November 25 , 2020.
Italy / Sicily , Etna :
Weekly bulletin, from November 16, 2020 to November 22, 2020 (issue date November 24, 2020).
SUMMARY OF THE STATE OF ACTIVITY
In the light of surveillance data, it is highlighted:
1) VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS: Strombolian activity of variable frequency and intensity accompanied by ash emissions at the New Southeast Crater. Intermittent intracrater strombolian activity at the level of the Bocca Nuova crater, associated with low emissions of dilute ash and degassing. Degassing activity at the Voragine crater.
2) SISMOLOGY: Moderate fracturing activity
3) INFRASON: Low infrasound activity.
4) DEFORMATIONS: During the last week, the trend of the time series of Etna soil deformation monitoring networks has not shown any significant changes.
5) GEOCHEMISTRY: SO2 flux: at medium-low level
HCl flux: at the average level (last measurement available the previous week)
The CO2 flux from the soil shows an increase in the degassing regime and is at average levels.
The partial pressure of dissolved CO2 does not show significant changes.
The value of the C / S ratio is at medium-low levels (last measurement dated 10/16/2020).
The helium isotope ratio is at average values (last update 04/11/2020).
6) SATELLITE OBSERVATIONS: The thermal activity in the summit area is at a medium-low level.
VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS
The monitoring of the volcanic activity of Etna, during the week in question, was carried out by analyzing the images of the