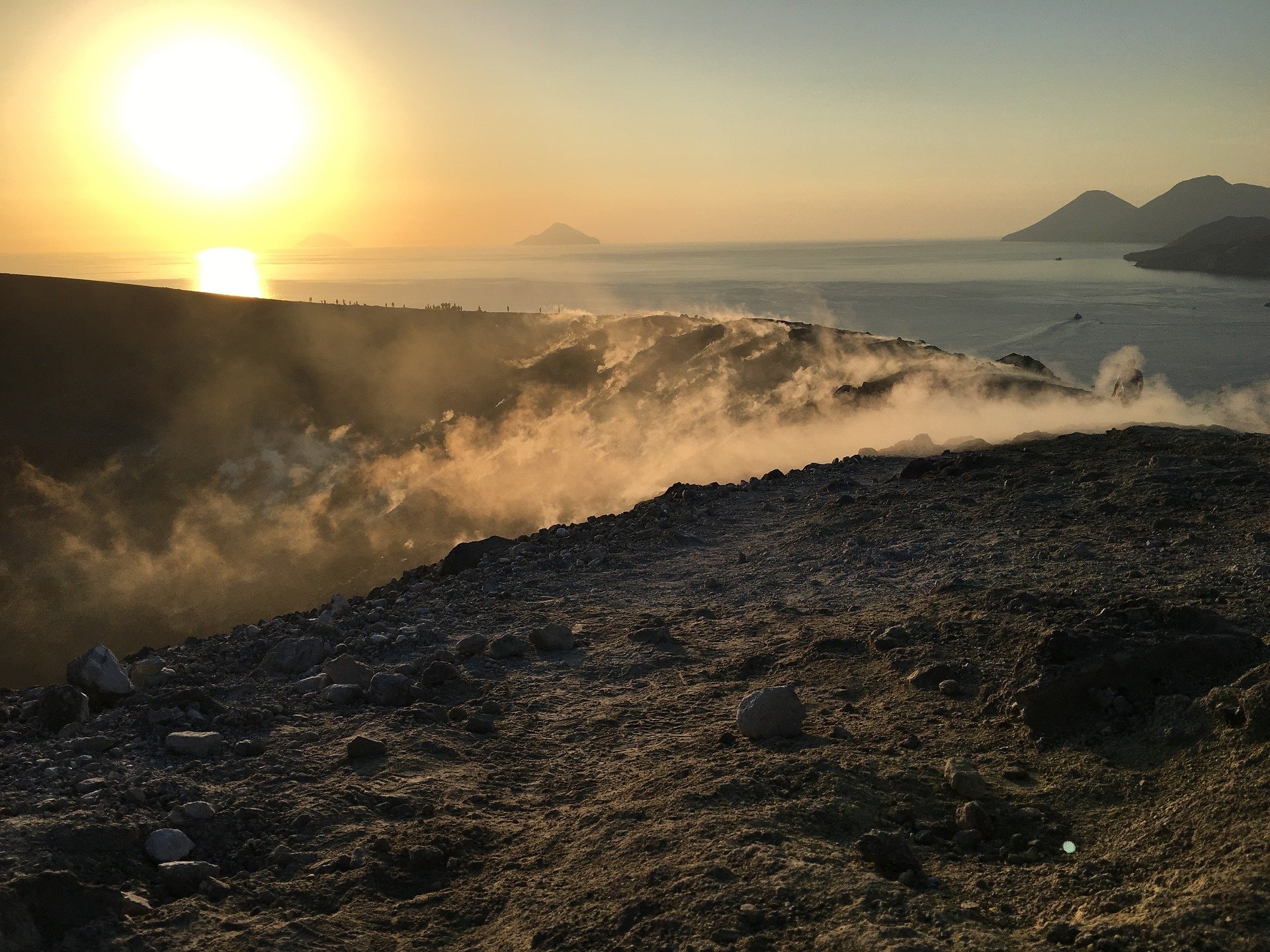
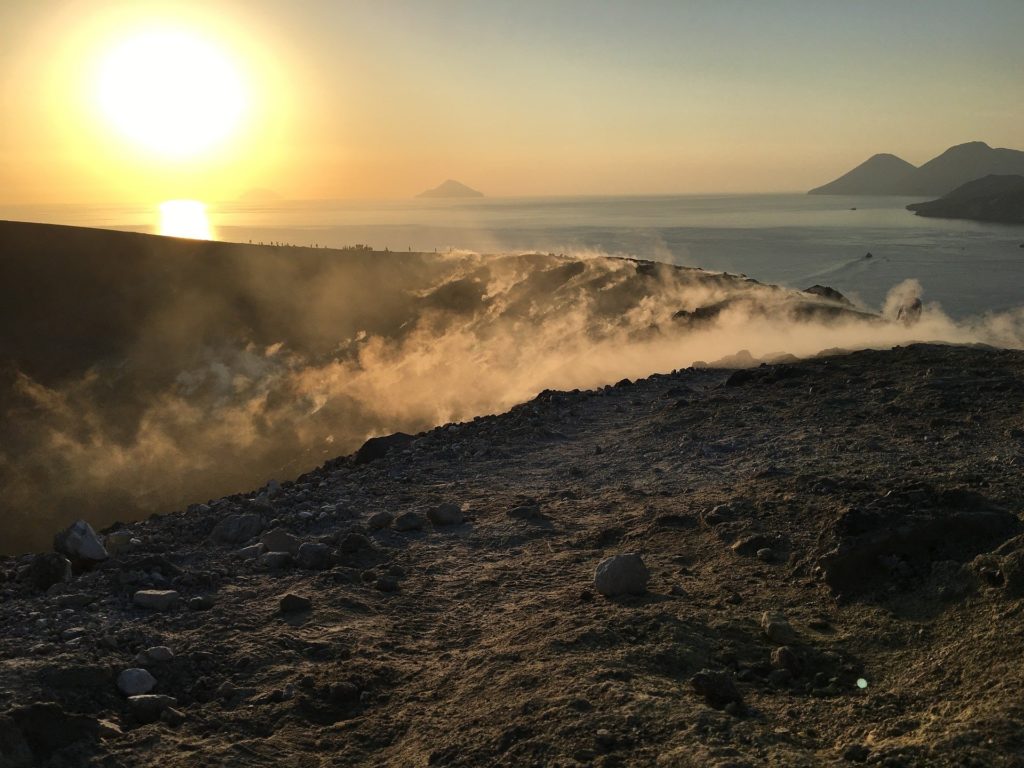
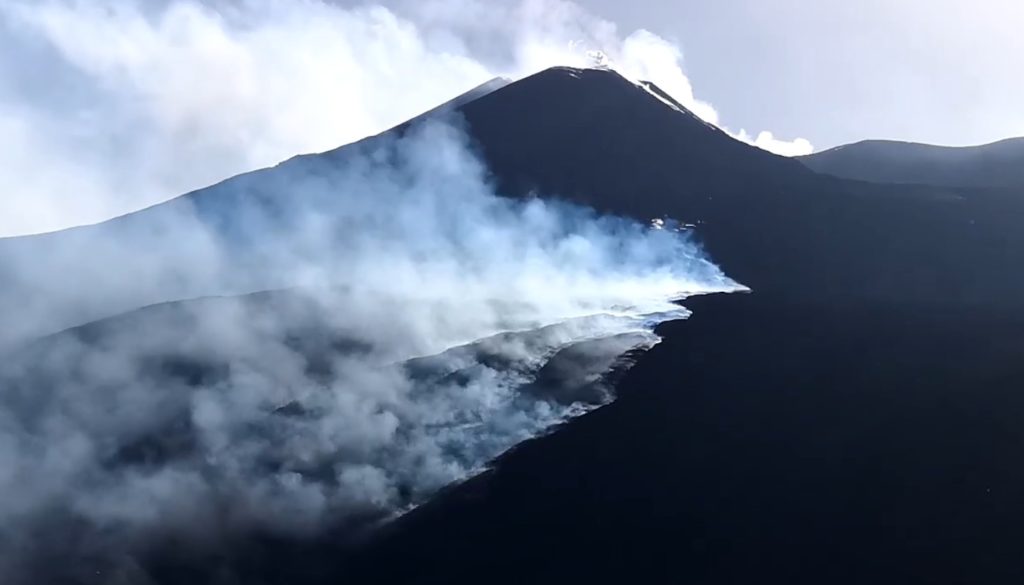
1) Temperature of the crater fumaroles: The temperatures at the edge of the crater remain stable at high values.
2) CO2 fluxes in the crater area: During the last week, CO2 fluxes in the summit area maintain constant values, around 9017 g/m2/g.
