03 Décembre 2018.
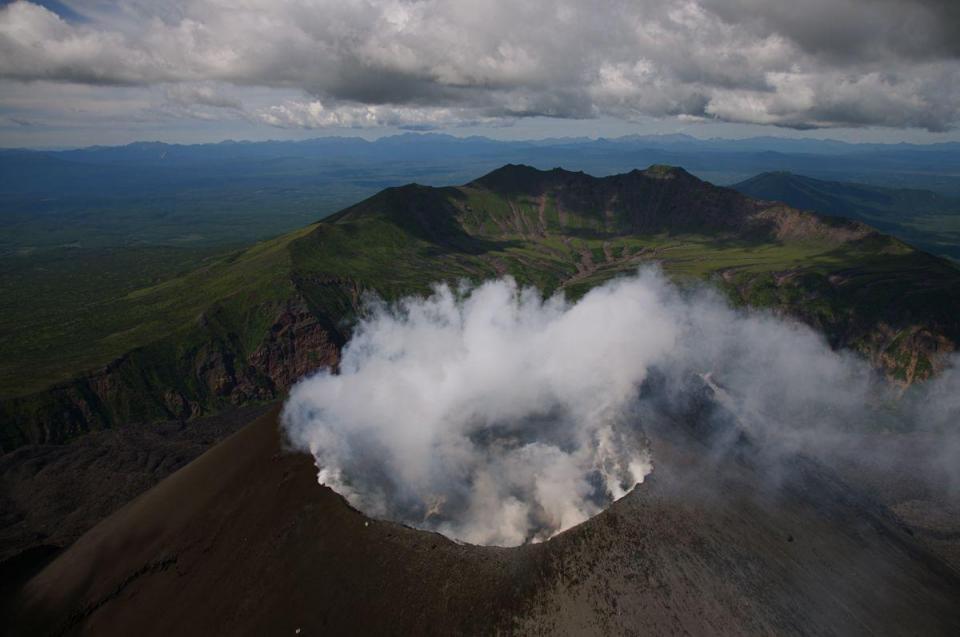
Alaska , Semisopochnoi :
51 ° 55’44 « N 179 ° 35’52 » E,
Altitude du sommet : 2625 pi (800 m)
Niveau d’alerte volcanique actuel: AVIS
Code couleur de l’aviation actuel : JAUNE
Les troubles se poursuivent sur le volcan Semisopochnoi. Une petite explosion sur le Semisopochnoi à 11h44 UTC (02h44 AKST) a été enregistrée par des capteurs d’infrasons régionaux à Adak. Aucune activité éruptive n’a été observée dans les vues satellites généralement claires avant ou après l’explosion détectée. Des explosions supplémentaires sont encore possibles et se produiront probablement sans avertissement. Les données sismiques locales restent hors ligne.
