December 11, 2020.
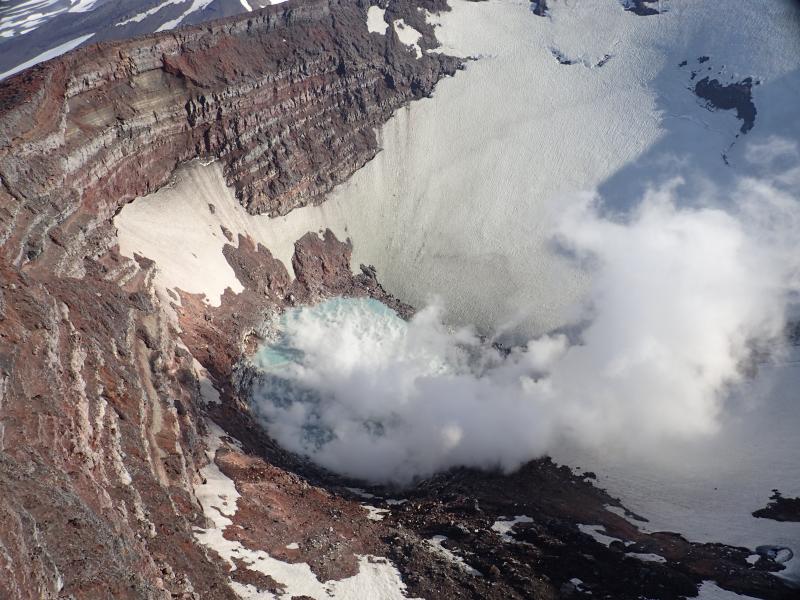
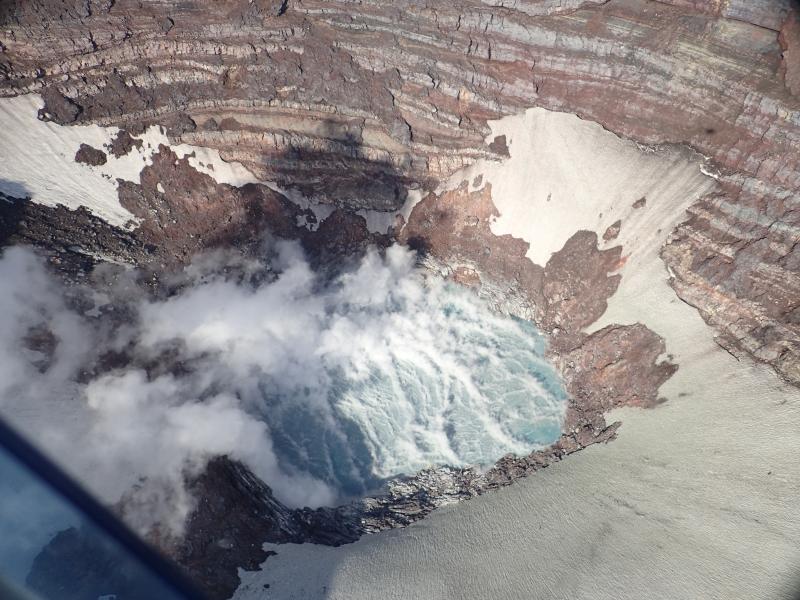
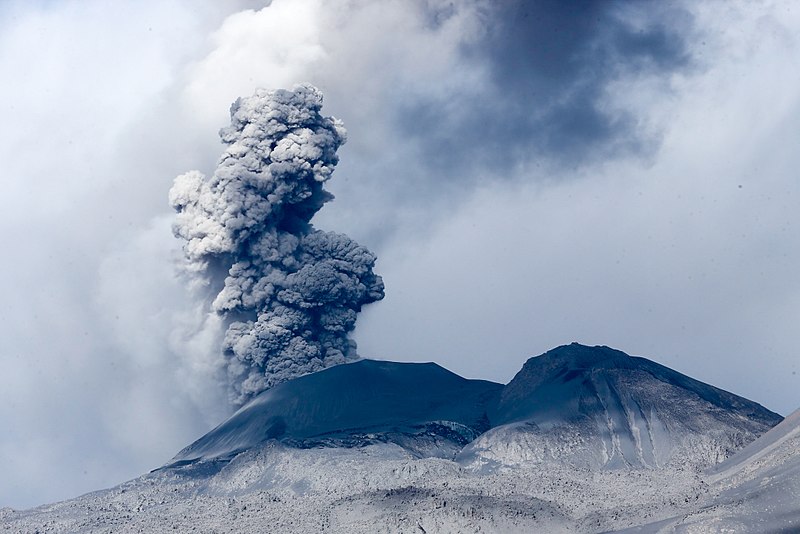
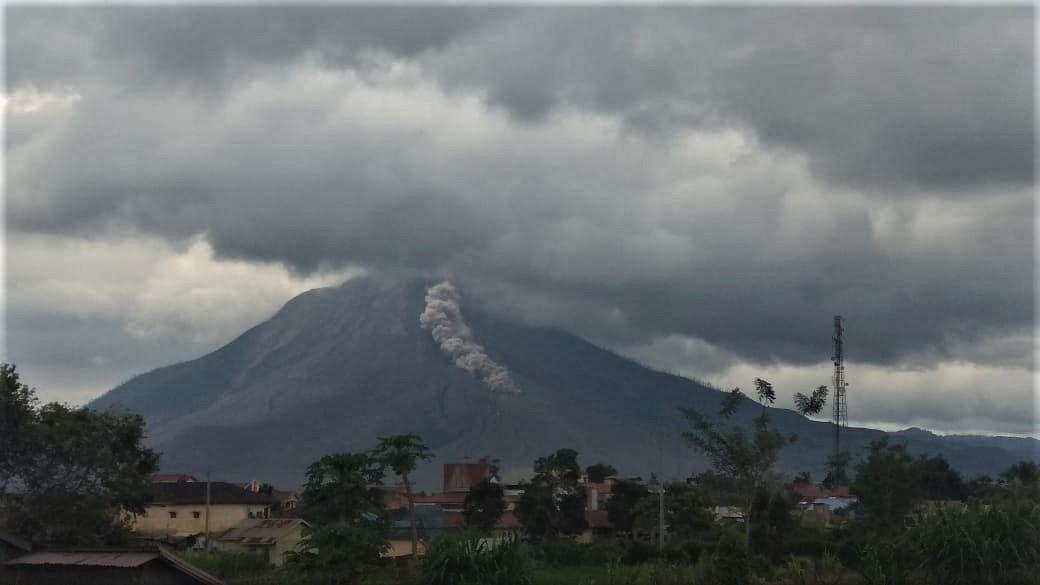
