22 Janvier 2022.
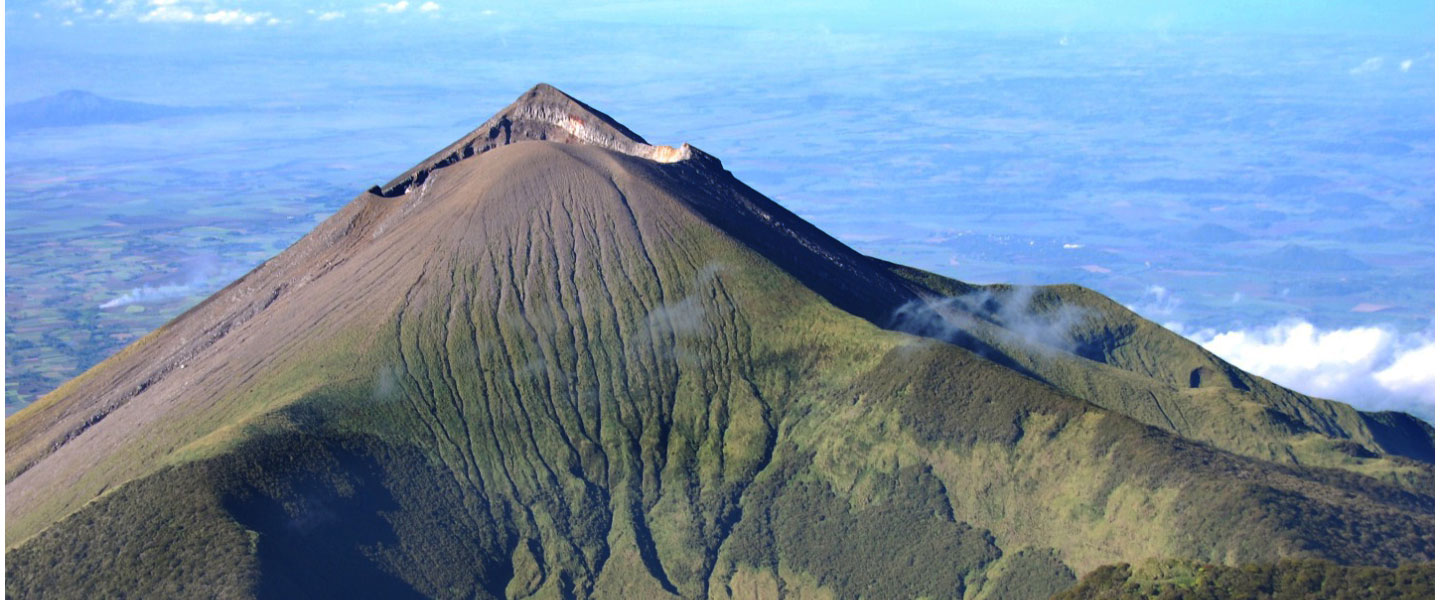
Philippines , Kanlaon :
KANLAON VOLCANO ADVISORY , 21 January 2022 , 10:30 A.M.
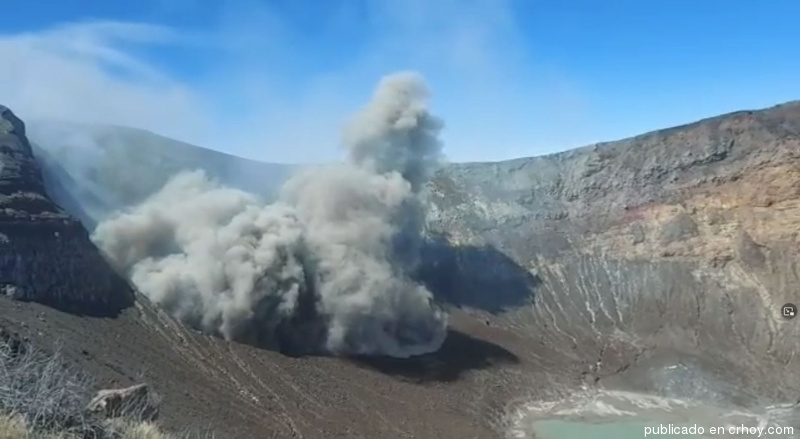
This is a notice of an increase in activity of Kanlaon Volcano. A total of eighteen (18) volcanic earthquakes were recorded within the last 24 hours by the Kanlaon Volcano Network or KVN. These included four (4) very shallow tornillo signals that are associated with magmatic gas movement along fractures within the upper volcanic slopes. Degassing activity from the crater has been very weak to moderate and low steam-laden plumes that rose only 200 meters before drifting northwest were last observed on 16 January 2022. In addition, ground deformation data from continuous GPS measurements indicate short-term slight inflation of the edifice since mid-October 2021. The increased seismic activity and short-term ground deformation are likely caused by shallow hydrothermal processes beneath the edifice that could generate phreatic or steam-driven eruptions from the summit crater.