3) SO2 flux in the crater area: SO2 flux at a medium-high level and decreasing
4) Geochemistry of fumarolic gases: There are no updates
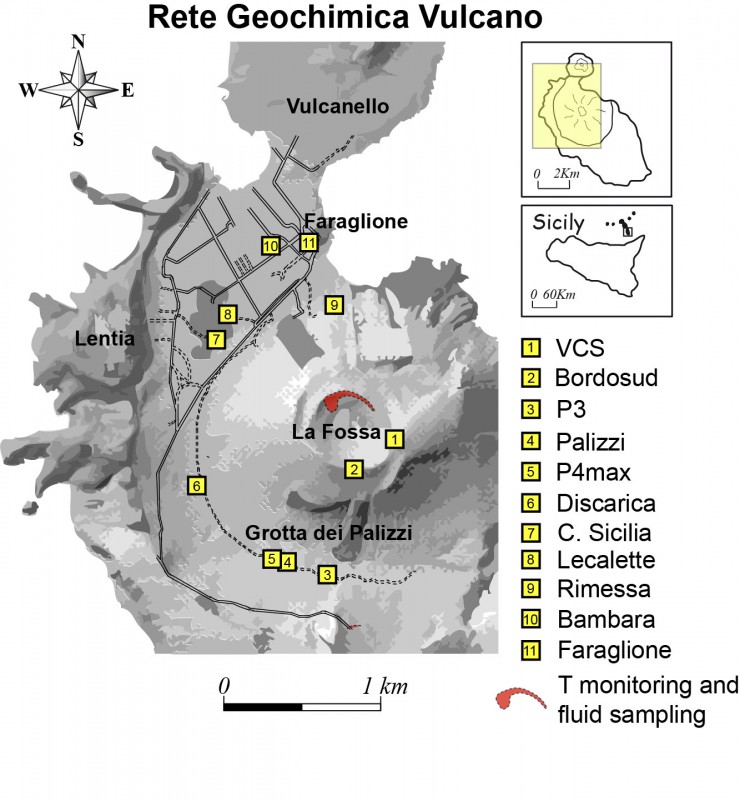
5) CO2 fluxes at the base of the La Fossa cone and in the Vulcano Porto area: The CO2 fluxes recorded in the C. Sicilia, Rimessa and P4max sites continue to show higher values than the background noise, while that in the Faraglione site, there are values close to the background level.
6) Geochemistry of thermal aquifers: The level values measured in the Bambara well do not show any significant variations. Conductivity values remain constant at medium-high levels.
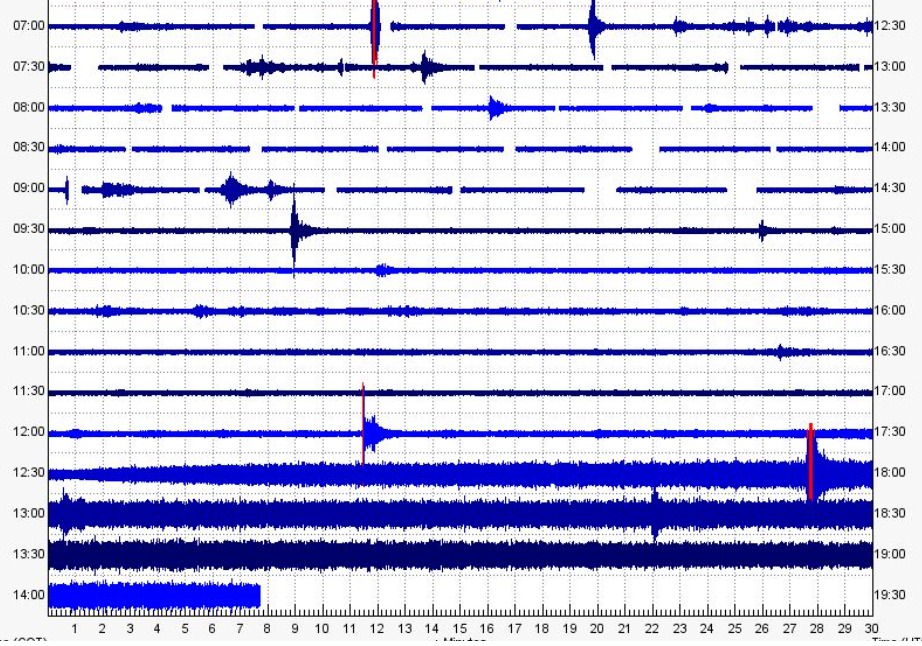
7) Local seismicity: low seismic activity both for high frequency events and for VLPs
8) Regional seismicity: No regional seismic activity.
9) Deformations – GNSS: The network of GNSS stations has not recorded any significant changes.
10) Deformations – Inclinometry: The inclinometric network has not recorded any significant changes.
11) Other observations: Gravimetry: No significant variation was recorded.
CRATER FUMEROLES TEMPERATURE:
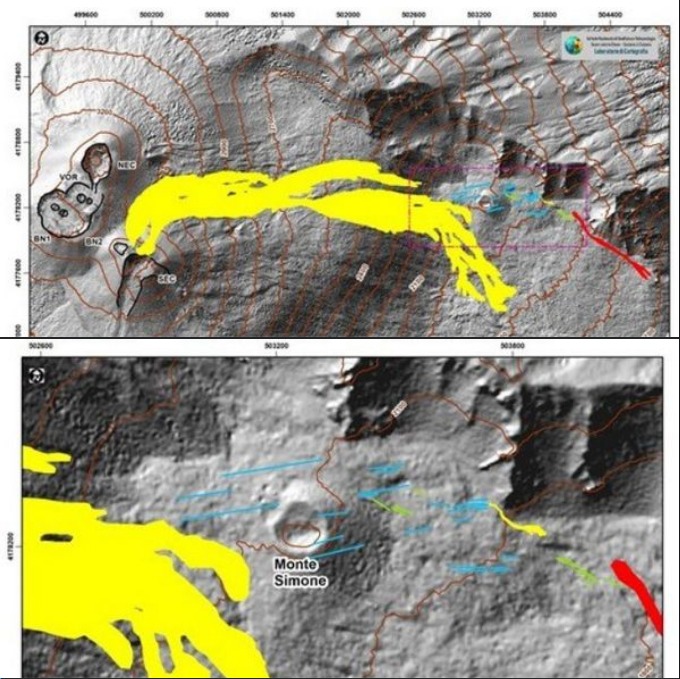
Along the upper edge, the maximum emission temperature has extremely stable values, with an hourly maximum of 380°C and a weekly average of 379°C (T1). The fumarolic field presents homogeneous emission temperatures along the summit fracture line, confirming a thermal anomaly still maintained by a stable vapor flow.
The thermal signal from the T3 sensor (fumarole F5) overlaps the temperatures recorded in T2 (fumarole F5AT) while the site on the interior side after June 6 maintains its regular trend
(Dtemperature/Dtempo = 0.0035°C/day) but shows frequent signal disturbances and numerous invalid data (Tmax = 112°C; last valid data July 2h7:00).
CO2 FLOW AT THE BASE OF THE CONE DE LA FOSSA AND IN THE VULCANO PORTO AREA:
The CO2 fluxes at the base of the crater in the C. Sicilia site show values higher than the background level, although in sharp decrease compared to the period November-December 2021; the Rimessa site recorded average values, stable compared to last week, above the background level; the P4max site displays medium-high values, which fluctuate cyclically; in the Faraglione site, there are values close to the background level.