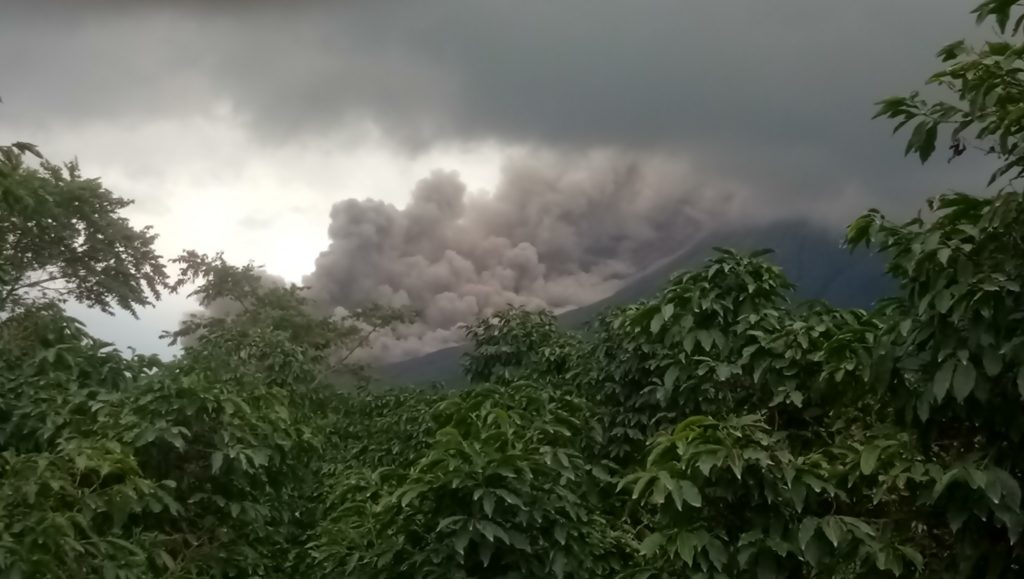
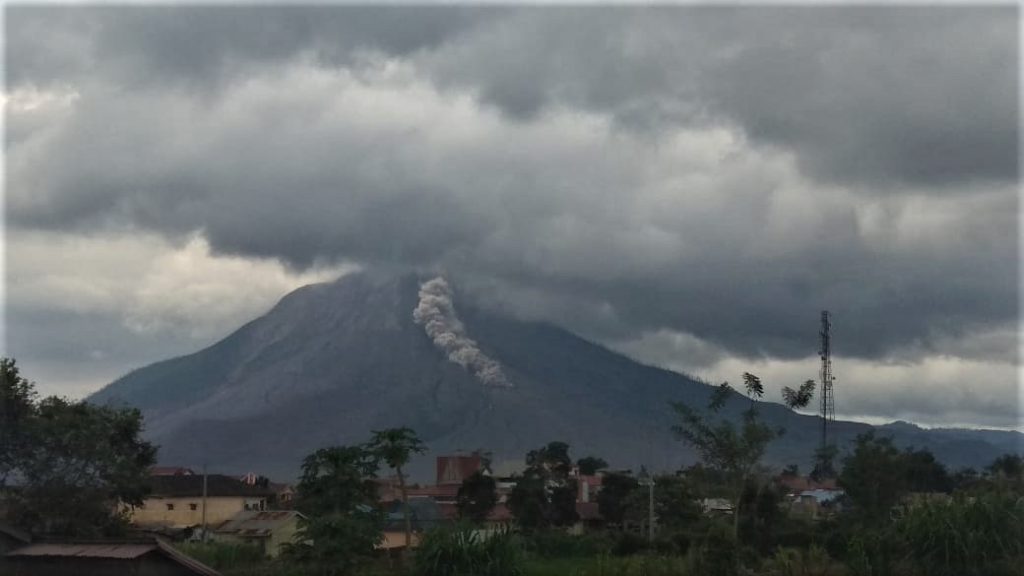
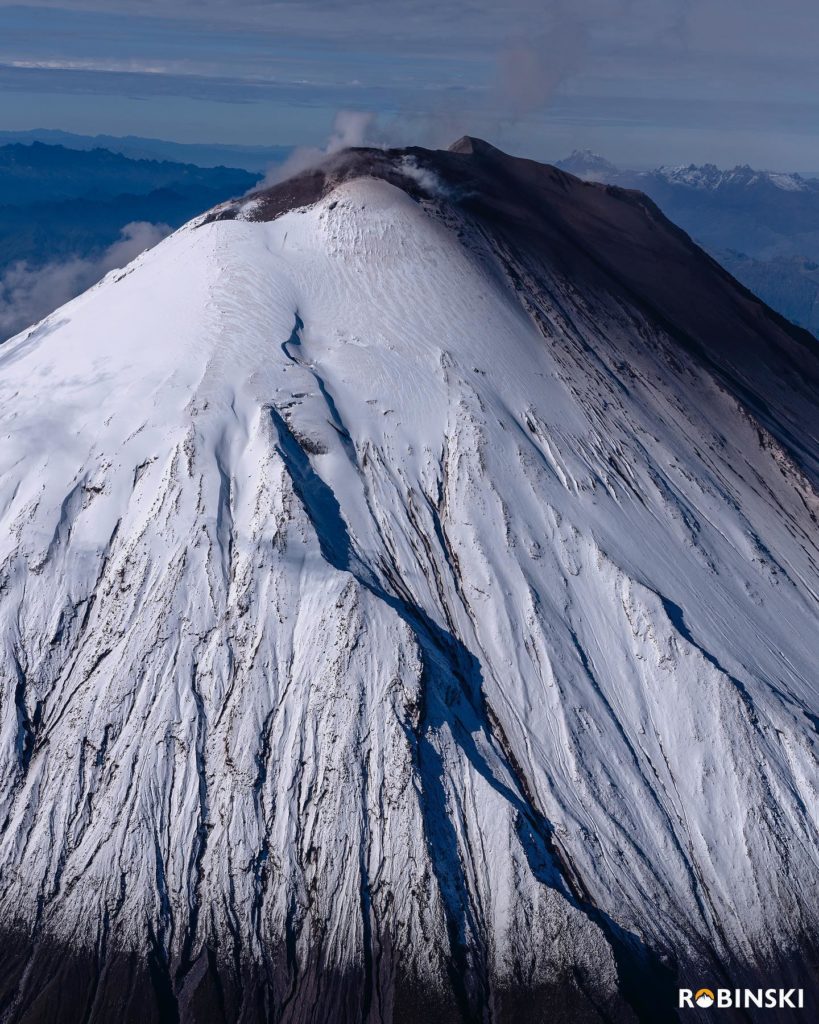
Indonesia, Sinabung:
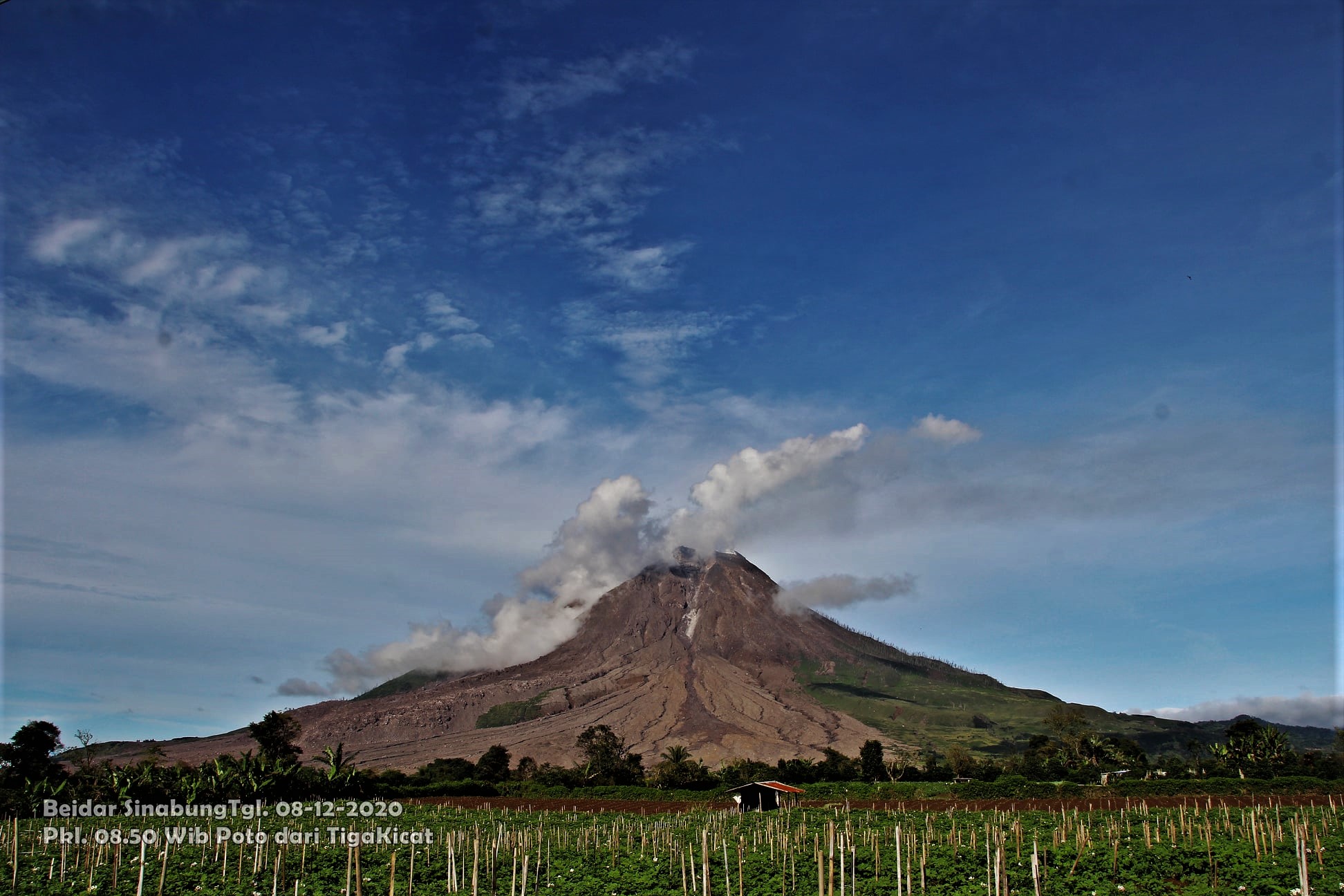
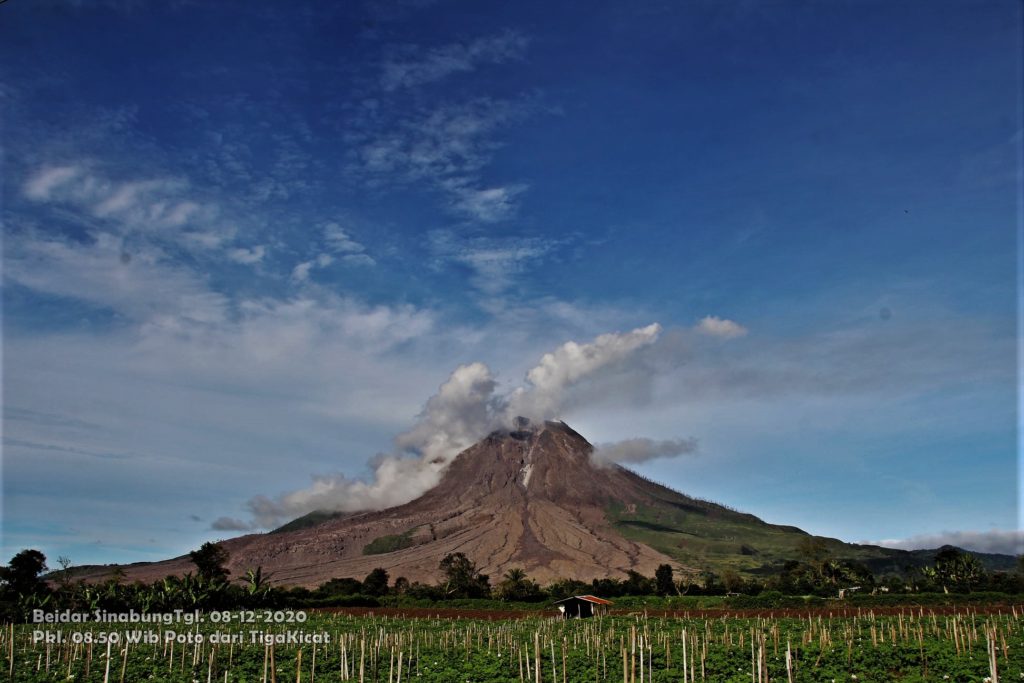
