February 04 , 2024.
Hawaii , Kilauea :
HVO/USGS Volcanic Activity Notice
Current Volcano Alert Level: ADVISORY
Previous Volcano Alert Level: WATCH
Current Aviation Color Code: YELLOW
Previous Aviation Color Code: ORANGE
Issued: Saturday, February 3, 2024, 8:10 AM HST
Source: Hawaiian Volcano Observatory
Notice Number: 2024/H53
Location: N 19 deg 25 min W 155 deg 17 min
Elevation: 4091 ft (1247 m)
Area: Hawaii
Volcanic Activity Summary:
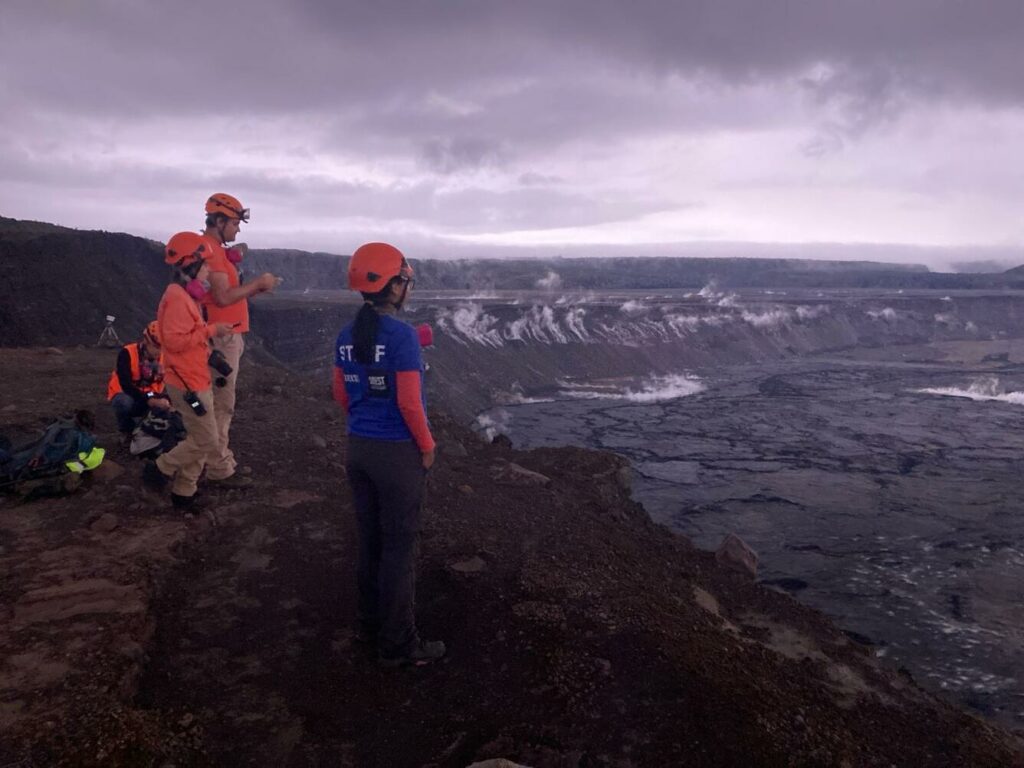
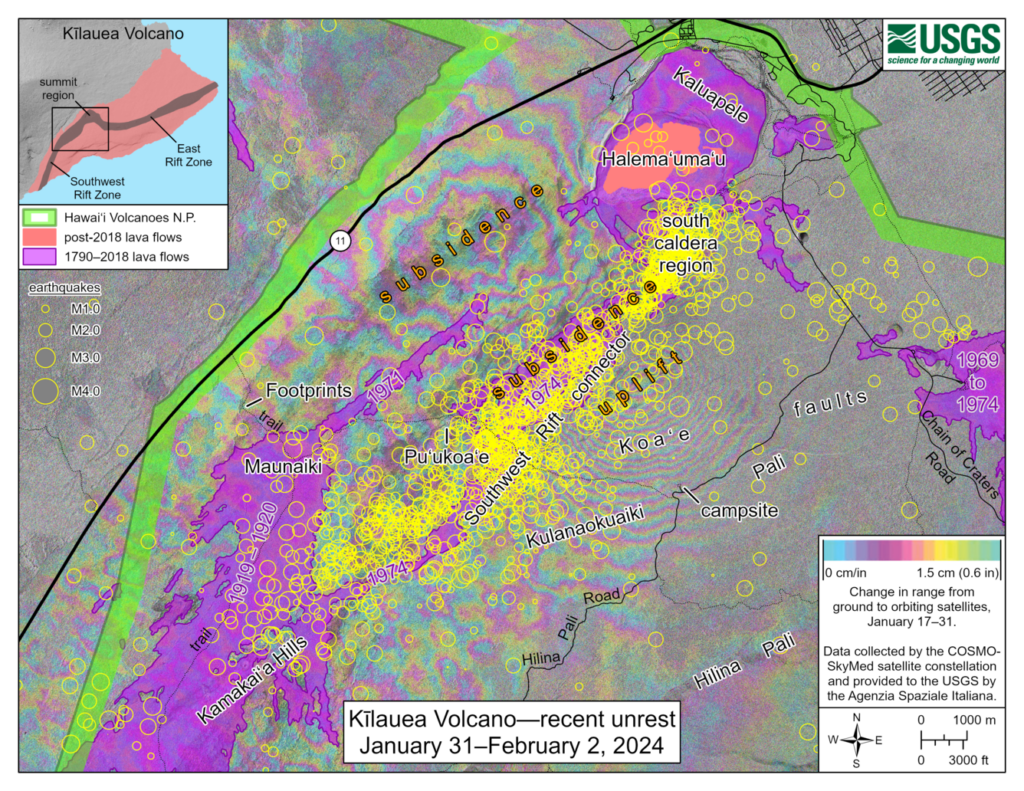
Earthquake and ground deformation rates extending from Kīlauea summit southwest along the Koa‘e fault system have decreased significantly over the past 24 hours. The intrusion of magma into this area appears to have slowed, and the likelihood of an eruption has decreased.
Accordingly, the USGS Hawaiian Volcano Observatory (HVO) is lowering the Volcano Alert Level for ground-based hazards from WATCH to ADVISORY and the Aviation Color Code from ORANGE to YELLOW.