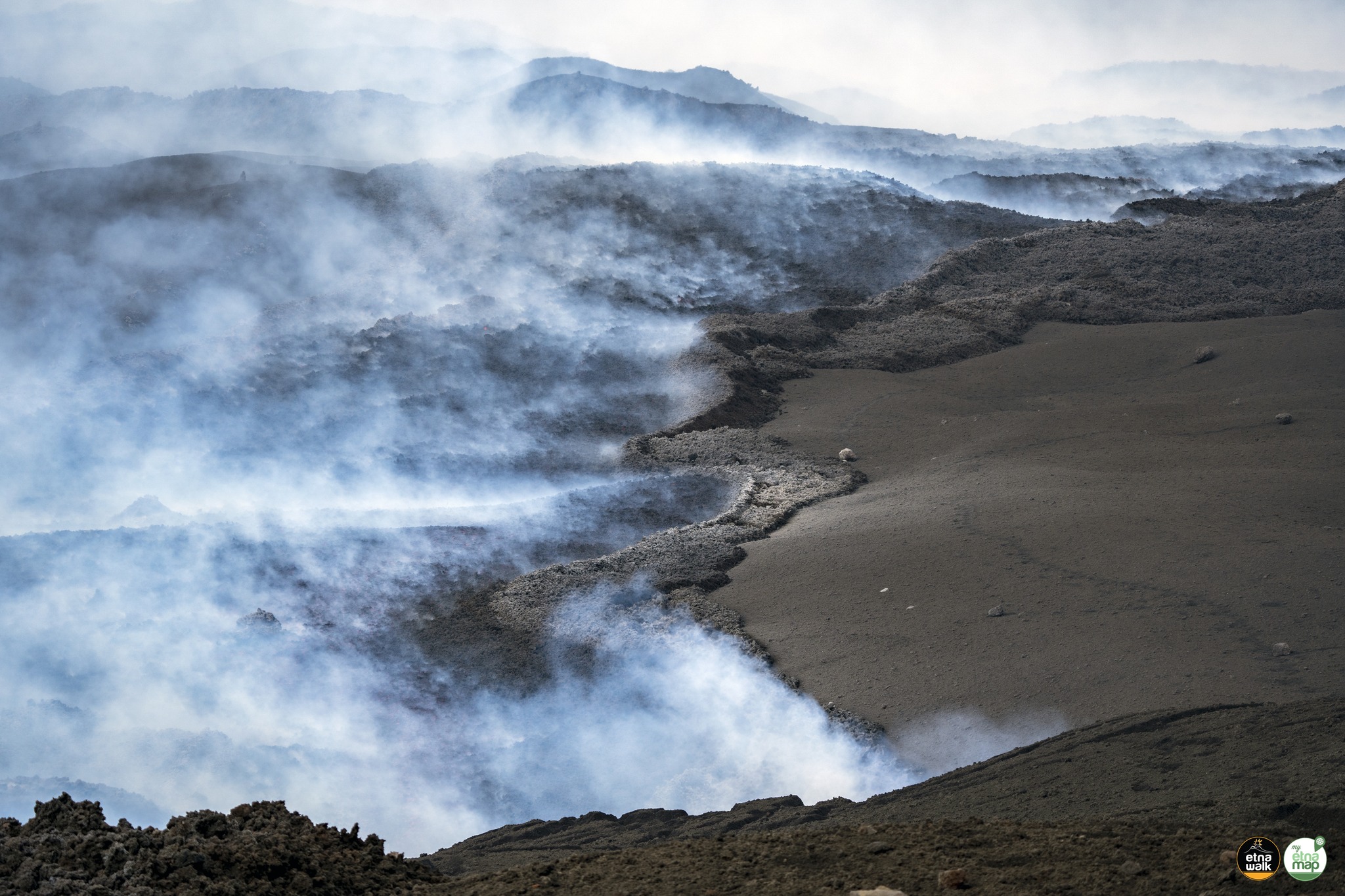
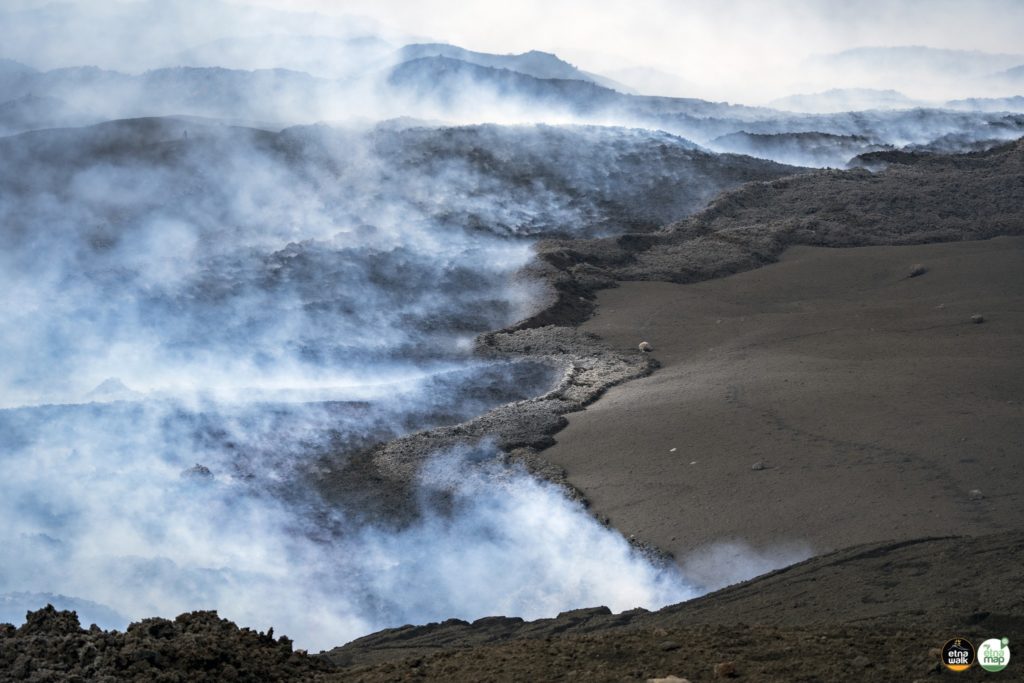
Source : INGV.
Photo : Ketty Zambuto via Vulcano Trekking.
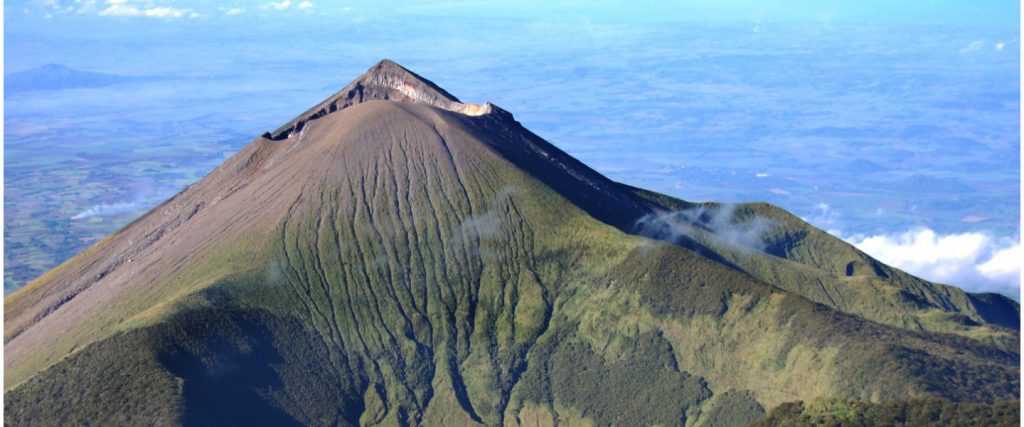
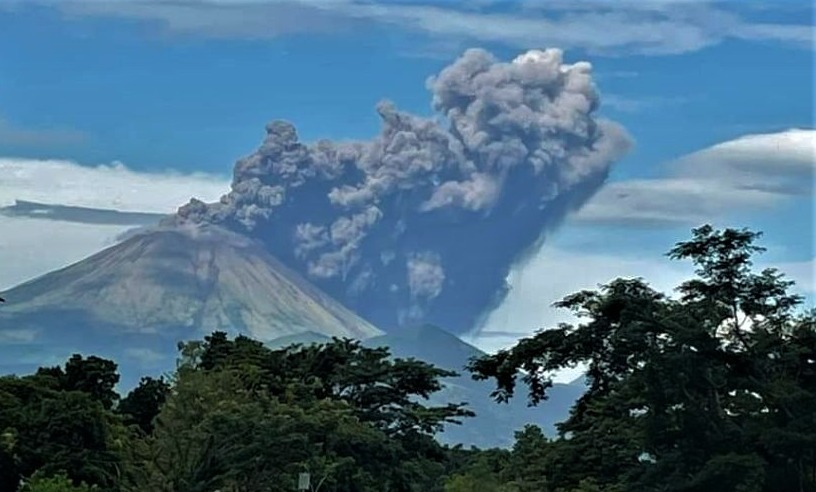
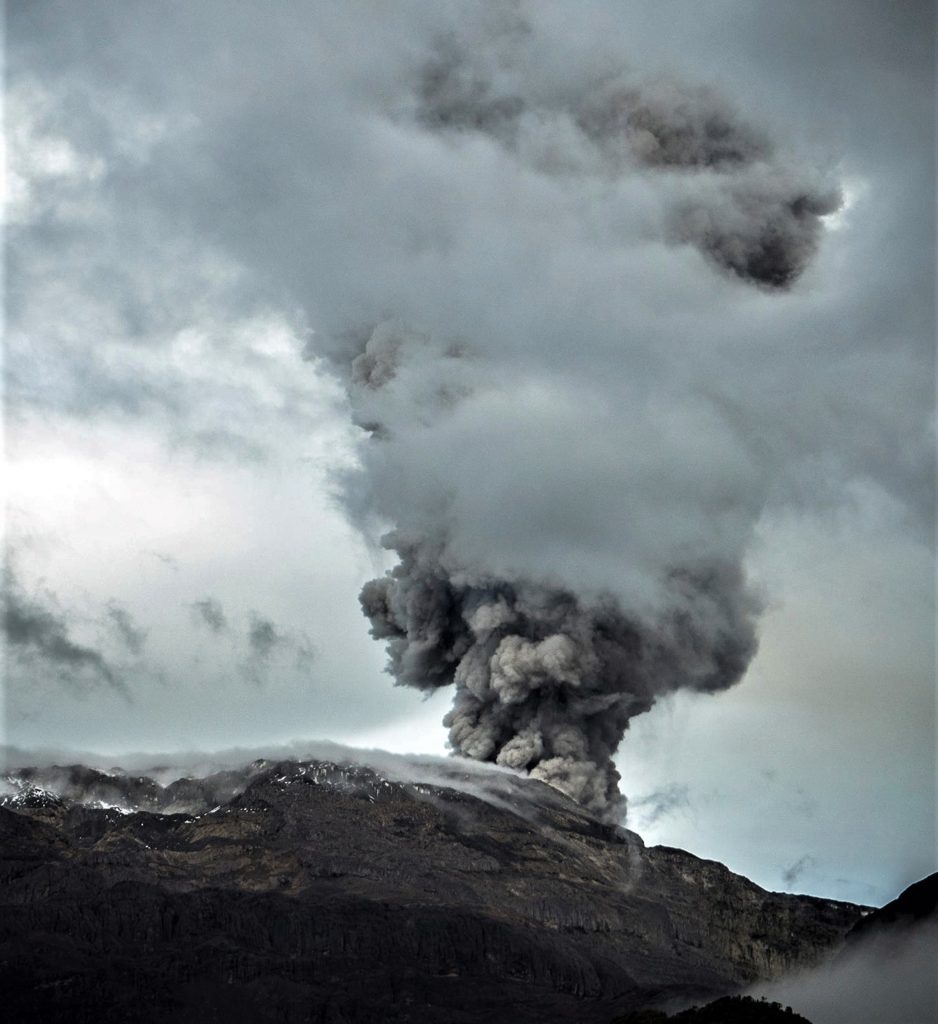
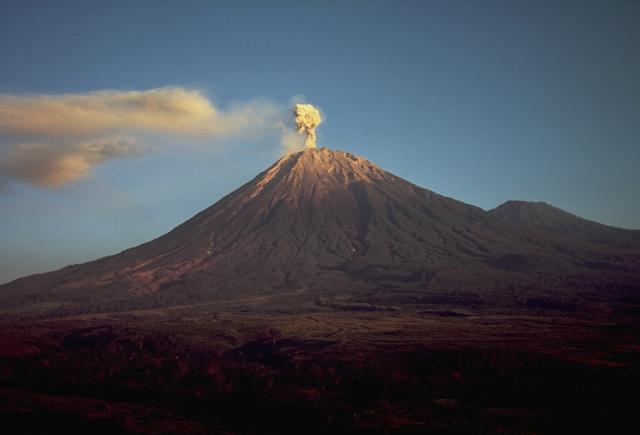
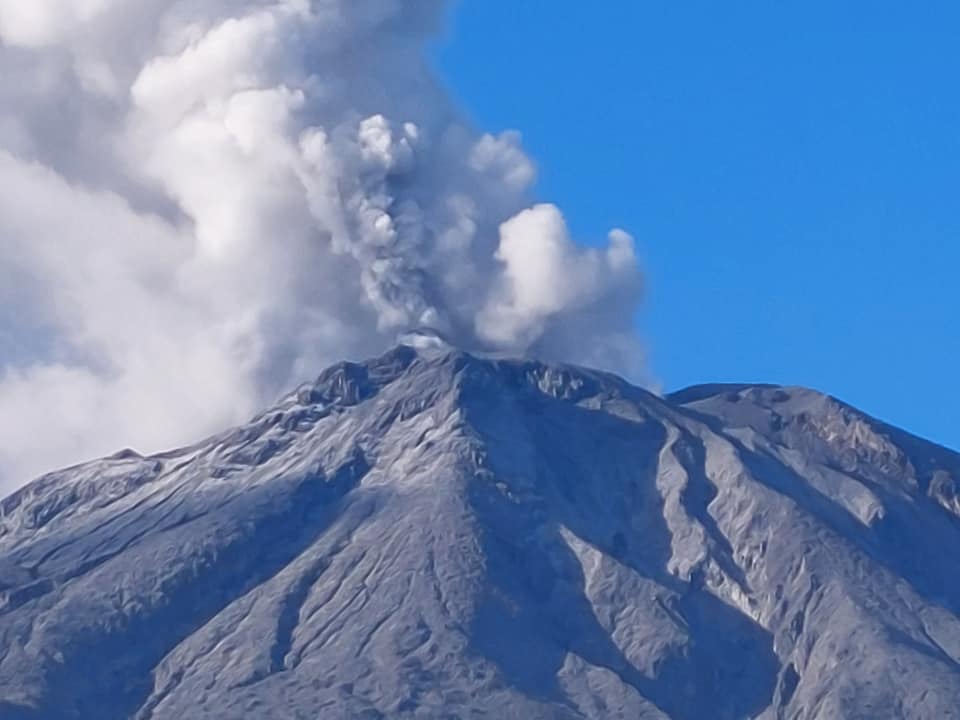
