July 30 , 2022.
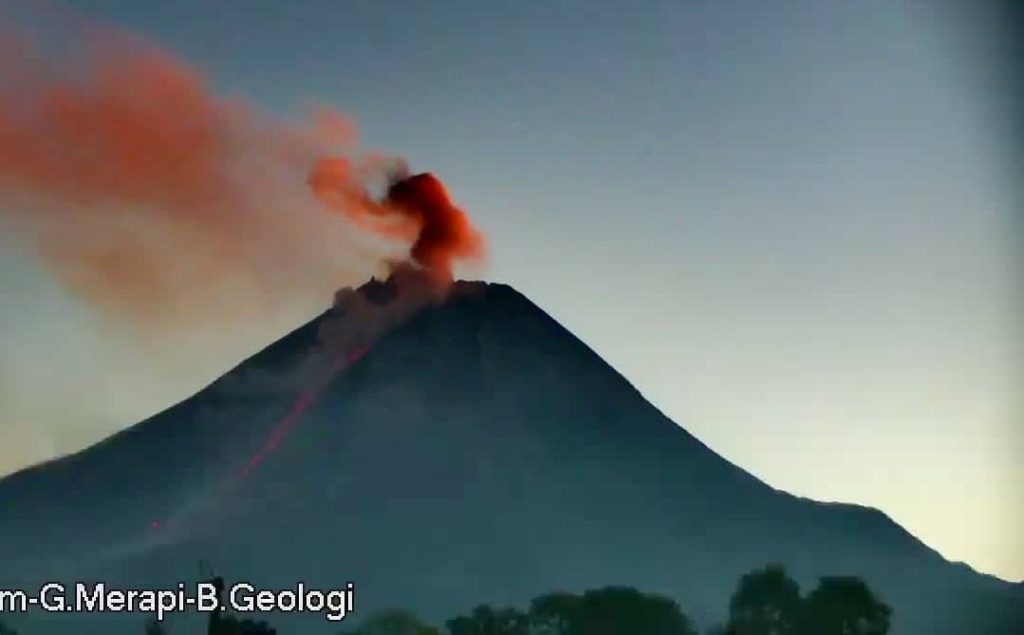
Indonesia , Merapi :
Merapi activity report from July 22 to 28, 2022:
This week, 47 lava avalanches were observed in a dominant South-West direction towards the Bebeng River with a maximum slip distance of 1800 m. For the Southwest dome, we observe the growth of the dome. According to photo analysis, the volume of the Southwest lava dome is 1,672,000 m3 and that of the central dome is 2,796,000 m3.
Seismicity:
This week, the seismicity of Mount Merapi recorded:
1 shallow volcanic earthquake (VTB),
19 multi-phase earthquakes (MP),
415 avalanche earthquakes (RF),
21 emission earthquakes (DG),
4 tectonic earthquakes (TT).
The intensity of seismicity this week is still quite high.
Mount Merapi’s deformation, which was monitored using EDM this week, showed no significant changes. Rainfall intensity was 11 mm/hour for 60 minutes at Kaliurang Post on July 22-23, 2022. There were no reports of lahars or additional flow in the rivers that originate at Mount Merapi.
Conclusion:
1. Merapi volcanic activity is still quite high in the form of effusive eruption activity. The state of the activity is defined at the « SIAGA » level.
2. The current potential danger is lava avalanches and hot clouds in the South-South-West sector covering the Boyong River for a maximum of 5 km, the Bedog River, Krasak, Bebeng for a maximum of 7 km. The Southeast sector covers the Woro River for a maximum of 3 km and the Gendol River for a maximum of 5 km. Meanwhile, the ejection of volcanic material in the event of an explosive eruption can reach a radius of 3 km around the summit.
The public should not carry out any activity in potentially dangerous areas, anticipate disturbances due to volcanic ash from the Merapi eruption and be aware of the dangers of lahars, especially when it rains around Merapi.
Source : BPPTKG
Photo :Frekom .
