August 22 , 2020.
Italy / Sicily , Etna :
ETNA COMMUNICATION [UPDATE n. 69]
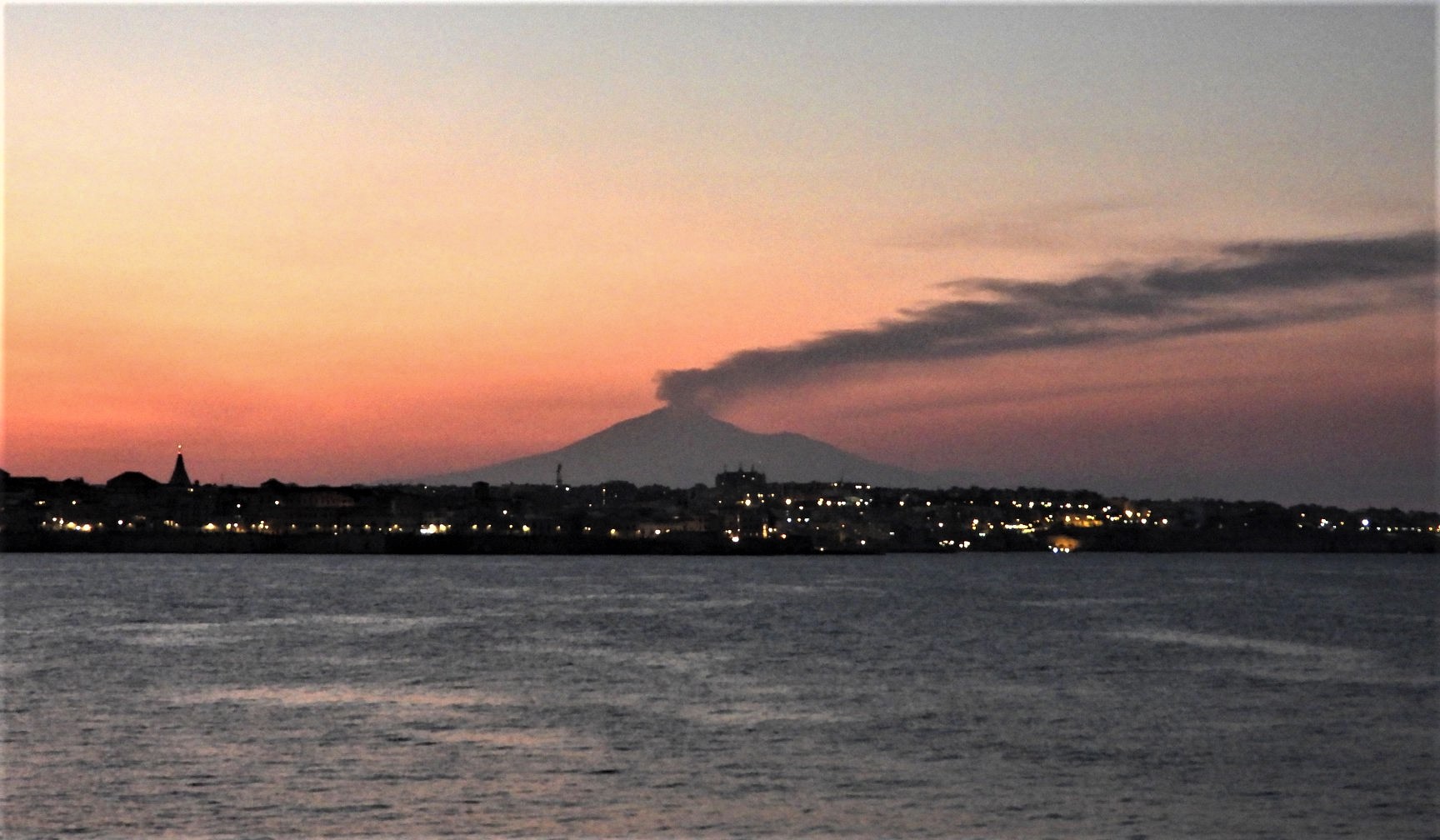
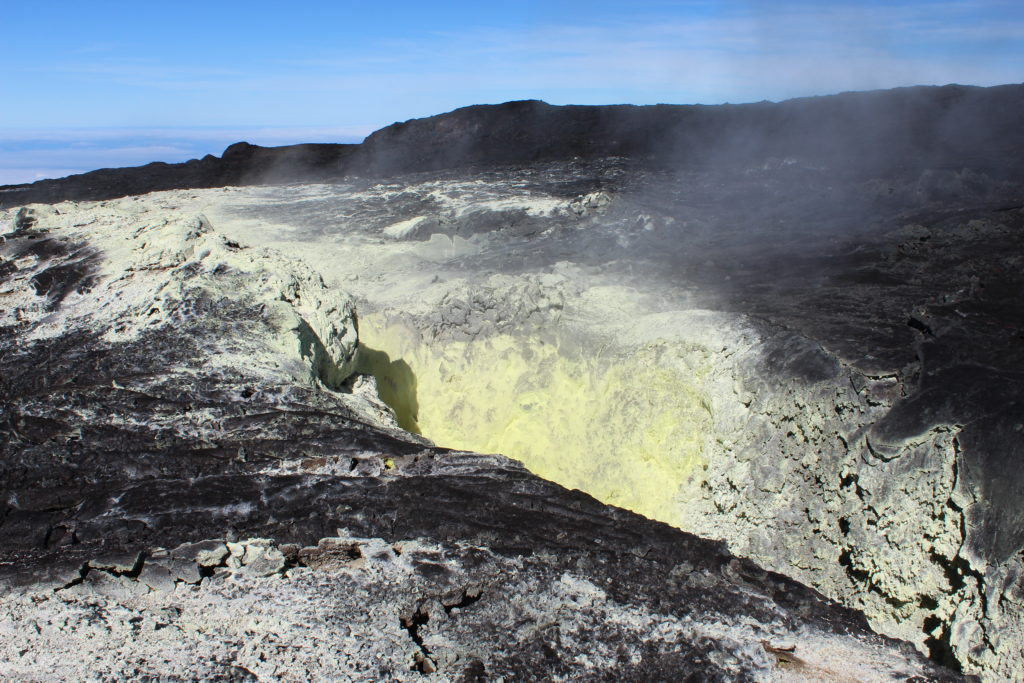
The National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology, Osservatorio Etneo, announces that as of approximately 5:45 GMT an increase in ash emissions was observed at the New Southeast Crater which formed a cloud of volcanic ash of approximately 4 km altitude above sea level scattered to the south. The explosive activity is very variable in time and intensity.
The temporal trend of the mean amplitude of the volcanic tremor continues to show marked amplitude fluctuations which together define a substantially stationary trend which remains within the range of mean values. The location