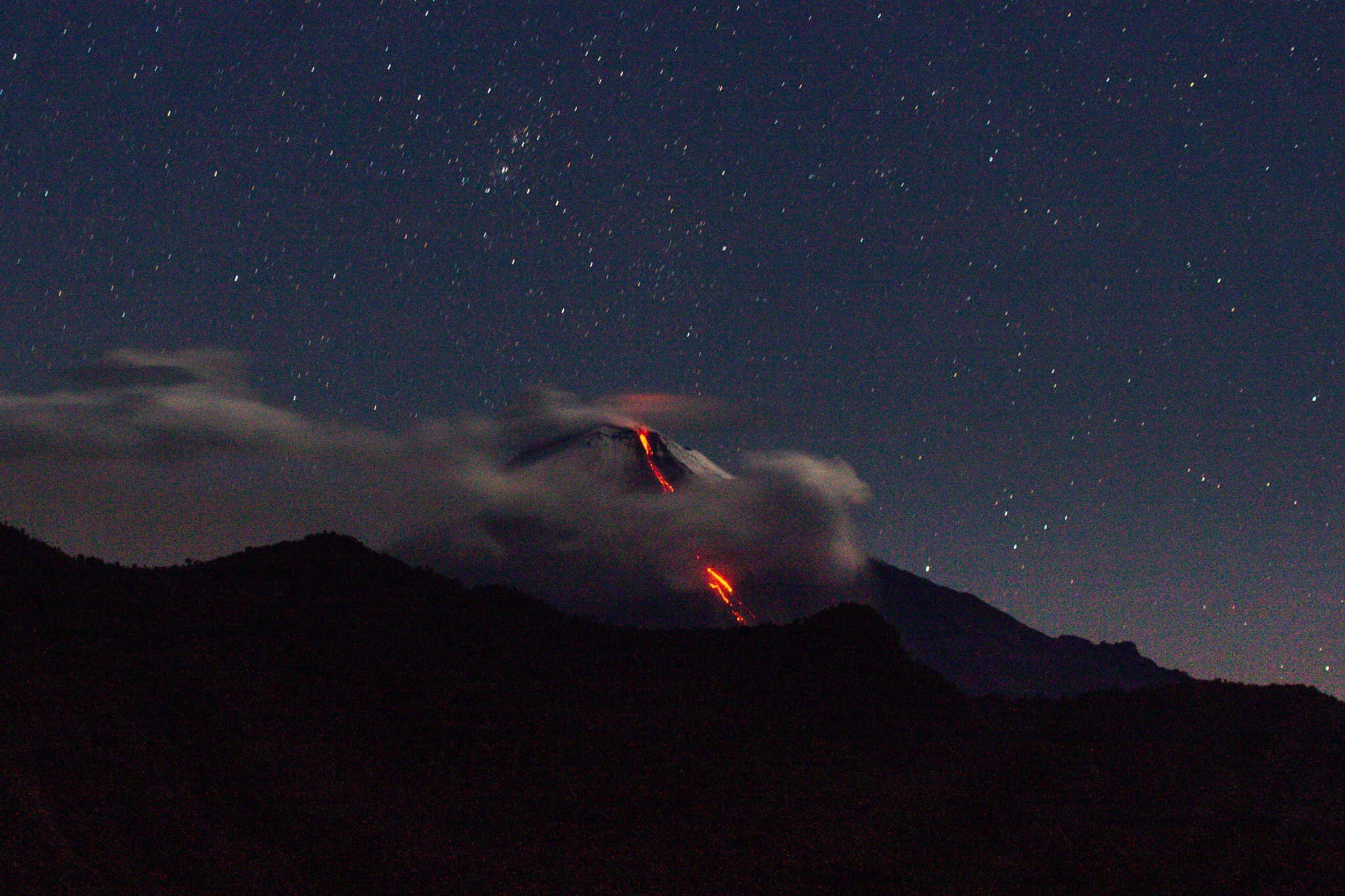
The activity level has been at level III (SIAGA) since May 20, 2019 at 10:00 a.m. Mount Api Sinabung (2460 m above sea level) has been erupting since 2013.
