January 18 , 2019.
Alaska , Cleveland :
AVO/USGS Volcanic Activity Notice
Current Volcano Alert Level: WATCH
Previous Volcano Alert Level: ADVISORY
Current Aviation Color Code: ORANGE
Previous Aviation Color Code: YELLOW
Issued: Thursday, January 17, 2019, 11:25 AM AKST
Source: Alaska Volcano Observatory
Notice Number: 2019/A53
Location: N 52 deg 49 min W 169 deg 56 min
Elevation: 5676 ft (1730 m)
Area: Aleutians

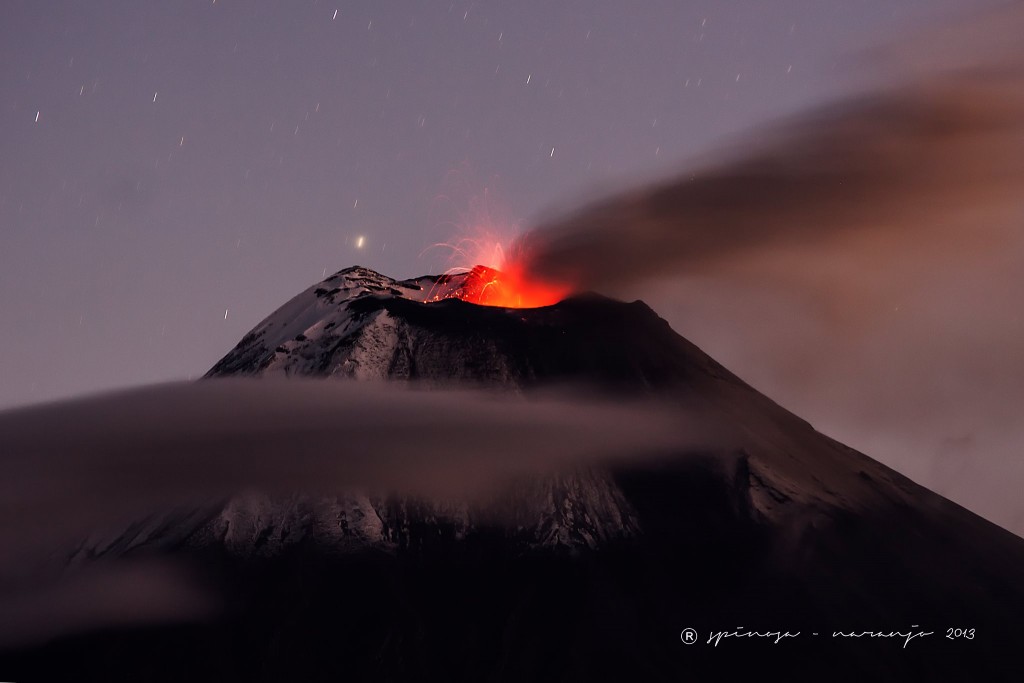
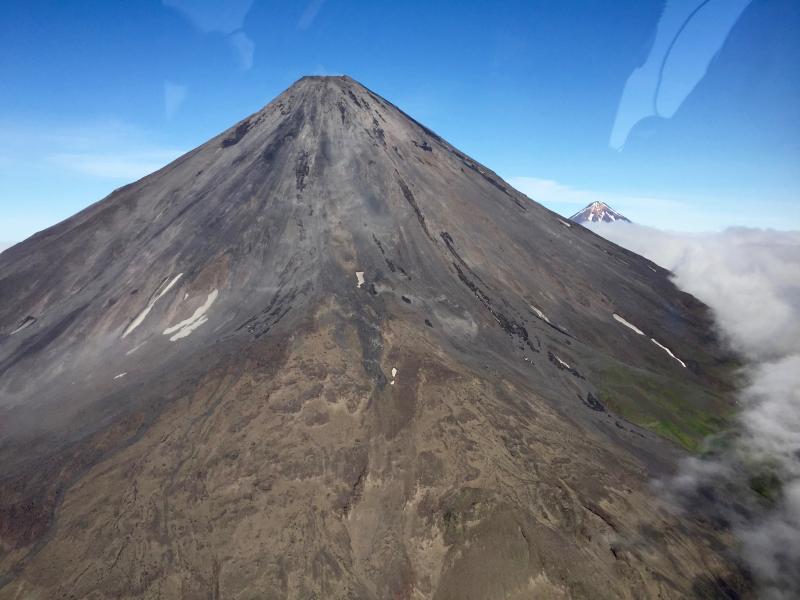
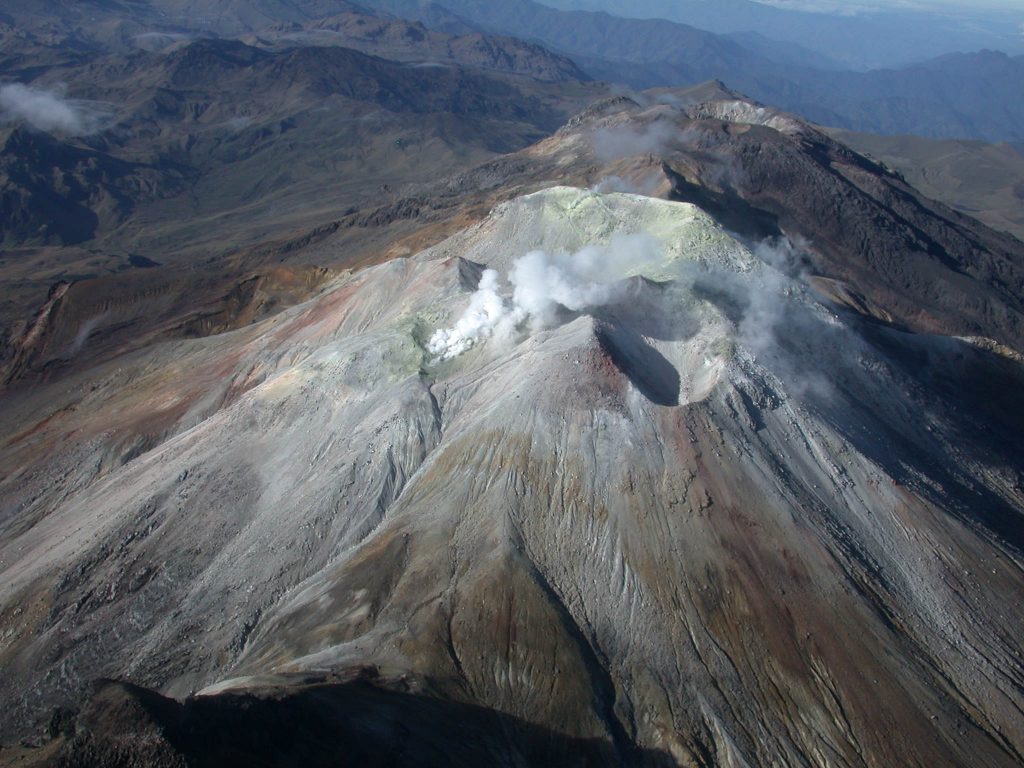
Cleveland Volcano overflight, August 4, 2015. View of lava dome within Cleveland’s summit crater, showing concentric rings and radial fractures in dome surface, surrounding elevated, hot dome core. Photo taken during the 2015 field season of the Islands of Four Mountains multidisciplinary project, work funded by the National Science Foundation, the USGS/AVO, and the Keck Geology Consortium.
Volcanic Activity Summary:
Satellite data show that starting around 12 January, a new and growing lava dome is present in Cleveland’s summit crater. Thus, AVO is raising the Aviation Color Code to ORANGE and the Volcano Alert Level to WATCH.
The presence of the lava dome may increase the likelihood of explosive activity at the volcano. Explosions at Cleveland usually occur without warning and typically produce relatively small volcanic ash clouds that dissipate within hours; however, more significant ash emissions are possible.
Recent Observations:
[Volcanic cloud height] None
[Other volcanic cloud information] n/a
[Lava flow/dome] new dome observed
Remarks:
Cleveland volcano is monitored by only one seismic station, which restricts AVO’s ability to detect precursory unrest that may lead to an explosive eruption. Rapid detection of an ash-producing eruption may be possible using a combination of seismic, infrasound, lightning, and satellite data.
Source : AVO.
Photo : Lyons, John; Schmitt, Joe.
Colombia , Chiles /Cerro Negro :
Weekly activity bulletin Chiles and Cerro Negro volcanoes
The activity level of volcanoes continues at: LEVEL YELLOW ■ (III): CHANGES IN THE BEHAVIOR OF VOLCANIC ACTIVITY.
Following the activities of the CHILE and CERRO NEGRO volcanoes, the COLOMBIAN GEOLOGICAL SERVICE (SGC) reports that:
For the period from 8 to 14 January 2019 and compared to the previous week, there is a decrease in seismic activity both in this case and in released energy, but there are fluctuations especially in occurrence of earthquakes. The majority of events continue to be associated with fracturing of the rock within the volcano, with a preferential location south-southwest of the Chiles volcano, with epicentral distances of less than 5 km, depths between 2 and 5.5 km from the summit (4700 m) and a local maximum magnitude of M1.8 on the Richter scale.

It was pointed out on January 15, 2019 at 2:44 pm that an earthquake of magnitude M3.2 was recorded, located southwest of the volcano Chiles, but that until the publication of this bulletin, it did not been reported as felt.
The COLOMBIAN GEOLOGICAL SERVICE is attentive to the evolution of the volcanic phenomenon and will continue to inform in a timely manner of the observed changes.
Source : SGC.
Photo : Ingeominas.
Indonesia , Ibu :
Activity Level at Level II (WASPADA). The Ibu volcano (1340 m altitude) has been continuously erupting since 2008.
Since yesterday and until this morning, the vision of the volcanic peak was clear until it was covered with fog. The smoke from the crater is not observed. The wind is blowing weakly to moderately south and west.
According to the seismographs, dated January 17, 2019, it was recorded:
85 earthquakes of eruption
69 emissions earthquakes
24 avalanche earthquakes
13 harmonic tremors.
2 local tectonic earthquakes
2 distant tectonic earthquakes.
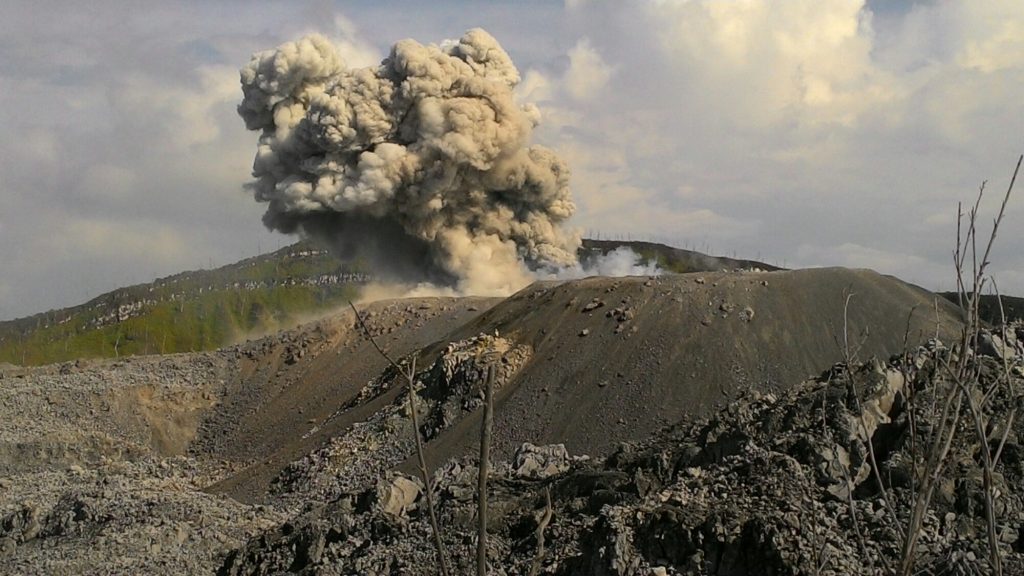

Recommendation: Communities around G. Ibu and visitors / tourists should not have activities, climb and approach within 2 km. The sectoral expansion is 3.5 km towards the openings in the northern part of the active crater of G. Ibu.
VONA: The last message VONA sent the color code ORANGE, published on January 13, 2019 at 8:01 am, which indicated an eruption with ash column height around 2125 m above sea level or about 800 m above the summit. The column of ashes was moving south.
Source : PVMBG , Magma Indonesia .
Photo : John Massolo – WordPress.com
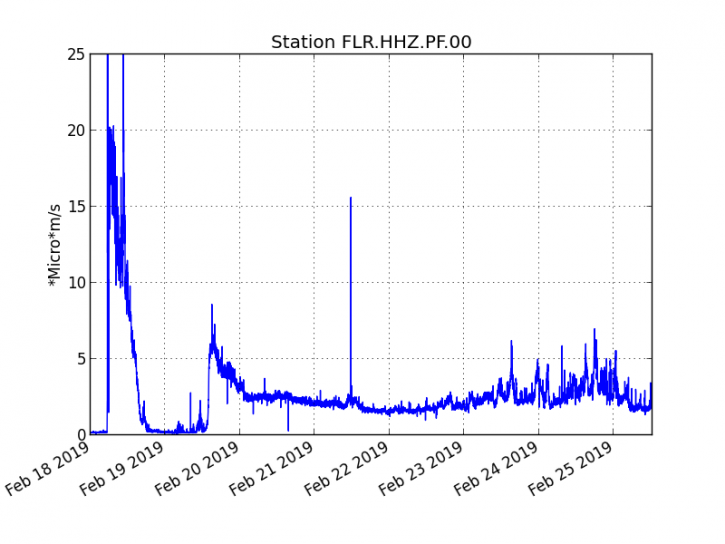
Mayotte , seismic activity :
Birth of a volcano off Mayotte?
Volcanic eruption imminent? Expulsion of gas pockets? The discovery of a large quantity of dead fish on the surface of the sea on the seismic swarm zone that touches Mayotte since May 10, 2018, questions scientists who make assumptions.
It is on the basis of observations similar to other places on the planet that these scientists share their theses. Franck Lavigne, professor at the University of Paris 1, director of the Laboratory Physical Geography at the CNRS evokes in particular the piton of the furnace in 2017 and the discoveries of hundreds of corpses fish depth where the lava was thrown into the sea:
« The volcanic eruption changes the usual biotope of underwater fauna and flora. There was a warming of the water temperature as well as a change in the salinity that disturbed the species »
Frédéric Léone, university professor at Montpellier 3, specializing in natural hazards, thinks of the release of gas pockets.
« Either methane trapped in marine sediments (from organic decomposition) or juvenile carbon monoxide (magmatic origin) accumulated at the base of the water column. Earthquakes had to disrupt the sea depths and release these pockets that rise to the surface »
But other more alarmist theses are also evoked as a rise of magma or gas that would pass through faults created during the multiple earthquakes that the island has experienced since May 10, 2018. Still others report an eruption volcanic imminent or ongoing, with a risk of Tsunami. However the seismic focus would be between 10 and 20 km below the sea floor, so the risks would be limited.
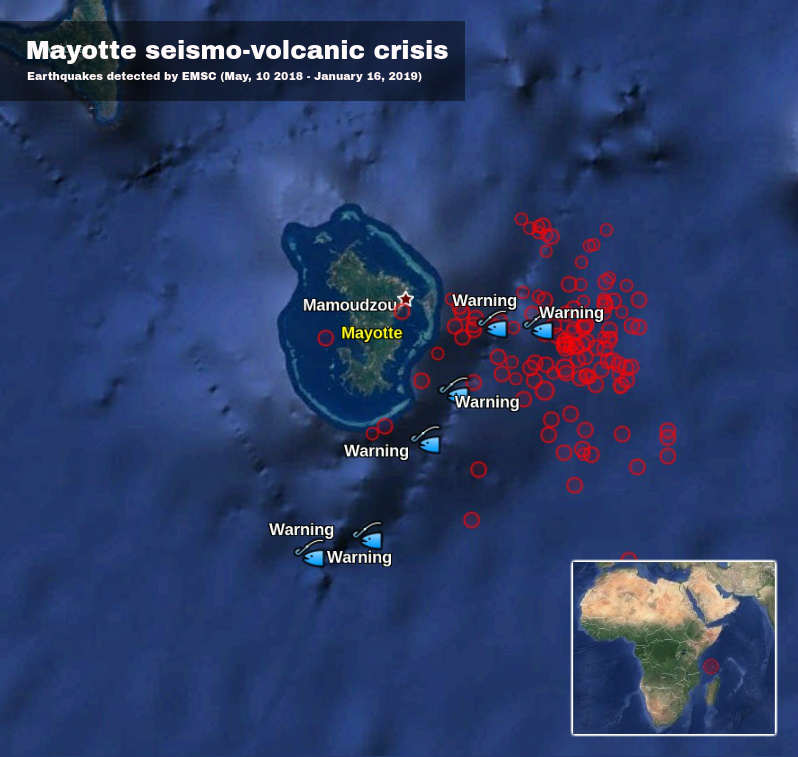
Large number of dead fish, sulfur smell reported, Mayotte seismo-volcanic crisis intensifies.
A large number of dead fish emerged at various sites off the barrier reef just east/southeast of Mayotte, the oldest volcanic island in the Comoros Basin located between Madagascar and Mozambique. This is the site of an intense earthquake swarm that started in May 2018 and continues to date.
Visual observations of dead fish are accompanied by a strong smell of gas, burning rubber, plastic or sulfur, officials said January 14. The information was confirmed by the representatives of the Fishermen’s Cooperative of Mtsapere.
…/…
…/…
Since mid-July [to November 2018], GPS stations on the island have tracked it sliding more than 61 mm (2.4 inches) to the east and 30 mm (1.2 inches) to the south, according to data provided by the Institut National de L’information Géographique et Forestière.
Using these measurements, Pierre Briole of the Ecole Normale Supérieure in Paris estimated that a magma body that measures about 1.4 km3 (0.3 mi3) is squishing its way through the subsurface near Mayotte.
The last known volcanic eruption in this area took place in 2050 BCE ± 500 years.
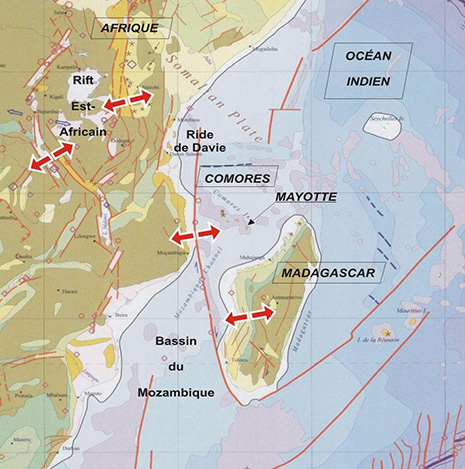
Geological background
Mayotte Island in the Mozambique Channel between the northern tip of Madagascar and the eastern coast of Africa consists of two volcanoes with diverse geochemistry that were active from the Pliocene to the Holocene.
Lavas on the NE were active from about 4.7 to 1.4 million years and on the south from about 7.7 to 2.7 million years.
Mafic activity resumed on the north from about 2.9 to 1.2 million years and on the south from about 2 to 1.5 million years. Morphologically youthful-looking maars are present on Mayotte Island, and Zinke et al. (2003) found several pumice layers of Holocene age in gravity cores on the barrier reef-lagoon complex at Mayotte. (GVP)
Source : la1ere.francetvinfo.fr , watchers.news.
Read the article from watchers.news in full : https://watchers.news/2019/01/16/large-number-of-dead-fish-sulfur-smell-mayotte-seismo-volcanic-crisis/?utm_source=dlvr.it&utm_medium=twitter&fbclid=IwAR3vM53WPiXTlU_jqE93EEmI-7Bya7W-7S3_kvhWYDUwTJqlP-BjITjzjak
Costa Rica , Turrialba / Poas / Rincon de la Vieja :
Daily report on the state of volcanoes. Date: January 17, 2019, Updated at: 11:42:00.
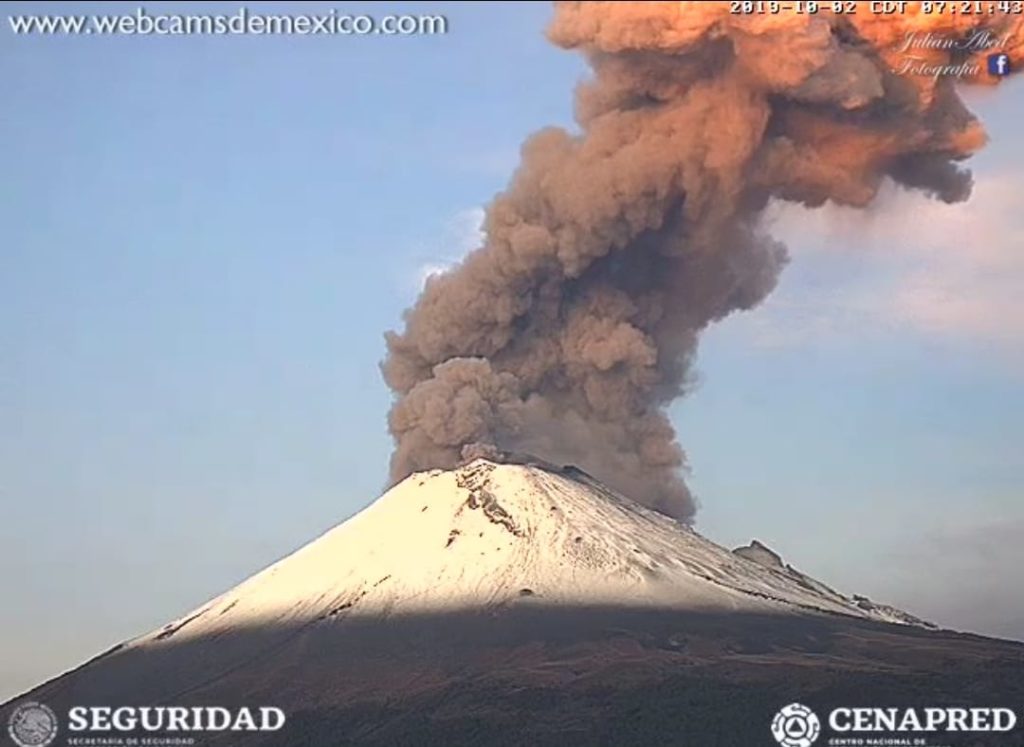
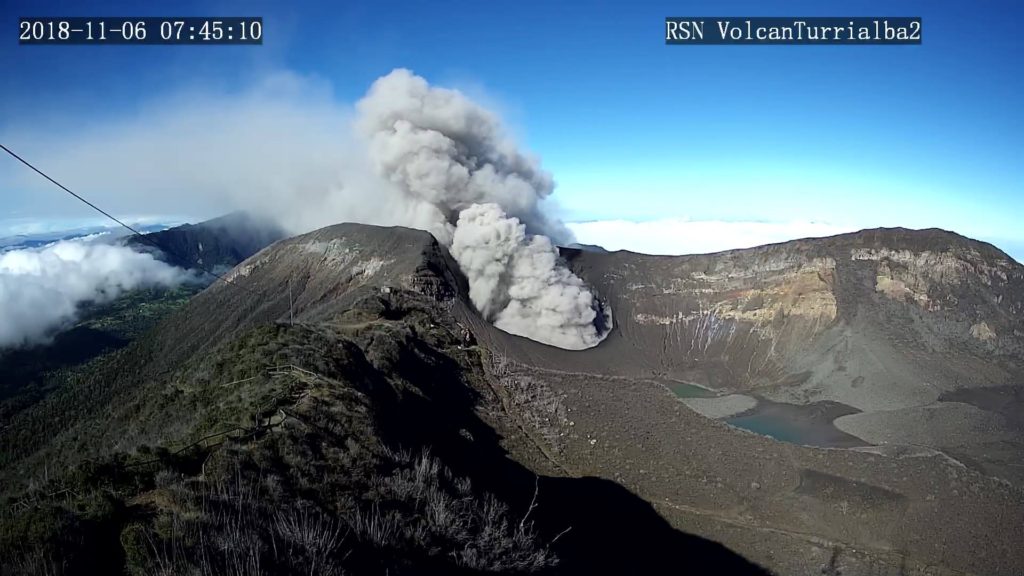
Turrialba Volcano:
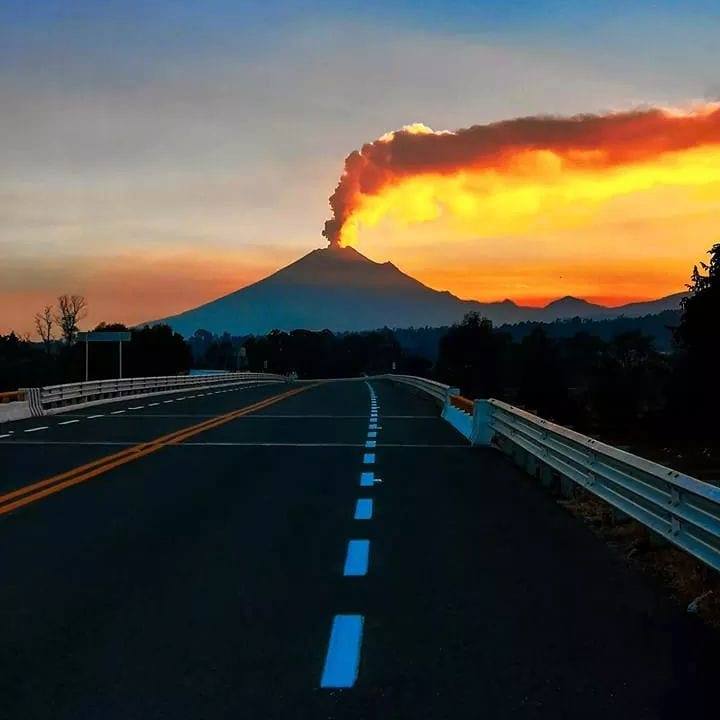
On January 17, 2019, at 00:00 local time, there is an eruption on the Turrialba volcano, with a column that rose 200 meters above crater height and 3540 meters above sea level. Wed (11611.2 ft).
Duration of the activity: minutes.
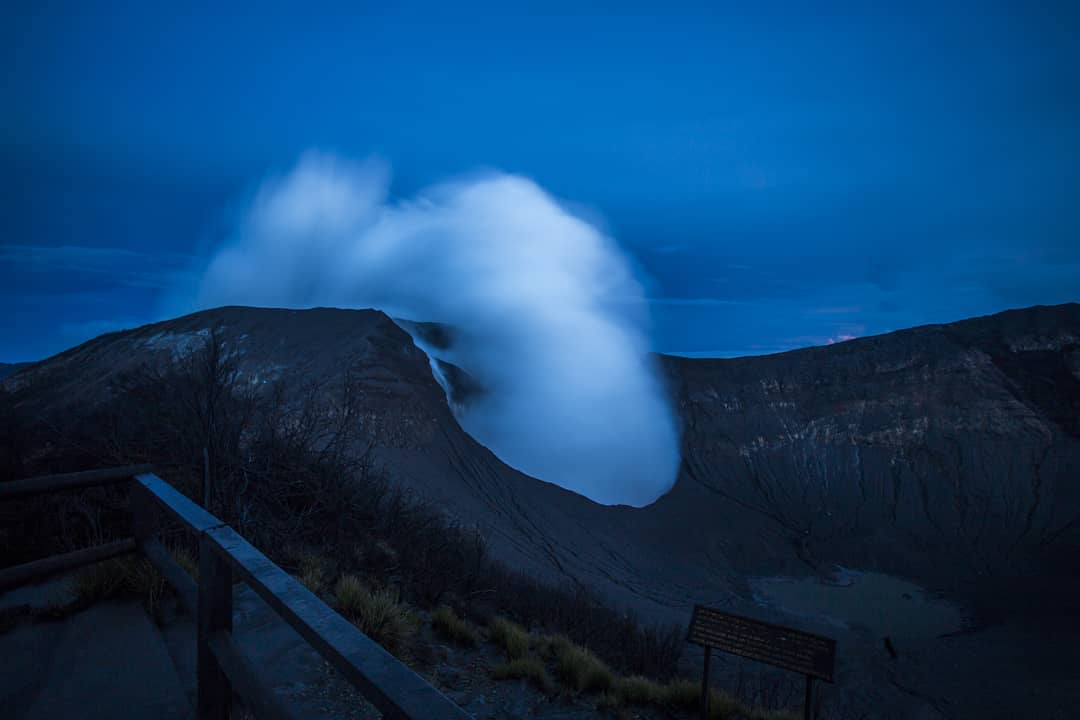

The seismic activity is similar to that of yesterday.
At the time of writing, winds are blowing from the southwest.
A passive, weak but continuous emission of ashes resumed at night. For the moment, no ash drop has been reported.
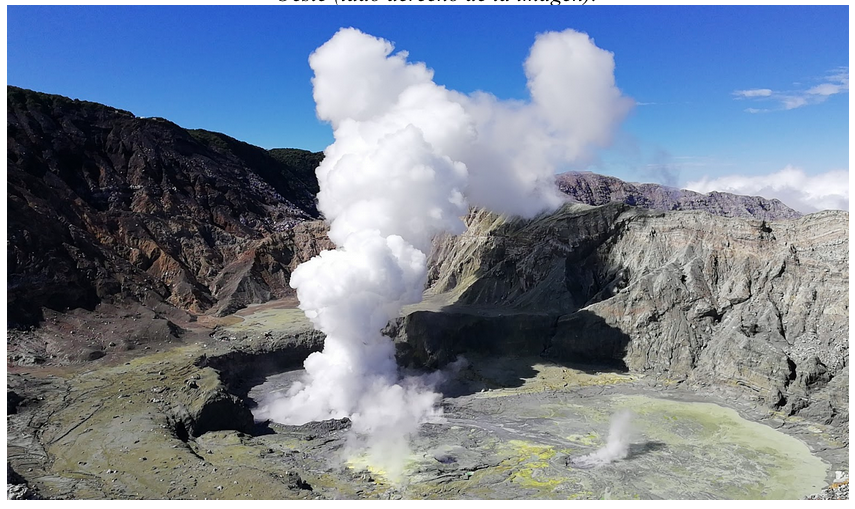
Poas Volcano:
Since 19 December 2018, a continuous eruption has been recorded on the Poas volcano, with a column rising 500 meters above the crater and 3208 meters above sea level (10522.24 ft).
The seismic activity is similar to that of yesterday.

At the time of writing, winds are blowing from the southwest.
The eruptions of the geyser type follow each other. An eruption of moderate amplitude was observed yesterday at 11:05.