DOST-PHIVOLCS would like to remind the public that Kanlaon Volcano is at Alert Level 1, which means that it is at an abnormal condition. The local government units and the public are strongly reminded that entry into the 4-kilometer radius Permanent Danger Zone (PDZ) must be strictly prohibited due to the further possibilities of sudden and hazardous steam-driven or phreatic eruptions. Civil aviation authorities must also advise pilots to avoid flying close to the volcano’s summit as ejecta from any sudden phreatic eruption can be hazardous to aircraft. DOST-PHIVOLCS is closely monitoring Kanlaon Volcano’s activity and any new development will be relayed to all concerned.
Source et photo : Phivolcs .
Alaska , Pavlof :
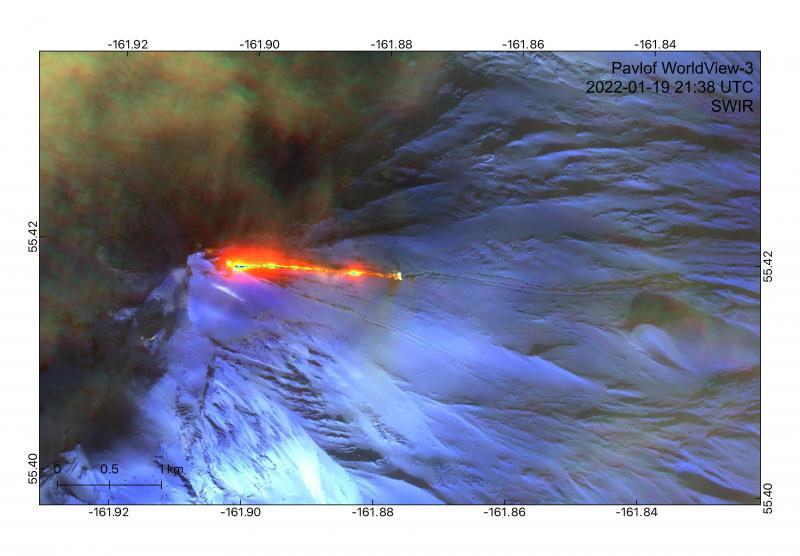
55°25’2″ N 161°53’37 » W,
Summit Elevation 8261 ft (2518 m)
Current Volcano Alert Level: WATCH
Current Aviation Color Code: ORANGE
The eruption of Pavlof Volcano continues. Strongly elevated surface temperatures corresponding to the active lava flow on the east flank of Pavlof were observed in satellite data throughout the week. Web camera views were mostly obscured throughout the week, but occasional clear views showed continued steam emissions. Clear satellite views on Wednesday, January 19 showed a lava flow and lahar extending 1.3 km and 4.4 km (0.8 and 2.7 miles) east of the volcano’s summit, respectively. Elevated seismicity, consisting of periods of sustained tremor, was detected throughout the week, and minor explosive activity was recorded by local and regional infrasound sensors on Wednesday.
Eruption of lava at Pavlof captured in this WorldView-3 short-wave infrared false color image from January 19, 2022. An active lava flow is erupting from a vent on the eastern flank of the volcano and extending 1.3 km east. Meltwater from interaction between the lava and snow and ice is then producing lahars that extend beyond the lava flow up to 4.4 km east from the vent.
