January 26 , 2023 .
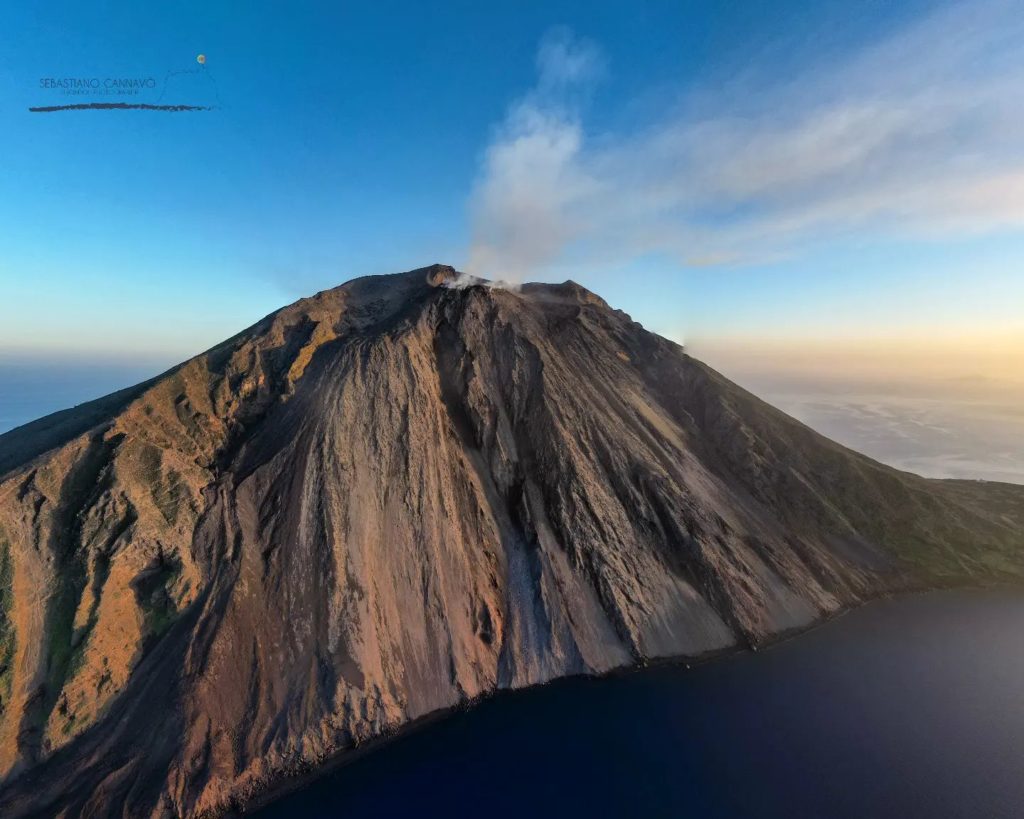
Italy , Stromboli :
Statement on the activity of Stromboli, January 25, 2023, 20:22 (19:22 UTC).
The National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology, Osservatorio Etneo, communicates that from the analysis of the images of the surveillance cameras, it can be observed that during the day, the feeding of the lava flow described in previous press releases has ended and at this time the casting is cooling.
During the last 24 hours, the average amplitude of the volcanic tremor did not show significant variations, always remaining within the range of average values.
We note the appearance of a few seismic transients linked to block rolling phenomena and no significant variation in the rate of occurrence and amplitude of explosion earthquakes.
Data from ground deformation monitoring networks did not show any significant changes since the last publication.
Further updates will be communicated soon.
Source : INGV.
Photo : Stromboli Stati d’animo / Sebastiano Cannavo.