of the center of gravity of the sources of the volcanic tremor remains confined to the area of the Southeast Crater complex at an altitude of between 2900 and 3000 m above sea level.
The infrasound activity, similar to volcanic tremor, shows an oscillating trend. The latest increase started at 05:42 GMT today and is still ongoing. The infrasound sources are mainly located in the area of the Southeast Crater Complex.
Analysis of the data available from the permanent GNSS and inclinometric networks does not show any anomalies and variations in soil deformation over the last few hours.
Further updates will be communicated shortly.
Source : INGV.
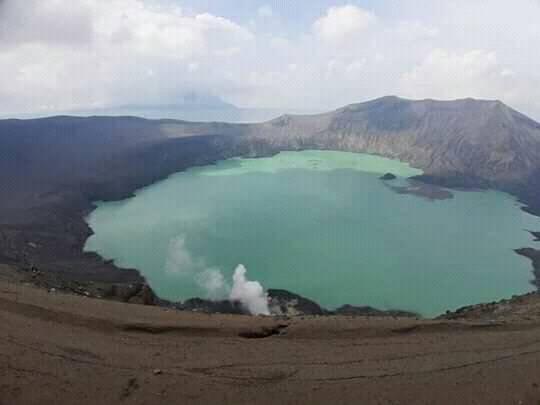
Philippines , Taal :
TAAL VOLCANO BULLETIN 22 August 2020 08:00 A.M.