network of surveillance cameras of the INGV, Osservatorio Etneo (INGV-OE) and by means of an inspection carried out on November 21 by INGV staff. During the week, the meteorological conditions severely limited the observation of the eruptive phenomena.
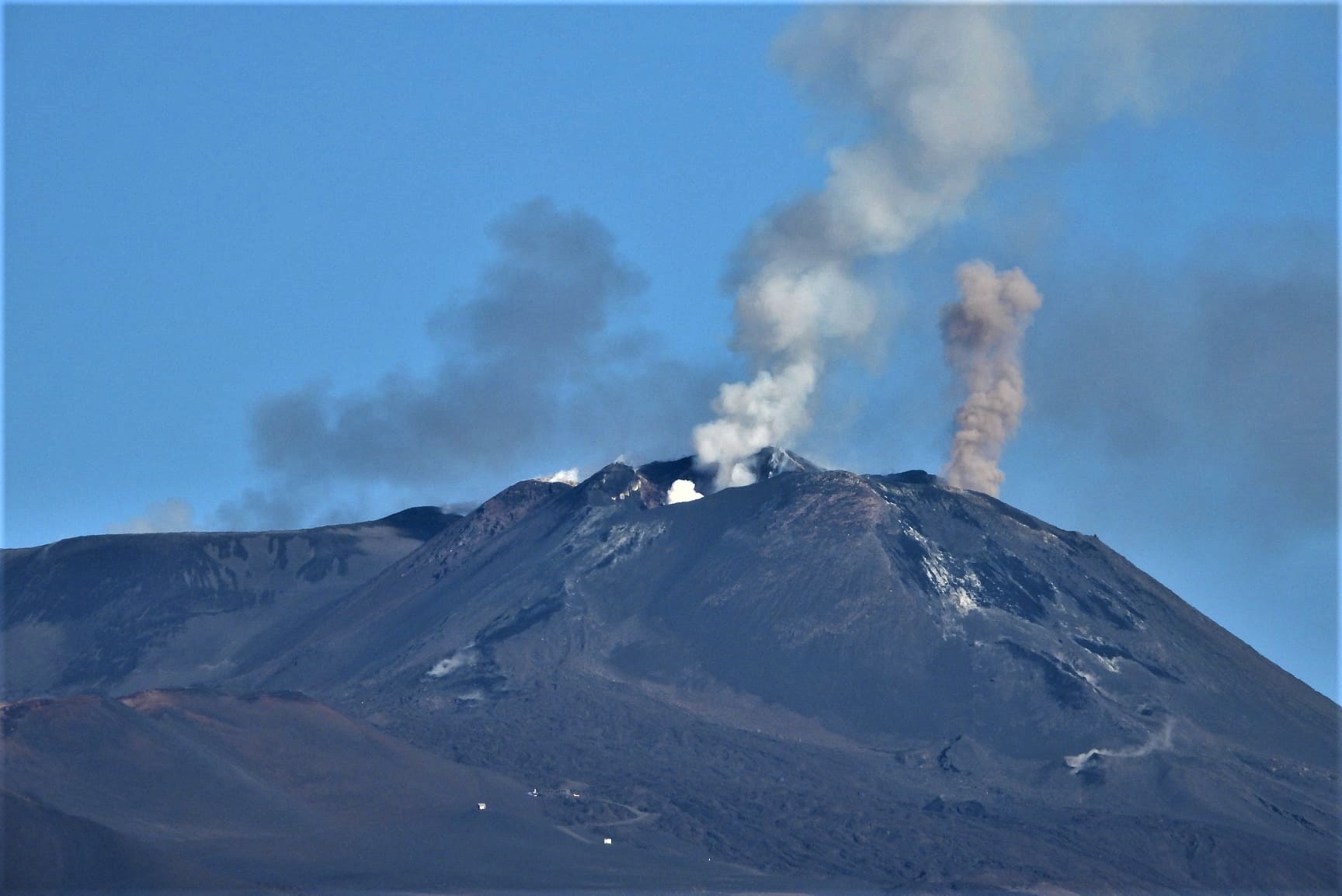
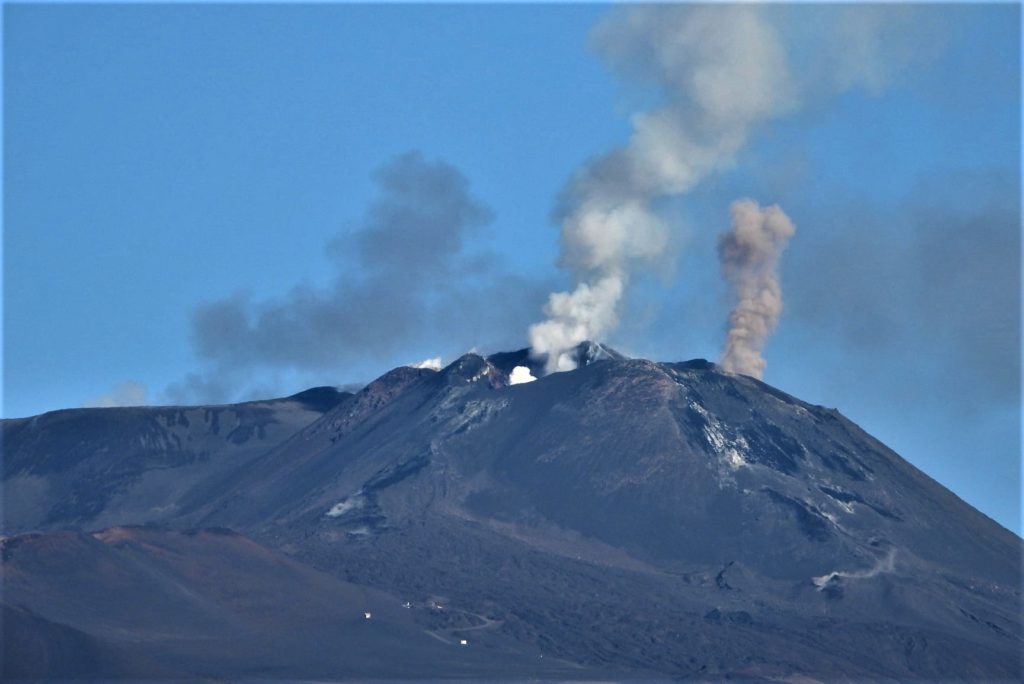
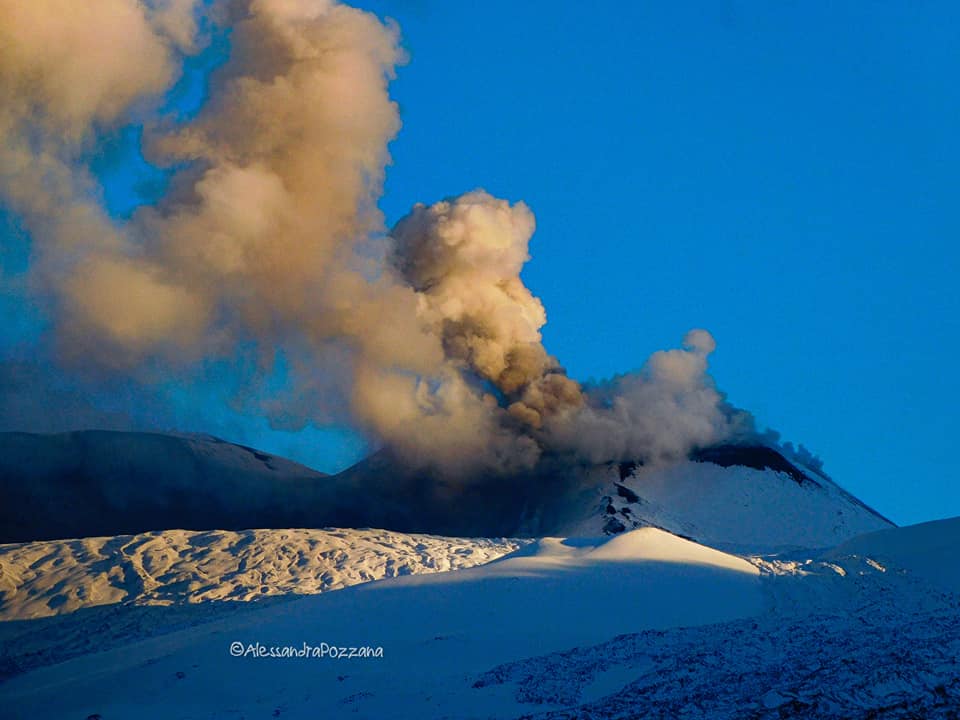
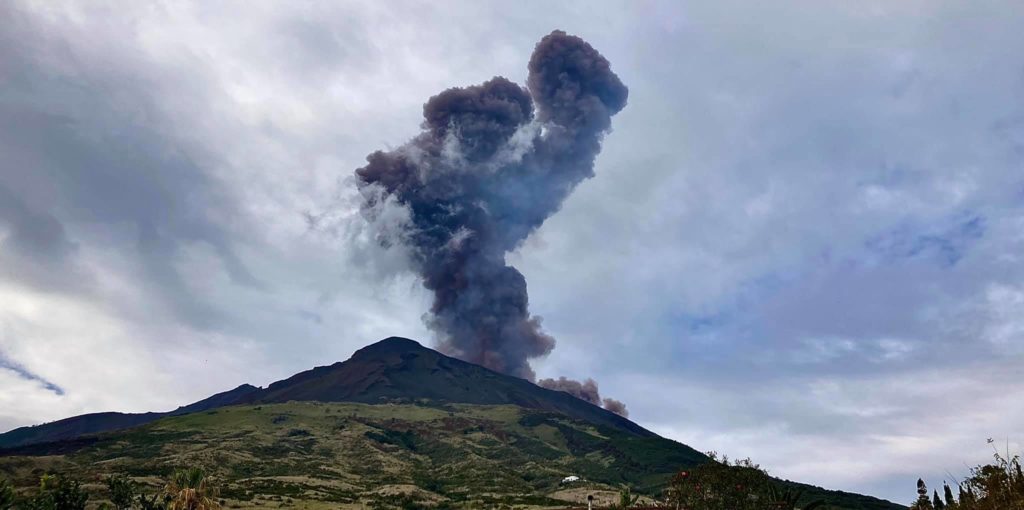
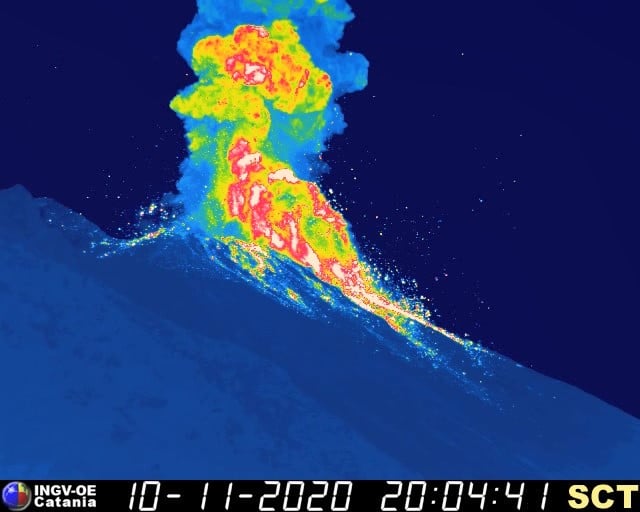
In particular, the New Southeast Crater was characterized, throughout the week, by intracrater Strombolian activity, with explosions whose intensity and frequency were variable over time. During the more energetic phases, the coarse material emissions exceeded the edge of the crater and the products sometimes fell back, settling out on the sides of the cone.