Le Semisopochnoi est surveillé par un réseau sismique sur l’île, bien qu’il soit actuellement hors ligne et à distance par satellite et par des capteurs de foudre. En outre, un réseau de capteurs d’infrasons sur l’île d’Adak peut détecter les émissions explosives du Semisopochnoi avec un délai de 13 minutes si les conditions atmosphériques le permettent.
Source : AVO
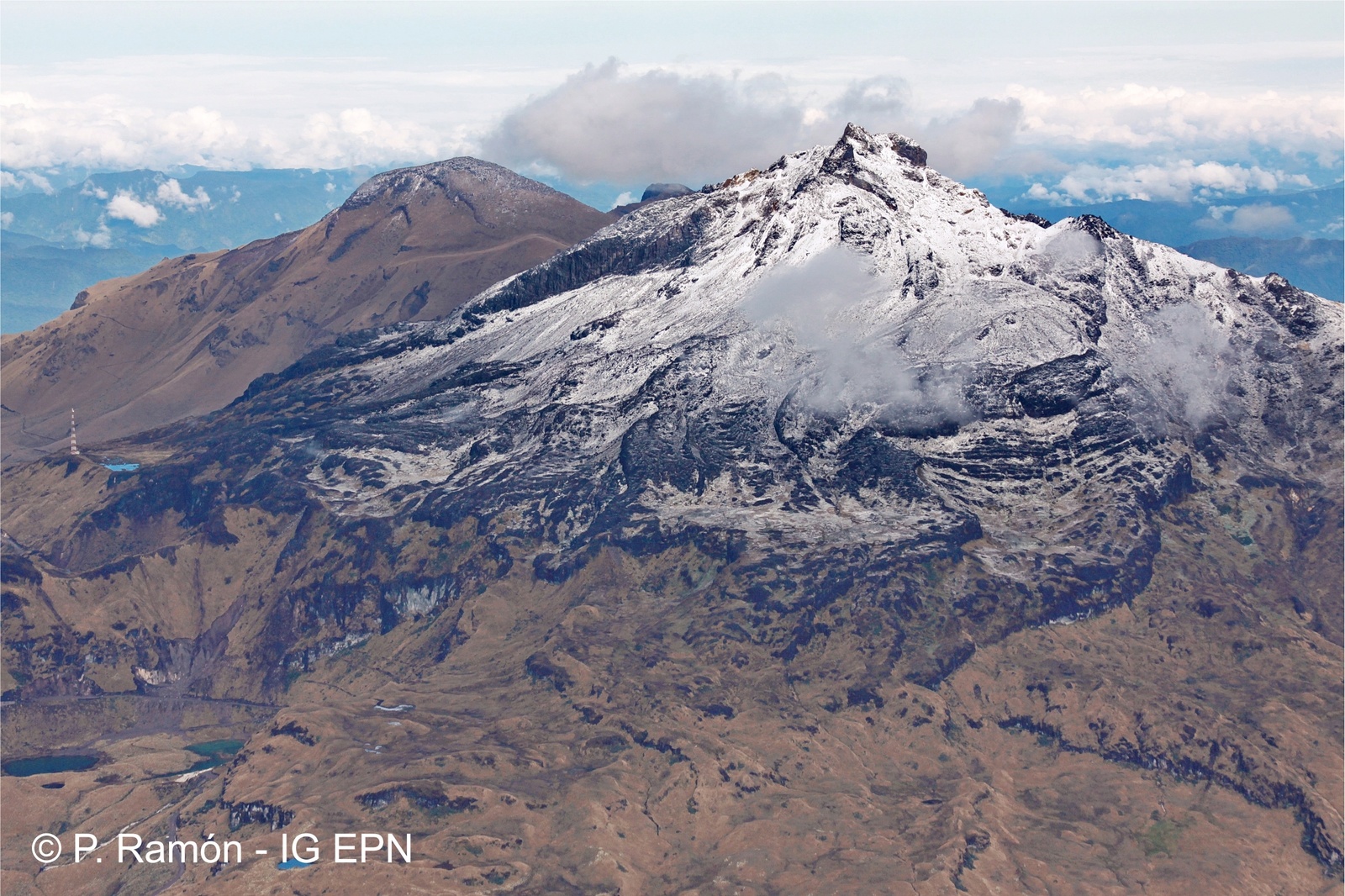
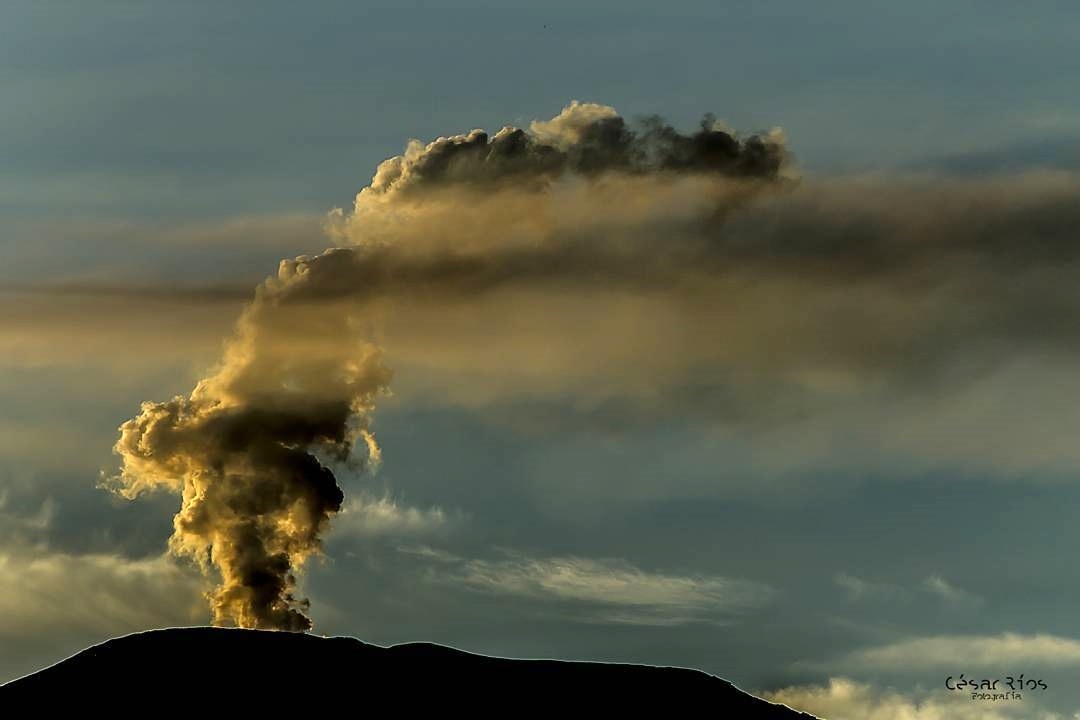
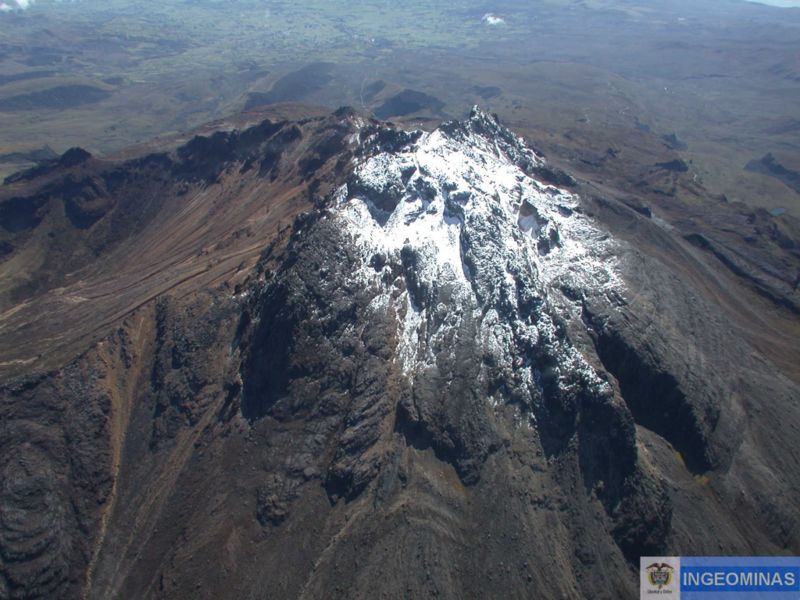
Colombie , Galeras :
Le niveau d’activité du volcan se poursuit au niveau : NIVEAU JAUNE ■ (III): CHANGEMENTS DANS LE COMPORTEMENT DE L’ACTIVITÉ VOLCANIQUE.