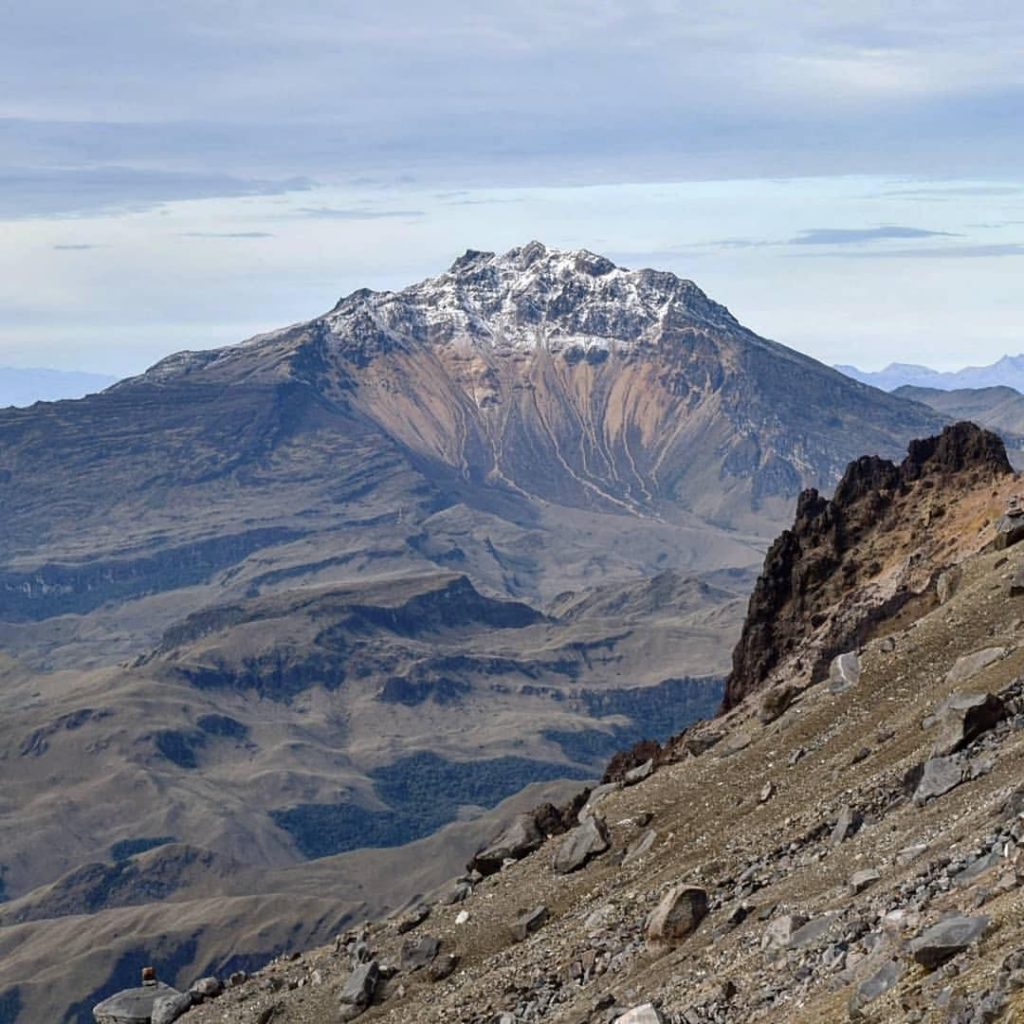
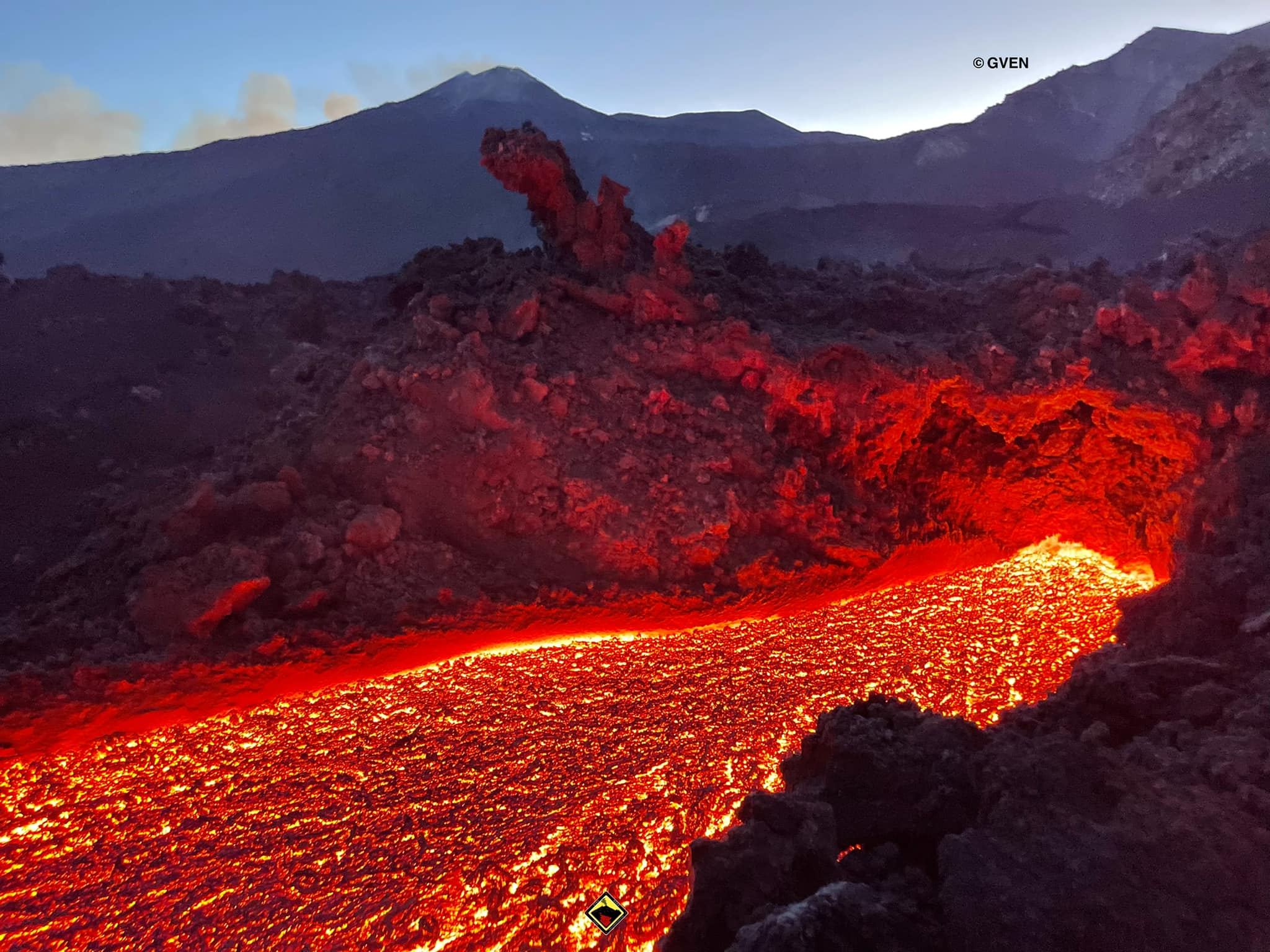
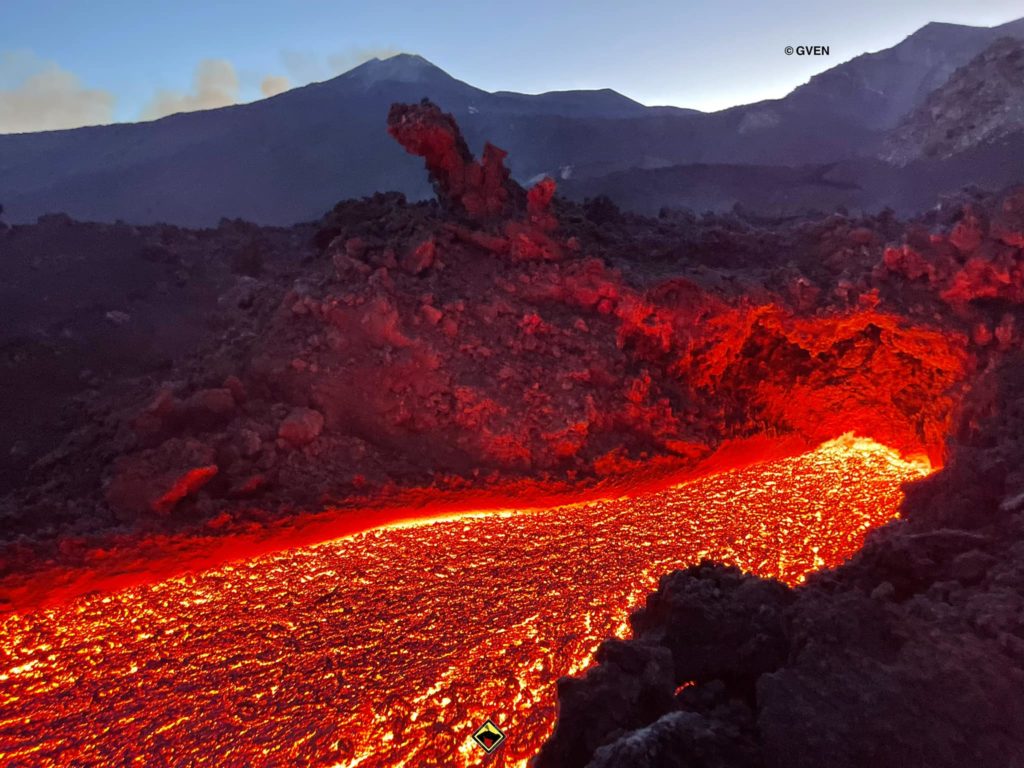
Guatemala , Fuego :
Weather conditions: Clear weather
Wind: East
Precipitation: 0.0 mm
Activity:
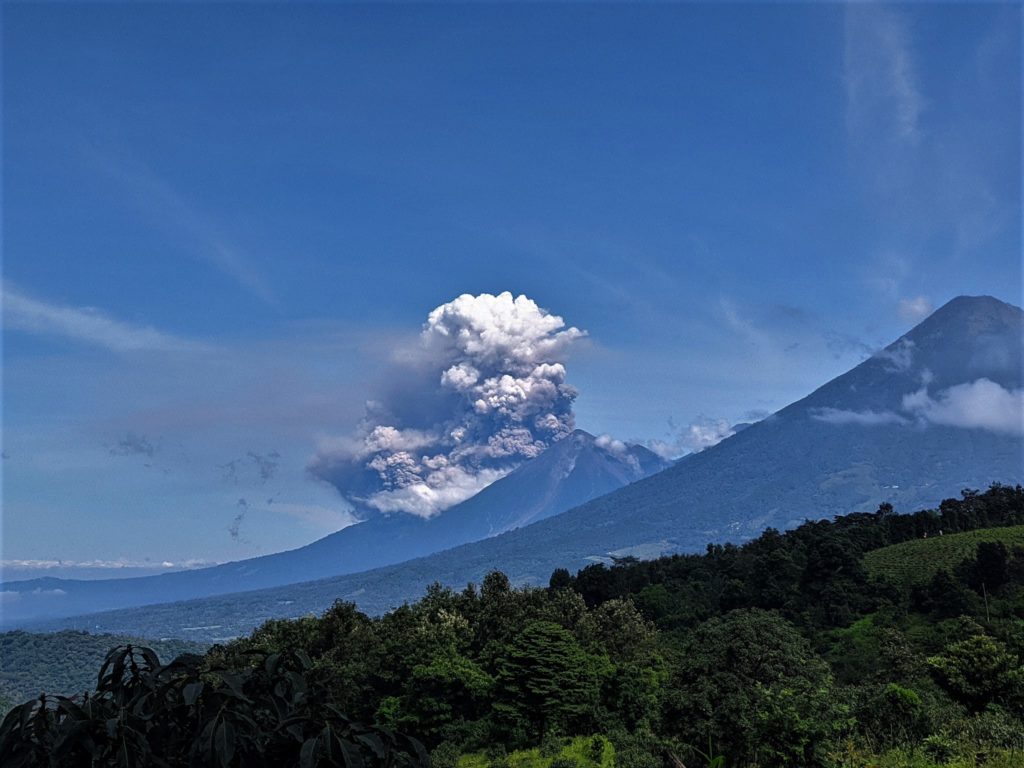
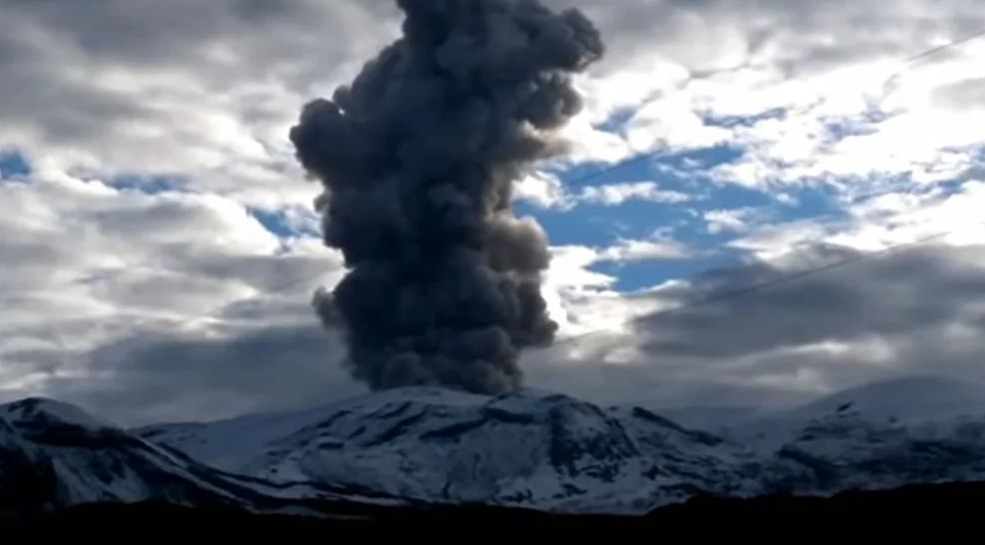
The Fuego OVFGO volcano observatory reports a weak white fumarole at a height of 4,500 meters above sea level which is spreading west and southwest. 5 to 8 explosions per hour of weak and moderate characteristics are reported, these explosions generate columns of gas and ash with a height of 4,500 to 4,900 meters above sea level (14,764 to 16,404 feet) which extend to west and south-west of the volcano over a distance of 15 kilometres.