In total, more than 3,000 earthquakes were recorded over the past week during this event, which coincided with ground deformation patterns indicative of magma moving from beneath the summit to the southwest under the Koa‘e fault system. More information on this intrusive activity will be available in the Kīlauea daily update published later today.
HVO continues to closely monitor Kīlauea for signs of renewed activity. Should volcanic activity change significantly, a new Volcanic Activity Notice will be issued.
Saturday, February 3, 2024, 11:06 AM HST (Saturday, February 3, 2024, 21:06 UTC)
Current Volcano Alert Level: ADVISORY
Current Aviation Color Code: YELLOW
Activity Summary:
Kīlauea volcano is not erupting. Seismicity in the summit and along the Koa‘e fault system southwest of the summit has decreased significantly over the past 24 hours. The intrusion of magma into this area appears to have slowed, and the likelihood of an eruption has decreased. A VAN/VONA was issued earlier this morning, lowering the Alert level from Orange/Watch to Yellow/Advisory.
Summit Observations:
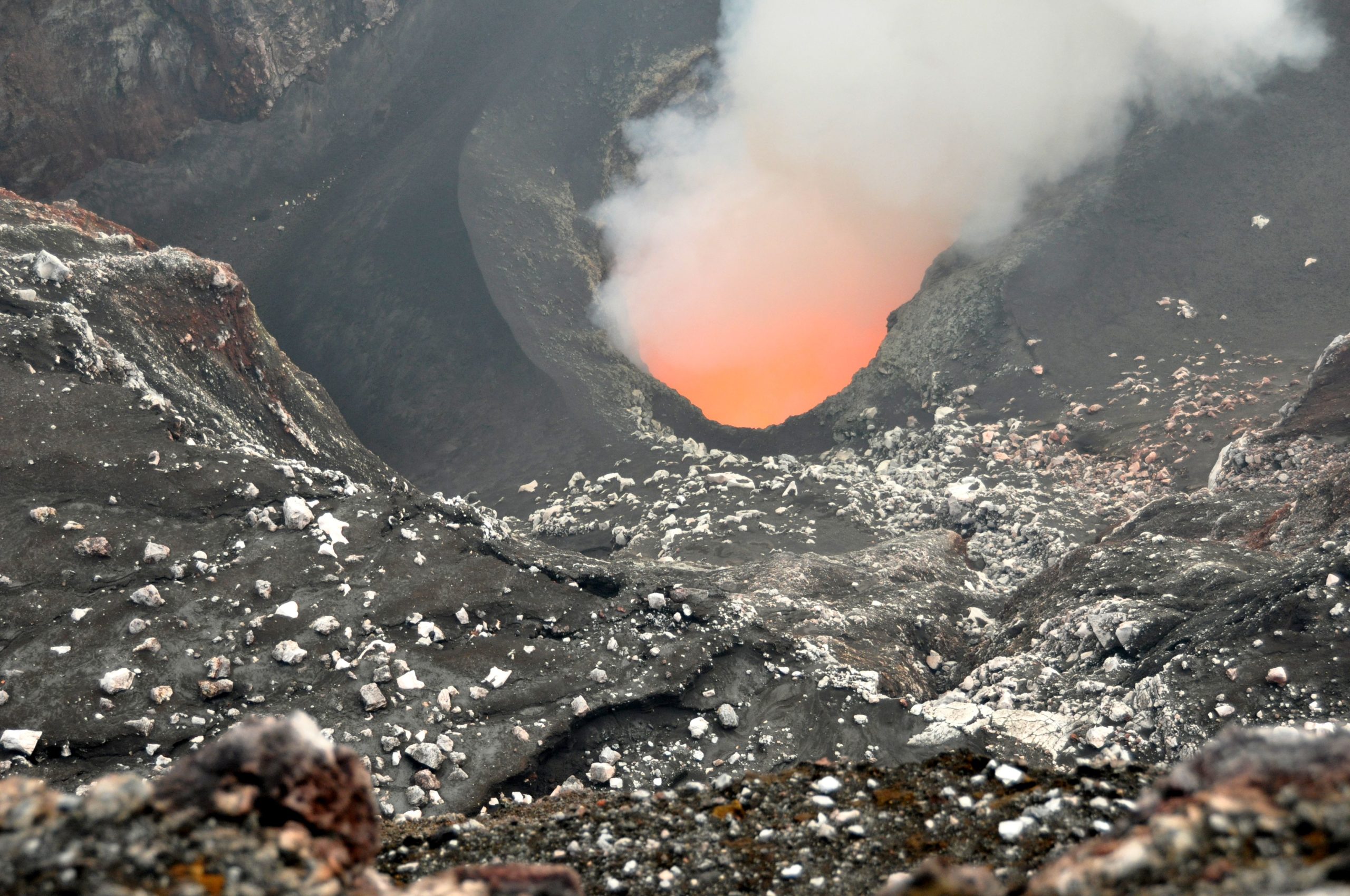
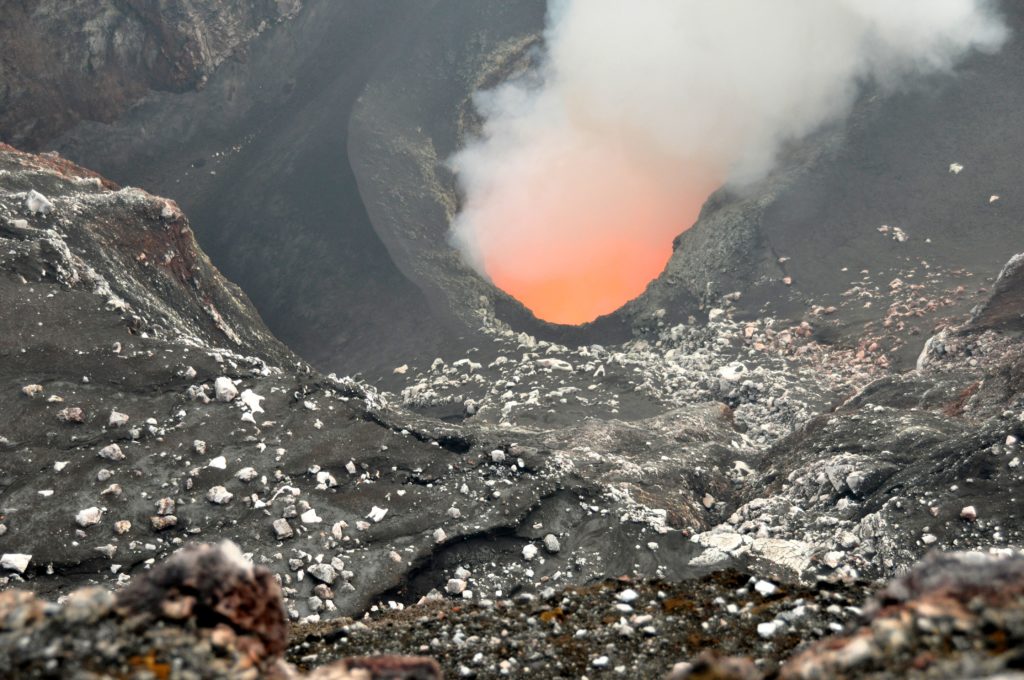
Seismicity and ground deformation beneath the summit and extending 5-7 miles (8-11 km) southwest of the caldera under the Koa‘e fault zone have decreased significantly in the past 24 hours. Earthquake counts have dropped from 20-30 events per hour to 5-10 events per hour and earthquakes are no longer clustering in the vicinity of Pu‘ukoa‘e, but are dispersed more widely from the summit to the southwest. Depths remain consistent, 1–4 km (less than a mile–2.5 mi) below the surface and magnitudes range a maximum of 3+ to less than 1. In total, less than 300 earthquakes have been recorded across this region over the past 24 hours, reflecting the continued decrease in seismicity.