Periods of lava fountaining from the vent on the volcano’s upper southeast flank have been occurring since mid-November 2021. This activity has built a small cone and sent flows down the flank that melt the snow and ice and produce variable amounts of meltwater. The meltwater typically incorporates loose debris on the flank of the volcano and forms thin (<2 m thick) lahars. The lahar deposits extend down the east-southeast flank for several kilometers, not quite to the base of the volcano.
Previous eruptions of Pavlof indicate that the level of unrest can change quickly and the progression to more significant eruptive activity can occur with little or no warning.
Pavlof is monitored by local seismic and infrasound sensors, satellite data, web cameras, and remote infrasound and lightning networks.
Pavlof Volcano is a snow- and ice-covered stratovolcano located on the southwestern end of the Alaska Peninsula about 953 km (592 mi) southwest of Anchorage. The volcano is about 7 km (4.4 mi) in diameter and has active vents on the north and east sides close to the summit. With over 40 historic eruptions, it is one of the most consistently active volcanoes in the Aleutian arc. Eruptive activity is generally characterized by sporadic Strombolian lava fountaining continuing for a several-month period. Ash plumes as high as 49,000 ft above sea level have been generated by past eruptions of Pavlof, and during the March 2016 eruption, ash plumes as high as 40,000 ft above sea level were generated and the ash was tracked in satellite data as distant as eastern Canada. The nearest community, King Cove, is located 48 km (30 miles) to the southwest of Pavlof.
Source : AVO.
Photos : Dietterich, Hannah/AVO , Fee, David , Volcano Observatory / University of Alaska Fairbanks, Geophysical Institute.
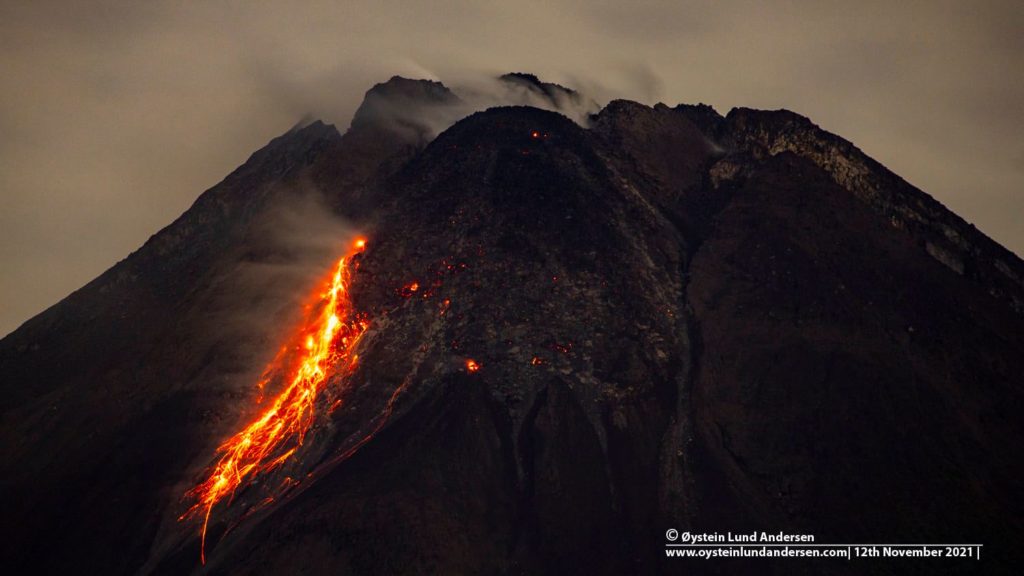
Indonesia , Merapi :
RESULT OF OBSERVATIONS
Visual
The weather around Mount Merapi is generally sunny in the morning and evening, while it is foggy in the afternoon. White, weak to thick, low pressure smoke 400m above the summit was observed from the Kaliurang observation post on 17 January 2022 at 08:40 WIB.
This week, a hot avalanche cloud was observed descending to the southwest, upstream of the Bebeng River with a maximum sliding distance of 2,000 m. Lava avalanches were observed 91 times in the southwest, descending the Bebeng River with a maximum slip distance of 2,000 m.