Volcanic ash emissions were also observed which dispersed in the summit area.
On November 20, from 2:59 a.m. UTC, sporadic explosive activity was observed in the crater of Bocca Nuova with emissions of dilute ash that dispersed rapidly.
Also during the same day at 4:40 UTC, a slight intensification of Strombolian activity was observed in the New Southeast Crater (NSEC) with emissions of ash and pyroclastic material that profusely exceeded the edge of the crater.
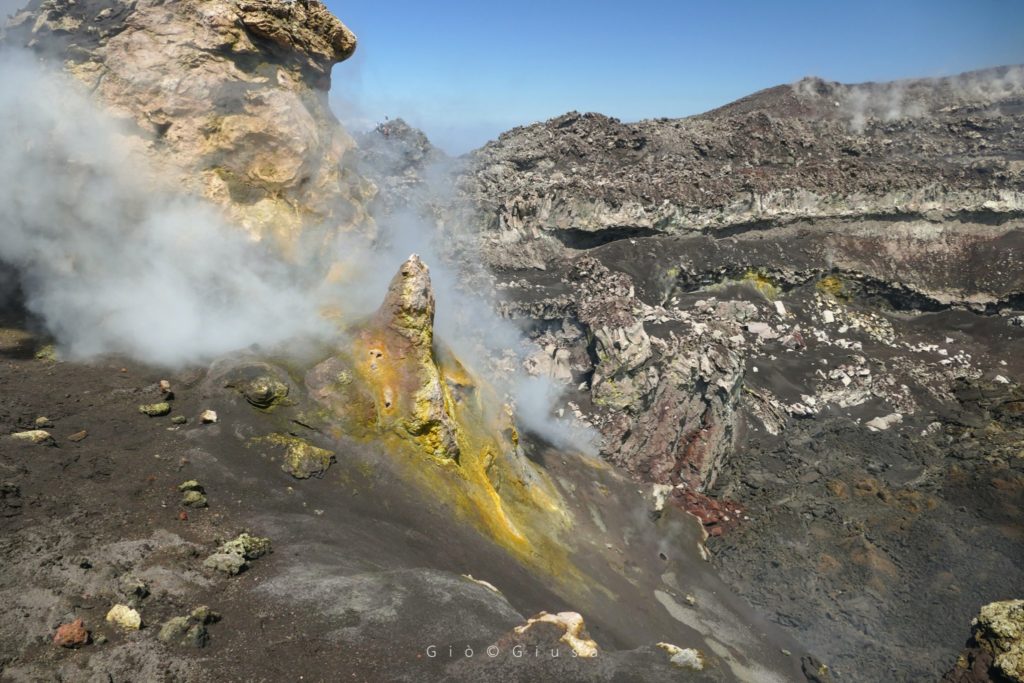
During the inspection carried out on November 21 in the summit area, it was noted, through images taken with the drone, that the Strombolian activity at the New Southeast Crater (NSEC) came from a single eruptive vent.