In the past 24-hour period, the Taal Volcano Network recorded sixteen (16) volcanic earthquakes. Weak steaming or fumarolic activity rising 10 meters high before drifting southwest was observed from vents on the Main Crater.
Alert Level 1 (Abnormal) is maintained over Taal Volcano. DOST-PHIVOLCS reminds the public that at Alert Level 1, sudden steam-driven or phreatic explosions, volcanic earthquakes, minor ashfall, and lethal accumulations or expulsions of volcanic gas can occur and threaten areas within the Taal Volcano Island (TVI). DOST-PHIVOLCS strongly recommends that entry into TVI, Taal’s Permanent Danger Zone or PDZ, especially the vicinities of the Main Crater and the Daang Kastila fissure, must remain strictly prohibited. Local government units are advised to continuously assess previously evacuated barangays around Taal Lake for damages and road accessibilities and to strengthen preparedness, contingency, and communication measures in case of renewed unrest. People are also advised to observe precautions due to ground displacement across fissures, possible ashfall, and minor earthquakes. Civil aviation authorities must advise pilots to avoid flying close to the volcano as airborne ash and ballistic fragments from sudden explosions and wind-remobilized ash may pose hazards to aircraft. DOST-PHIVOLCS is closely monitoring Taal Volcano’s activity and any new significant development will be immediately communicated to all stakeholders.
Source : Phivolcs
Photo : yuri harmony
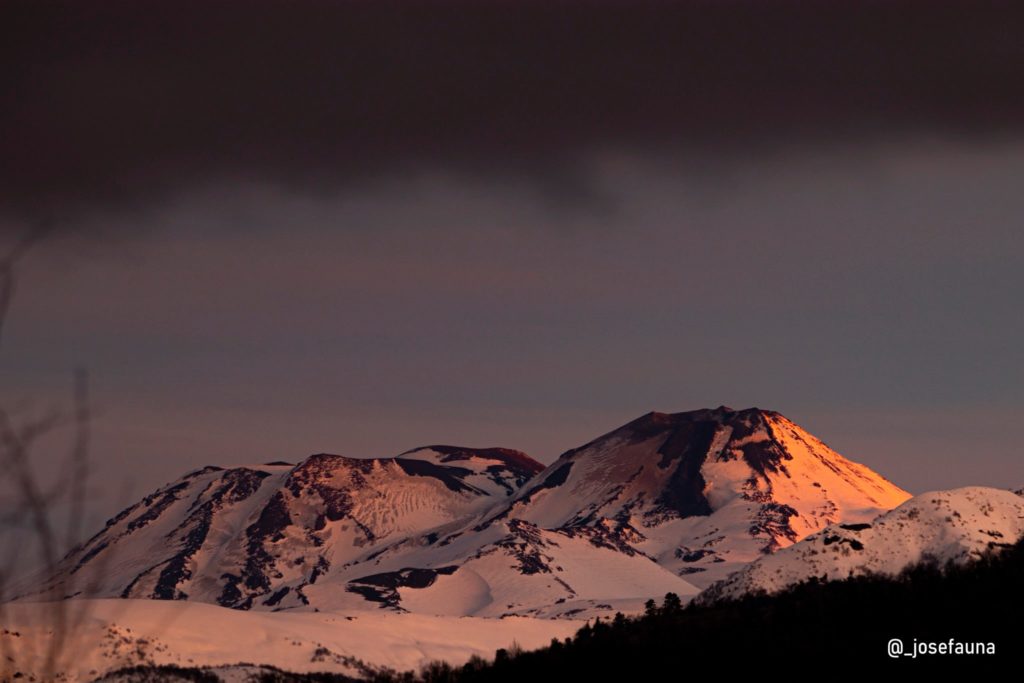
Chile , Nevados of Chillan :
Special Report on Volcanic Activity (REAV).