Suite à l’activité du VOLCÁN GALERAS, le SERVICE GÉOLOGIQUE COLOMBIEN (SGC) informe que:
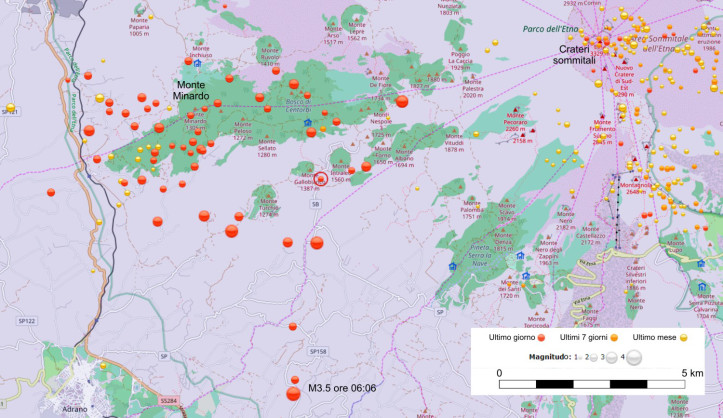
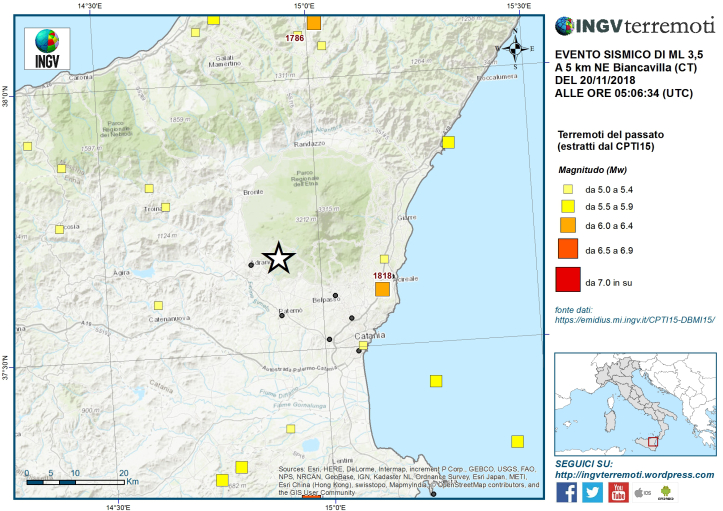
Pour la période du 20 au 26 novembre 2018 et par rapport à la semaine précédente, la sismicité du volcan Galeras a diminué par rapport à la semaine précédente, avec la prédominance des séismes de type VT (séismes volcano-tectoniques, associés à des fractures du matériel cortical à l’intérieur du volcan). Ces événements ont été localisés de manière dispersée, à des profondeurs comprises entre 2,5 et 10,5 km et des magnitudes locales inférieures à M2,6 sur l’échelle de Richter.
Au cours de la semaine évaluée, nous avons observé des émissions de gaz blancs, de basse pression, à une faible hauteur et une direction variable en raison de l’action des vents.
Les autres paramètres de type géophysique et géochimique de la surveillance du volcan Galeras n’ont pas montré de variations importantes.
Le SERVICE GÉOLOGIQUE COLOMBIEN est attentif à l’évolution du phénomène volcanique et continuera d’informer en temps utile des changements observés.
Source : SGC
Photo : Capra.
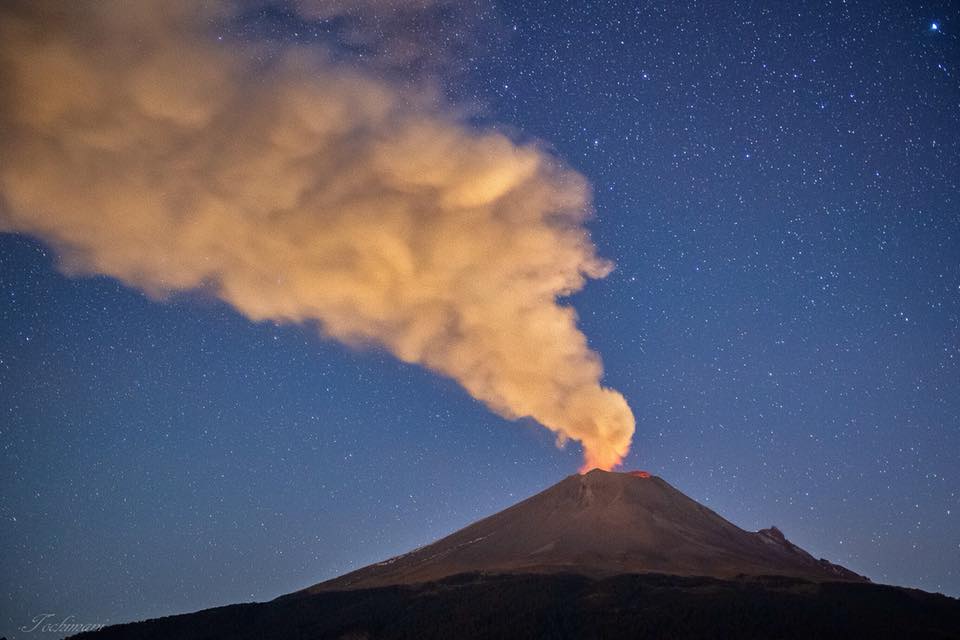
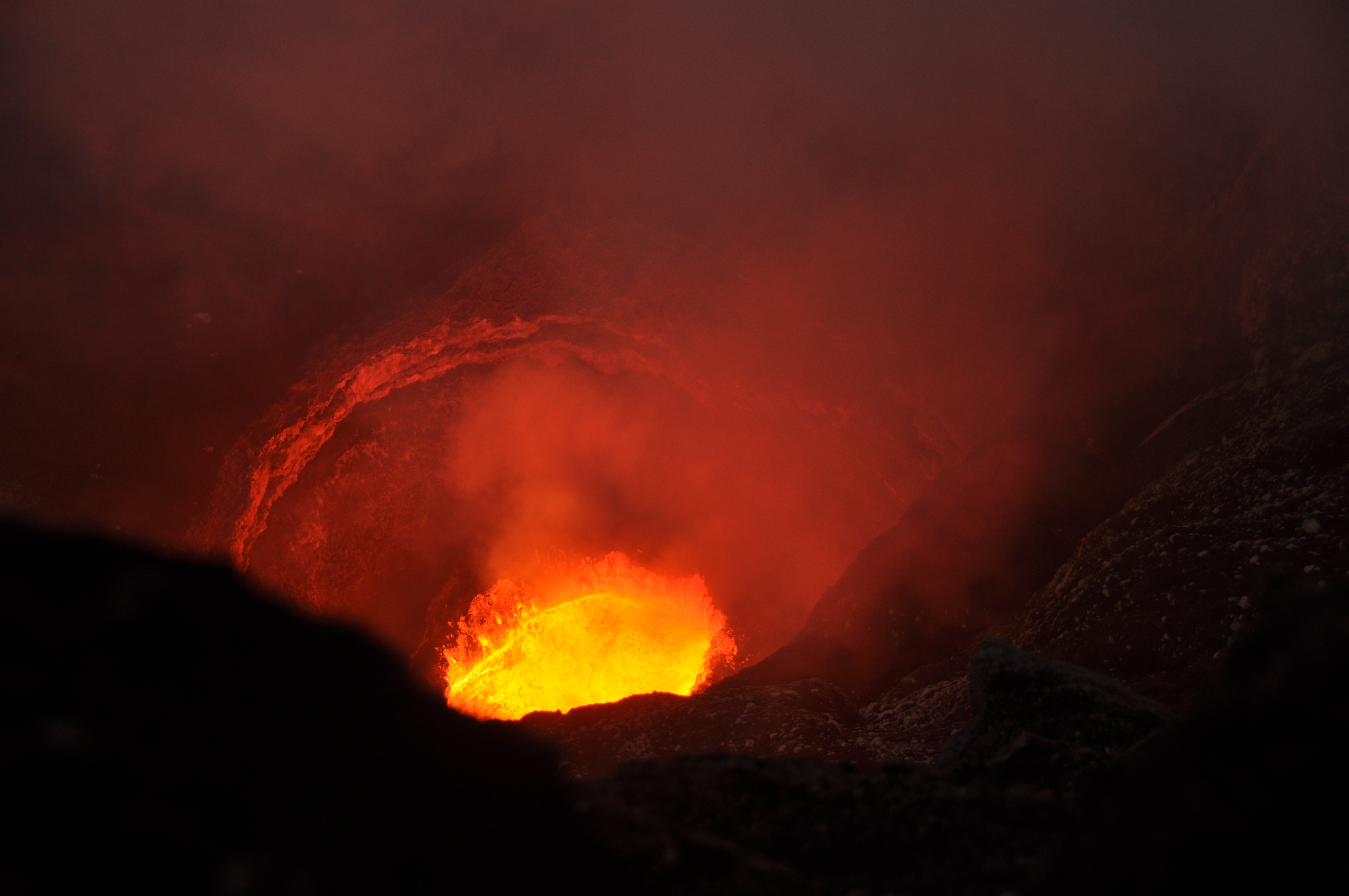
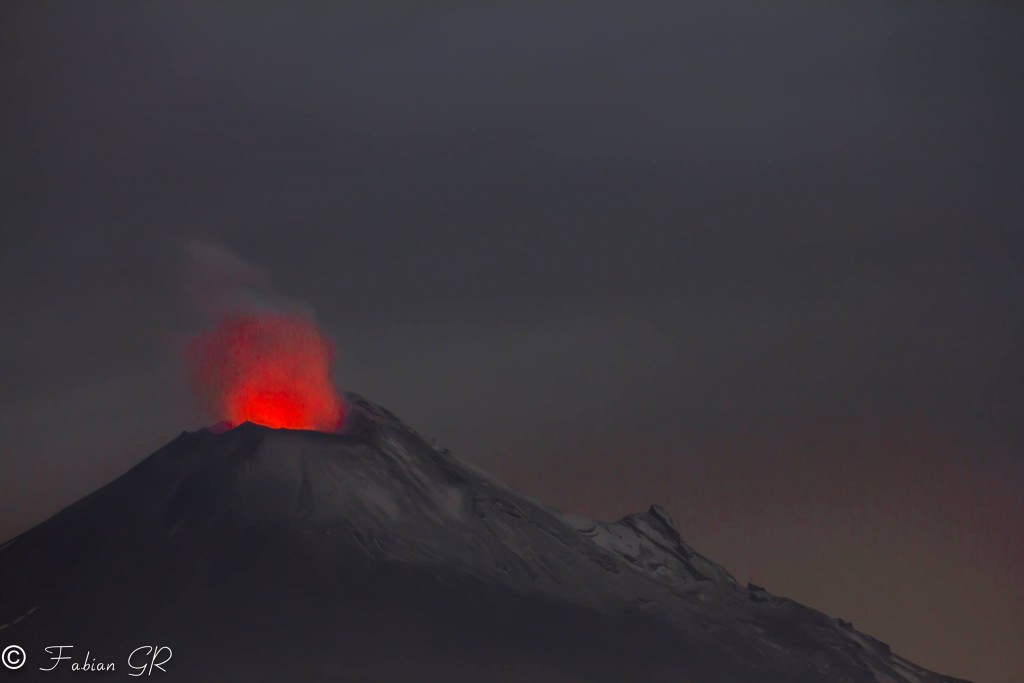
Mexique , Popocatepetl :
Au cours des dernières 24 heures, grâce aux systèmes de surveillance du volcan Popocatepetl, 51 exhalations ont été identifiées, accompagnées de vapeur d’eau et de gaz, ainsi que 3 minutes de tremor harmonique.
Ce matin, deux explosions ont éjecté des fragments incandescents sur les hautes pentes du volcan et généré des colonnes de cendres atteignant une hauteur de 2,5 km, que le vent a dispersées vers le Nord-Est. La première s’est produite à 5h09 et la seconde à 9h22.
Au moment de ce rapport, le volcan est observé, avec une émission constante de vapeur d’eau et de gaz dirigée vers le Nord-Est.
Le CENAPRED insiste pour que le volcan et surtout le cratère ne soient pas abordés, car ils risquent de provoquer la chute de fragments balistiques et, en cas de fortes pluies, de s’éloigner des fonds de ravins à cause du danger de glissements de terrain et de coulées de boue.
Le feu de signalisation d’alerte volcanique du Popocatepetl est situé à Amarillo Phase 2.
Source : Cenapred.
Photo : Erik Gómez Tochimani Fotógrafo
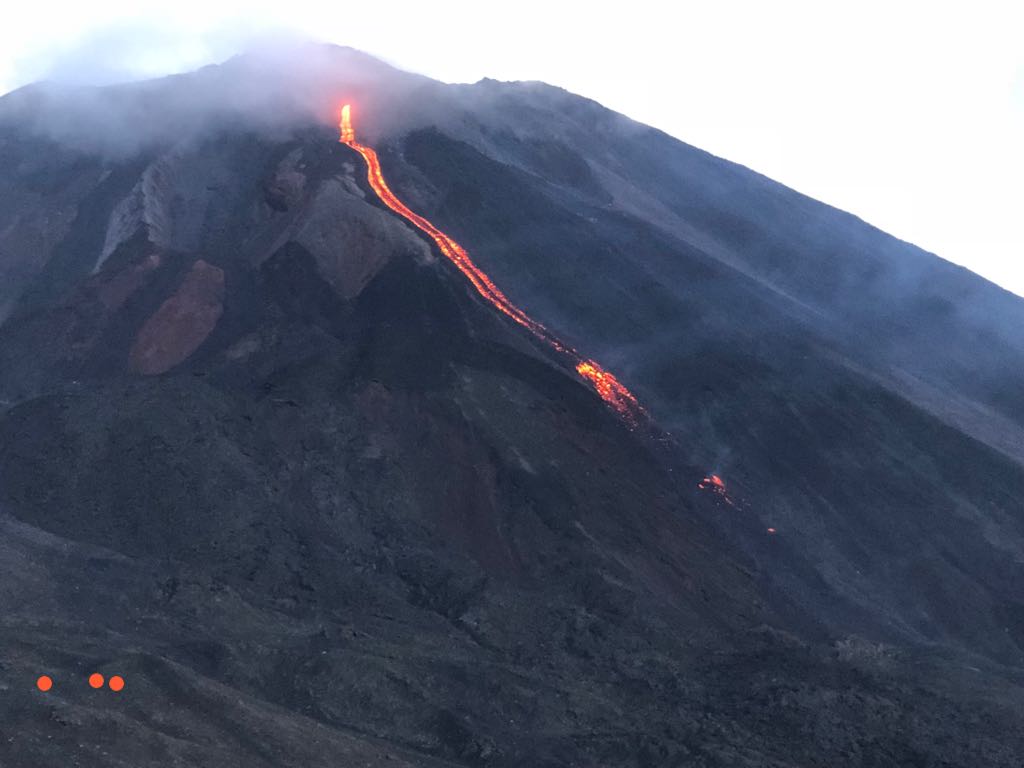
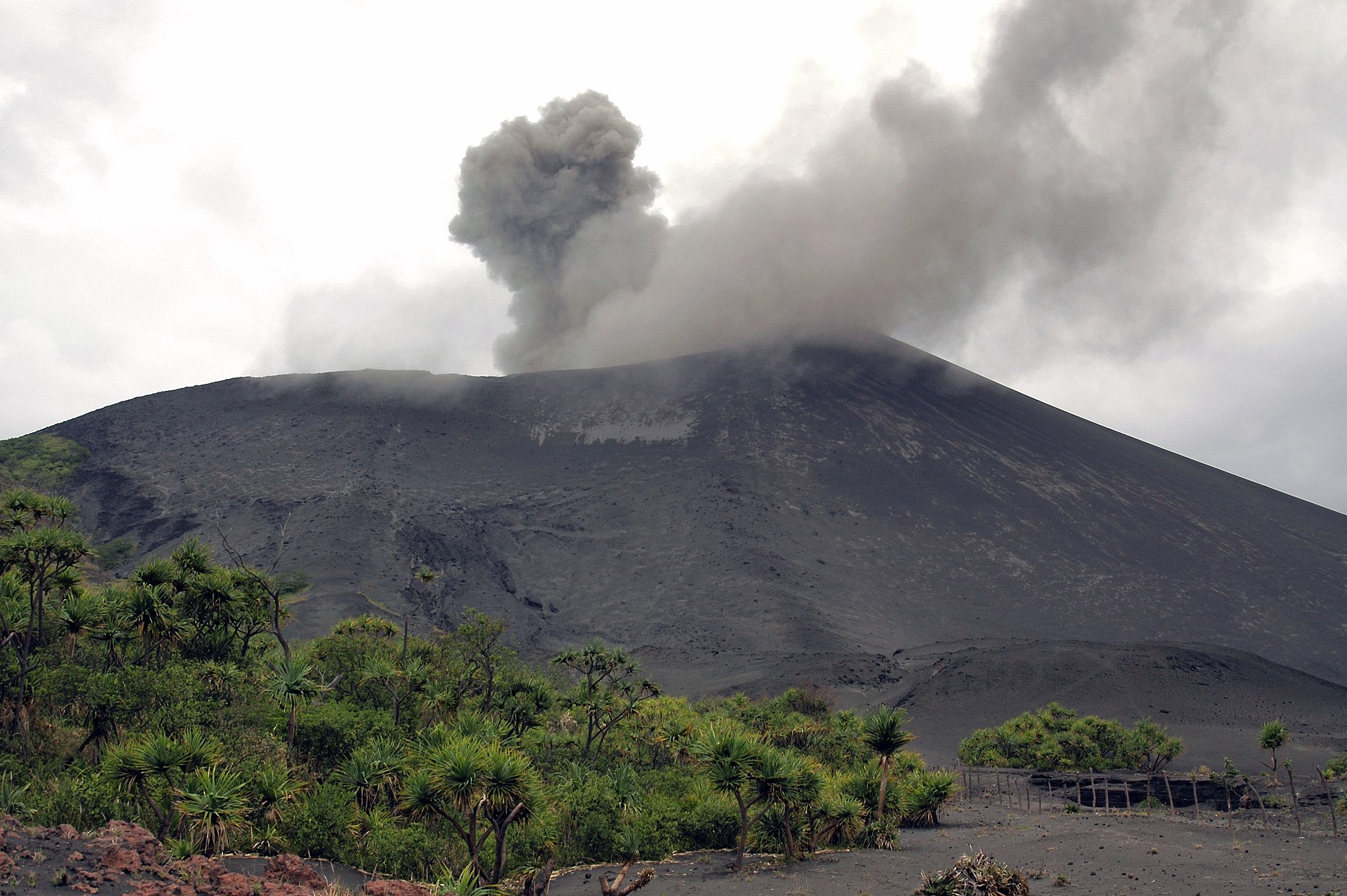
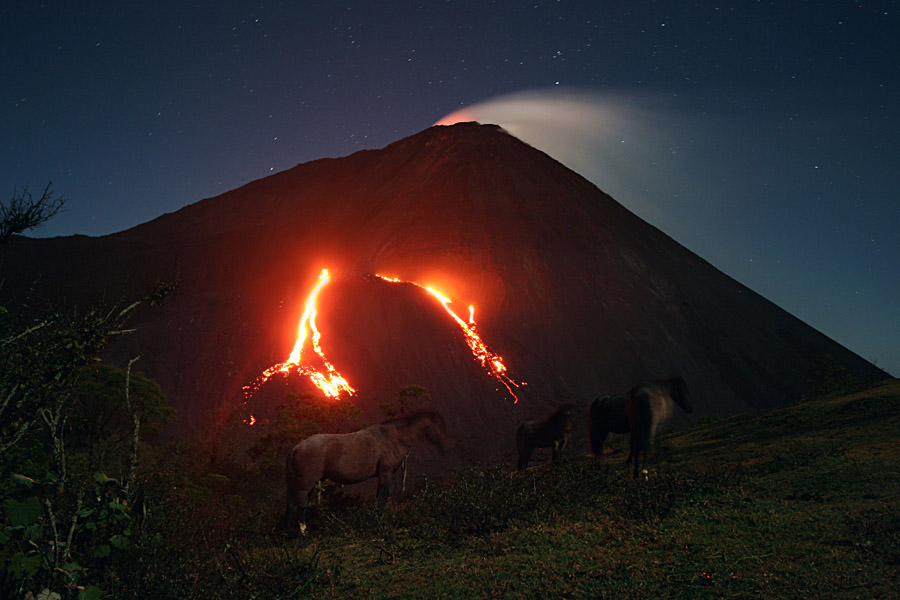
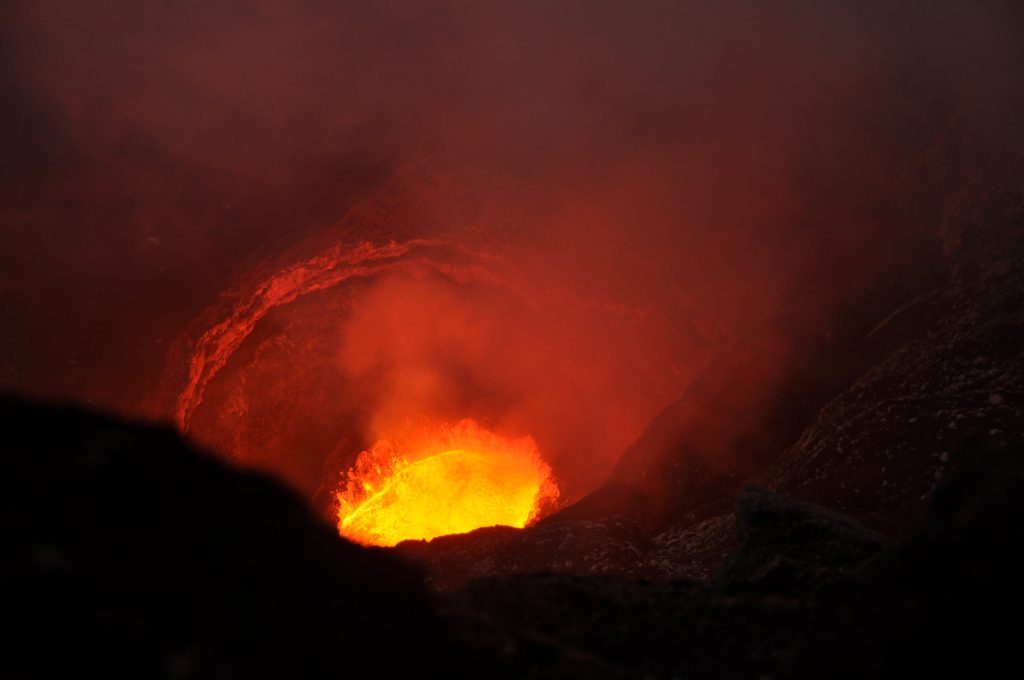
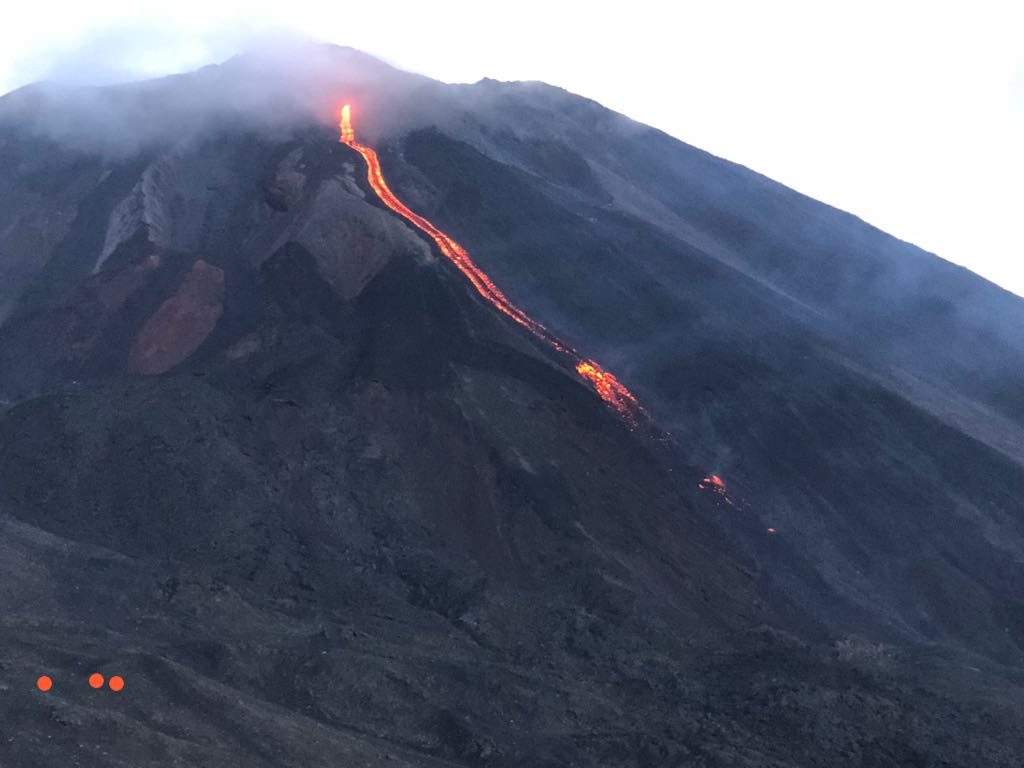
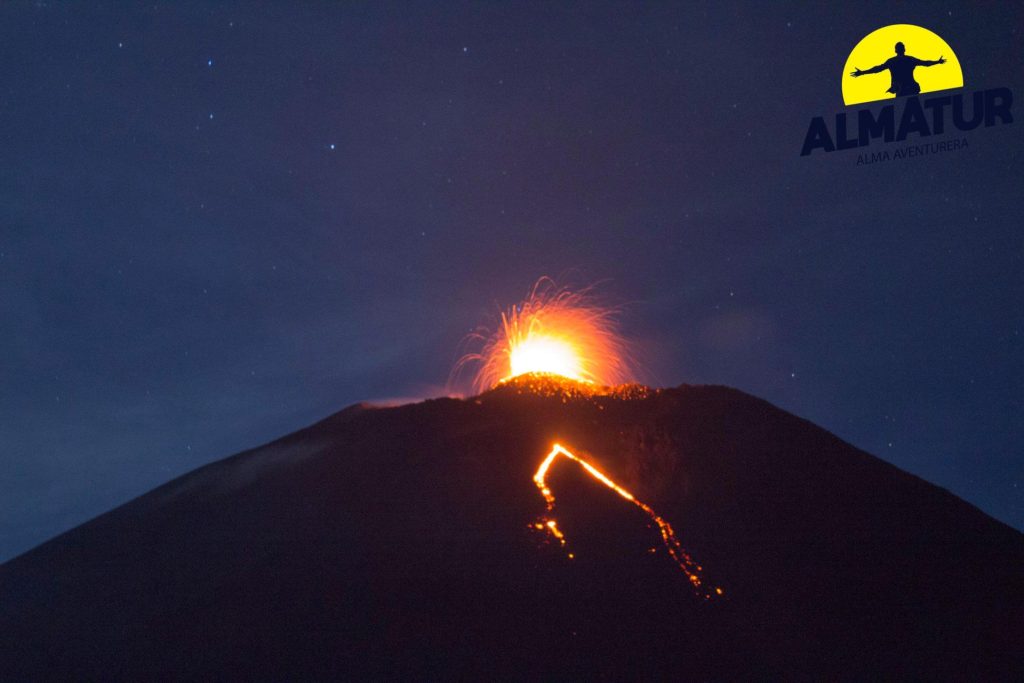
Guatemala , Pacaya :
Type d’activité: Strombolienne
Morphologie: Stratovolcan composite.
Localisation géographique: 14 ° 22’50˝ Latitude N; 90 ° 36’00˝ Longitude O.
Hauteur: 2,552msnm.
Conditions météorologiques: Temps clair
Vent: nord
Précipitations: 0,5 mm
Activité:
Présence de faibles fumeroles blanches de dégazage à une hauteur approximative de 2 700 mètres (8 858 pieds) qui sont dispersées par le vent dans une direction Nord. La station sismique enregistre les tremors internes associés au dégazage et aux explosions stromboliennes constantes. Celles-ci