January 28 , 2023.
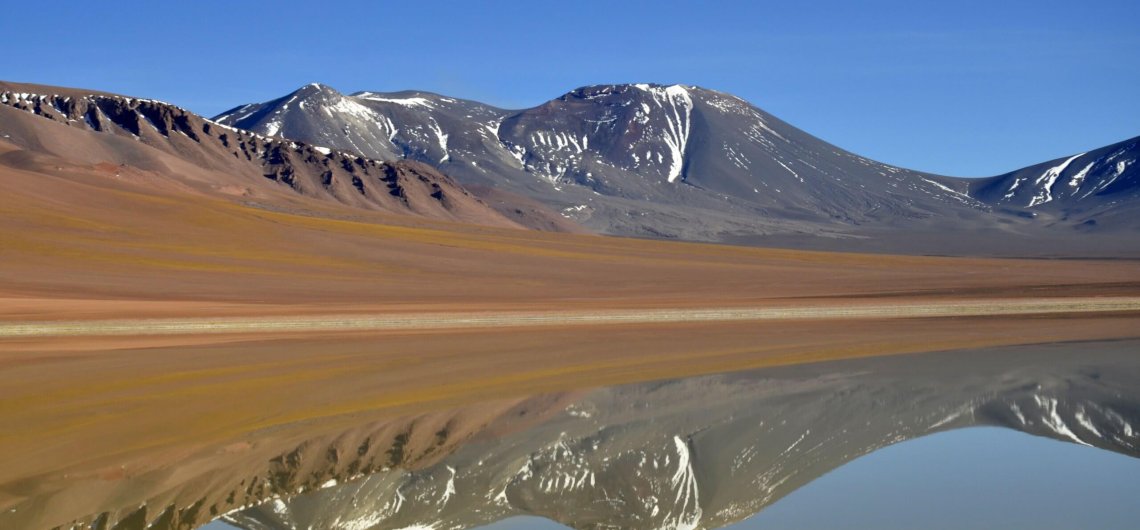
Chile , Lascar :
Special Report on Volcanic Activity (REAV), Antofagasta Region, Láscar Volcano, January 28, 2023, 04:30 local time (mainland Chile)
The National Geology and Mining Service of Chile (Sernageomin) announces the following information obtained through the monitoring equipment of the National Volcanic Monitoring Network (RNVV), processed and analyzed at the Observatory of Volcanoes of the Southern Andes (Ovdas ):
Since yesterday, Friday, January 27 at 23:00 local time (02:00 UTC, January 28), monitoring stations installed near the Láscar volcano have recorded an increase in seismicity, mainly that associated with fluid dynamics within the system. volcanic type Long Period (LP). According to what has been reported in recent special reports (REAV of January 27 and 28), the highest energy LP earthquake presented since the instrumental recording was recorded with a reduced displacement (DR) equal to 717 cm2, for this volcano.
With this event and during the following hours, a significant energy LP seismicity was recorded but with a DR of less than 400 cm2, also considered abnormal. Similarly, a volcano-tectonic earthquake (VT) of magnitude ML equal to 3.2 was recorded, with epicenter in the volcanic edifice, perceptible by the local population.
In this scenario, the possible appearance of eruptive impulses with columns exceeding 5 km in height, the projection of ballistic blocks and the dispersion of ash in the vicinity of the volcano are expected.
As part of the Sernageomin operational protocol, and given the need to promote preventive actions against possible impacts associated with a superficial process on the Láscar volcano, the volcanic technical alert is modified to: ORANGE level volcanic technical alert.
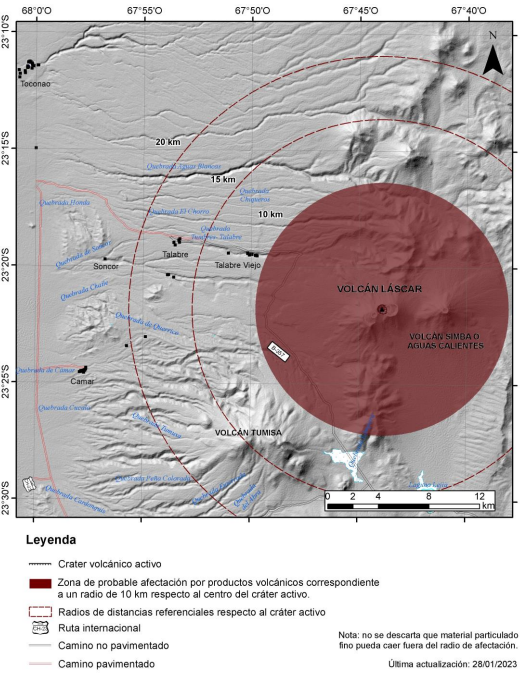
Note: A danger zone is considered within 10 km of the active crater (see map).