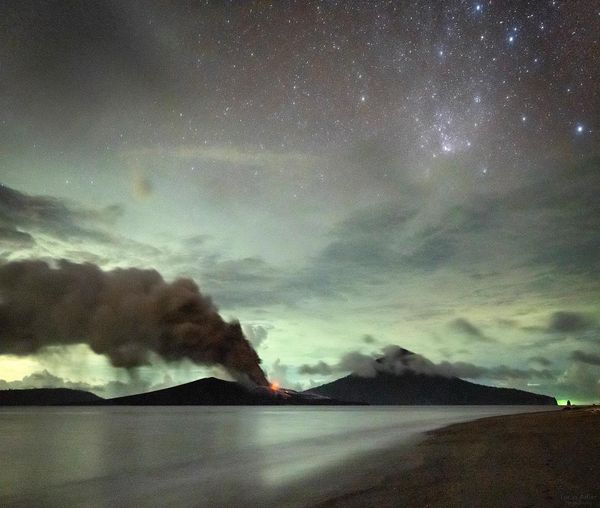
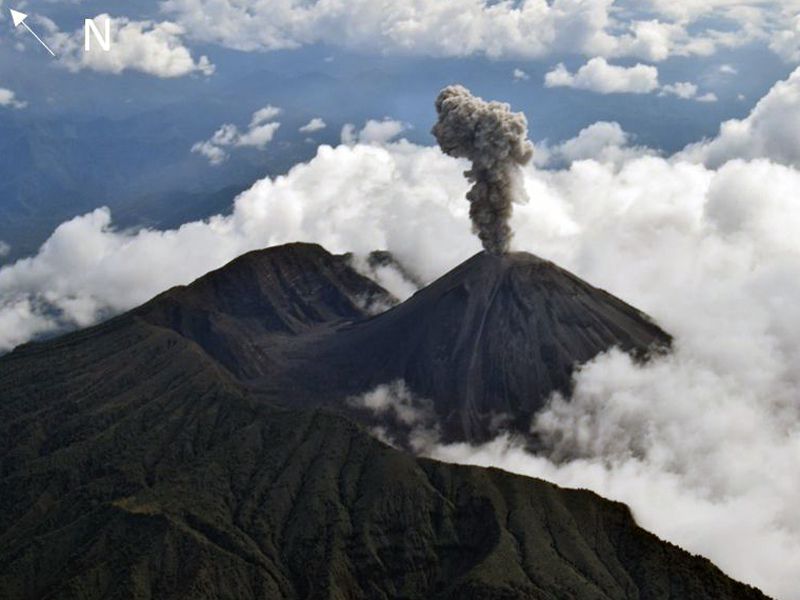
Indonesia , Anak Krakatau :
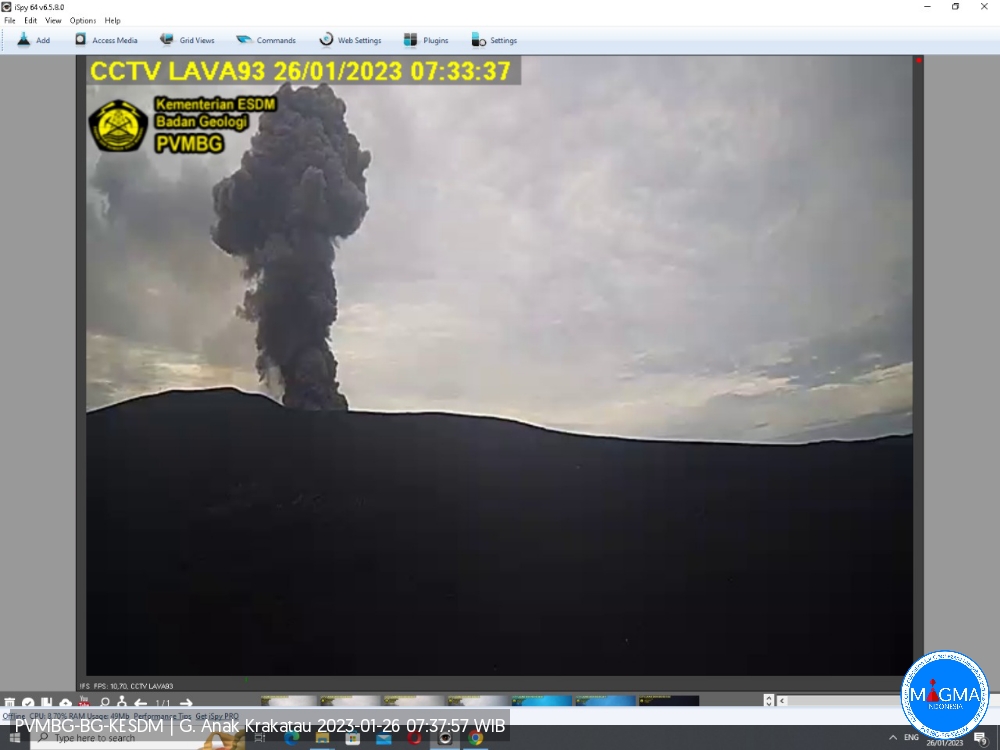
Une éruption du mont Anak Krakatau s’est produite le jeudi 26 janvier 2023 à 07h32 , avec une hauteur de la colonne de cendres observée à ± 500 m au-dessus du pic (± 657 m au-dessus du niveau de la mer). La colonne de cendres a été observée comme étant grise avec une intensité épaisse , orientée au Sud-Est. Au moment de la rédaction de ce rapport, l’éruption était toujours en cours.
