October 14 , 2019.
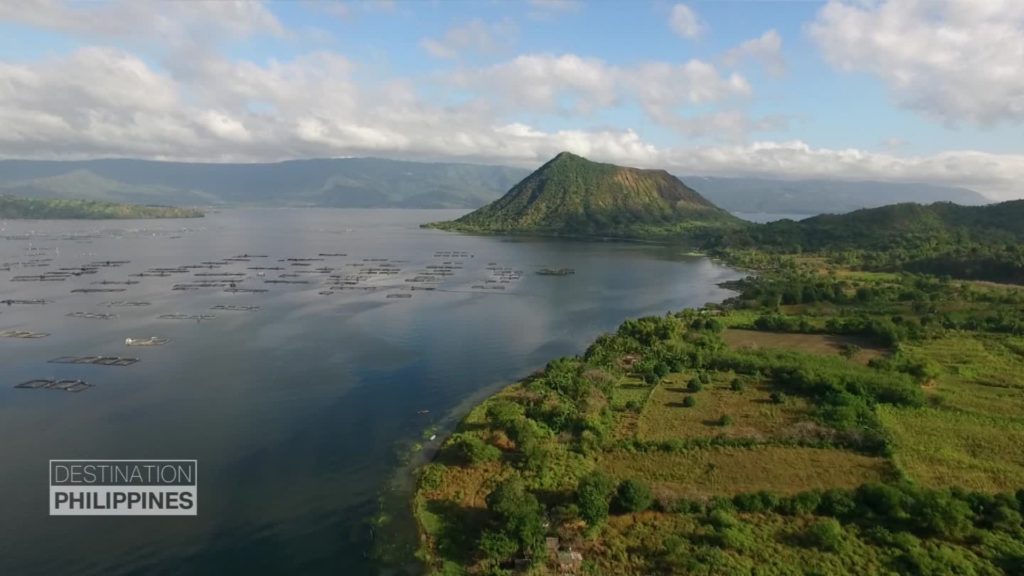
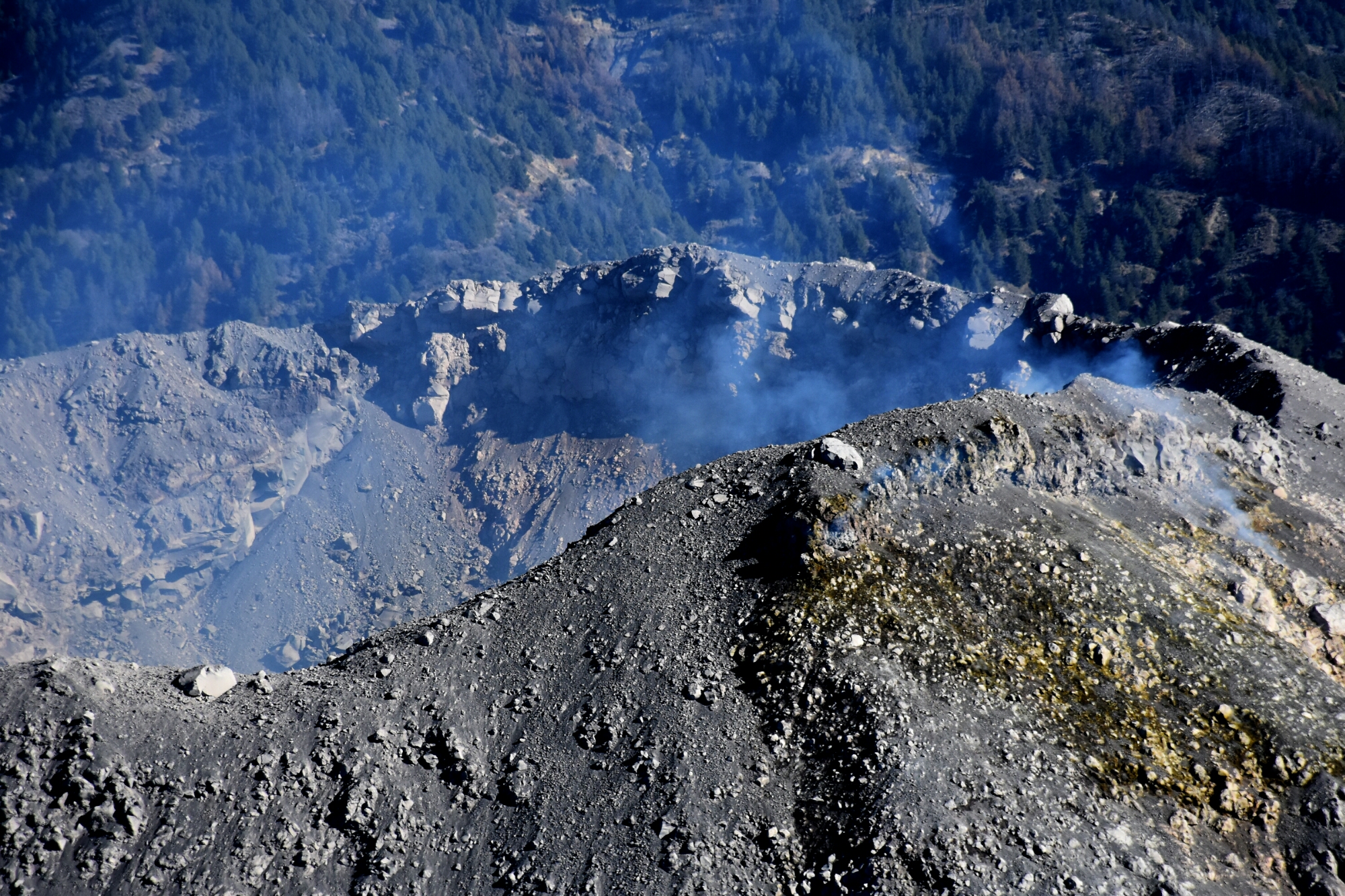