Source : Sernageomin.
Photos : 80 jours voyages / Sylvain Chermette , Sernageomin.
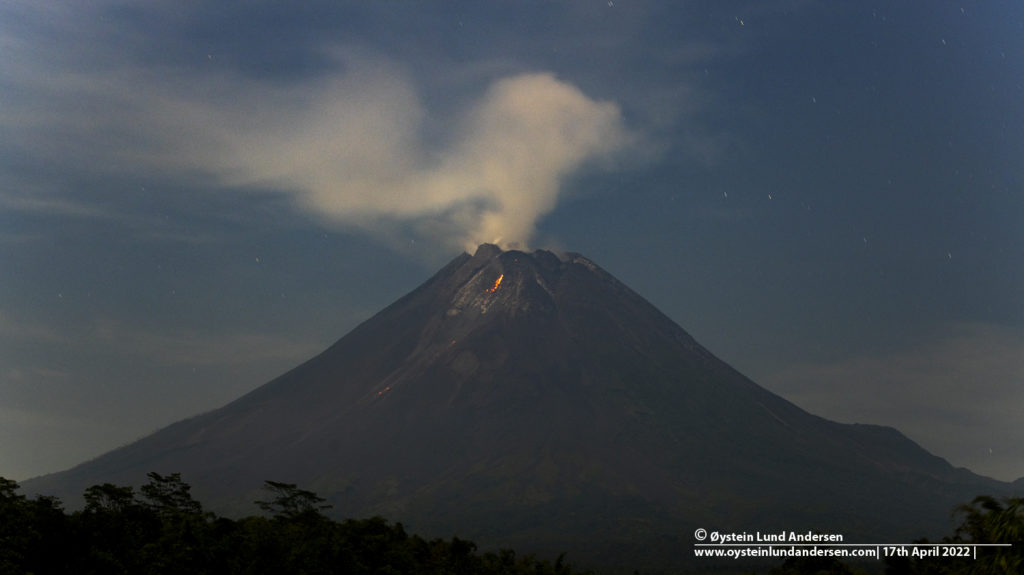
Indonesia , Merapi :
Report on the activity of Mount Merapi from January 20, 2023 to January 26, 2023, Published on January 27, 2023
RESULTS OF OBSERVATIONS
Visual
The weather around Mount Merapi is usually sunny in the morning and afternoon, while the evening is foggy. White smoke, thin to medium thickness, low pressure and 250 m high was observed from the Mount Merapi observation post of Pos Babadan on January 25, 2023 at 06:20 WIB.
This week there were 14 southwestward lava avalanches (first to Kali Bebeng and then Kali Sat/Putih) with a maximum slip distance of 1800m. The sound of avalanches was heard from Pos Babadan 7 times with low to medium intensity
In the central dome, a decrease in the height of the dome was observed, while in the Southwest dome, no significant change was observed. Based on aerial photographs from January 13, 2023, the measured volume of the Southwest dome is 1,598,700 m3 and the central dome is 2,267,400 m3.
Seismicity
This week, the seismicity of Mount Merapi showed:
12 deep volcanic earthquakes (VTB)
766 deep volcanic earthquakes (VTA),
277 avalanche earthquakes (RF),
6 emission earthquakes (DG),
7 tectonic earthquakes (TT).
53 multi-phase (MP) earthquakes
The intensity of this week’s seismicity is still quite high.
Deformation
The Mount Merapi deformation that was monitored using EDM and GPS this week showed a shortening rate of 0.6 cm/day.
Rain and lahars:
This week, there was rain with a rain intensity of 70 mm/h for 240 minutes in Pos Babadan on January 25, 2023, and an increase in flow was reported in Kali Boyong.
Conclusion
Based on the results of visual and instrumental observations, it is concluded that:
-The volcanic activity of Mount Merapi is still quite high in the form of effusive eruption activity. The state of the activity is defined at the « SIAGA » level.