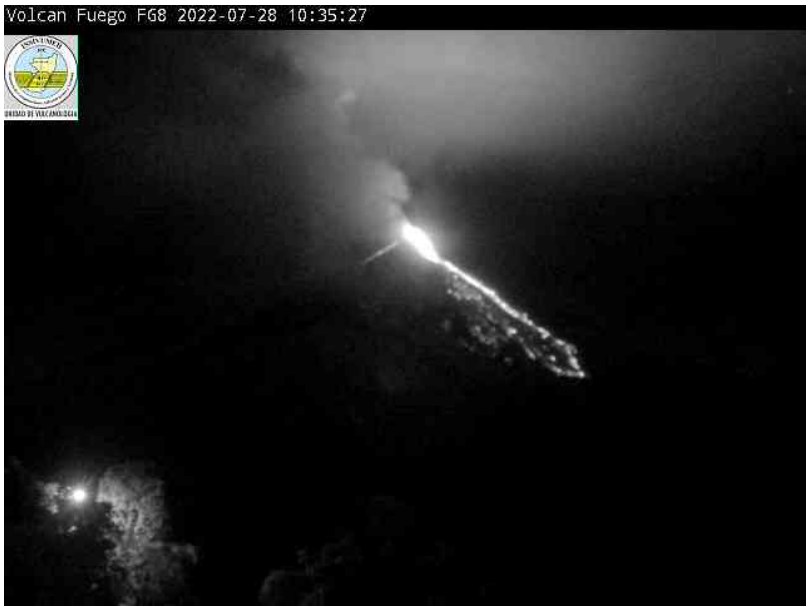
Guatemala , Fuego :
BEFGO SPECIAL VOLCANOLOGICAL BULLETIN #063-2022
The monitoring parameters of the seismic and acoustic stations around the Fuego volcano show an increase which translates into greater degassing and incandescence observed in the crater, since the early hours of July 28. It has gradually been observed that low sounds similar to those of a train locomotive predominate for periods longer than 30 minutes. This increase allowed the formation of a lava flow of about 300 meters in length towards the Ceniza ravine, constantly causing avalanches of moderate characteristics in the same direction. These could cover distances close to 2 km, with the probability of reaching the top of the hill known as « El Cucurucho ». Curtains of ash several tens of meters high can be generated from the said ravine and then be dispersed over several kilometers by the wind, which would favor the constant fall of fine ash in the communes of the South-West, South and South East.
Image 1: lava flow observed by the camera at the Fuego volcano observatory.
It is not excluded that this activity continues to increase and generates new lava flows in other directions, violent ash-laden explosions and moderate to strong avalanches towards more ravines, such as Santa Teresa and Las Lajas.
INSIVUMEH maintains visual and instrumental monitoring of volcanic activity through seismic stations, volcano spotters and web cameras.
Source : Insivumeh
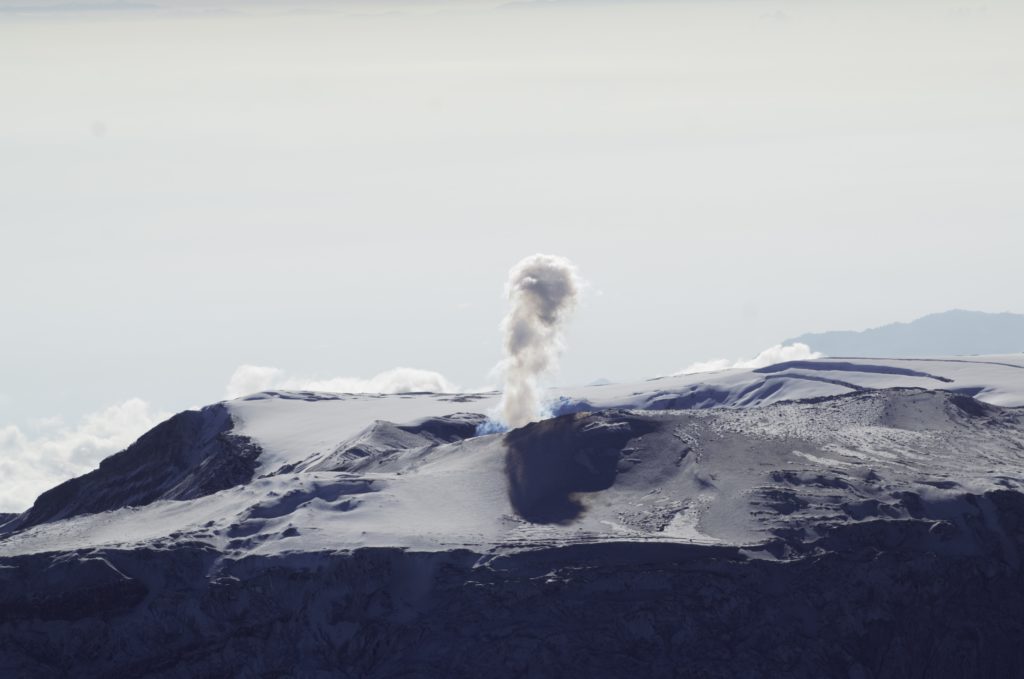
Colombia , Nevado del Ruiz :
Bulletin of activity level of the Nevado del Ruiz volcano.