No significant morphological changes were observed either in the Southwest lava dome or in the central dome. The volume of the Southwest lava dome is 1,670,000 m3 and the central dome is 3,007,000 m3.
Seismicity
This week, the seismicity of Mount Merapi showed:
1 hot cloud avalanche earthquake (AP),
5 shallow volcanic earthquakes (VTB),
62 multi-phase earthquakes (MP),
864 avalanche earthquakes (RF),
40 emission earthquakes (DG),
9 tectonic earthquakes (TT).
The intensity of this week’s earthquake is still quite high.
Deformation
Mount Merapi’s deformation, which was monitored using EDM this week, showed a distance shortening rate of 0.2 cm/day.
Rain and lahars
This week, it rained at the Mount Merapi observation post with an intensity of 62 mm/hour for 40 minutes at the Kaliurang post on January 17, 2022. There were no reports of lahars or additional flow in the rivers that have their source on Mount Merapi.
Conclusion
Based on the results of visual and instrumental observations, it is concluded that:
Volcanic activity at Mount Merapi is still quite high in the form of effusive eruption activity. The state of the activity is defined at the « SIAGA » level.
Source : BPPTKG.
Photos : Oystein Lund Andersen (which I salute) ,
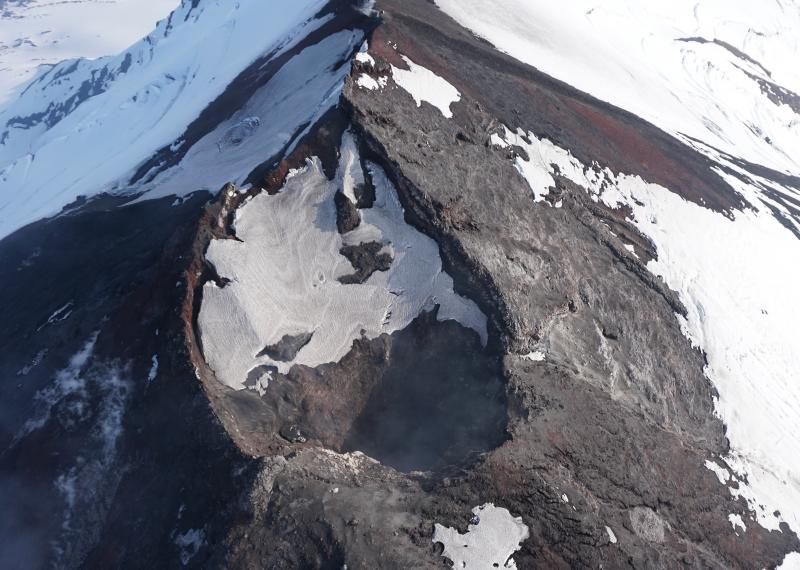
Costa Rica , Turrialba :
Turrialba Volcano National Park is temporarily closed until authorities recommend its reopening.
The Volcanological and Seismological Observatory of Costa Rica (Ovsicori) reported on Thursday the increase in the level of activity of the Turrialba volcano, which went from level two (active) to level three (erupting).
The director of the protected area, Reina Sánchez, indicated that the National System of Conservation Areas (Sinac) has decided to temporarily close this area until the corresponding entities notify a greater stability of the volcano that allows its reopening.
For their part, the Costa Rican authorities urged to maintain greater surveillance of the volcano, as part of the protection protocol activated since January 17, when explosions were recorded.
These explosions triggered alerts from monitoring entities because it released residue at a height between 500 and 1,000 meters above the crater, and ashfall was recorded in several surrounding areas. Since that date, other minor eruptions have been reported.
Local authorities pointed out that this process shown by the Turrialba last Monday was the most energetic in the past two years.
Source : telesurtv.net
Photo : Diego Nunez Salmeron et Reina Sanchez Solano / crhoy.com .