Source : BPPTKG
Photo : Oystein Lund Andersen.
Philippines , Mayon :
MAYON VOLCANO BULLETIN 28 January 2023 8:00 AM
In the past 24-hour period, the Mayon Volcano Network did not detect any volcanic earthquake. Moderate emission of white steam-laden plumes that crept downslope before drifting to west-northwest and southwest was observed. Sulfur dioxide (SO2) emission was last measured at an average of 294 tonnes/day on 18 January 2023. Based on ground deformation parameters from EDM, Precise Leveling, electronic tilt, and continuous GPS monitoring, Mayon Volcano has been slightly inflated since 2020.
Alert Level 2 (Increased Unrest) prevails over Mayon Volcano. The public is reminded that there is current unrest driven by shallow magmatic processes that could eventually lead to phreatic eruptions or even precede hazardous magmatic eruptions. Entry into the six (6) kilometer-radius Permanent Danger Zone (PDZ) is strictly prohibited to minimize risks from sudden explosions, rockfalls, and landslides. In case of ash fall events that may affect communities downwind of Mayon’s crater, people should cover their nose and mouth with a damp, clean cloth, or dust mask. Civil aviation authorities must also advise pilots to avoid flying close to the volcano’s summit as ash from any sudden eruption can be hazardous to aircraft.
DOST-PHIVOLCS maintains close monitoring of Mayon Volcano and any new development will be communicated to all concerned stakeholders.
Source : Phivolcs.
Photo : Auteur inconnu.
Alaska , Great Sitkin :
52°4’35 » N 176°6’39 » W,
Summit Elevation 5709 ft (1740 m)
Current Volcano Alert Level: WATCH
Current Aviation Color Code: ORANGE
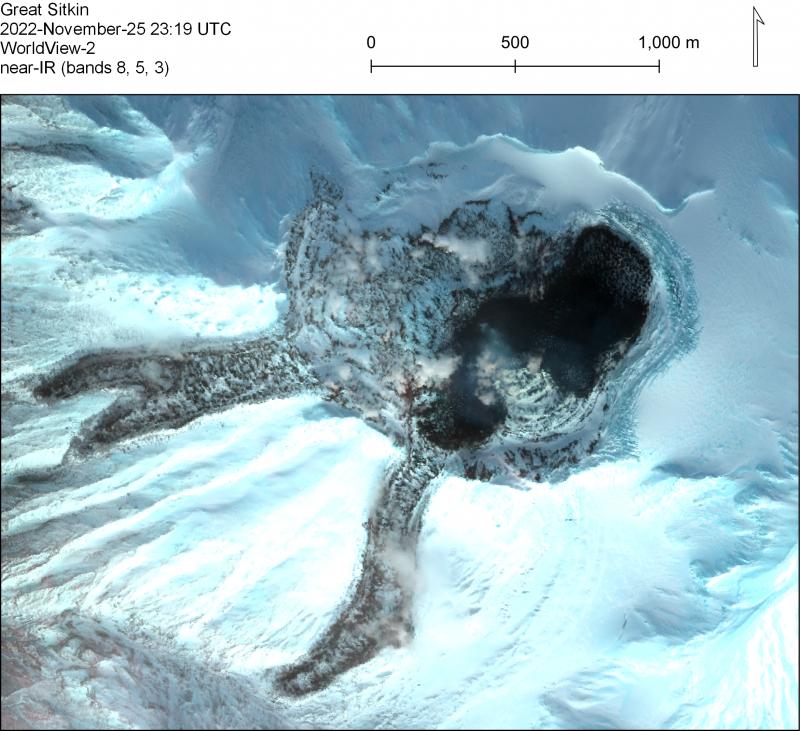
The low-level eruption of lava continues within the summit crater of Great Sitkin. Weather conditions were cloudy at the volcano for most of the week but weakly elevated surface temperatures were observed in satellite data on Thursday. The active lava is advancing primarily to the south, burying earlier 2021–2022 lava, and east into the remaining summit crater icefield.
Near-IR false color satellite images from WorldView-2 on November 25, 2022. The 2021–2022 lava flow fields are visible: older flows emplaced July 2021–June 2022 are partially snow covered while a newer overtopping flow is snow-free.