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION – VONA
Issued : January 26 , 2023
Volcano : Anak Krakatau (262000)
Current Aviation Colour Code : ORANGE
Previous Aviation Colour Code : orange
Source : Anak Krakatau Volcano Observatory
Notice Number : 2023KRA031
Volcano Location : S 06 deg 06 min 07 sec E 105 deg 25 min 23 sec
Area : Lampung, Indonesia
Summit Elevation : 502 FT (157 M)
Volcanic Activity Summary :
Eruption with volcanic ash cloud at 00h32 UTC (07h32 local).
Volcanic Cloud Height :
Best estimate of ash-cloud top is around 2102 FT (657 M) above sea level or 1600 FT (500 M) above summit. May be higher than what can be observed clearly. Source of height data: ground observer.
Other Volcanic Cloud Information :
Ash cloud moving to southeast. Volcanic ash is observed to be gray. The intensity of volcanic ash is observed to be thick.
Remarks :
Eruption and ash emission is continuing.
PVMBG reported that the eruption at Anak Krakatau intensified at the end of the week during 17-23 January. White steam-and-gas plumes rose as high as 200 m above the summit and drifted NE, E, and S. Strombolian activity was visible in webcam images at 00h41, 00h43, and 04h50 on 23 January. At 06h07 and 07h01 dense gray ash plumes rose 300 m above summit and drifted E. At 07h58, 07h59, 08h08, and 09h28 dense gray-to-black ash plumes rose 200-500 m and drifted SE. Webcam photos showed progressively intensifying Strombolian activity at 19h19, 19h58, and 21h13 on 24 January. A dense gray ash plume rose 300 m and drifted E at 19h57. The Alert Level remained at 3 (on a scale of 1-4), and the public was warned to stay at least 5 km away from the crater.
Source : Magma Indonésie , GVP.
Photos : Magma Indonesie , Lucas Adler via Sherine France.
Colombia , Nevado del Ruiz :
Subject: Nevado del Ruiz volcano activity level bulletin.
The activity level continues at the yellow activity level or (III): changes in the behavior of volcanic activity.
Regarding the monitoring of the activity of the Nevado del Ruiz volcano, the COLOMBIAN GEOLOGICAL SERVICE reports that:
The seismic activity related to fluid dynamics inside the volcanic conduits decreased in the number of events recorded and in the seismic energy released compared to the previous week. According to images captured by cameras installed in the volcano area, several gas and ash emissions associated with some of the seismic signals have been confirmed. On January 23, ash falls were reported in Manizales (Caldas).
Seismic activity associated with rock fracturing decreased in number of earthquakes recorded and seismic energy released compared to the previous week. The earthquakes were located mainly in the northeast sector and in the Arenas crater and, to a lesser extent, in the distal north, west and south sectors of the volcano, with depths between 0.5 and 9.8 km. The maximum magnitude observed during the week was 1.0 ML (Local Magnitude) corresponding to the earthquake recorded on January 17 at 10:58 p.m. (local time), located 1.0 km east-northeast of the Arenas crater , at a depth of 3.7 km.
While monitoring the thermal activity of the volcano, web portals have reported several thermal anomalies in the Arenas crater, low energy for this week.