Due to the bad weather conditions, the observation of crater activity was severely limited and it was therefore not possible to verify if the activity of the Northeast crater described in last week’s bulletin was continuing. .
Volcanic tremor:
The amplitude of the tremor is mostly at medium levels, with short time intervals at medium-high levels. The signal sources are located southeast of the Southeast craters, at a depth of approximately 2800 m.
Source : INGV.
Photos : INGV , Alessandra Pozzana , Gio Giusa .
Italy , Stromboli :
Weekly bulletin, from November 16, 2020 to November 22, 2020 (issue date November 24, 2020).
SUMMARY OF THE STATE OF ACTIVITY
In the light of surveillance data, it is highlighted:
1) VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS: Ordinary explosive volcanic activity of Strombolian type on medium-low levels (4-9 events / h) with the sole exception of 11 events / h on November 21 with an average intensity both in the areas of the crater North and Center -South. Major explosion on November 16 in the North zone.
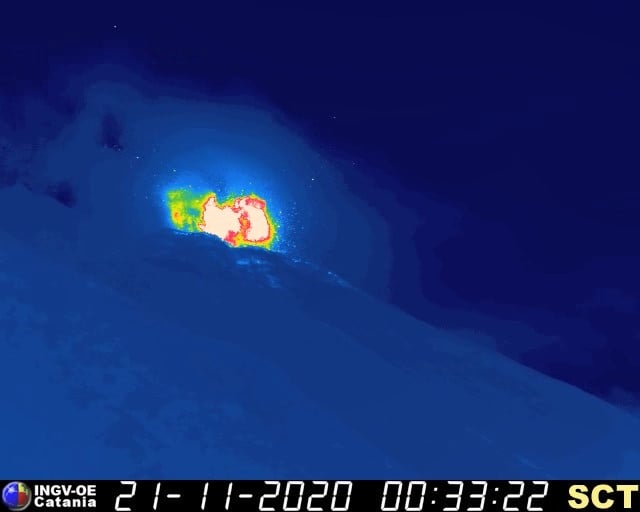
2) SEISMOLOGY: The seismological parameters do not show significant variations, with the exception of the major event of 11/16 at 09:17 UTC and the strongest explosive event compared to the ordinary activity recorded at 00: 33:21 UTC on 11/21.
3) DEFORMATIONS: The island’s soil deformation monitoring networks did not show any significant changes to report for the period under review.
4) GEOCHEMISTRY: Medium-low SO2 flux
C / S Ratio – Latest values (C / S = 9.35) are average levels.
The isotopic ratio of Helium is located at average values (R / Ra = 4.38 sampling of November 03).
5) SATELLITE OBSERVATIONS: The thermal activity in the summit area is at a low level.
VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS
During the period under observation, the eruptive activity of Stromboli was characterized by the analysis of the images recorded by the surveillance cameras INGV-OE located at 190 m altitude, Punta dei Corvi and 400 m.
The period was characterized by two high energy explosive events, the first occurred on 11/16/20 at 09:17 UTC consistent with a major event, the second occurred on 11/21/20 at 00:33 UTC and was characterized by a moderately higher energy level than ordinary activity.
Chronology of the major event of November 16:
On 11/16/2020 at 09:17:45 UTC, a high energy explosive event located in the area of the North crater at the edge of the N2 crater began. After only half a second, on the thermal and visible images of the cameras at the altitude of 190m, a very rapid emission of incandescent material was observed which extended for about 100 m around the point of emission probably located in the same crater N2, even if the observation from Q190 does not make it possible to discriminate with certainty the mouths C and S2 located just beyond. The « blast » type explosive event also produced a sound pressure wave 2.5 times the intensity of the previous major explosion of 11/10/2020.