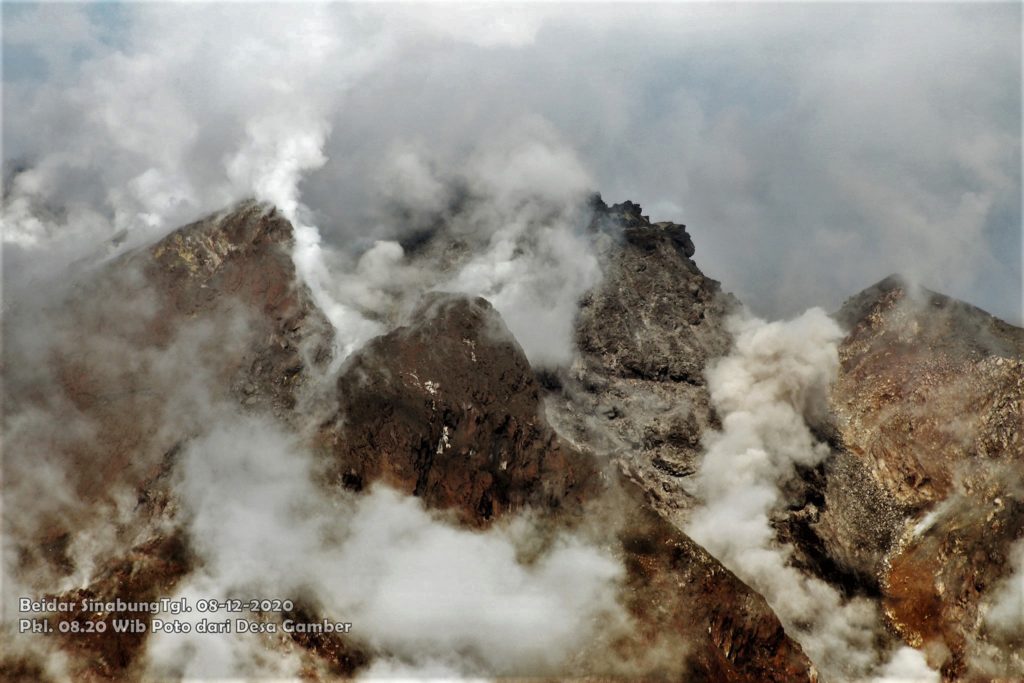
The volcano was clearly visible until it was covered in fog. It was observed that the crater emits white smoke with moderate height, thick, about 50-400 meters above the summit. There was an avalanche, but visually the distance and direction of the slide were not observed. The weather is sunny to rainy, with light to moderate winds to the east, northeast and southeast. The air temperature is around 17-26 ° C.
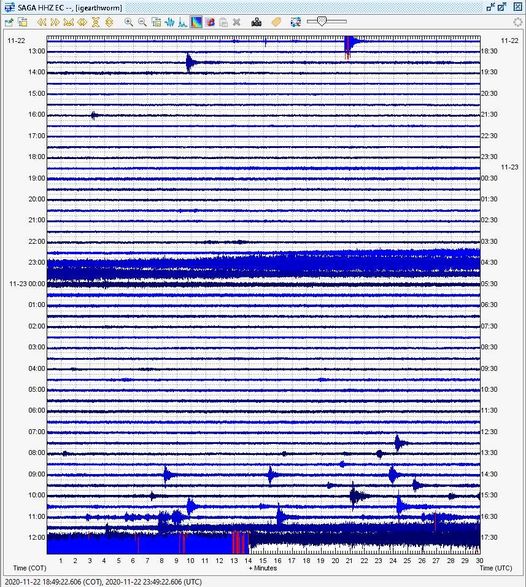
According to the seismographs of December 10, 2020, it was recorded:
71 avalanche earthquakes
3 emission earthquakes
25 low frequency earthquakes
3 hybrid / multi-phase earthquakes
2 local tectonic earthquakes
2 distant tectonic earthquakes
1 felt earthquake
Recommendation:
The community and visitors / tourists should not carry out activities in villages that have been moved, as well as within a radial radius of 3 km around the summit of G. Sinabung, with a sector radius of 5 km for the southern sector -East and 4 km for the North-East sector.
In the event of ash rain, people are advised to wear masks when leaving the house to reduce the health effects of volcanic ash. Secure the drinking water facilities and clean the roof of the house from dense volcanic ash so that it does not collapse.
People who live near rivers flowing from Mount Sinabung should be aware of the dangers of lahars.
VONA:
The last VONA message was sent with the color code ORANGE, published on December 2, 2020 at 08:01:00 WIB. Volcanic ash was observed at an altitude of 2,960 m above sea level or 500 m above the summit.
Source : PVMBG.
Photos : Firdaus Surbakti , Sagrah Peranginangin . Magma indonesia .
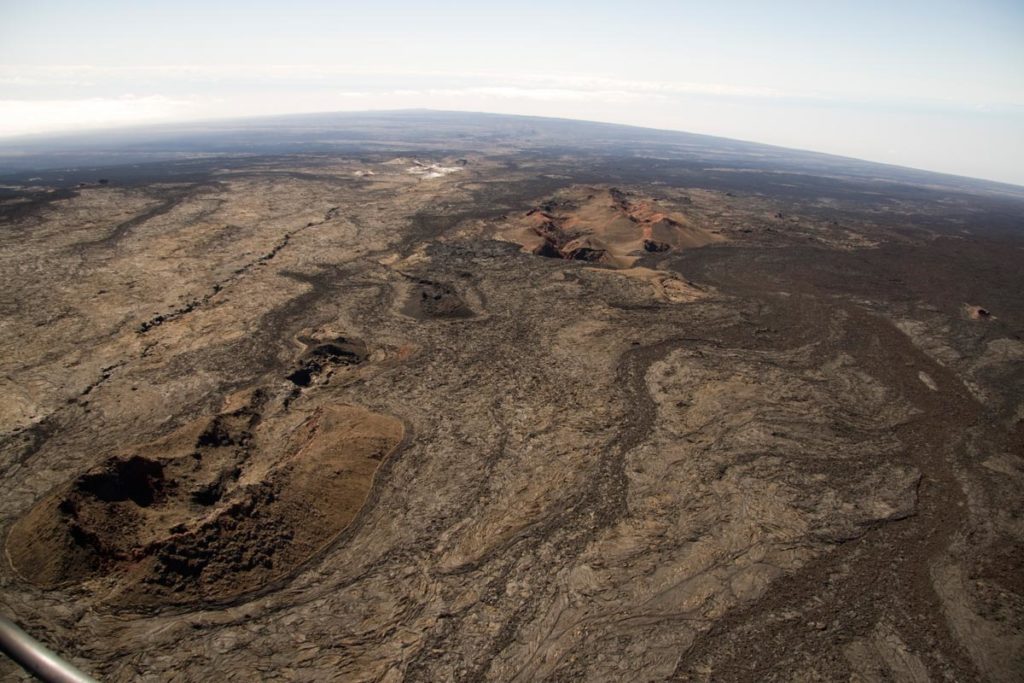
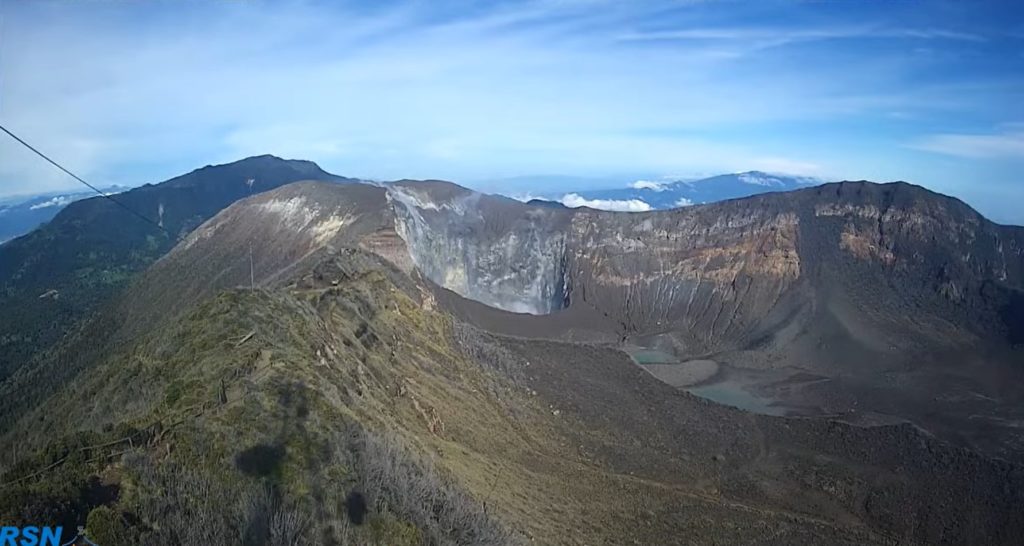
Hawaii , Mauna Loa :
19°28’30 » N 155°36’29 » W,
Summit Elevation 13681 ft (4170 m)
Current Volcano Alert Level: ADVISORY
Current Aviation Color Code: YELLOW
Activity Summary:
Mauna Loa Volcano is not erupting. Rates of deformation and seismicity have not changed significantly over the past week and remain above long-term background levels.