Region Ñuble, Nevados de Chillán Volcanic Complex, August 19, 2020, 03:05 local time (Continental Chile)
The National Service of Geology and Mines of Chile (Sernageomin) publishes the following PRELIMINARY information, obtained thanks to the monitoring equipment of the National Volcanic Monitoring Network (RNVV), processed and analyzed at the Volcanological Observatory of the South Andes ( Ovdas):
On Wednesday August 19 at 02:30 local time (06:30 UTC), the monitoring stations installed near the Nevados de Chillán Volcanic Complex recorded an earthquake linked to the fracturing of rocks (Volcano-Tectonics).
The characteristics of the earthquake after its analysis are as follows:
TIME OF ORIGIN: 02:30 local time (06:30 UTC)
LATITUDE: 36,830 ° S
LONGITUDE: 71.304 ° W
DEPTH: 3.7 km
LOCAL MAGNITUDE: 3.8 (ML)
OBSERVATIONS:
No surface activity associated with the reported event is observed. There is no report from neighboring communities on the perception of the earthquake.
The volcanic technical alert remains at the Yellow level.
Source : Sernageomin .
Photo : josefauna .
Guatemala , Santiaguito :
SPECIAL VOLCANOLOGICAL BULLETIN
UPDATE ON THE VOLCANIC ACTIVITY OF VOLCÁN SANTIAGUITO (1402-03)
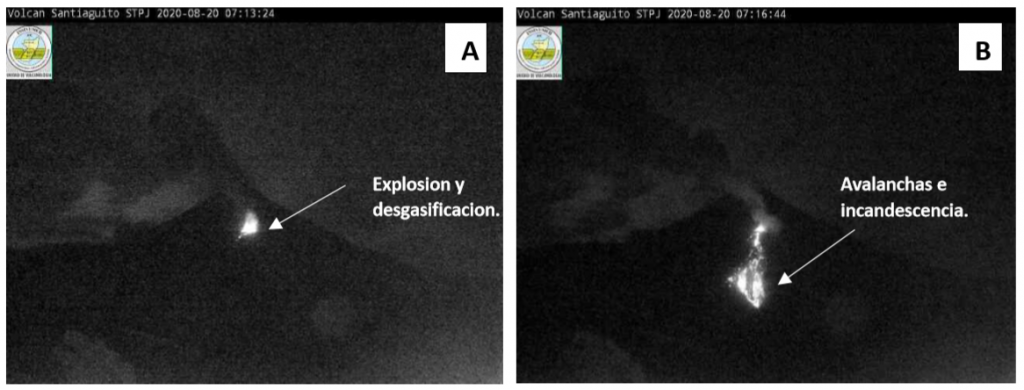
On the Santiaguito volcano, the Caliente dome continues to generate avalanches in the South, South-East and South-West directions. The formation of volcanic material also persists in the western part of the dome, causing continuous avalanches in this same direction. During the night and early in the morning, it is possible to observe the incandescence of the dome (see figure n ° 1 A) and the extent of the avalanches which reach the base of the domes (figure n ° 1 B).
The image on the left (A) shows the top of the Caliente dome and the incandescence generated by continuous degassing generated by the explosions. The image on the right (B) is a southerly avalanche with weak characteristics and a path towards the base of the domes.
In the Caliente Dome crater, explosions remain weak to moderate, some ash-laden reaching 3300 to 3600 meters (10,826 to 11,811 feet) elevation and dispersing in the direction of the wind reaching towns within a radius of 10 12 kilometers around the volcanic complex. Some explosions are accompanied by reaction turbine-type degassing sounds audible 5 kilometers from the volcanic building. The activity described above increases the likelihood of generating pyroclastic density fluxes of different dimensions, as described in previous bulletins. It is not excluded that more pyroclastic flows can be generated, with larger dimensions and an even greater range.
Source : Insivumeh .