These explosions are accompanied by low to moderate rumblings with a weak shock wave. At night and early in the morning, an incandescent pulse was observed 200 meters above the crater. Weak to moderate avalanches are also recorded around the crater and towards the ravines of Ceniza, Taniluyá, Santa Teresa, Honda and Las Lajas. A locomotive noise lasting 1 to 3 minutes is reported. Ash falls are reported at Panimaché I, Panimaché II, Morelia, Santa Sofía, Finca Palo Verde, Sangre de Cristo and others in that direction. A lava flow is reported in the direction of the Ceniza ravine with a length of 100 meters, avalanches originate at the front of this flow.
On July 4, pyroclastic flows traveled 6 km in the Ceniza watershed and generated ash plumes that rose 5 km.
Source : Insivumeh, GVP.
Photo : Francisco via Objectif volcans.
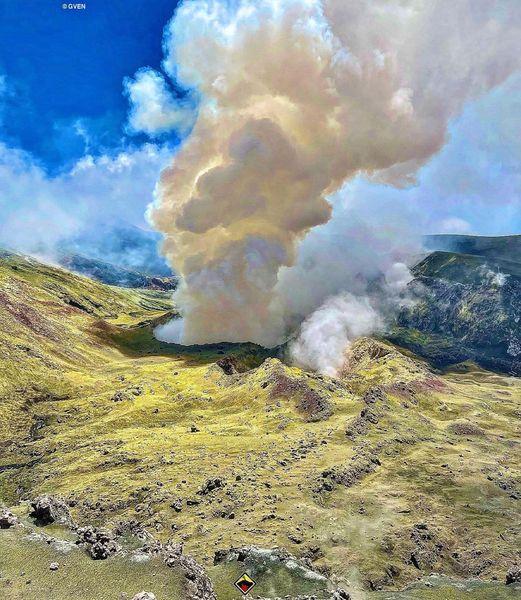
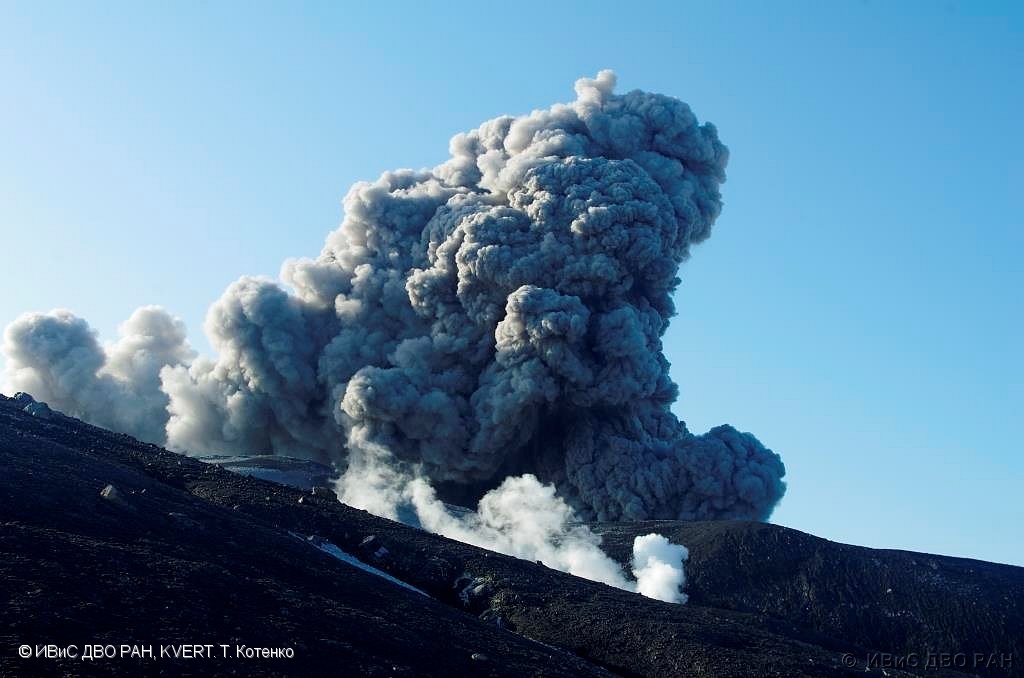
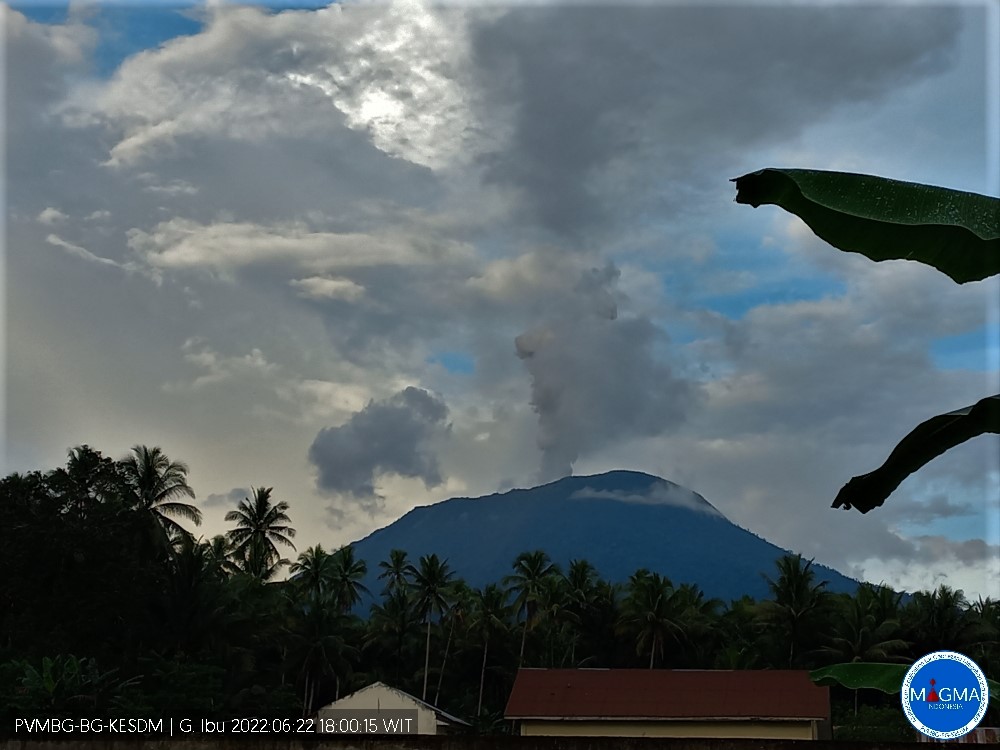
Russia / Kuril Islands , Ebeko :
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION (VONA)
Issued: July 07 , 2022 .