Hawaii , Kilauea :
19°25’16 » N 155°17’13 » W,
Summit Elevation 4091 ft (1247 m)
Current Volcano Alert Level: WATCH
Current Aviation Color Code: ORANGE
Activity Summary:
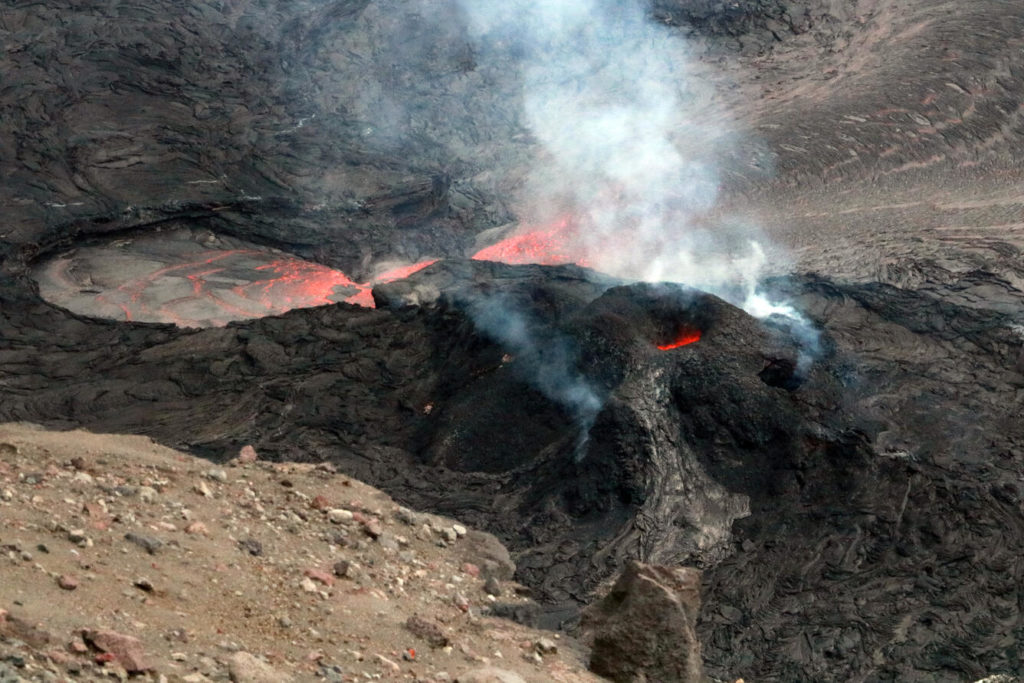
The summit eruption of Kīlauea Volcano, within Halemaʻumaʻu crater, greatly decreased in output starting yesterday midday to early this morning. After about 4 a.m. HST this morning, the eruption output began to increase. All recent lava activity has been confined to the crater, and there are no indications of activity migrating elsewhere on Kīlauea.
Telephoto view of the west vent in Halema‘uma‘u crater after it resumed erupting in the late morning of January 18, 2022. A lighter gray gray recent lava flow is visible emanating from the west vent, and active lava upwells from the lava pond adjacent to the west vent in the upper left part of the photo. Cascades from the lava pond are filling the active portion of the lava lake.
Summit Observations:
Summit tiltmeters recorded overall gradual deflation starting January 19, 2022 at about 04:15 p.m. HST, which continued until yesterday evening January 20 at 8 p.m. HST. Inflation began at last night January 20 at 11 p.m. HST and has continued since. Volcanic tremor associated with the eruption—as recorded by nearby seismometers— decreased yesterday until about 8 p.m. HST, and then started increasing since about 5:30 a.m. this morning. The most recent sulfur dioxide (SO2) emission rate of approximately 2100 tonnes per day was measured January 19, 2022.
Halemaʻumaʻu Lava Lake Observations:
Lava returned to the western vent within Halemaʻumaʻu crater at about 10:45 a.m. HST on January 18, 2022. The extent of the active lava lake and the overall effusion rate started decreasing yesterday afternoon. The active lava lake was limited to a small pond north of the west vent cone overnight. Just after 4 a.m. HST this morning, the lava effusion rate increased, and by 7 a.m. HST this morning the active lava lake extent has resumed to its previous extent. The lava lake has seen a total rise of about 83 meters (272 feet) since lava emerged on September 29, 2021.
Source : HVO
Photo : USGS / K. Mulliken.