Observations:
During the past week, HVO seismometers recorded approximately 165 small-magnitude (below M2.5) earthquakes at Mauna Loa, mostly beneath the volcano’s summit and upper flanks. The majority of these earthquakes occurred at shallow depths of less than 8 kilometers (~5 miles) below sea level.
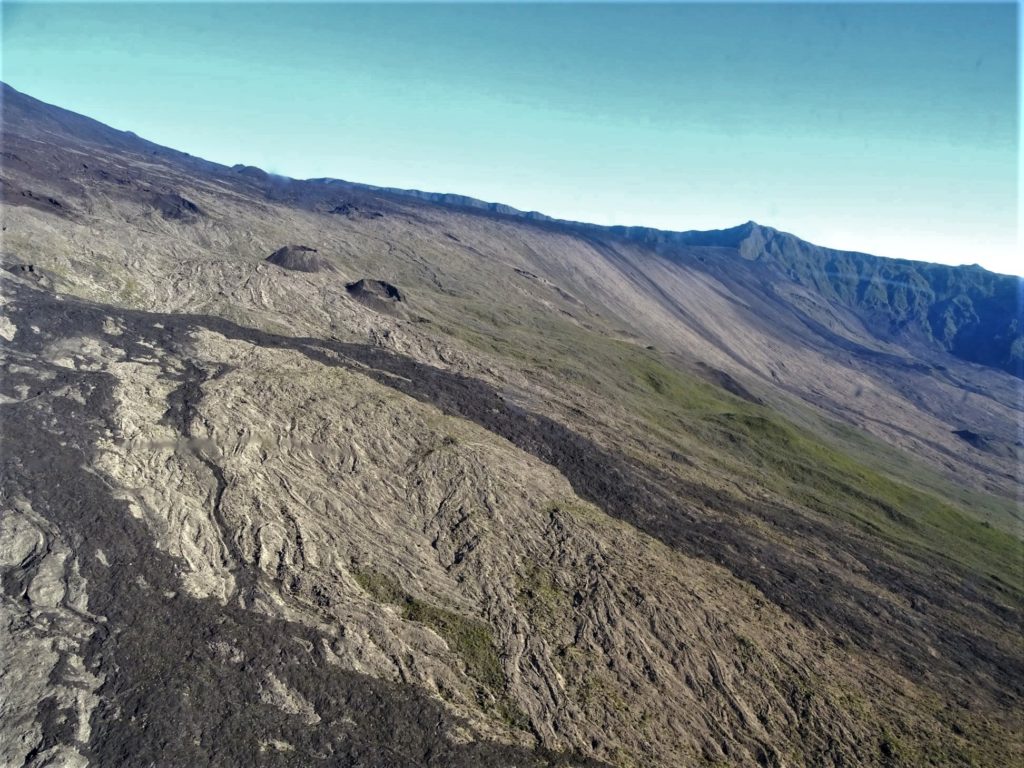
View from just below the summit of Mauna Loa looking back down the Southwest Rift. The Sulfur Cone is the white area just above center frame. Pu‘u o Keokeo is the barely visible bump just above Sulfur Cone at the crest of the Southwest Rift.
Earthquake activity increased on Mauna Loa’s northwest flank on December 4, 2020, including a magnitude-4.1 earthquake and clusters of small, shallow earthquakes occurring closely in time and location. Since December 4, HVO has recorded over 150 earthquakes in this region, at depths from 1–9 km (1–6 miles) below the surface, over an area of less than 4 km (2 miles) and extending 6 km (4 miles) north. The bulk of the seismicity has been below magnitude-2, and deeper than 4 km (2 miles) beneath the surface. Elevated seismicity in this region continues at the time of this report although events have occurred less frequently over the past 48 hours.
Clustering of shallow earthquakes in this region is not unprecedented. Previous earthquake swarms at this location and depth occurred in October 2018, April 2017, July 2016, August 2015, and earlier.
Global Positioning System (GPS) measurements continue to show slow, long-term summit inflation, consistent with magma supply to the volcano’s shallow storage system.