Over the past day, tiltmeters near Sand Hill and Uēkahuna bluff have recorded very little change after the steep deflation of the past 2 days related to magma moving southwest.
Global Positioning System (GPS) instruments have recorded up to 8 inches (20 cm) of horizontal motion at stations around the SWRZ and immediately to the south along the Koa‘e fault zone.
Sulfur dioxide (SO2) gas emission rates remain low. Field measurements indicated an SO2 emission rate of approximately 70 tonnes per day, on January 17, which was similar to measurements in October, November, and early December.
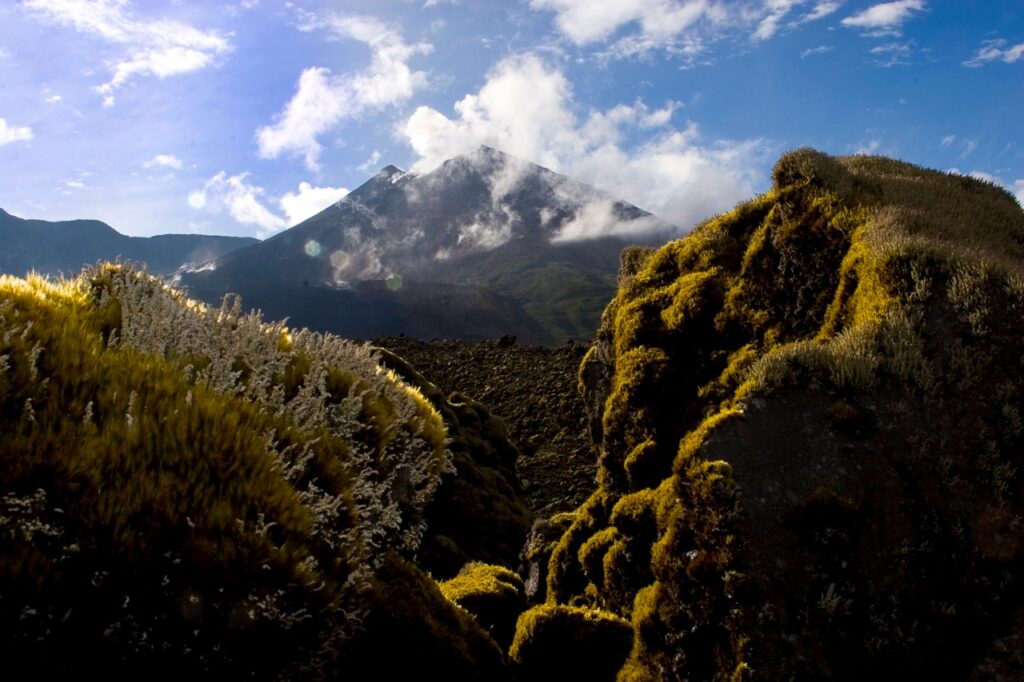
Patterns of earthquakes and ground deformation indicate that magma intruded beneath the south end of the caldera beginning on the morning of January 27th. This activity waxed and waned until Wednesday, January 31, when greatly increased seismicity and tilt indicated a dike was being emplaced, triggering episodic felt earthquakes and rockfalls within Halema‘uma‘u. By 5 p.m. HST on January 31st, seismicity migrated southwest of the caldera towards the Ko‘ae fault system and tiltmeters in the south caldera area began to record strong deflation. Modeling of tiltmeter, GPS, and satellite radar interferometry (INSAR) images suggest that magma within the initial dike migrated southwest into the new intrusion as it opened beneath the Ko‘ae fault zone. The overall decrease in seismicity and deformation over the past 24 hours suggests that this event is waning. However, renewed episodes of activity remain a possibility and an eruption could occur with little advanced warning.