Hawaii , Mauna Loa :
19°28’30 » N 155°36’29 » W,
Summit Elevation 13681 ft (4170 m)
Current Volcano Alert Level: ADVISORY
Current Aviation Color Code: YELLOW
Activity Summary:
Mauna Loa Volcano is not erupting. Rates of deformation and seismicity have not changed significantly over the past week and remain above long-term background levels.
Observations:
Over the past week, HVO seismometers detected approximately 144 small-magnitude earthquakes (all below M2.5) below the volcano’s summit and upper-elevation flanks. Most of these earthquakes occurred at shallow depths of less than 8 kilometers, or approximately 5 miles, below ground level.
Global Positioning System (GPS) measurements show continued, slow inflation of the summit, consistent with magma supply to the volcano’s shallow storage system.
Gas concentrations at the summit and Sulphur Cone monitoring sites remain stable, both below 2 ppm SO2. Fumarole temperatures as measured at the summit are approximately 98 C, within the normal range; temperatures at Sulphur Cone are lower, but within the normal range for this site.
Webcam views have revealed no changes to the landscape over the past week.
Source : HVO.
Japan , Nishinoshima :
27.247°N, 140.874°E
Elevation 25 m
Based on satellite data, the Tokyo VAAC reported that during 12-18 August ash plumes from Nishinoshima rose to 2.4-5.5 km (8,000-18,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted NE, NW, W, and SW.
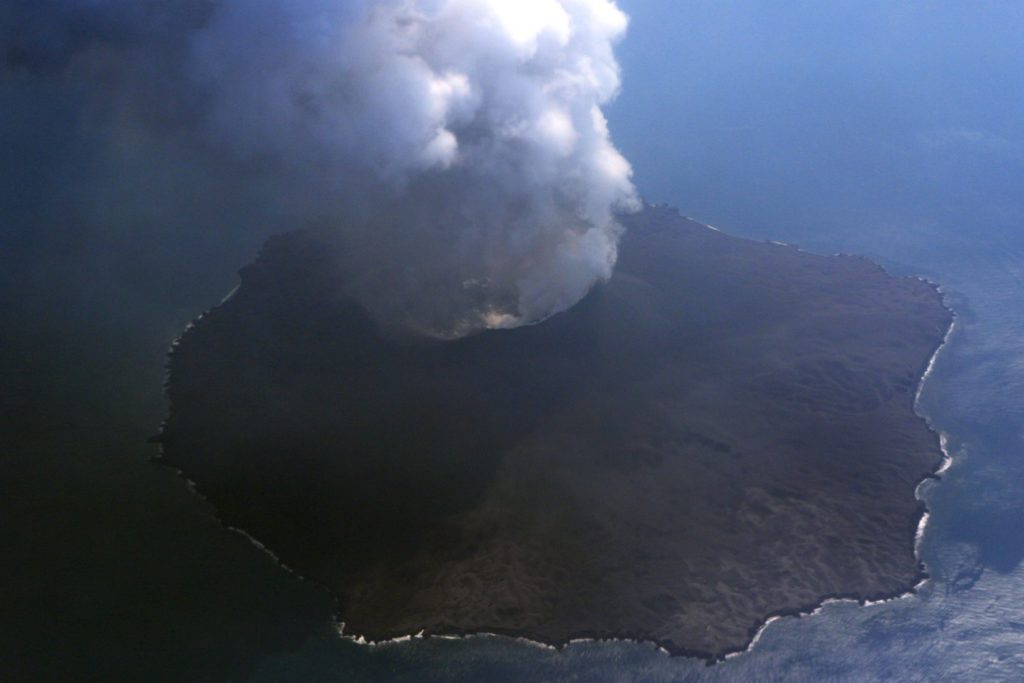
On August 19, an overflight was carried out by the Japan Coast Guards who took this photo of the pyroclastic cone.
The crater of the pyroclastic cone has widened considerably. We notice a strong activity in this one.
Degassing generates a white plume, with an absence of ash.
Source: GVP , Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC).