September 22 , 2021.
Spain / La Palma , Cumbre Vieja :
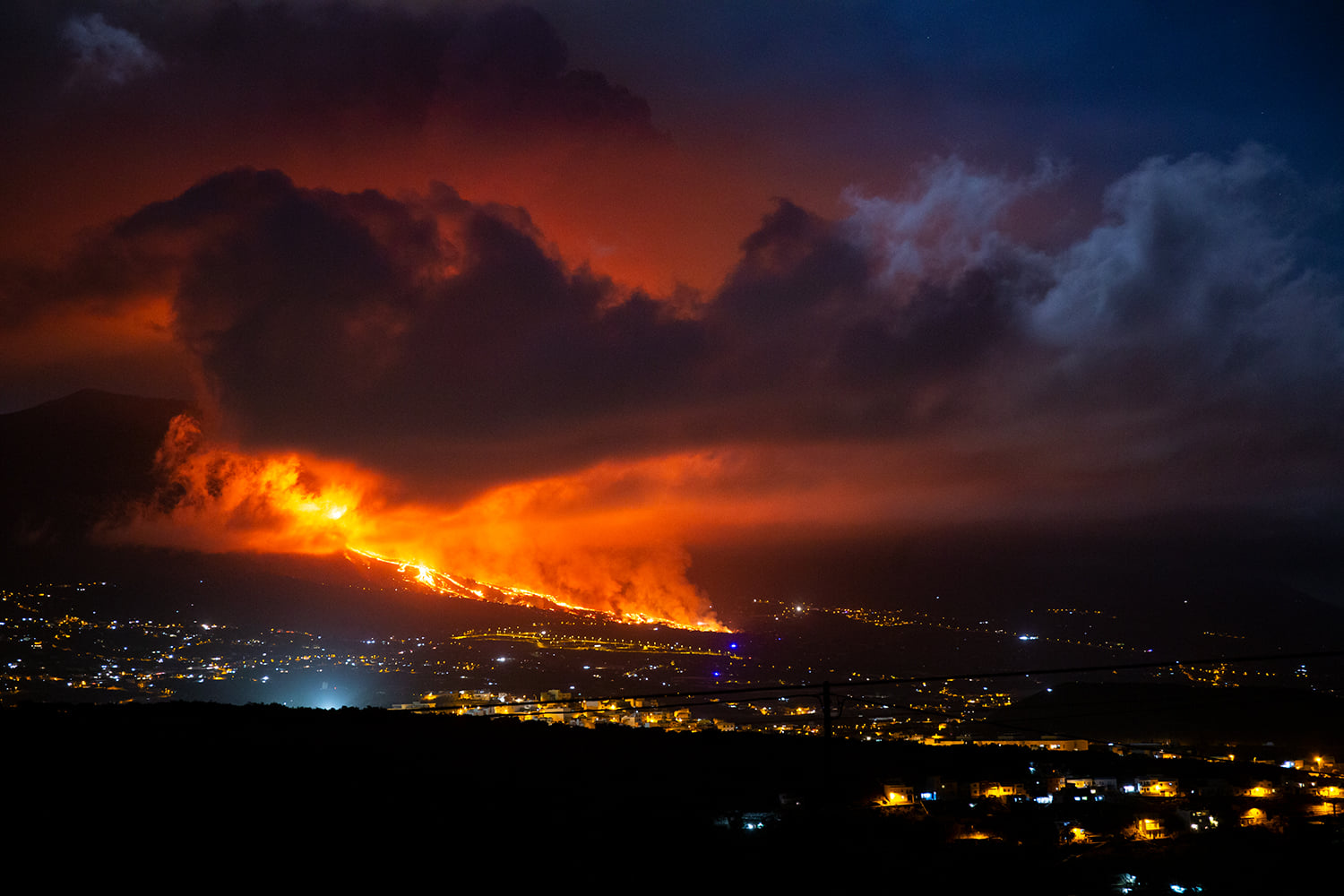
Lava is approaching the sea and contact with water will increase the risk of toxic gas emissions.
Civil protection and the harbor master’s office are stepping up their security measures to prevent visitors from accessing the site. On Monday night, it widened the exclusion perimeter at sea, parallel to the coast, by two nautical miles, going from Puerto Naos in the south to the beach of Las Viñas (Tazacorte) in the north. By land, security forces will prevent access to the area.
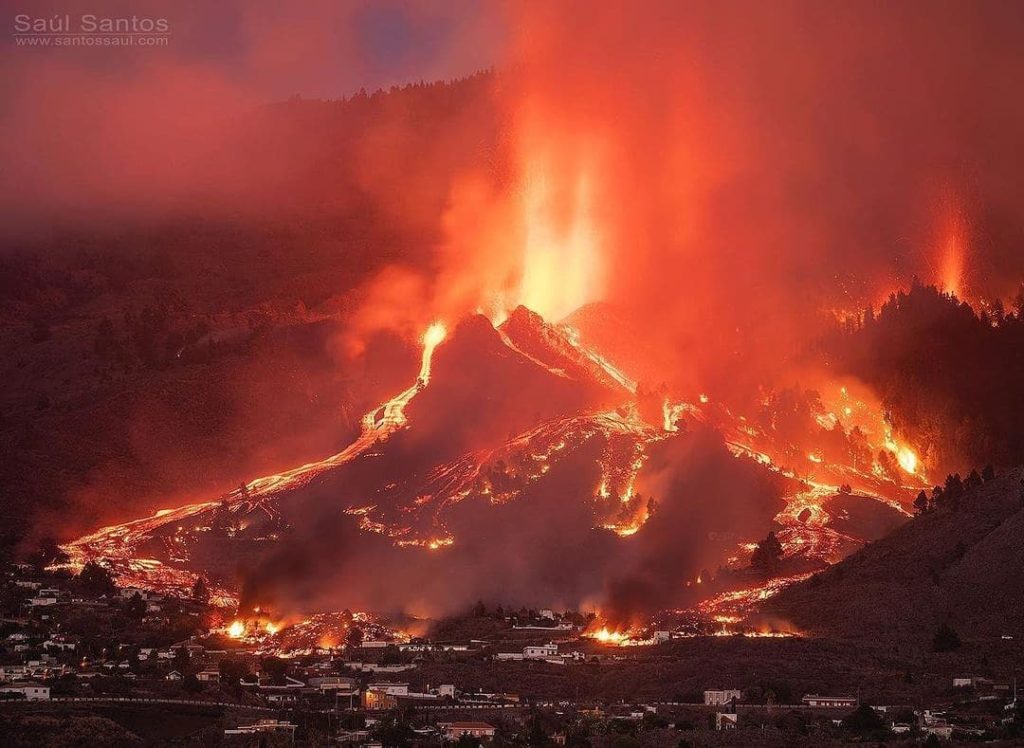
Scientists believed that the lava would reach the coast around 8 p.m. on Monday (local Canarian time). However, the slowdown in the advance of magmatic rivers prevented this forecast from being met. Miguel Angel Morcuende, technical director of Pevolca (Canary Islands Volcanic Emergency Plan), explained overnight: “We had less activity on the volcano, less magma volume. The activity of the volcano slows down. The lava is located above the district of Todoque. There is still half the way to go to reach the sea. ”It is not yet known when it will reach the ocean and if the flows will do so above or below the mountain of Todoque, with a slower march. and after the opening of a new eruptive mouth in Tacande, 900 meters from the main mouth.
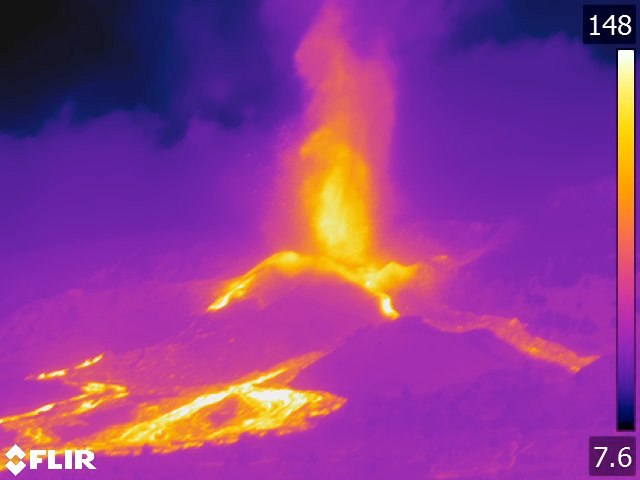
Thermal image freshly acquired by our team on board the Civil Guard aircraft. Lava sources and lava flows are clearly visible.
Information update:
the seismic swarm continues on the Cumbre Vieja volcano (La Palma, Canary Islands) with more than 26,000 earthquakes detected and nearly 1,600 located.
Since last Saturday September 11, 2021, the Canaria Seismic Network, managed by the Canary Islands Volcanological Institute (INVOLCAN), has detected more than 26,000 earthquakes on the island of La Palma, with a maximum magnitude observed of M 4.2 on Richter scale,
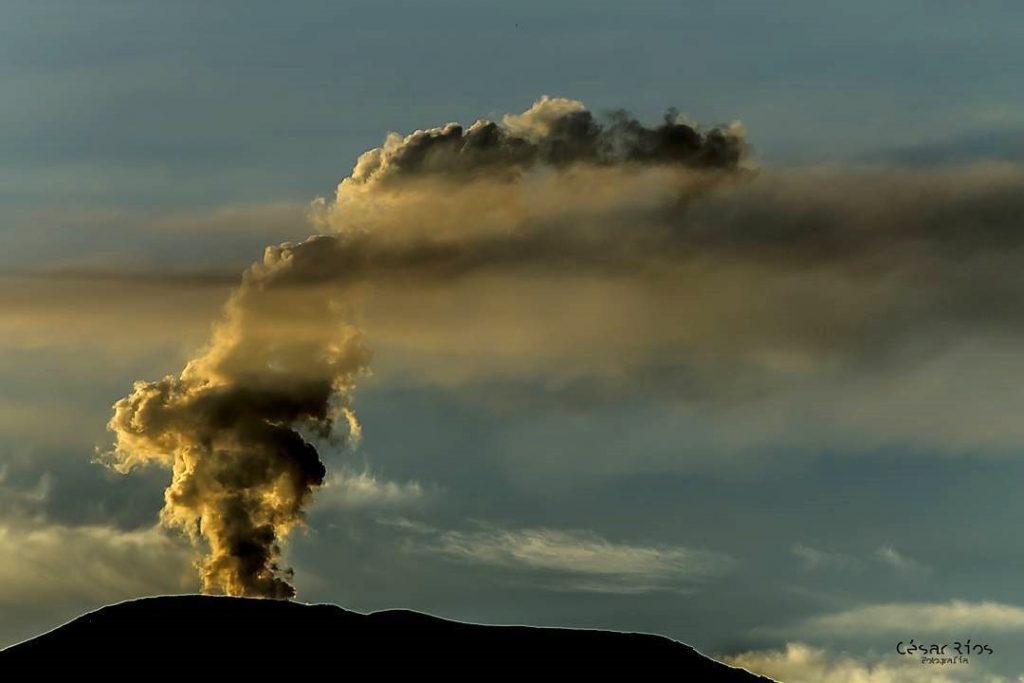
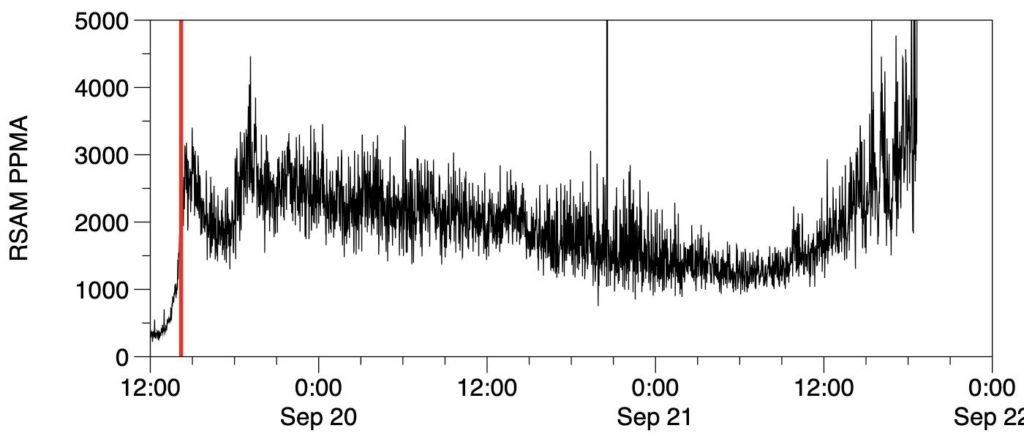
The Canary Islands Seismic Network has recorded in the last 4 hours a sharp increase in the magnitude of the volcanic tremor under Cumbre Vieja, which is an indicator of the intensity of the strombolian explosive activity in the active vents at the moment. The red line marks the start of this eruption.
A new lava-emitting fissure about 900 meters from the main eruption point and seven new earthquakes measuring between 2.3 and 3.8 on the Richter scale. These are the latest events observed yesterday in La Palma, in the Canary Islands in Spain, as the volcano continued to erupt, increasing tensions among the local population. Lava has already consumed at least 183 homes, according to government spokeswoman Isabel Rodríguez, speaking today after the weekly cabinet meeting. Including infrastructure such as swimming pools and sports facilities, the total comes to 200.
By the early hours of Tuesday morning, the lava had spread to cover 103 hectares. This emerges from an analysis of the situation at 6 a.m. on Tuesday by Copernicus, the European Union’s earth observation program. The new crack led to the preventive evacuation of 150 to 200 residents of the Tacande neighborhood in El Paso.
Sources : El Pais , Involcan ,
Photos : Saul Santos , Involcan , ATHOS Centro Astronómico La Palma.
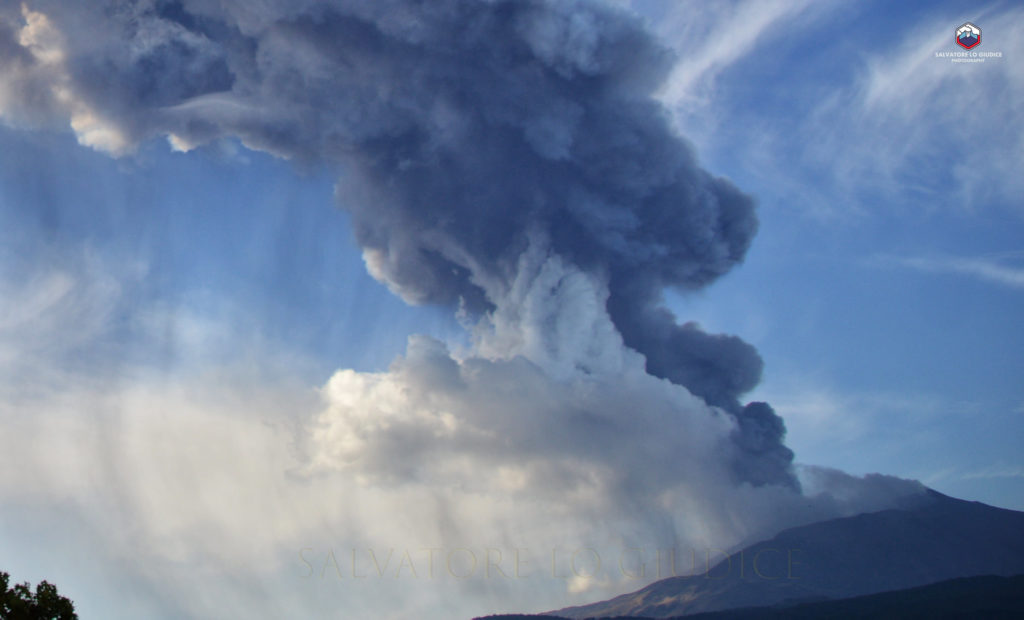
Italy / Sicily , Etna :
Weekly Bulletin, from September 13, 2021 to September 19, 2021 (issue date September 21, 2021)
SUMMARY STATEMENT OF ACTIVITY
In view of the monitoring data, it is highlighted:
1) VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS: Degassing activity at summit craters
2) SEISMOLOGY: Weak seismic activity of fracturing; average amplitude of the volcanic tremor in the low level.
3) INFRASONO: Moderate infrasound activity.
4) DEFORMATIONS: During the last week, there has been no significant change in the soil deformation data.
5) GEOCHEMISTRY: SO2 flux at an average level
HCl flow at a medium level
The flux of CO2 emitted by the soils is characterized during the last 10 days by values which oscillate from high to very high, with some peaks on 12 and 17 m.c ..
The partial pressure of CO2 dissolved in water shows no significant change.
The isotopic ratio of helium appears on medium-high values (latest data from 08/31/2021) slightly increasing.
There are no updates for the C / S report.
6) SATELLITE OBSERVATIONS: The thermal activity in the summit area is at a low level.
VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS
During the week, the monitoring of the volcanic activity of Etna was carried out by analyzing the images of the surveillance cameras of the INGV, Osservatorio Etneo (INGV-OE) and by means of an inspection carried out in the summit area on September 16.
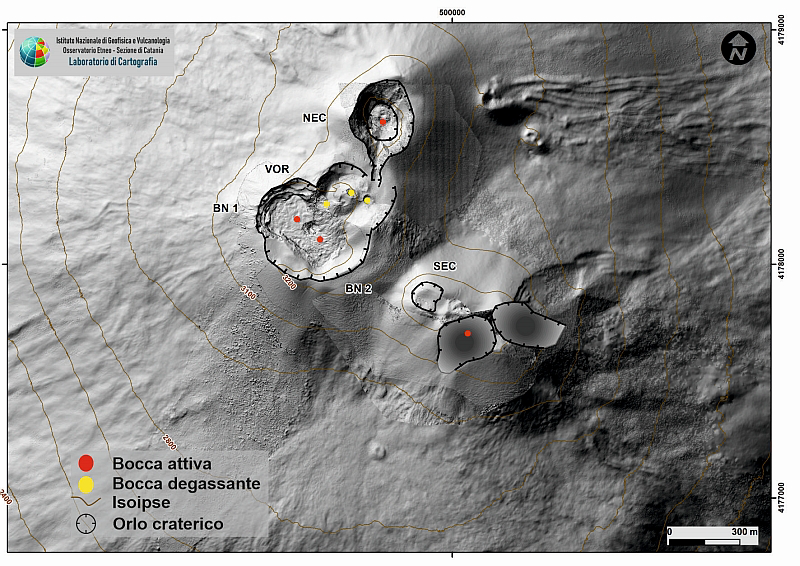
Overall, the state of activity of the summit craters showed no change from what had been observed the previous week. In particular, the activity of degassing the summit craters was mainly carried out by the collapse crater located in the North-West sector of Bocca Nuova (BN-1 in Fig), and secondarily by the North-East crater. The craters of Voragine and Crater Sud-Est, on the other hand, showed intense degassing linked to the fumarole systems present along the edges of the crater.
Fig. 3.1 – Map of the summit craters of Etna. BN: Bocca Nuova, VOR: Voragine; NEC: northeast crater; SEC: south-eastern crater. The topographic reference base on which the morphological updates have been superimposed is the DEM 2014 developed by the Aerogeophysical Laboratory-Section Rome 2
Volcanic tremor:
The average amplitude of the volcanic tremor remained in the low range, with a slight tendency to increase during the last two days of the week, during which, in a few short moments, the amplitude reached the average level.
In most cases, the sources of the tremor were located in a volume located just east of the Bocca Nuova crater, between the Voragine crater and the Southeast Crater, in a depth range between 2,500 and 2,900 meters above mean sea level.
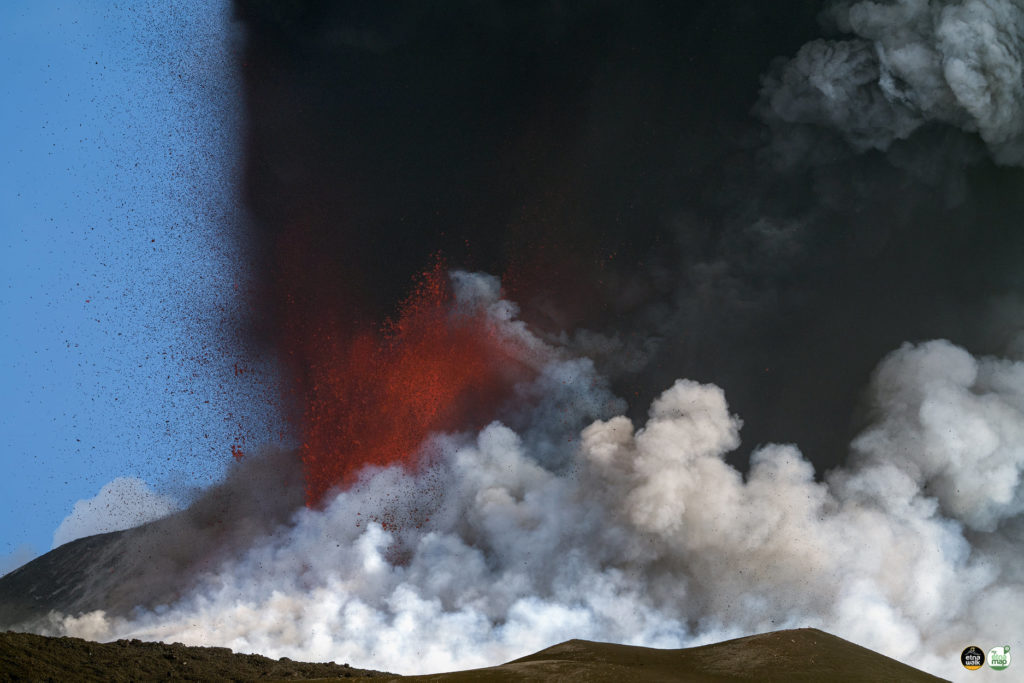
COMMUNICATION ON THE ACTIVITY OF ETNA, September 21, 2021, 19:59 (17:59 UTC).
The National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology, Osservatorio Etneo announces that the images of the CCTV cameras and an inspection carried out in the afternoon in the summit area by the staff of INGV, indicate that the explosive activity at the Crater Southeast has ceased. The lava flow to the southwest has been channeled between Mount Barbagallo and Mount Frumento Supino and is cooling.
After the lava fountain episode, around 10:50 UTC, the mean amplitude of the volcanic tremor reached low pre-eruptive values. At the same time, the centroid of the sources of the volcanic tremor was also repositioned in its pre-eruptive position in a volume located just east of the crater of Bocca Nuova, at a depth of about 2700 m above the sea level. At present, the average amplitude of the tremor shows medium-low values. The infrasound activity decreased significantly around 09:20 UTC and now remains at a low level; the sources of infrasound events are localized in the Bocca Nuova crater area.
Signals acquired by inclinometric and GNSS networks show no significant change since the lava fountain episode.
Further updates will be communicated shortly.
Source : INGV
Photos : Salvatore Lo Giudice via Boris Behncke. , INGV , Etna walk / Giuseppe Distefano / Marco Restivo .
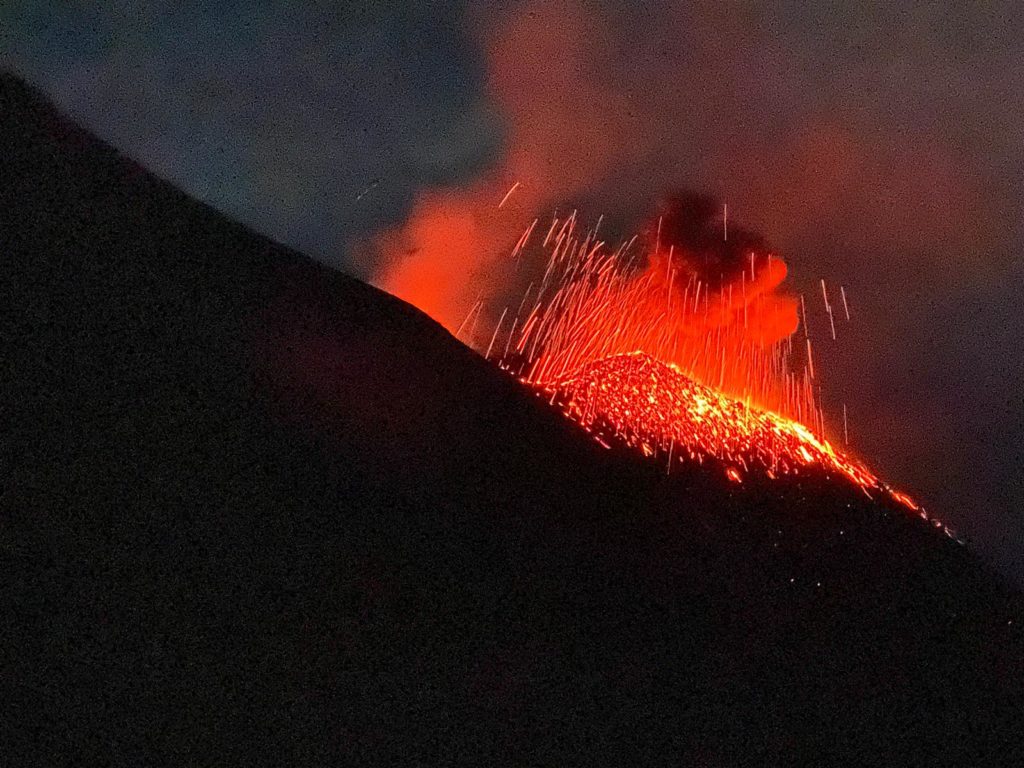
Italy , Stromboli :
Weekly Bulletin, from September 13, 2021 to September 19, 2021 (issue date September 21, 2021).
In view of the monitoring data, it is highlighted:
1) VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS: During this period an ordinary explosive activity of strombolian type was observed. The hourly frequency of explosions fluctuated between medium-low and medium values (9-15 events / h). The intensity of the explosions was mainly low from the North crater area, and medium-low from the Center-South area.
2) SEISMOLOGY: The seismological parameters monitored do not show significant variations.
3) DEFORMATIONS: The island’s soil deformation monitoring networks have not shown any significant changes over the past week.
4) GEOCHEMISTRY: The flow of SO2 at a medium-low level
The flow of CO2 from the ground to the Pizzo Sopra la Fossa is at average levels and does not show significant changes.
The weekly average C / S ratio is at average values (C / S = 6.98).
The isotopic ratio of helium dissolved in the thermal aquifer (latest data dated 06/09/2021) remains at medium-high values.
5) SATELLITE OBSERVATIONS: The thermal activity in the summit area is at a low level.
VOLCANOLOGICAL REMARKS.
Due to adverse weather conditions, visibility from the crater terrace on September 13 was not sufficient for an adequate description of the explosive activity.
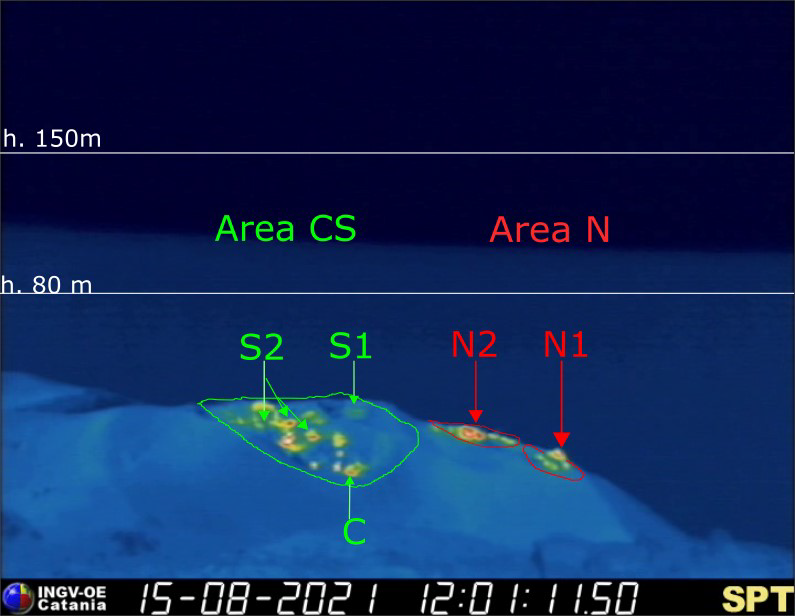
Fig. 3.1 – The crater terrace seen by the thermal camera placed on the Pizzo above the Fossa with the delimitation of the zones of the crater, Center-South Zone and North Zone (ZONE N, ZONE C-S respectively).