Volcano: Ebeko (CAVW #290380)
Current aviation colour code: ORANGE
Previous aviation colour code: orange
Source: KVERT
Notice Number: 2022-63
Volcano Location: N 50 deg 41 min E 156 deg 0 min
Area: Northern Kuriles, Russia
Summit Elevation: 1156 m (3791.68 ft)
Volcanic Activity Summary:
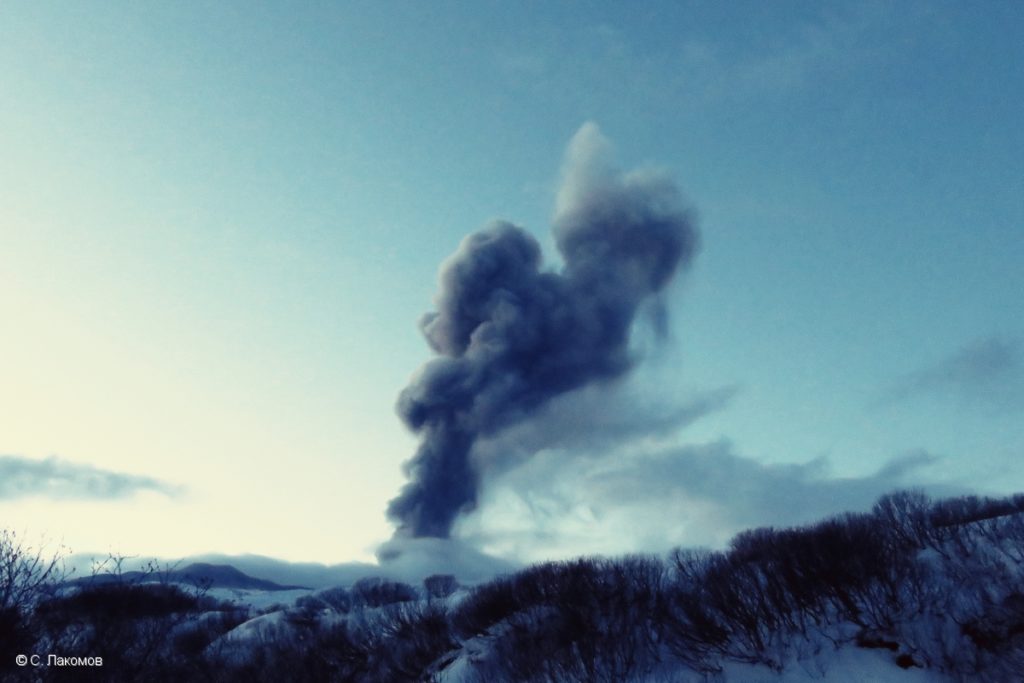
A moderate eruptive activity of the volcano continues. According to visual data by volcanologists from Severo-Kurilsk, an explosion sent ash up to 1.8 km a.s.l., an ash cloud is drifting to the south-east of the volcano.
A moderate eruptive activity of the volcano continues. Ash explosions up to 6 km (19,700 ft) a.s.l. could occur at any time. Ongoing activity could affect low-flying aircraft and airport of Severo-Kurilsk.
Volcanic cloud height:
1800 m (5904 ft) AMSL Time and method of ash plume/cloud height determination: 20220707/0108Z – Visual data
Other volcanic cloud information:
Distance of ash plume/cloud of the volcano: 5 km (3 mi)
Direction of drift of ash plume/cloud of the volcano: ESE / azimuth 120 deg
Time and method of ash plume/cloud determination: 20220707/0108Z – Visual data
Source : Kvert.
Photo : S. Lakomov
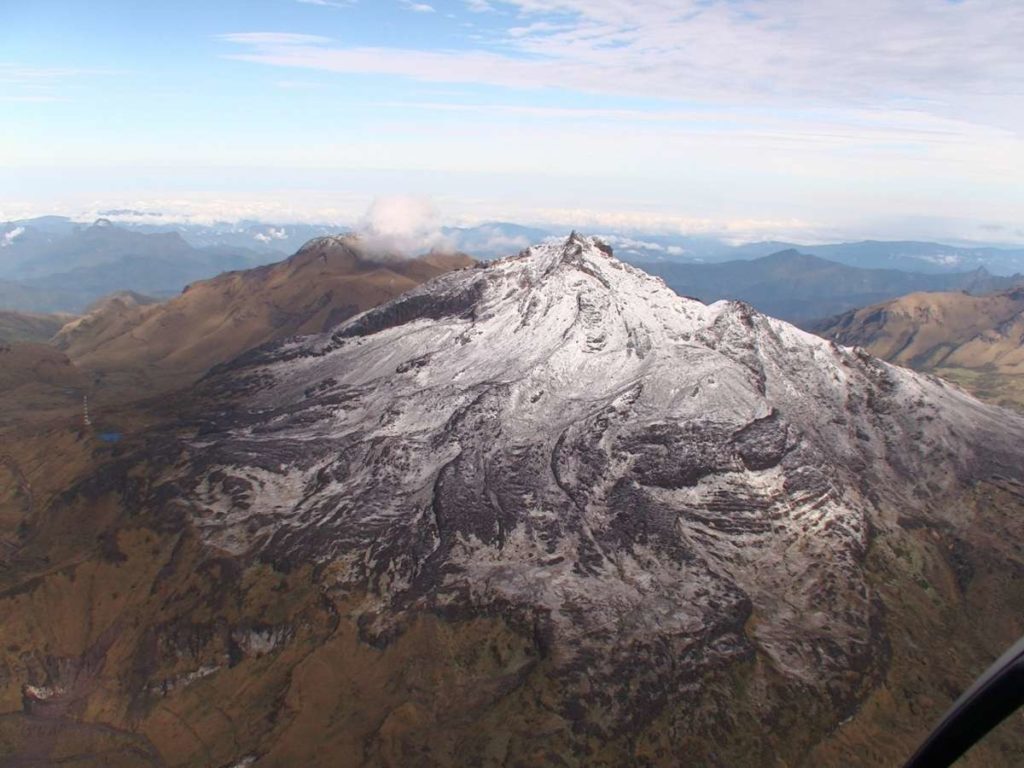
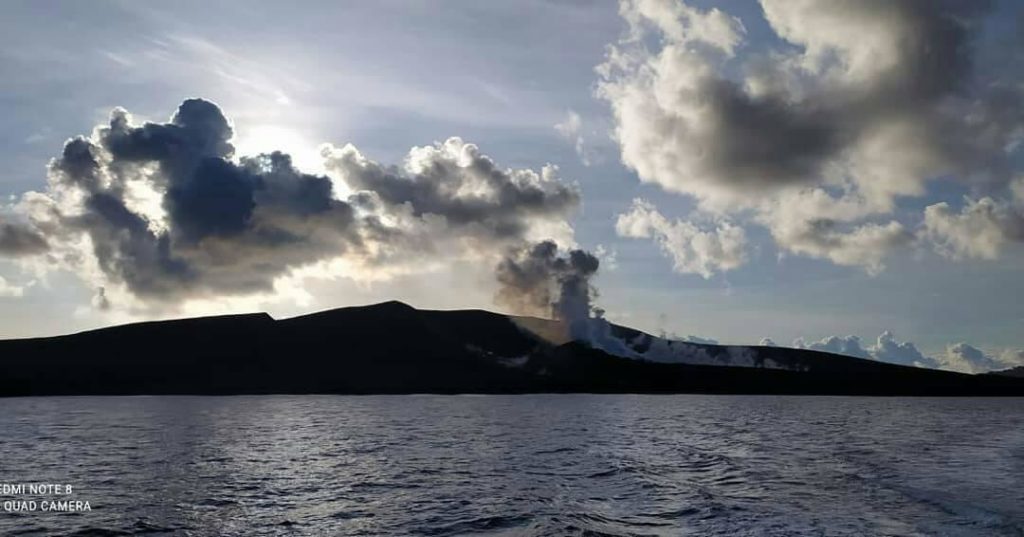
Colombia , Chiles / Cerro Negro :
Weekly activity bulletin of the Chiles and Cerro Negro volcanoes.
Volcano activity continues at YELLOW LEVEL ■ (III): CHANGES IN THE BEHAVIOR OF VOLCANIC ACTIVITY.
From monitoring the activity of the CHILES AND CERRO NEGRO VOLCANOES, the COLOMBIAN GEOLOGICAL SERVICE (SGC) reports that:
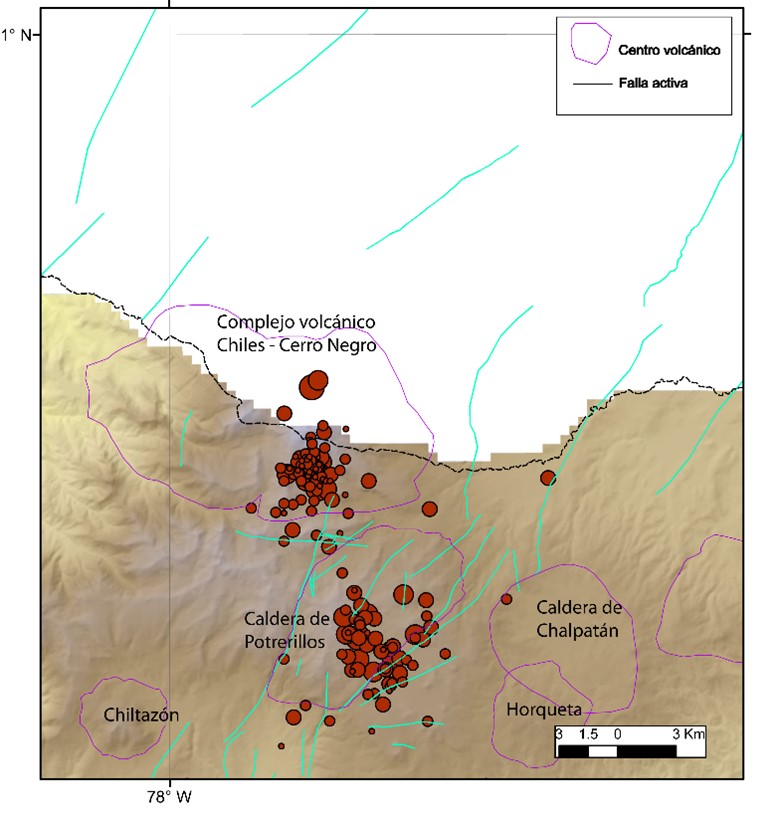
For the period evaluated between June 28 and July 4, 2022, the seismic swarm process started on May 27, 2022 was maintained, showing fluctuations, both in the number and in the daily energy of earthquakes. During this week, 9912 events were recorded, with the predominance of earthquakes associated with a fracture of the cortical material inside the volcano, which were located mainly near the summit and south of the Chiles volcano, with epicentral distances up to 3.5 km. and depths less than 6 km from its summit (4700 m).