soulèvent des matériaux à une hauteur approximative de 5 à 15 mètres au-dessus du cratère. On observe une incandescence dans le cratère Mackenney et 2 coulées de lave en direction du Nord-Ouest, avec des longueurs de 200 et 250 m. On note des avalanches modérées sur les fronts des coulées de lave.
Source : Insivumeh
Photo : tn8.tv
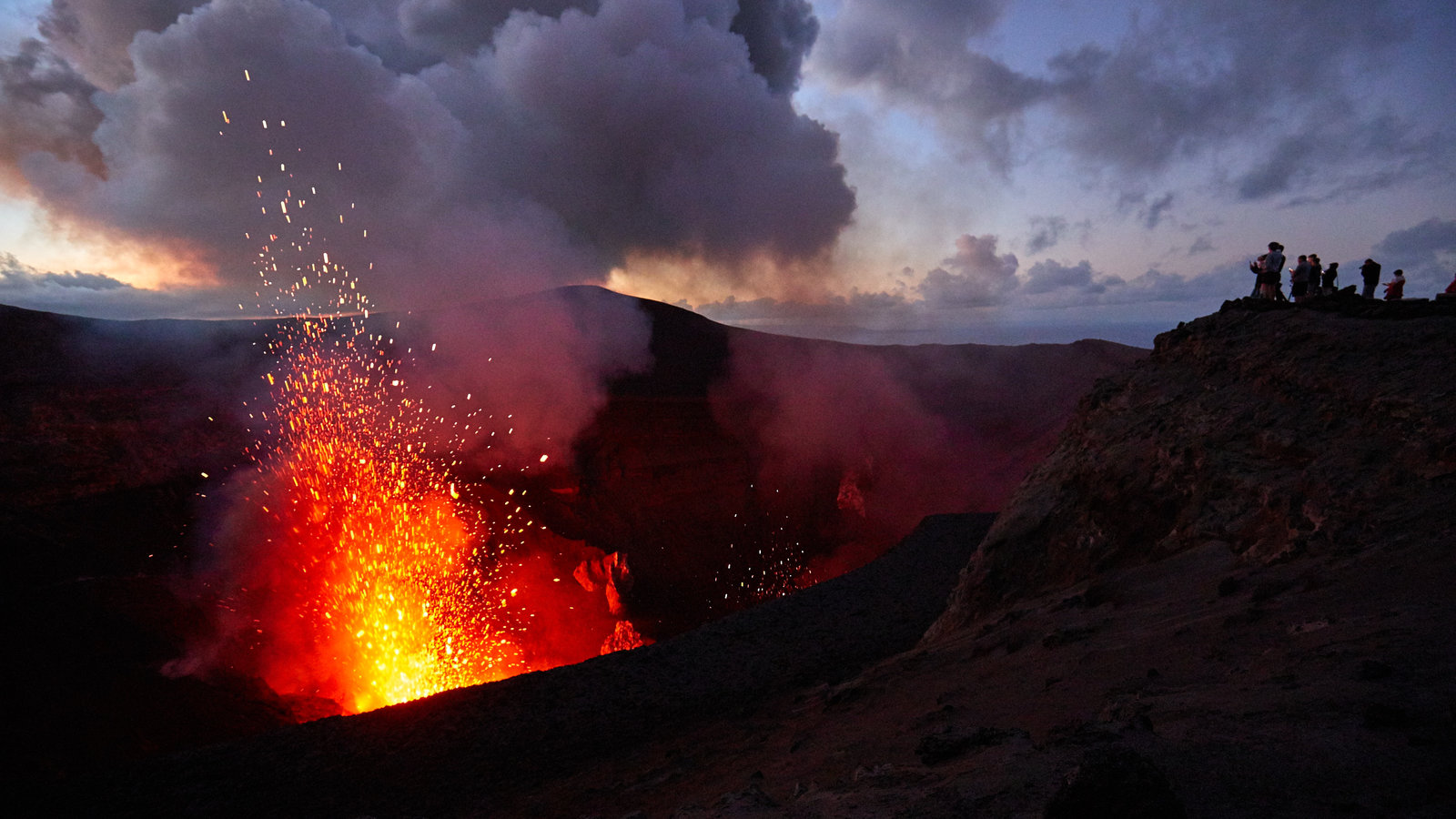
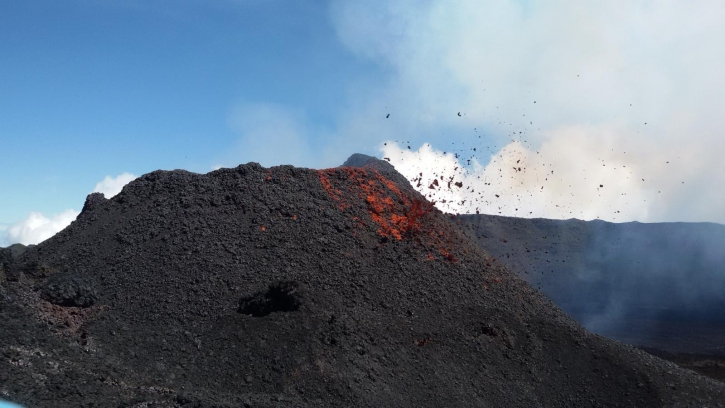
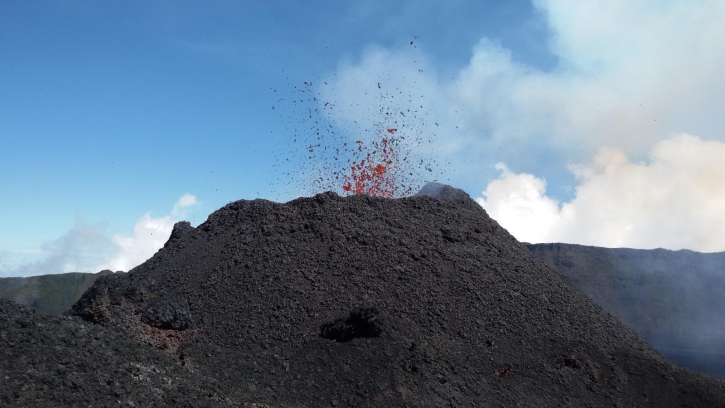
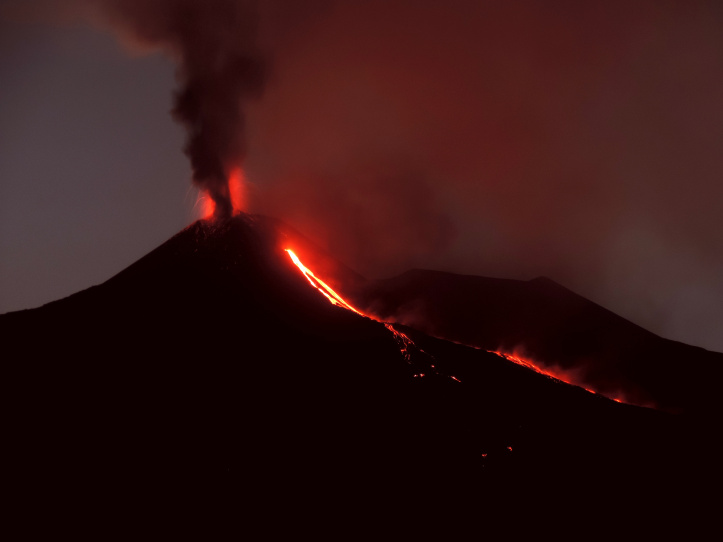
Indonésie , Anak Krakatau :
AVIS D’OBSERVATION DU VOLCAN POUR L’AVIATION – VONA.
Émis: 03 Décembre 2018
Volcan: Anak Krakatau (262000)
Code couleur de l’aviation actuel : ORANGE
Code de couleur d’aviation précédent: orange
Source: Observatoire du volcan Anak Krakatau
Numéro de l’avis: 2018KRA92
Localisation du volcan : S 06 deg 06 min 07 sec E 105 deg 25 min 23 sec