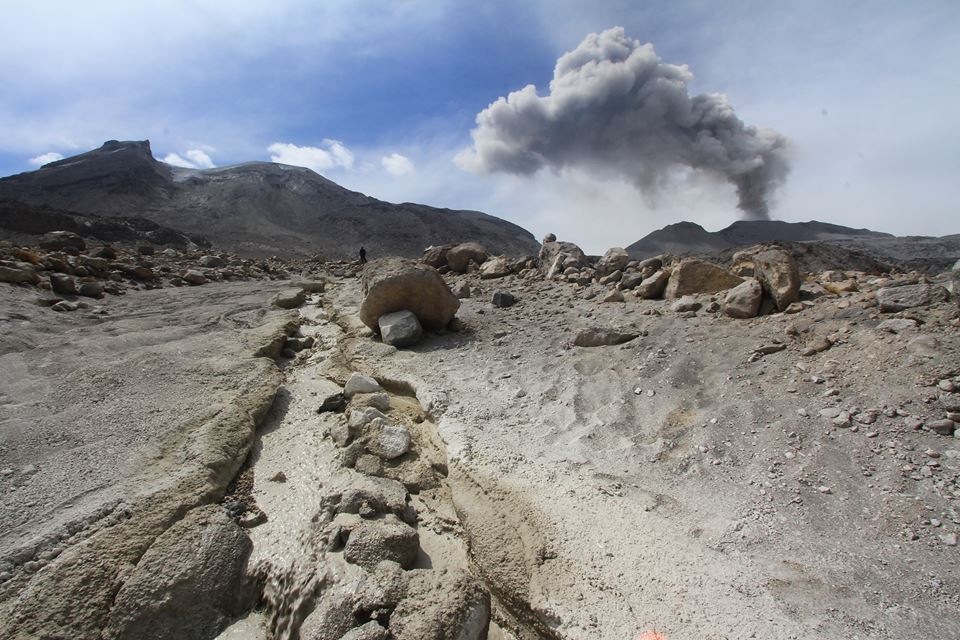
Rincon de la Vieja volcano:
January 17, 2019, at 1:30 local time, there is an eruption on the volcano Rincon de la Vieja; the height reached by the column due to visibility conditions of the site is unknown.
Duration of the activity: 2 minutes.
The seismic activity is similar to that of yesterday.
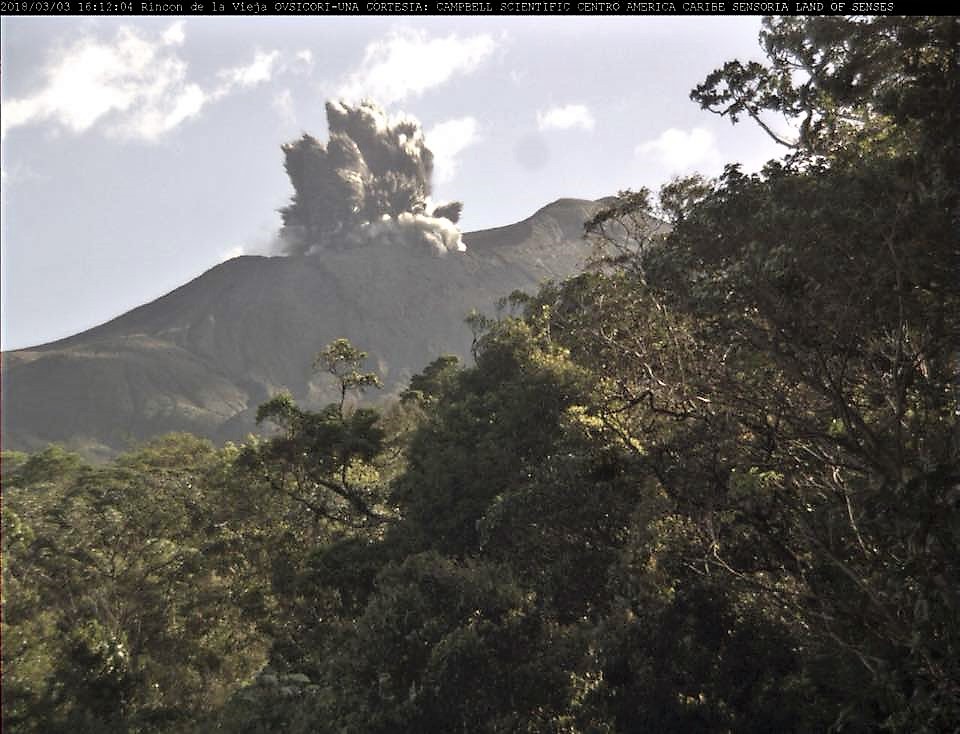

The wind direction is unknown at the moment.
There was an eruption around 1:30 in the morning which was enough to generate a little lahar.
Source : OVSICORI-UNA
Photos : Dr. Paulo Ruiz Cubillo , Dr. Paulo Ruiz, vulcanólogo de la RSN. Ovsicori .