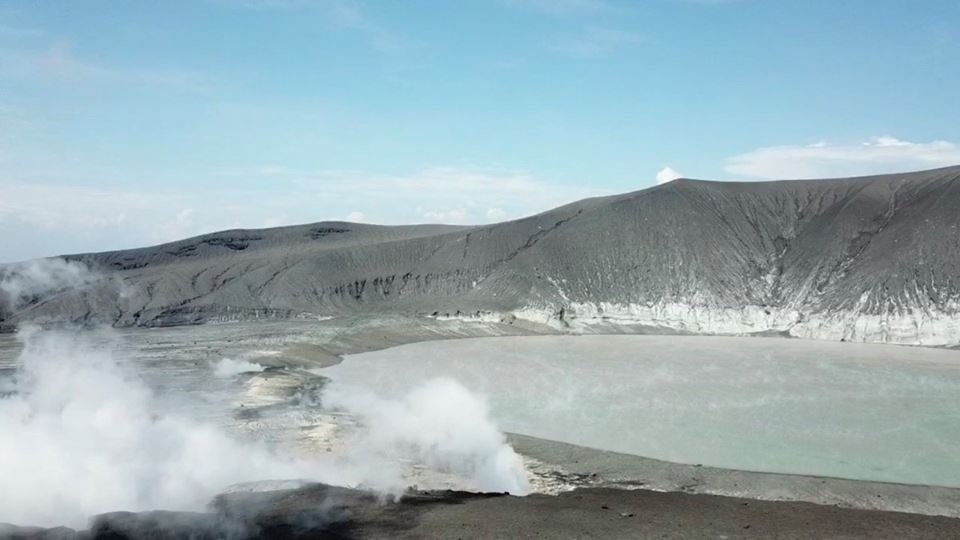
Philippines , Taal :
TAAL VOLCANO BULLETIN: 14 October 2019 8:00 A.M.
Taal Volcano’s seismic monitoring network recorded twenty-three (23) volcanic earthquakes during the 24-hour observation period. Field measurements on 10 October 2019 at the eastern sector of the Main Crater Lake yielded an increase in water temperature from 32.6°C to 32.8°C, a decrease in water level from 0.50 meters to 0.48 meters and an increase in acidity from a pH of 3.12 to 2.86. Ground deformation measurements through precise leveling surveys from 19 – 26 September 2019 indicated inflation of the edifice consistent with recent results from continuous GPS data.
Alert Level 1 remains in effect over Taal Volcano. This means that hazardous eruption is not imminent. The public, however, is reminded that the Main Crater should be strictly off-limits because sudden steam explosions may occur and high concentrations of toxic gases may accumulate. The northern portion of the Main Crater rim, in the vicinity of Daang Kastila Trail, may also becom hazardous when steam emission along existing fissures suddenly increases. Furthermore, the public is also reminded that the entire Volcano Island is a Permanent Danger Zone (PDZ), and permanent settlement in the island is strongly not recommended.
Source : Phivolcs
Photo : destination philippines.
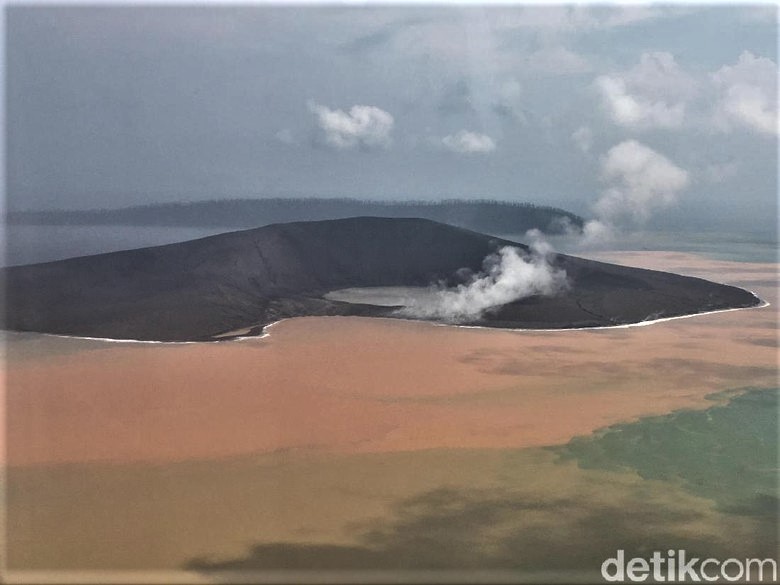
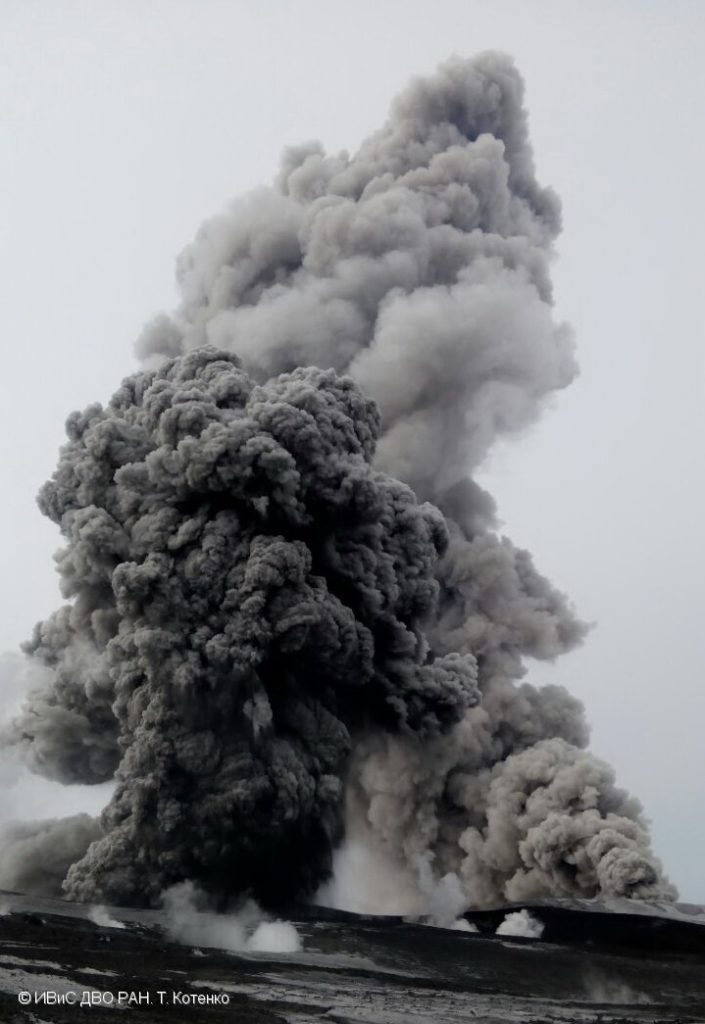