The N1 crater located in the North zone, with two emission points, produced low intensity explosions (less than 80 m in height), with the emission of fine material (ash) mixed with coarse material (lapilli and bombs). Vent N2 showed low intensity explosive activity (less than 80 m in height), with the emission of coarse materials sometimes mixed with fine materials. The average frequency of explosions was found to oscillate between 4 and 6 events / h.
In the Center-South zone, sector S1 showed persistent explosive activity until September 15 with low-intensity explosions and emissions of fine materials, while the three vents located in sector S2 produced explosions, even simultaneously, of medium and low intensity (products of some explosions reached a height of 150 m) with the emission of coarse materials mixed with fine materials. Sector C produced only intense degassing activity. The overall frequency of explosions oscillates between 4 and 11 events / h.
Source : INGV.
Photos : Alessandro Gattuso (INGV-Palerme). INGV.
Alaska , Katmai :
58°16’44 » N 154°57’12 » W,
Summit Elevation 6716 ft (2047 m)
Current Volcano Alert Level: NORMAL
Current Aviation Color Code: GREEN
Strong northwesterly winds in the vicinity of Katmai and the Valley of Ten Thousand Smokes have picked up loose volcanic ash erupted during the 1912 Novarupta-Katmai eruption and carried it to the southeast toward Kodiak Island early this morning. The National Weather Service has issued a SIGMET for this low-level event and suggests that the maximum cloud height is 8,000 ft above sea level.
This phenomenon is not the result of recent volcanic activity and occurs during times of high winds and dry snow-free conditions in the Katmai area and other young volcanic areas of Alaska. No eruption is in progress. All of the volcanoes of the Katmai area (Snowy, Griggs, Katmai, Novarupta, Trident, Mageik, Martin) remain at color code GREEN.
Resuspended volcanic ash should be considered hazardous and could be damaging to aircraft and health.
Source : AVO
Photo : Park National.
Colombia , Nevado del Ruiz :
Subject: Bulletin on the activity level of the Nevado del Ruiz volcano.
The activity level continues at: Yellow activity level or (III): Changes in the behavior of volcanic activity.
Regarding the monitoring of the activity of the Nevado del Ruiz volcano, the COLOMBIAN GEOLOGICAL SERVICE reports that:
The seismicity generated by the fracturing of the rock showed an increase in the number of earthquakes and the seismic energy released, compared to the previous week. This seismic activity was located mainly in the South-East and North-East sectors of the volcano as well as in the Arenas crater. The depths of the earthquakes ranged from 0.6 to 6.9 km. The highest magnitude recorded during the week was 2.5 ML (Local Magnitude), corresponding to the earthquake that occurred on September 15 at 3:54 p.m. (local time), located 6.5 km southeast of the Arenas crater, at a depth of 3.3 km.
There were several episodes of low energy drumbeat type seismicity associated with rock fracturing on September 17th and 19th. This seismicity has been linked to the processes of ascent, location-growth and evolution of a lava dome at the bottom of the Arenas crater.
The seismicity related to the dynamics of the fluids inside the volcanic conduits slightly decreased in number of earthquakes recorded and increased in seismic energy released, compared to the previous week. This type of seismicity was characterized by the recording of continuous volcanic tremors of low energy, tremor pulses, long-type and very long-period earthquakes with varying energy levels. Some of these signals were associated with gas and ash emissions confirmed by cameras installed in the area of the volcano and by the report of officials of the Colombian Geological Service and Los Nevados National Natural Park.
The deformation of the volcanic surface, measured from GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) stations and electronic inclinometers, continued to show minor changes.
Source : SGC
Photo : c Rios