Rift Zone Observations:
Seismicity in Kīlauea’s upper East Rift Zone and Southwest Rift Zone remained low in the past 24 hours. No unusual activity has been noted along the middle and lower sections of Kīlauea’s East Rift Zone. We continue to closely monitor both rift zones.
Source : HVO
Photos : USGS / M. Patrick , USGS .
Indonesia , Awu :
PRESS RELEASE on the volcanic activity of Mount Awu, February 1, 2024.
Geographically, Mount Awu is located at coordinates 3.6828460o N and 125.455980o E. The summit of Mount Awu is 1,320 m above sea level. Administratively, Mount Awu is located on Sangihe Island, part of Sangihe Islands Regency, North Sulawesi Province. Awu Volcano was observed visually and instrumentally from the Volcano Observation Post (PGA) located at Jl. Radar Tahuna.
Awu Volcano has an eruption interval ranging from 1 to 101 years. The last eruption occurred in June 2004, as a magmatic eruption producing an eruptive column reaching 3,000 m above the summit. G. Awu’s activity level has been Level II (WASPADA) since August 25, 2022.
The latest developments in the activity of the Awu volcano until January 31, 2024 are as follows:
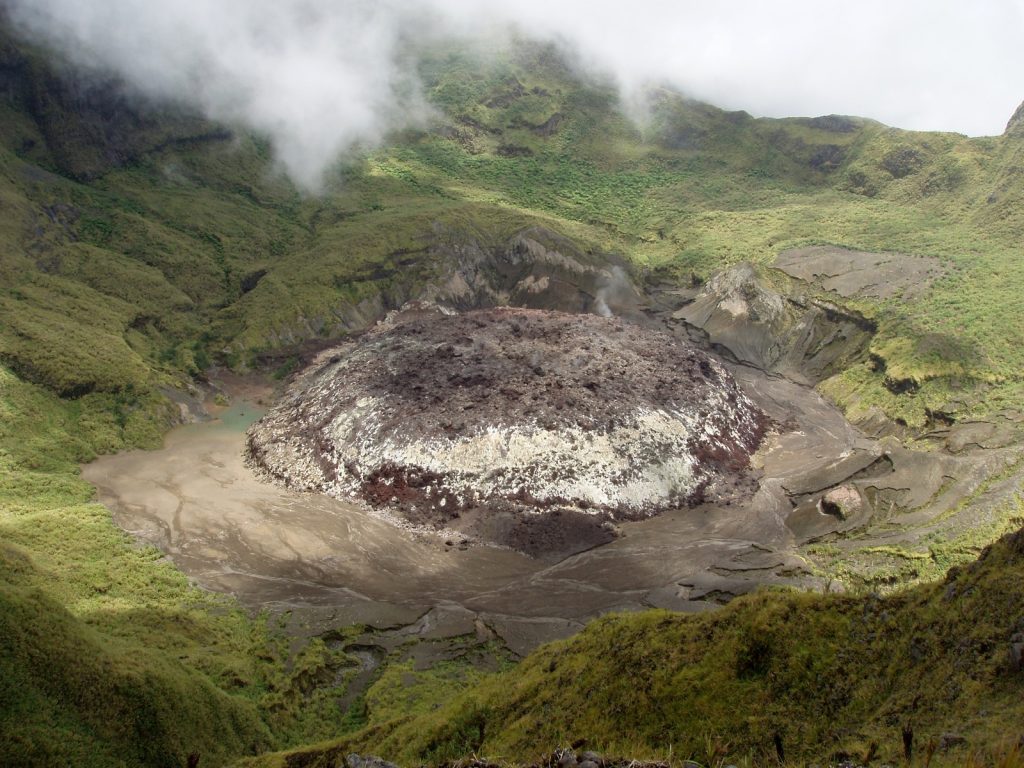
Current visual observations show that surface activity is still in the form of gas releases, no rocky material or ash has been brought to the surface. In January 2024, thanks to video surveillance observations installed in the summit area, gas emissions were observed only on January 2, 2024. The mountain peak was often covered in fog and on clear days no gas emissions was not observed.