Région :Lampung, Indonésie
Altitude du sommet: 1082 FT (338 M)
Résumé de l’activité volcanique:
Eruption avec nuages de cendres à 01h16 UTC (08h16 heure locale). L’éruption a duré 69 secondes. L’éruption et les émissions de cendres se poursuivent.
Hauteur du nuage volcanique:
La meilleure estimation de la surface des nuages de cendres est d’environ 1038 M (3322 FT) au-dessus du niveau de la mer, peut être plus élevé que ce qui peut être observé clairement. Source des données de hauteur: observateur au sol.
Autres informations sur les nuages volcaniques:
Nuage de cendres se déplaçant vers le Nord
Remarques:
Eruption enregistrée sur un sismogramme d’amplitude maximale de 58 mm et de durée maximale de 69 secondes.
Activité de l’ Anak Krakatau: Cette semaine, l’activité de type vulcanienne est encore observée de nuit sous forme de rougeoiements et d’émission de matériaux incandescents dans toutes les directions, à une hauteur de 200 m au dessus du sommet. Les éruptions sont accompagnées de coulées de lave sur le versant Sud en direction de la mer. L’éruption a également été accompagnée par des détonations faibles à fortes entendues au PGA Post de Pasauran-Banten. Pendant la journée, la montagne est souvent recouverte de brouillard, bien que l’épaisse colonne de cendres d’éruption noire atteigne une hauteur maximale de 100 à 700 m du sommet. Le sismographe a enregistré 154 tremblements de terre d’éruption, 45 tremblements de terre d’émission, 60 séismes volcaniques peu profonds, 80 séismes volcaniques profonds, 57 tremblements harmoniques et un tremor continu d’amplitude de 1 à 58 mm.
Source : Magma Indonésie, PVMBG.
Vidéo : Yohannes Tyas Galih Jati / Volcanodiscovery.