Gas concentrations and fumarole temperatures at both the summit and Sulphur Cone on the Southwest Rift Zone remain stable.
Webcam views have revealed no changes to the landscape over the past week.
Source et photo : HVO .
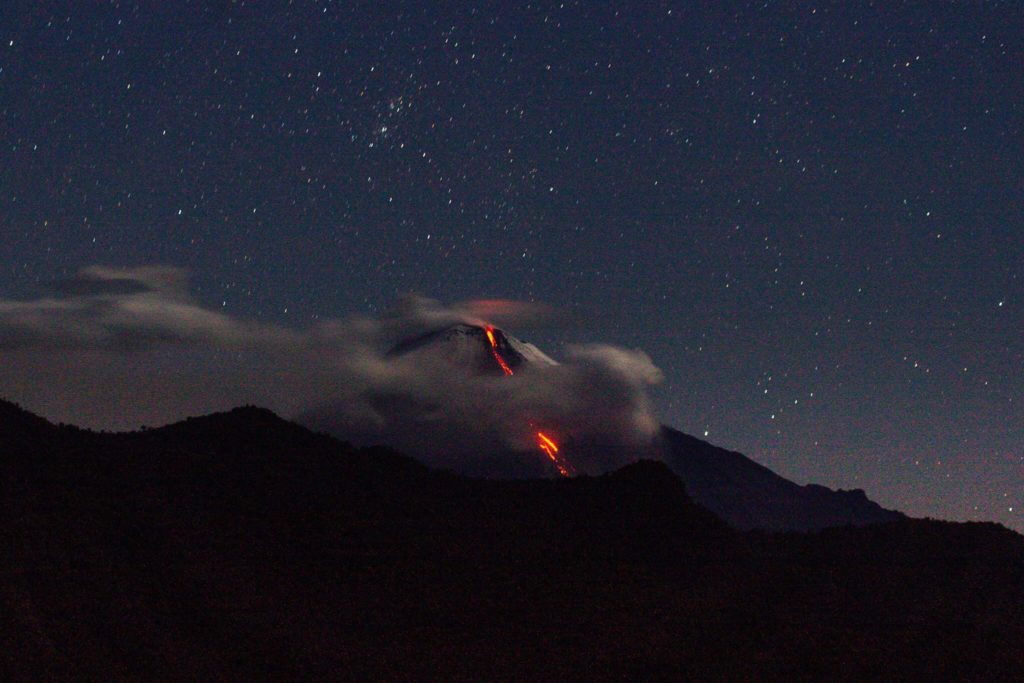
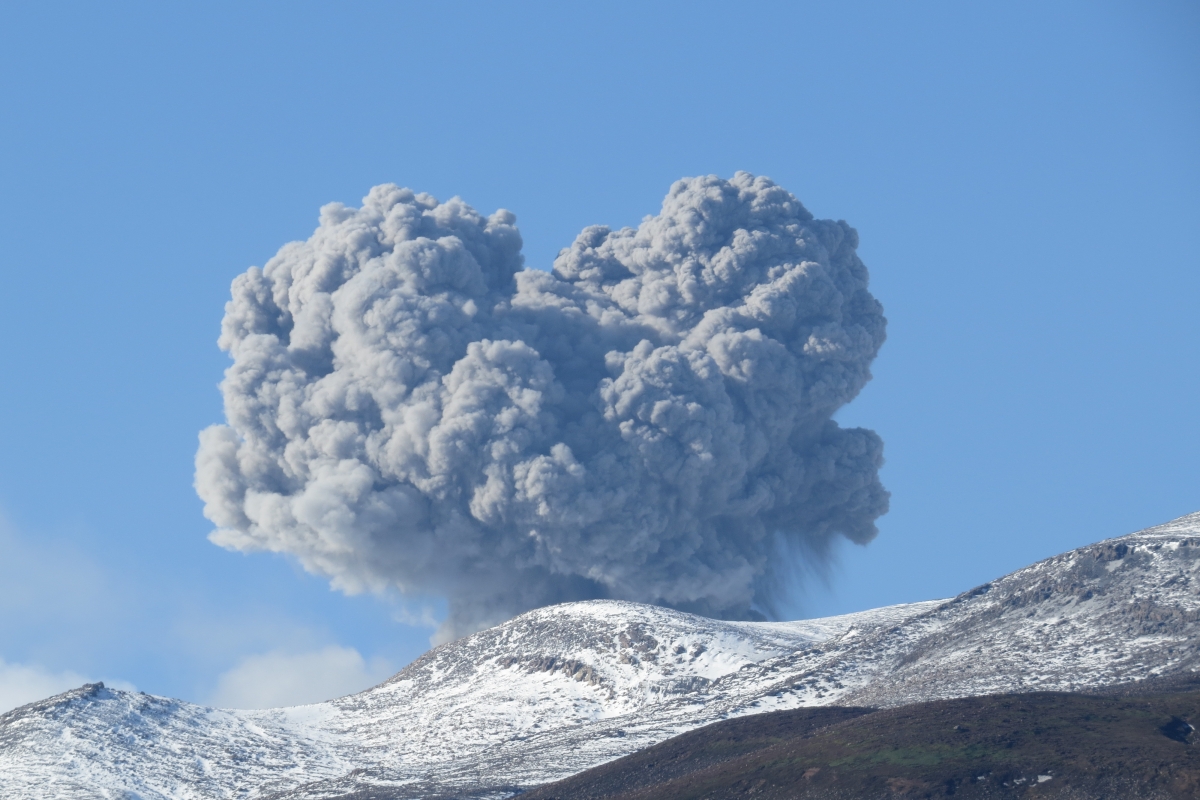
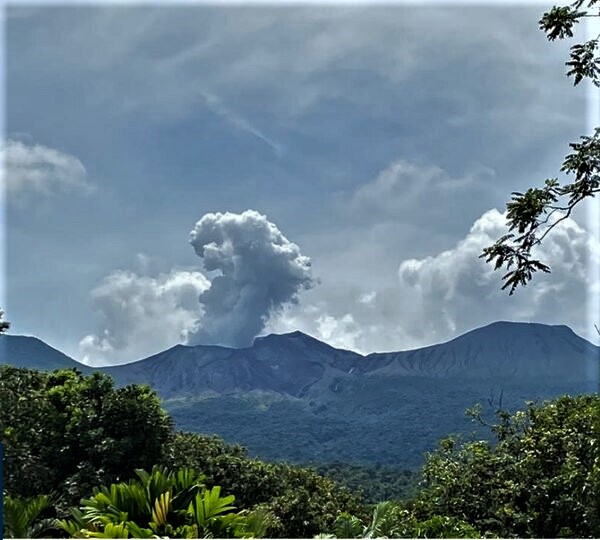
Ecuador , Sangay :
DAILY REPORT ON THE STATE OF SANGAY VOLCANO, Thursday December 10, 2020.
Surface activity level: High, Surface trend: Increasing.
Internal activity level: High, Internal trend: Increasing.
Seismicity: From December 09, 2020, 11:00 a.m. to December 10, 2020, 11:00 a.m.
Long period type events (LP): 25
Emission tremor (TE): 33
Explosions (EXP): 99
Harmonic Tremor (TA): 2
Rains / lahars:
In the morning, there was rains in the area which generated signals associated with flows of mud and debris.
** In case of heavy rains, lahars can be generated in the Volcán, Upano rivers and other tributaries **
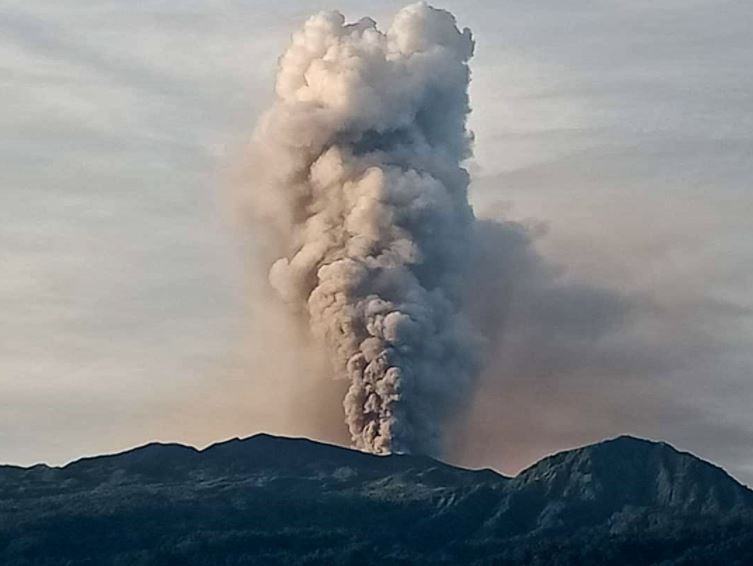
Ash Emission / Column: Since early morning and part of the morning today, continuous gas and ash emissions have been observed at altitudes exceeding 2000 meters above crater level, oriented towards West. The VAAC recorded 4 ash emission alerts observed by the satellites which reached altitudes of 1500 and 2100 meters above the level of the crater in a West and North-West direction
Other monitoring parameters: FIRMS recorded 34 thermal alerts on the Sangay in the last 24 hours.
MIROVA recorded 3 moderate thermal alerts on the Sangay in the last 24 hours.