Two seconds after the initial radial expansion of the pyroclastic products which reached 300 meters in height, an ash cloud emerged from the edge of the crater, followed by the relapse of incandescent and lithic materials, along the side of Sciara, which produced a pyroclastic flow which reached the coast after 45 s, and advanced on the surface of the sea for a few hundred meters. With the products expelled in the first 4 seconds, an ash plume rose in the direction of the zenith up to about 1 km above the mouth, causing the products to fall on the Pizzo sopra la Fossa. The total duration of the event was approximately 1 minute.
On 11/21/2020 at 00:33:17 UTC, a sequence of three explosive events affected three different vents of the crater terrace, the last of which had higher energy than ordinary activity but not comparable to that of ‘a major explosion. The first two events were produced by the N1 and N2 mouths, while the third was produced by the C mouth. The coarse products of the explosion reached a height of about 300 m while the radial distribution of the numerous ballistic emissions also affected the upper part of the Sciara del Fuoco. The formation of a small plume of ash concluded the event.
The explosion lasted about 25 seconds.
Major explosion of 11/16/20 at 9:18 a.m.
In the area of the north crater, the N1 crater, with two emission points, produced explosions of low intensity (less than 80 m high) to medium (sometimes the projectiles exceeded 150 m high) emitting coarse materials ( lapilli and bomb) sometimes mixed with fine materials (ash). The N2 muzzle, at two points of emission, showed mainly an explosive activity of low and medium intensity emitting coarse materials sometimes mixed with fine materials. The average frequency of the explosions varied from 3 to 8 events / h. In the Center-South zone, the explosions emitted mainly fine materials, with an average intensity (the products reached 150 m in height). The explosive activity showed frequency values varying between less than 1 and 4 events / h.
Source : INGV.
Photos : Daniele Andronique, INGV , Stromboli Adventures.
Colombia , Nevado del Ruiz :
Weekly activity bulletin of the Nevado del Ruiz volcano
The activity level continues at Yellow Activity Level or (III): changes in the behavior of volcanic activity.
Regarding the monitoring of the activity of the Nevado del Ruiz volcano, the COLOMBIAN GEOLOGICAL SERVICE reports that:
Seismicity linked to fluid dynamics, inside volcanic conduits, decreased in the number of events and in the seismic energy released, compared to the previous week. This seismic activity was characterized by the appearance of continuous volcanic tremor, tremor pulses, earthquakes of long and very long period types, which presented variable energy levels and spectral content. Some of these signals were associated with gas and ash emissions.
The seismicity generated by the fracturing of the rock maintained a similar level in the number of earthquakes recorded and increased in the seismic energy released, compared to the previous week. This seismic activity was located mainly in the East-North-East, South-South-West sectors and in the Arenas crater, and to a lesser extent, in the South-East and in the North at depths between 0.3 and 6, 5 km. The occurrence of an increase in this type of seismic activity on November 21 and 22 stands out, about 1.4 km east-northeast of the Arenas crater, at depths between 2.5 and 4 , 4 km. The highest magnitude recorded during the surge, and the largest of the week was 2.7 ML (local magnitude), corresponding to the November 21 earthquake at 2:42 a.m. (local time), at a depth of 3.6 km. This earthquake was reported as felt by PNNN staff.
During the week, several episodes of low energy « Drumbeat » type seismicity associated with rock fracturing were recorded. This seismicity has been linked to the processes of ascent, location-growth and evolution of a lava dome at the bottom of the Arenas crater of the Nevado del Ruiz volcano.
The Nevado del Ruiz volcano continues at the yellow activity level.
Source : SGC.
Photo : Diana M Bustamante.