Source : SGC
Photo : Álex Palacio
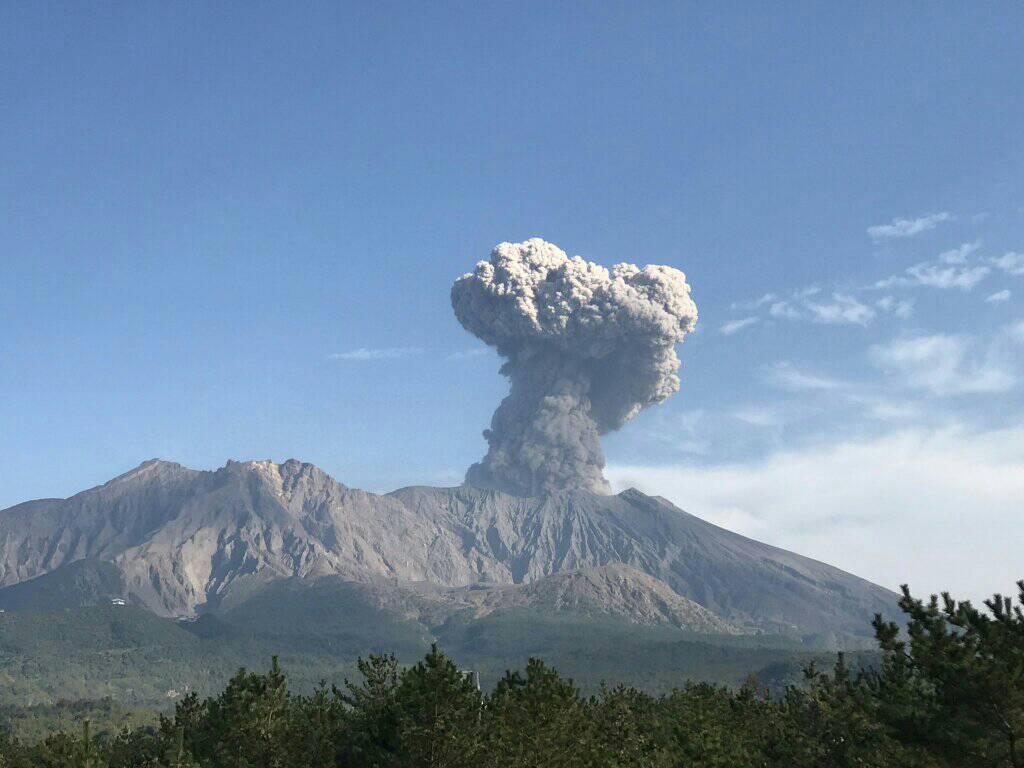
Japan , Sakurajima :
JMA reported ongoing eruptive activity at Minamidake Crater (at Aira Caldera’s Sakurajima volcano) during 14-23 January. Crater incandescence was visible nightly. An explosion at 12h15 on 18 January produced an ash plume that rose 1.4 km above the crater rim and ejected blocks as far as 1.1 km. Sulfur dioxide emissions were high at 1,400 tons per day. An explosion at 06h59 on 19 January generated an ash plume that rose 1.3 km and ejected blocks 600-900 m and an explosion at 03h07 on 21 January generated an ash plume that rose 1.6 km and ejected blocks as far as 1.1 km. Occasional very small eruptive events were recorded during 21-22 January. The Alert Level remained at 3 (on a 5-level scale), and residents were warned to stay 2 km away from the crater.
The Aira caldera in the northern half of Kagoshima Bay contains the post-caldera Sakurajima volcano, one of Japan’s most active. Eruption of the voluminous Ito pyroclastic flow accompanied formation of the 17 x 23 km caldera about 22,000 years ago. The smaller Wakamiko caldera was formed during the early Holocene in the NE corner of the Aira caldera, along with several post-caldera cones. The construction of Sakurajima began about 13,000 years ago on the southern rim of Aira caldera and built an island that was finally joined to the Osumi Peninsula during the major explosive and effusive eruption of 1914. Activity at the Kitadake summit cone ended about 4850 years ago, after which eruptions took place at Minamidake. Frequent historical eruptions, recorded since the 8th century, have deposited ash on Kagoshima, one of Kyushu’s largest cities, located across Kagoshima Bay only 8 km from the summit. The largest historical eruption took place during 1471-76.
Source : AJapan Meteorological Agency (JMA) , GVP.
Photo : Rizal M.
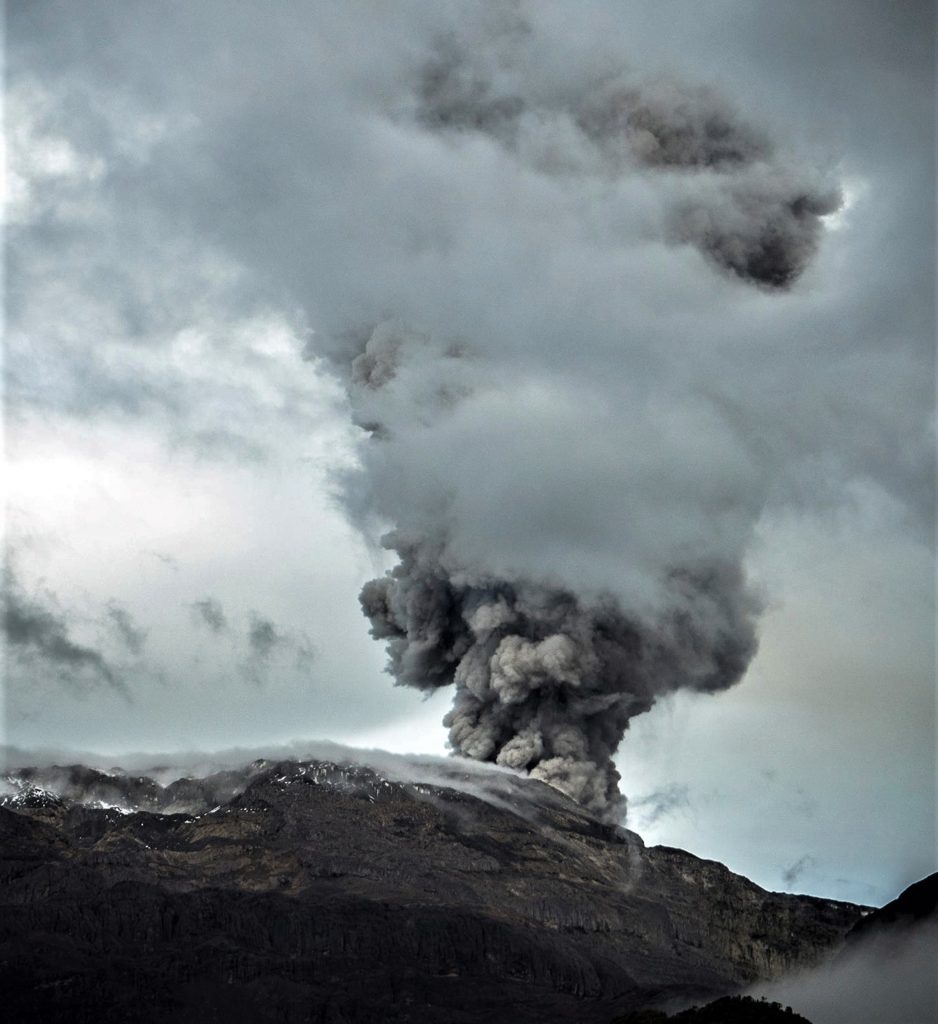
Ecuador , Reventador :
IG described the ongoing eruption at Reventador as moderate during 17-24 January. Daily seismicity was characterized by explosions, long-period earthquakes, periods of harmonic tremor, and signals that indicated emissions. The daily count of explosions ranged from 22-96; seismic data transmission was interrupted during 22-23 January. Although weather clouds often prevented observations of the summit, daily gas, steam, and ash plumes were observed in IG webcam images and described in Washington VAAC volcanic activity notifications almost daily. The plumes rose as high as 2.2 km above the volcano and drifted in multiple directions. Crater incandescence was visible nightly and incandescent blocks were ejected onto the flanks sometimes in all directions; incandescent blocks were also visible rolling as far as 800 m down the flanks. Servicio Nacional de Gestión de Riesgos y Emergencias (SNGRE) maintained the Alert Level at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
DAILY REPORT OF THE STATE OF THE REVENTADOR VOLCANO, Wednesday January 25, 2023.
Information Geophysical Institute – EPN.
Surface Activity Level: Moderate, Surface Trend: No change
Internal activity level: Moderate, Internal trend: No change.
Seismicity: From January 24, 2023, 11:00 a.m. to January 25, 2023, 11:00 a.m.:
The seismicity data correspond to 24 hours of emission from the reference station (REVS).
Explosion (EXP): 41
Long Periods (LP): 63
Emission Tremors (TREMI): 9.
Harmonic Trempor (TRARM): 1
Rains / Lahars:
There was no rain in the volcano area.
Emission / Ash Column:
Gas and ash emissions were observed, with a maximum height of 900 meters above crater level in a westerly direction. Washington’s VAAC reported no emissions.
Other Monitoring Parameters:
No thermal anomaly has been recorded in the last 24 hours.
Observation:
The area of the volcano partially cleared from late afternoon yesterday until early morning today. In the early morning and in the morning of today, the descent of incandescent material was observed on the northeast flank. For the moment, it remains cloudy.
Alert level: Orange.
Sources : GVP , IGEPN.
Photo : f-Naranjo , GVP.