Observations: From early morning and part of the morning today, the volcano appeared clear, allowing us to observe the previously reported activity. In images shared by the Volcanic Observatory Network (ROVE), this activity was also observed. Until the close of this bulletin, there are reports of slight ash fall in the villages of Capzol, Palmira and Cebadas and in the townships of Chunchi and Guamote.
Alert level: yellow.
Sources : INSTITUT GÉOPHYSIQUE / ÉCOLE NATIONALE DE POLYTECHNIQUE.
Photo : TopMotor Storee.
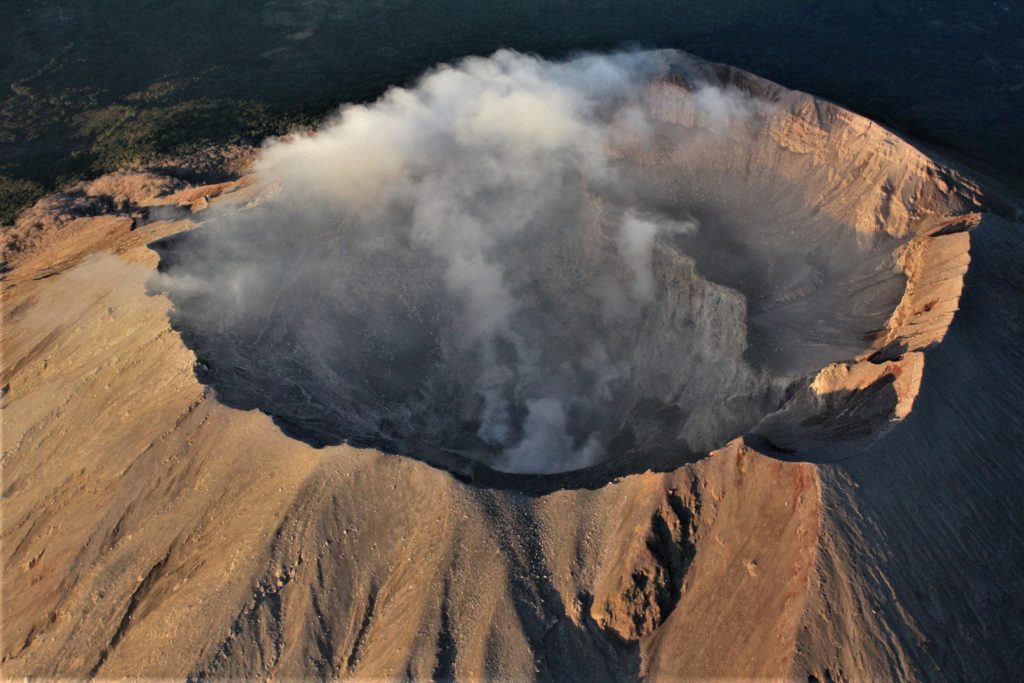
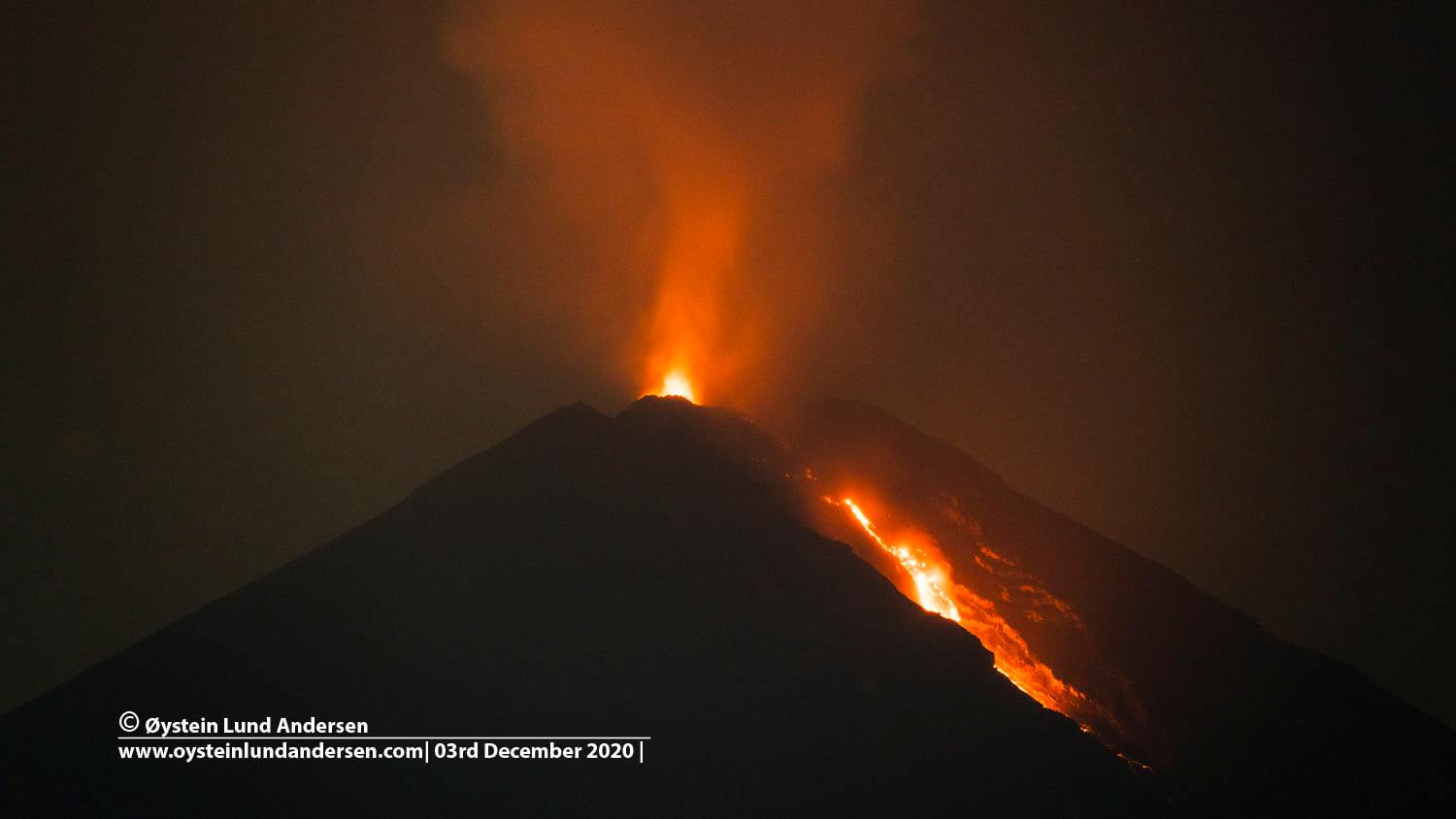
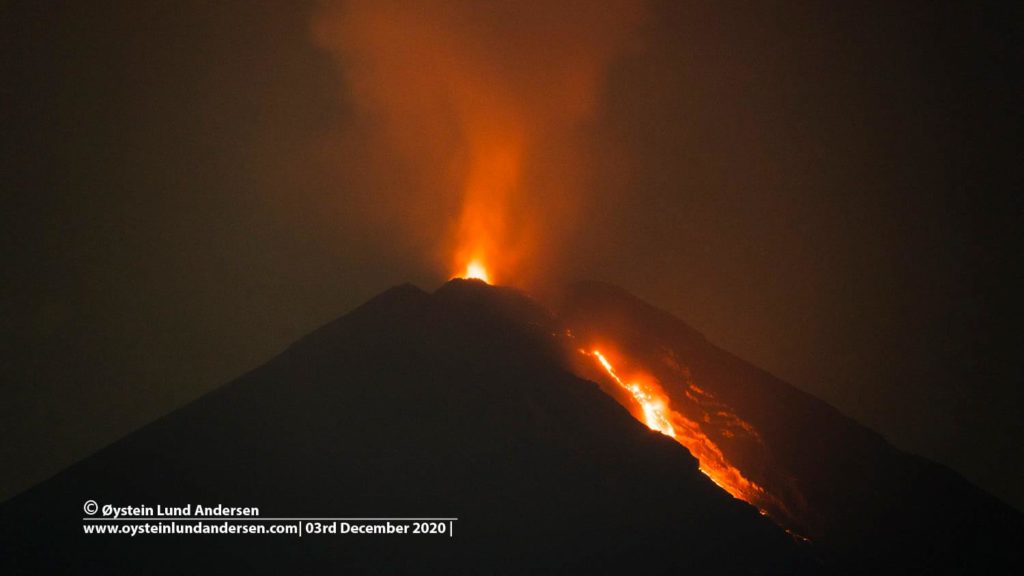
Guatemala , Pacaya :
SPECIAL BEPAC VOLCANOLOGICAL INFORMATION BULLETIN # 119-2020
« VOLCANIC ACTIVITY UPDATE »
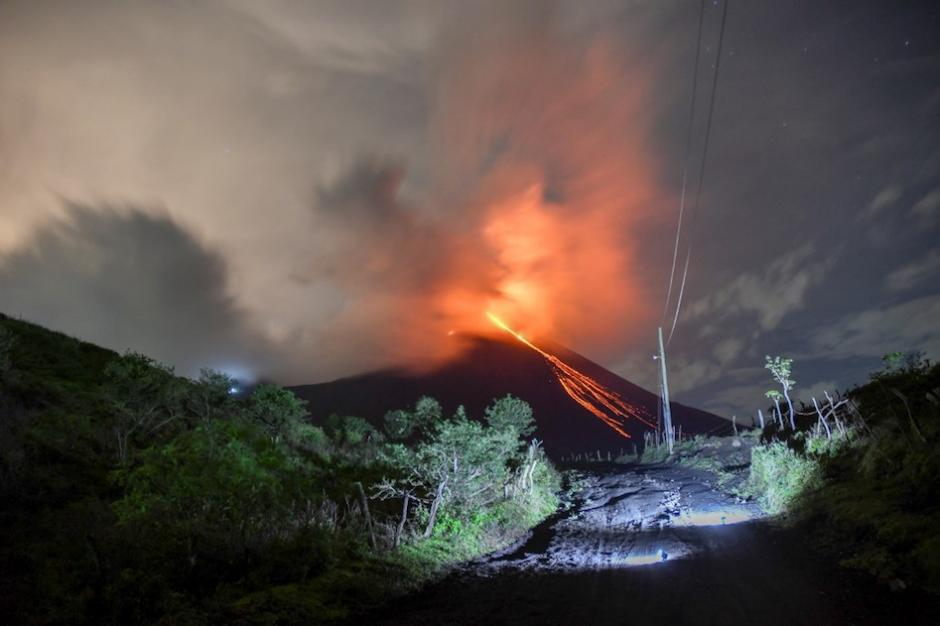
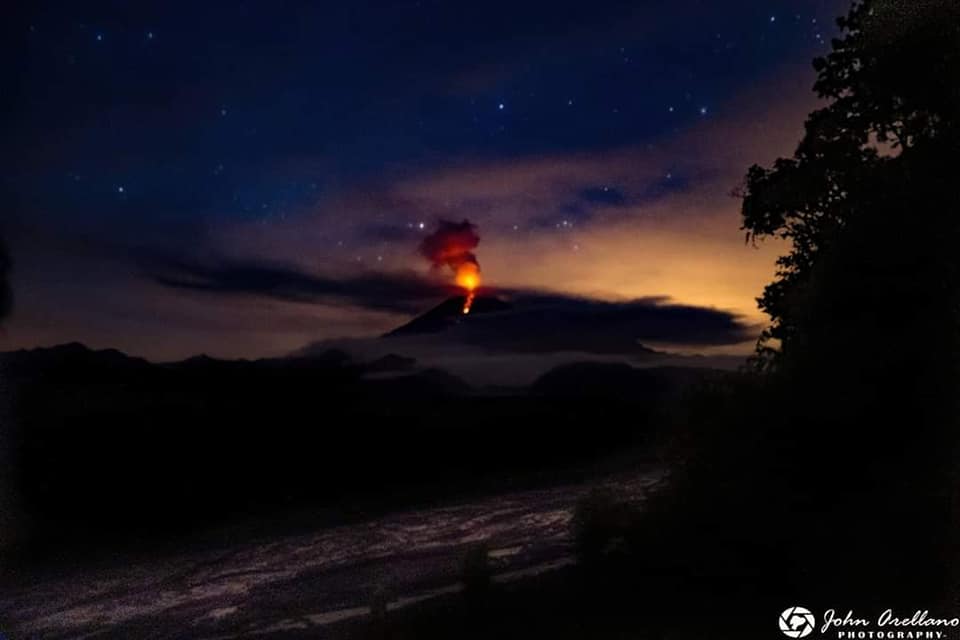
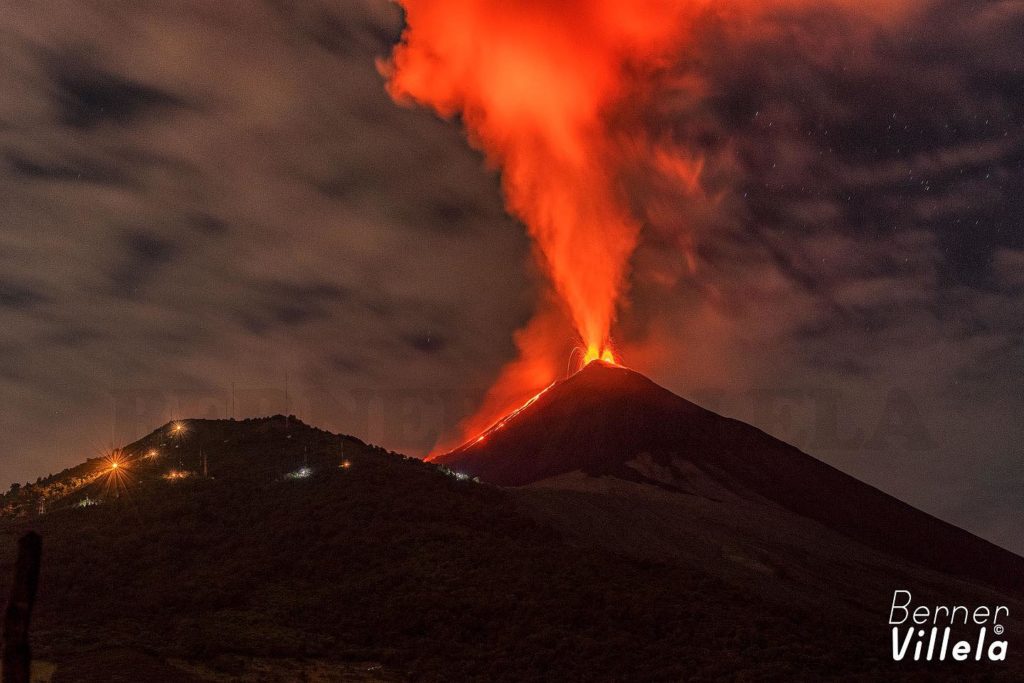
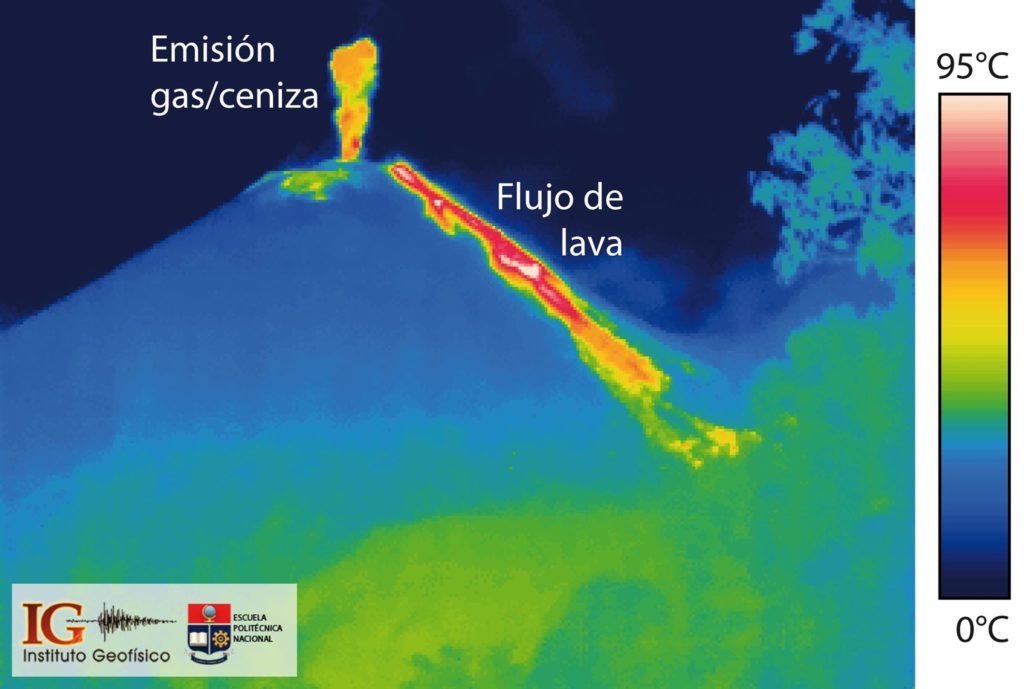
Since December 9, 2020, the Pacaya volcano observatory, OVPAC has reported a new lava flow in a West-North-West direction, in front of Cerro Chino, reaching a variable length between 50 and 250 meters, approximately. The lava flow reported from the middle part of the volcano in a West-South-West direction is still active and has several branches, having lengths of between 400 and 600 meters approximately. Both lava flows have avalanches that are up to 100 meters long, areas near the lava flows are areas with high temperatures, so it is not recommended to approach them.