10 of these events had local magnitudes (ML) greater than 2.0, of which 1 was reported as felt within the volcanic influence zone, recorded on June 29 at 1:06 p.m. with a local magnitude of 3.5. Also today, July 5, an earthquake reported as felt was recorded at 1:00 a.m., with a local magnitude of M3.0.
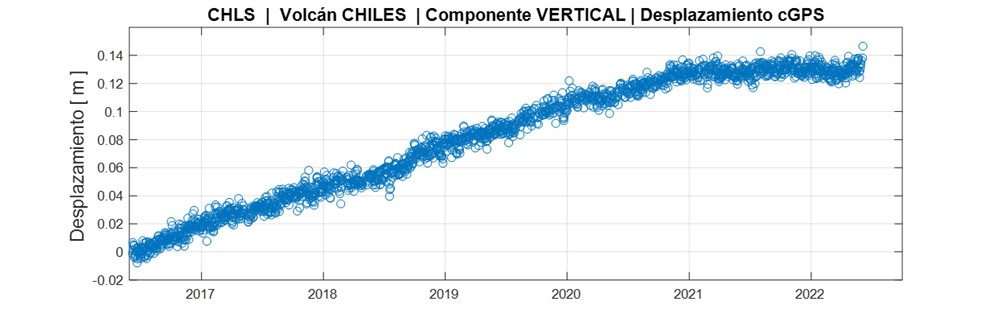
On the other hand, some sensors that are part of the deformation network show low amplitude changes. No manifestation of surface activity has been observed and the other volcanic monitoring parameters remain stable.
Source : SGC
Photo : hablemosdevolcanes.com
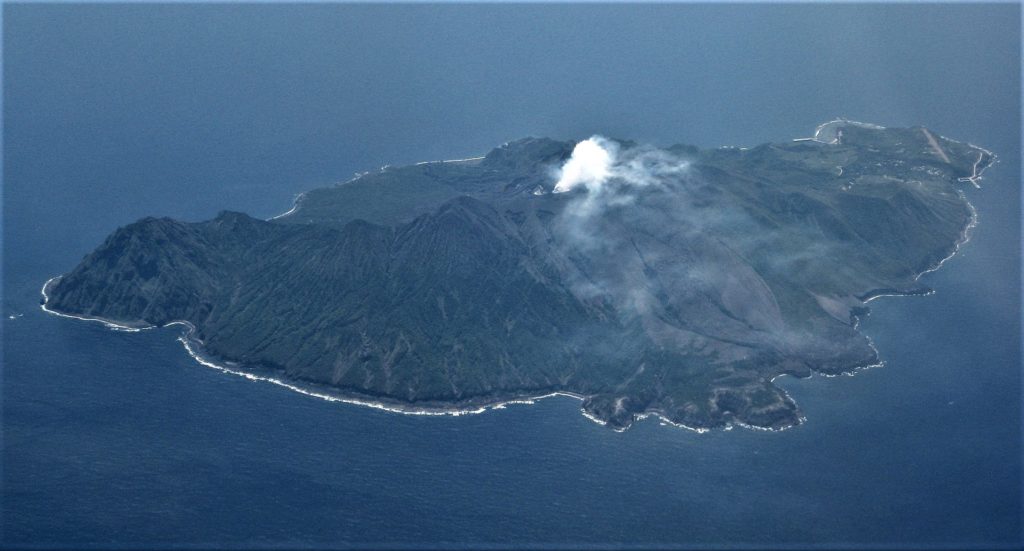
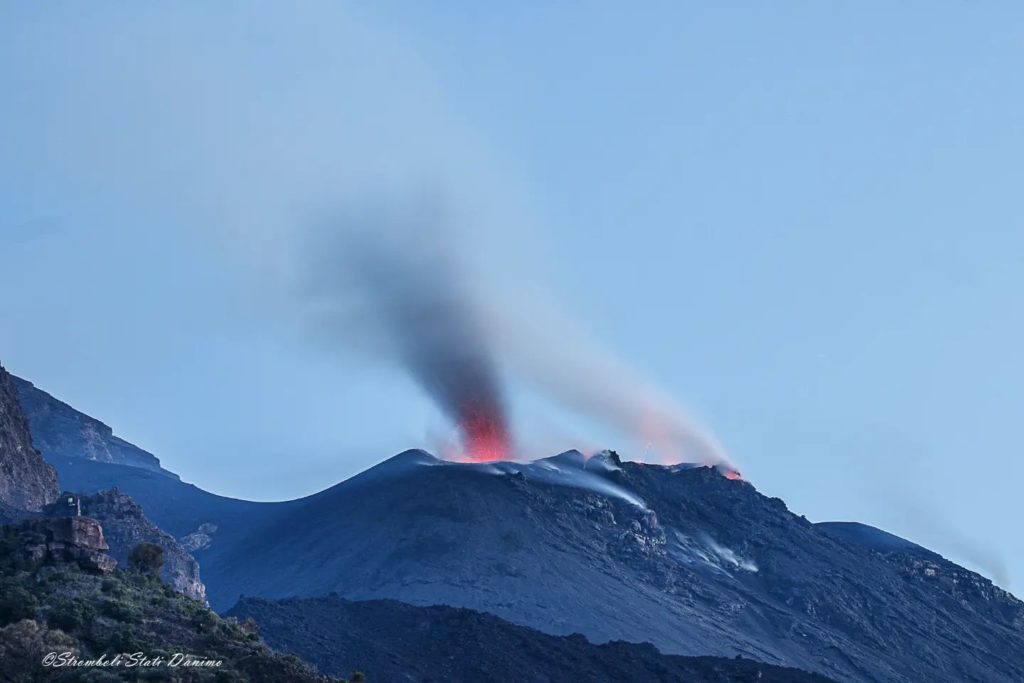
Japan , Suwanosejima :
JMA reported that the eruption at Suwanosejima’s Ontake Crater continued during 27 June-4 July and crater incandescence was visible nightly. Emissions rose as high as 1 km above the crater rim and tephra was ejected 200-600 m from the vent. The Alert Level remained at 3 and the public was warned to stay 2 km away from the crater.
The 8-km-long, spindle-shaped island of Suwanosejima in the northern Ryukyu Islands consists of an andesitic stratovolcano with two historically active summit craters. The summit is truncated by a large breached crater extending to the sea on the east flank that was formed by edifice collapse. Suwanosejima, one of Japan’s most frequently active volcanoes, was in a state of intermittent strombolian activity from Otake, the NE summit crater, that began in 1949 and lasted until 1996, after which periods of inactivity lengthened. The largest historical eruption took place in 1813-14, when thick scoria deposits blanketed residential areas, and the SW crater produced two lava flows that reached the western coast. At the end of the eruption the summit of Otake collapsed forming a large debris avalanche and creating the horseshoe-shaped Sakuchi caldera, which extends to the eastern coast. The island remained uninhabited for about 70 years after the 1813-1814 eruption. Lava flows reached the eastern coast of the island in 1884. Only about 50 people live on the island.
Sources : Japan météorological agency (JMA) , GVP.
Photo : N. Geshi. Geological Survey of Japan, H.Seo.
Philippines : Kanlaon :
The volcano is at Alert Level 1.
Slight increase in volcanic earthquake and steam/gas activity. Sporadic explosions from the summit crater or new vents. Notable increase in the temperature, acidity and volcanic gas concentrations of monitored springs and fumaroles. Slight inflation or swelling of the edifice.
Seismicity :
5 volcanic earthquakes
SO2 / Sulfur Dioxide Flux :
151 tonnes / day (01 May 2022)
Ground Deformation :
Volcano edifice has slightly inflated
PHIVOLCS issued a special notice for Kanlaon at 1400 on 3 July, noting increased earthquake activity beneath the summit. A total of 41 volcanic earthquakes were recorded by the seismic network beginning at 0500 on 30 June, including seven shallow tornillo signals indicating gas movement through fractures in the upper flanks. Ground deformation data from continuous GPS indicated minor, short-term inflation of the lower and mid-flanks of the volcano since January 2022, consistent with continuous electronic tilt data that had recorded inflation on the SE flanks since mid-March 2022. The seismicity and inflation likely reflected shallow hydrothermal processes. The Alert Level remained at 1 (on a scale of 0-5) and PHIVOLCS reminded the public to remain outside of the 4-km-radius Permanent Danger Zone.
Sources : Philippine Institute of Volcanology and Seismology (PHIVOLCS) , GVP
Photo : Phivolcs