The last high-resolution radar image showing lava growth was obtained on January 20. Small earthquakes have been occurring on some days, but seismic activity overall remains very low.
Great Sitkin is monitored by local seismic and infrasound sensors, satellite data, web cameras, and regional infrasound and lightning networks.
Source : AVO.
Photo : Loewen, Matt.
Ecuador , Cotopaxi :
DAILY REPORT OF THE STATE OF COTOPAXI VOLCANO, Friday January 27, 2023.
Information Geophysical Institute – EPN.
Surface Activity Level: Moderate, Surface Trend: Unchanged.
Internal activity level: Moderate, Internal trend: Ascending.
Seismicity: From January 26, 2023, 11:00 a.m. to January 27, 2023, 11:00 a.m.:
There were no interruptions in the transmission of the reference station data (BREF).
Emission tremor (TREMI) 16
Long Period (LP): 27
Rains / Lahars:
There are no reports of rain in the area.
Emission / Ash Column:
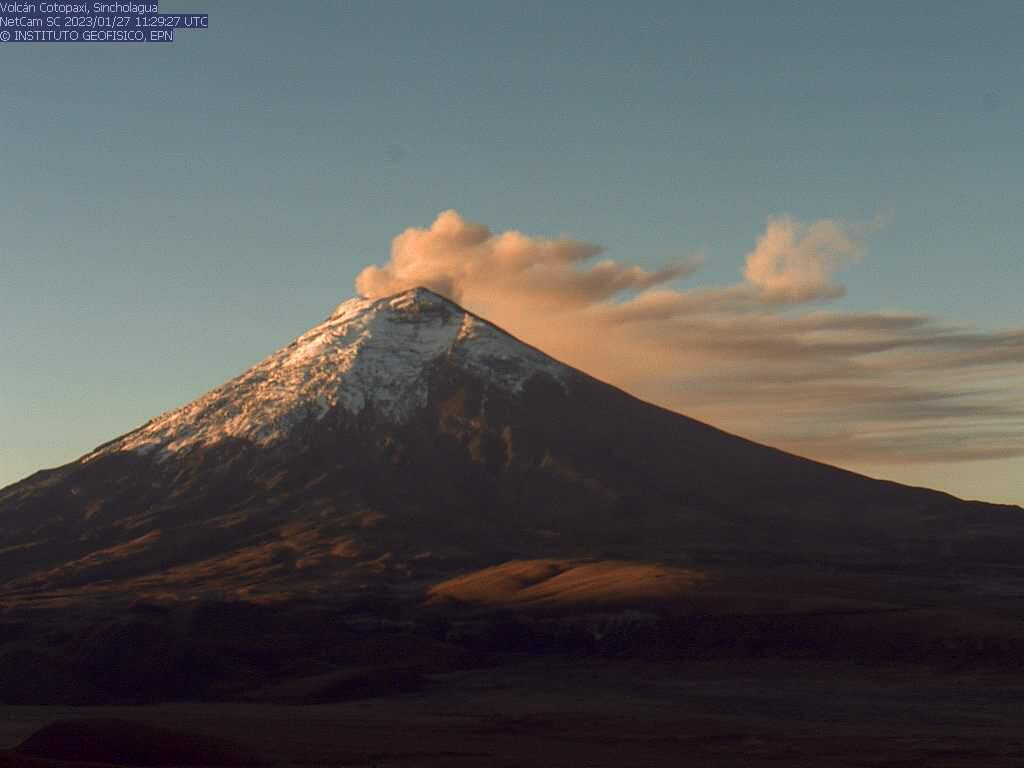
Various gas and ash emissions were observed through cameras, which had heights between 500 and 600 meters above the summit, the direction remained towards the Southwest and West. These emissions caused ash falls in the municipality of Mulaló, in the sectors of Barrancas, Ticatilín, Caspi and San Ramon. Using satellite imagery, Washington’s VAAC reported 2 ash emissions in the past 24 hours, which reached 800 meters above the summit, heading southwest.
Gas:
The MOUNTS system detected 514.8 tons of sulfur dioxide (SO2), measured on 01/26/2023 at 1:23 p.m. TL.
Observation:
In the early hours of the morning and today, the volcano has cleared, showing various gas and ash emissions.
Alert level: Yellow.
Source et photo : IGEPN