The activity level continues at the Yellow Activity Level or (III): changes in the behavior of volcanic activity.
Regarding the monitoring of the activity of the Nevado del Ruiz volcano, the COLOMBIAN GEOLOGICAL SERVICE reports that:
Seismicity related to fluid dynamics within volcanic conduits increased in number of earthquakes and maintained a similar level of seismic energy released, compared to last week. This seismic activity was characterized by the occurrence of continuous volcanic tremors, tremor pulses, long and very long period earthquakes. In general, these signals exhibited moderate to low energy levels, variable spectral content, and were located primarily within Arenas Crater. Thanks to the cameras installed in the area of the volcano and the report of the officials of the National Natural Park of Los Nevados and the personnel of the Colombian Geological Service in the field, the confirmation of the gas and ash emissions associated with some of these seismic signals has been noted. Likewise, thanks to the FLIR cameras (thermographic cameras) of the volcanic monitoring network, changes in the relative temperature of the emitted material have been observed.
Seismicity associated with rock fracturing decreased in the number of earthquakes and maintained a similar level in released seismic energy, compared to the previous week. This seismic activity was located mainly in the South-South-West, South-West and North-East sectors of the volcanic edifice and in the Arenas crater, as well as to a lesser extent in the South-East sector. The depth of the earthquakes varied between 0.3 and 5.8 km. The maximum magnitude recorded during the week was 1.5 ML (Local Magnitude), corresponding to the earthquake that occurred today at 12:04 p.m. (local time), located 2.4 km northeast of the Arenas crater, at a depth of 4.4 km.
Source et photo : SGC.
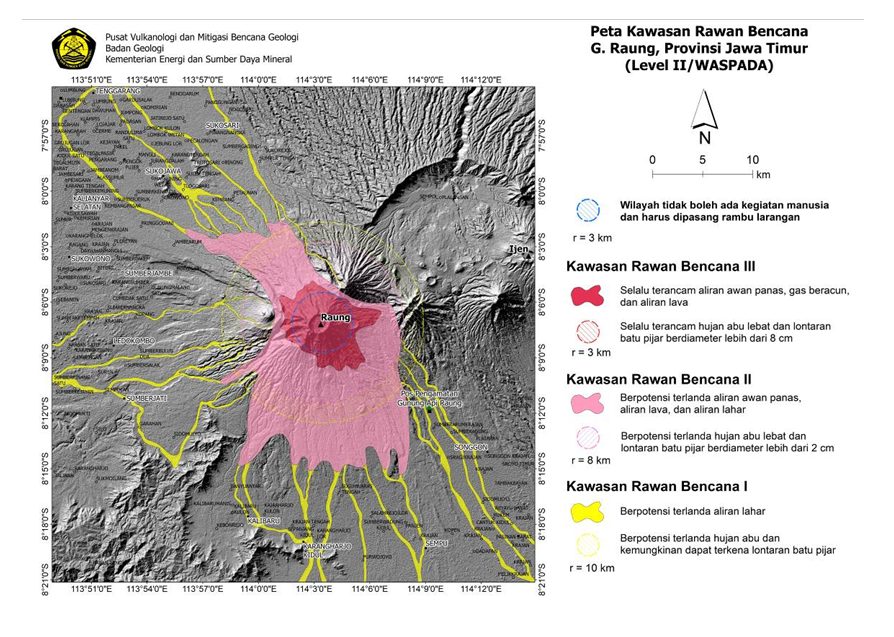
Indonesia , Raung :
Visual observations in July 2022 generally observed white smoke from the main crater, of moderate intensity, with a height of approximately 50 to 400 meters above the summit. Seismicity was observed dominated by emission earthquakes and continuous tremors. From July 8 to July 19, 2022, there was an increase in emission earthquakes to an average of 28 events per day. Additionally, on July 27, 2022, at 5:19 p.m. WIB, an eruption earthquake was recorded on the seismograph, but visually could not be seen from the PGA Raung post as it was covered in fog.
Visual observations from other directions showed an eruption of ash with the height of the eruption column about 1000-1500 meters above the summit. On July 28, 2022, a heat anomaly was detected on the surface of the crater using images from the Terra and Aqua satellites, worth 2 MW, which indicated magma dynamics at the level of the G. Raung crater. GPS measurements show an inflationary pattern indicating the onset of mass migration at depths (2900 m below the peak) that caused a dimensional change of 1.7 million m3. The seismicity of July 29, 2022 at 00:00 – 06:00 WIB was dominated by a continuous tremor with an amplitude of 0.5 to 4 mm.