There has been an increase in seismicity which is believed to be due to the movement of magma to shallower depths. This is characterized by an increase in the number of superficial volcanic earthquakes (VB). From January 29 to 31, 2024 (3 days), 62 VB earthquakes were recorded and 9 VA earthquakes were recorded. The energy of earthquakes has increased, as shown in the RSAM graph. On January 31, 2024, at 6:59 p.m. WITA, a low-frequency tremor was recorded with a dominant frequency of approximately 1.5 Hz and a seismic duration of 91 seconds, indicating an increase in surface earthquakes.
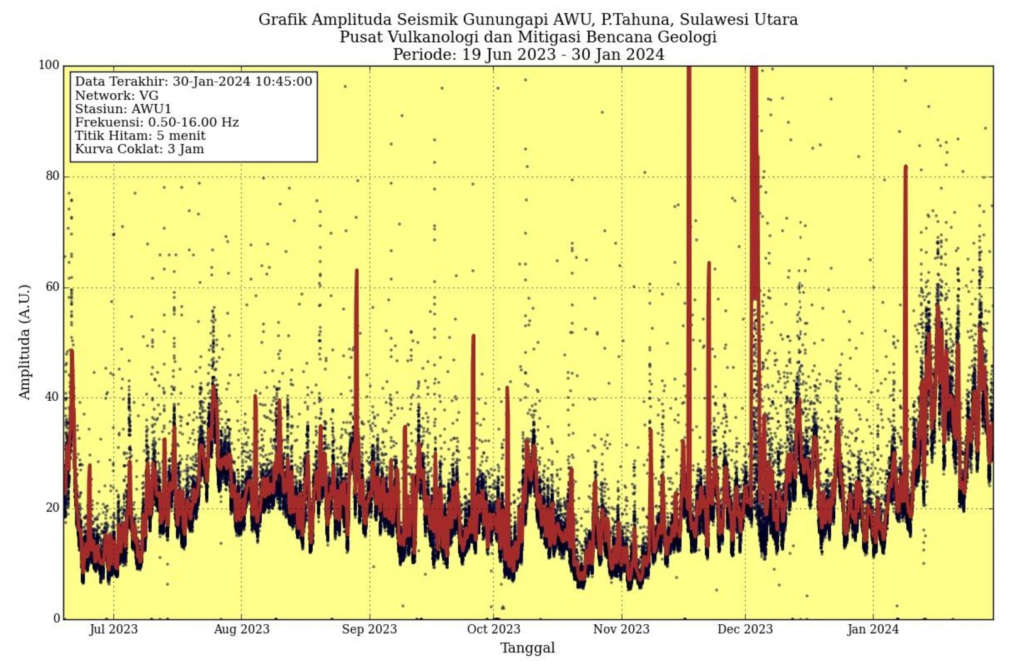
By observing deformation using GNSS monitoring on Mount Awu between June 1, 2023 and January 31, 2024, inflation was detected, which indicated the presence of a volume of magma moving toward the surface .
Potential Mount Awu hazards that may occur include explosive magmatic eruptions producing incandescent material and/or pyroclastic flows, effusive lava flows producing magma, or phreatic eruptions dominated by steam, volcanic gas, or volcanic material. previous eruptions. The potential for dismantling of the lava dome could occur if the pressure in the magma system increases significantly. Another potential danger is emissions of volcanic gases such as CO, CO2, H2S, N2 and CH4. These gases can be life threatening if the concentration inhaled exceeds the safety threshold value.
The community is aware of the danger posed by lava flows in the rivers that originate at the top of Mount Awu during the rainy season.
Based on visual and instrumental monitoring until February 1, 2024, the Geological Agency declared that the activity level of Mount Awu is still at Level II (WASPADA).
At Level II Activity Level (WASPADA), the public and visitors/tourists should not approach and conduct activities within a 3 km radius of the summit crater of Mount Awu due to the potential danger of high concentrations of volcanic gas and rock projections if a sudden phreatic eruption occurs, without prior warning, with symptoms of a marked increase in activity. The recommended radius and distance will continue to be evaluated to anticipate symptoms of evolving danger. The activity level of Mount Awu will be reviewed in the event of significant visual and seismic changes.