Guatemala , Santiaguito :
Activity type: Pelean
Morphology: Complex of dacitic domes
Geographical location: 14 ° 44 ’33 ˝ Latitude N; 91 ° 34’13˝ Longitude W
Height: 2500msnm
Weather conditions: Partly cloudy.
Wind: northeast
Precipitation: 0.0 mm.
Activity:
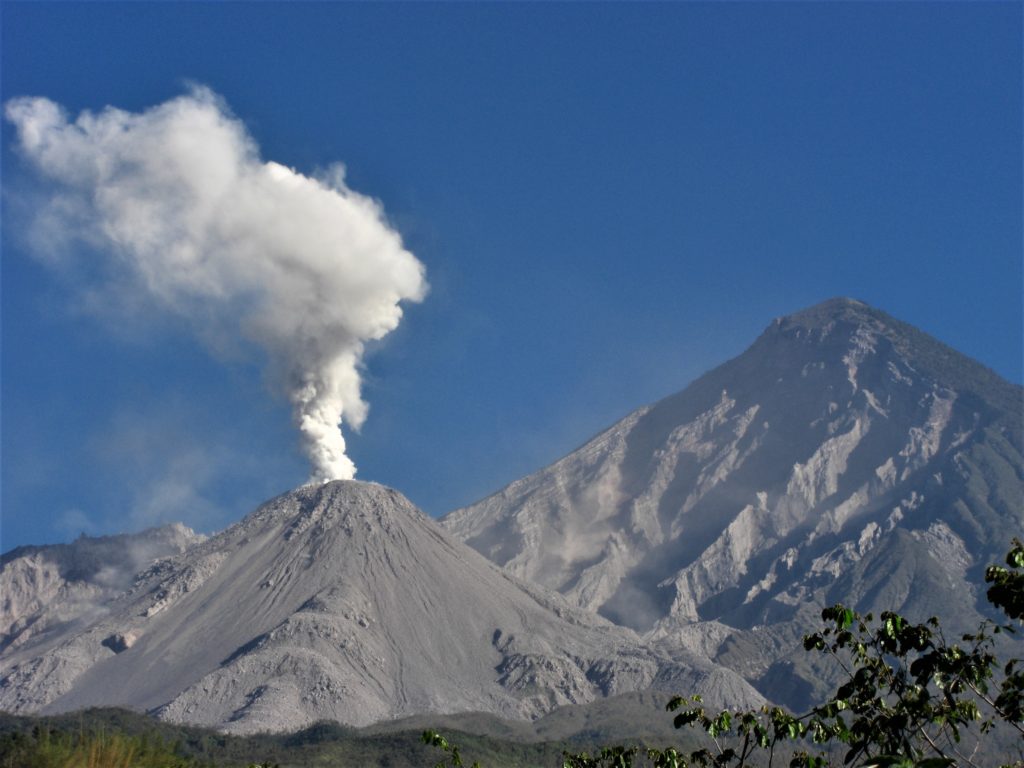
A degassing is observed, for a few prolonged moments, of white and gray color which disperses towards the southwest, which reaches heights of 100 to 500 meters above the Caliente dome. Seismic recording makes it possible to observe weak to moderate explosions. These generate plumes of gas and ash, with altitudes of up to 3,200 meters (10,498 feet). Weak to moderate boulder and ash avalanches are also recorded mainly towards the southwest flank, but they can be generated towards the south, southeast and west flanks. The path of these materials reaches the base of the dome and drops fine particles of ash on the volcanic perimeter. Due to the location of the block lava flows on the Caliente dome in a West-South-West direction, the appearance of boulder and ash avalanches in this same direction, as well as pyroclastic flows over long distances , are not excluded. For short periods, it is possible to hear sounds similar to those of an airplane turbine, due to the prolonged degassing on the Caliente dome. The recommendations of the special BESAN bulletin n ° 118-2020 remain in force.
Source : Insivumeh
Photo : Annie Winson , earthobservatory.sg