Based on the results of seismicity monitoring and analysis, as of July 29, 2022, 08:00 WIB, the activity level of G. Raung has been raised from Level I (Normal) to Level II ( WASPADA). The public and visitors/tourists are not permitted to approach the eruption center in the summit crater within 3 km. The current potential threat of danger is in the form of glowing rock material, but the distribution is still limited to the crater, while the cinder-sized material can be dispersed further depending on the direction and speed of the wind.
Source : PVMBG.
Photos : Istimewa , PVMBG.
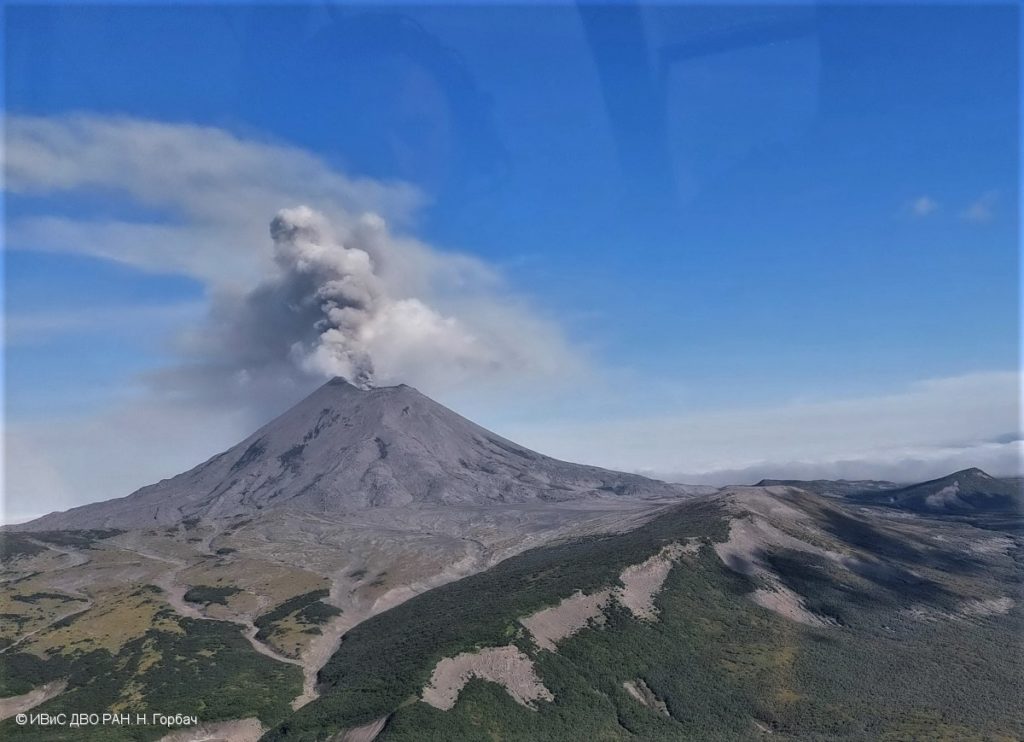
Kamchatka , Karymsky :
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION (VONA)
Issued: July 29 , 2022
Volcano: Karymsky (CAVW #300130)
Current aviation colour code: ORANGE
Previous aviation colour code: orange
Source: KVERT
Notice Number: 2022-84
Volcano Location: N 54 deg 2 min E 159 deg 26 min
Area: Kamchatka, Russia
Summit Elevation: 1486 m (4874.08 ft)
Volcanic Activity Summary:
A moderate explosive activity of the volcano continues. Satellite data showed an ash cloud drifting about 43 km to the south-east of the volcano.
A moderate activity of the volcano continues. Ash explosions up to 12 km (39,400 ft) a.s.l. could occur at any time. Ongoing activity could affect international and low-flying aircraft.
Volcanic cloud height:
3500-4000 m (11480-13120 ft) AMSL Time and method of ash plume/cloud height determination: 20220729/2233Z – NOAA 19 (4m5)
Other volcanic cloud information:
Distance of ash plume/cloud of the volcano: 43 km (27 mi)
Direction of drift of ash plume/cloud of the volcano: SE / azimuth 124 deg
Time and method of ash plume/cloud determination: 20220729/2233Z – NOAA 19 (4m5)
Start time of explosion and how determined: 20220729/2200Z – Satellite data
Source : Kvert.
Photo : N. Gorbach, IVS FEB RAS.