The activity of the last few months has been mainly effusive with some periods of moderate Strombolian explosive which emit materials up to 175 meters above the crater. Some explosions generate rumbles and the fall of ballistic projectiles within a radius of about 50 meters. There is a constant incandescence and the degassing of a plume with white / blue tones due to its composition of water, sulfur dioxide and other magmatic gases. An eruptive plume that reaches 200 meters above the crater has also been reported and dispersed in the direction of the wind. Explosive activity keeps the cycle of building and destroying the intracrater cone active.
INSIVUMEH, provides visual and instrumental surveillance, by means of a web camera, of seismic stations (PCG and PCG5) and OVPAC observers.
Source : Insivumeh .
El Salvador , San Miguel ( Chaparrastique) :
Location: San Miguel Department
Altitude: 2130 meters above sea level
Type of volcano: Stratovolcano
Type of activity: Strombolian-Vulcanian
Last significant eruption: December 29, 2013
In November, the seismic vibration of the San Miguel volcano continued to fluctuate between 31 and 50 RSAM units, on average per day. There is no report, by the inhabitants, who live in the area of the volcano, of felt earthquakes. In conclusion, the volcano continues to exhibit a low level of activity, although it continues to emit gases from the central crater.
Sulfur dioxide (SO2) emissions remained fluctuating within the normal range, indicating that no new injection of magma into the volcanic system has occurred. Thus, the activity of the volcano is kept in balance.
However, it is not excluded that a new ascent of magma may occur and its activity suddenly changes, as happened on previous dates. Therefore, it is suggested that climbers and the general population avoid visiting the crater.
Source et photo : Marn .