Source et photos : PVMBG.
Vanuatu , Ambrym :
16°15’00”S 168°07’00”E
Summit Elevation 4377ft (1334m)
Current Volcano Alert Level: Level 2
Ambrym volcano activity is continuing in the major unrest state. The Volcanic Alert Level remains at Level 2.
Ambrym volcano activity is continuing in the major level of unrest, consistent with the Volcanic Alert Level 2. Latest seismic analysis and observation confirmed ongoing steam emissions from the active craters of Ambrym volcano. Earlier this month, the Benbow crater underwent a short lived (4 days) eruption producing lava flow within the Benbow crater.
.
With the ongoing activity and the associated hazards, the danger zone at the summit is maintained at Danger Zone B (See Ambrym caldera safety map below). These danger zones are about 2 km around Benbow and 4 km around Marum craters including Maben-Mbwelesu, Niri-Mbwelesu and Mbwelesu. Additional danger zone is at the South-East of Ambrym within 500 meters from major cracks (Opened during the 2018 Eruption).
The level of risk for visitors accessing areas from the caldera is high. People on Ambrym especially, villages close to the volcano are expected to experience acid rain and are advised to follow the Ambrym key messages for volcanic ash, gas and acid rain, to protect water supply sources.
Source : Geohazard
Photo : G Vitton / Le Chaudron de Vulcain
Chile , Villarica :
Special Report on Volcanic Activity (REAV), La Araucanía and Los Ríos regions, Villarrica volcano, February 3, 2024, 2:42 p.m. local time (mainland Chile)
The National Geology and Mining Service of Chile (Sernageomin) announces the following PRELIMINARY information, obtained through the monitoring equipment of the National Volcanic Monitoring Network (RNVV), processed and analyzed at the Southern Andean Volcano Observatory (Ovdas):
On Saturday February 3, 2024, at 1:55 p.m. local time (4:55 p.m. UTC), monitoring stations installed near the Villarrica volcano recorded an earthquake associated with fluid dynamics inside the volcanic system (long period type).
The characteristics of this earthquake after its analysis are as follows:
ORIGINAL TIME: 1:55 p.m. local time (4:55 p.m. UTC)
REDUCED DISPLAY: 71.2 (cm*cm)
ACOUSTIC SIGNAL: 4.9 Pascals (Pa) reduced to 1 km
Observation :
After the long-term earthquake mentioned in this report, no changes were recorded in the seismic behavior of the volcano. In addition, no surface activity associated with this earthquake was observed.
The technical volcanic alert is maintained at YELLOW level.
Source et photo : Sernageomin.
Ecuador , Reventador :
DAILY REPORT ON THE STATE OF THE REVENTADOR VOLCANO, Saturday February 3, 2024.
Information Geophysical Institute – EPN.
Surface activity level: Moderate, Surface trend: No changes
Internal activity level: Moderate, Internal trend: No changes
Seismicity: From February 2, 2024, 11:00 a.m. to February 3, 2024, 11:00 a.m.:
The following table shows the number of seismic events from the reference station in the last 24 hours.
Explosion (EXP) 37
Long Period (LP) 6
Transmitting tremor (TREMI) 5
Tremor Harmonic (TRARM): 2
Precipitation/Lahars:
Rainfall is not recorded. **In the event of heavy rains, these could remobilize the accumulated materials, generating mud and debris flows which would descend the sides of the volcano and flow into adjacent rivers.
Emissions/ash column:
Since yesterday evening, thanks to the surveillance camera system, emissions have been recorded with heights between 400 and 1,100 meters above the level of the crater in the West, North-West and West-North-West direction. Additionally, associated with these events, the Washington VAAC released four emissions reports with heights between 700 and 1,100 meters above the crater level in a northwest direction.
Other monitoring parameters:
The FIRMS satellite system recorded 1 thermal anomaly in the last 24 hours.
Observation:
Since yesterday evening, thanks to the camera system, it has been observed that the volcano has remained clear most of the time, which is why several episodes of incandescence have been observed accompanied by the descent of the same material on its flanks at more than 800 meters below the level of the crater. At the time of this report, the volcano is cloudy.
Alert level: Orange.
Source : IGEPN.
Photo : volcan reventador/FB