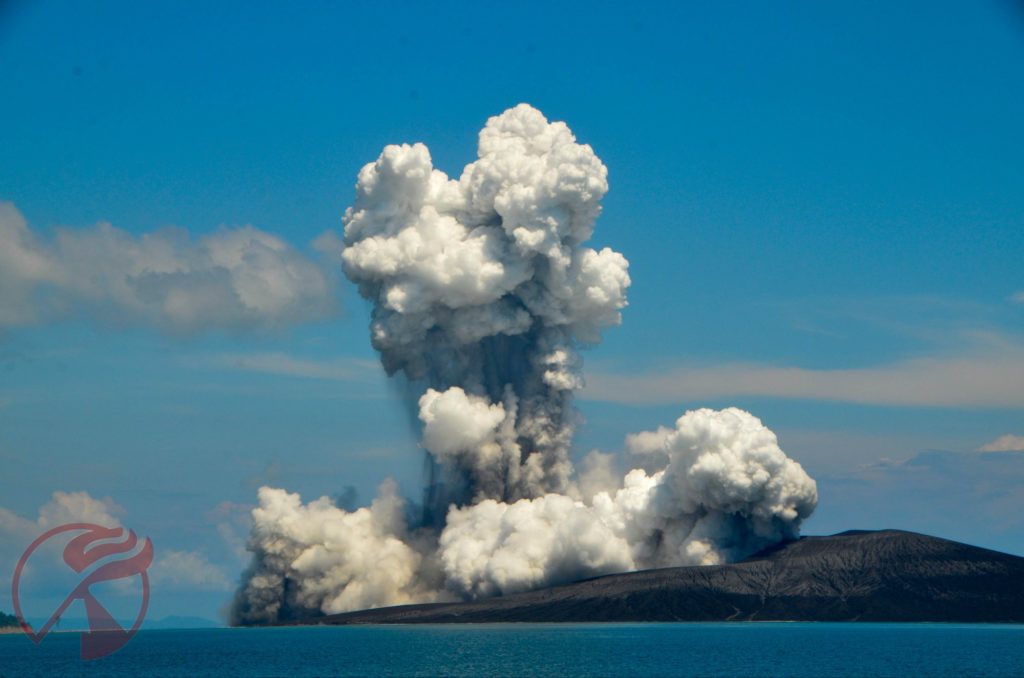
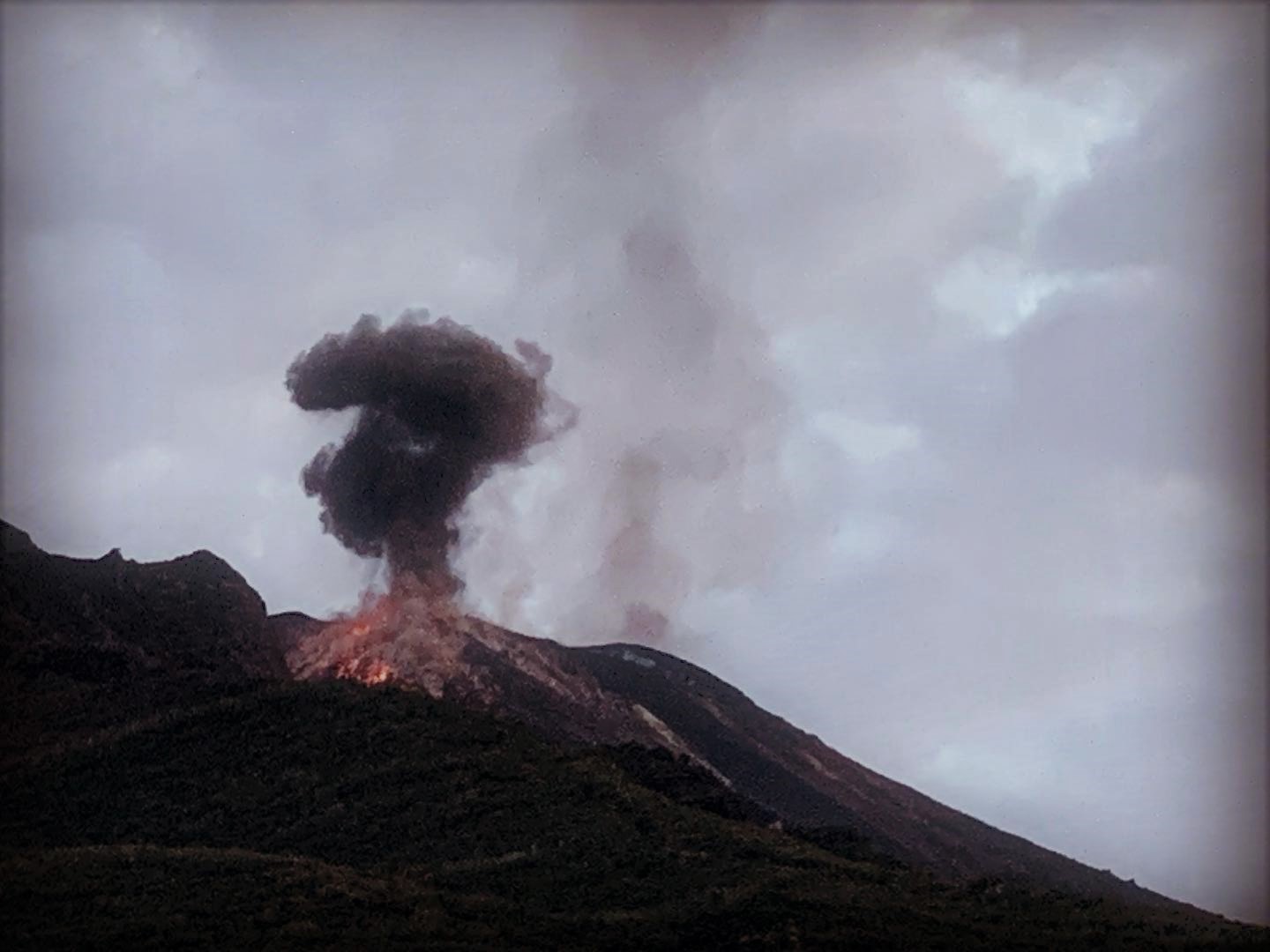
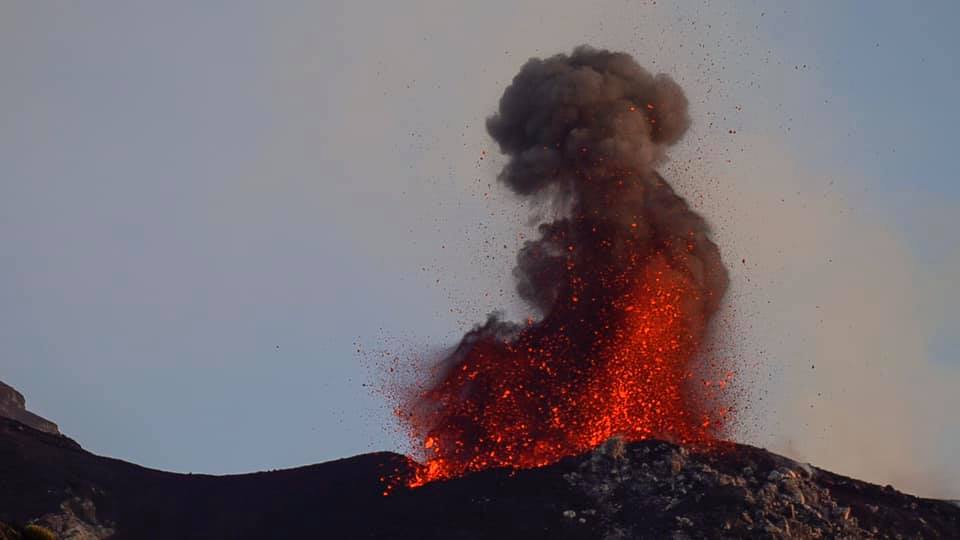
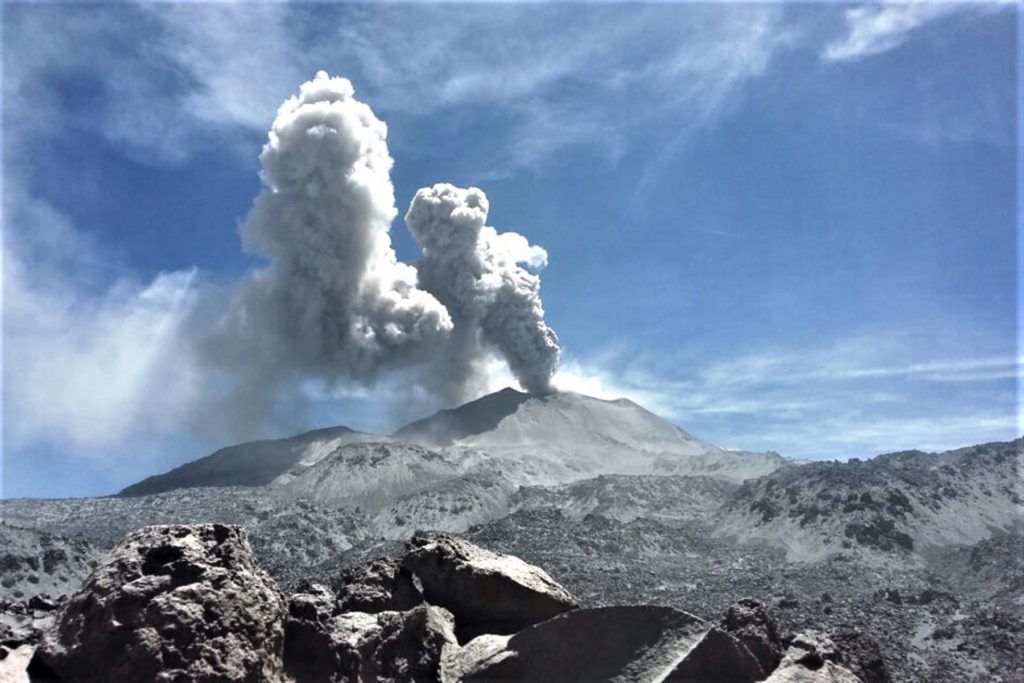
Indonesia , Anak Krakatau :
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION – VONA.
Issued: 20191014/0551Z
Volcano: Anak Krakatau (262000)
Current Aviation Colour Code: ORANGE
Previous Aviation Colour Code: orange
Source: Anak Krakatau Volcano Observatory
Notice Number: 2019KRA173
Volcano Location: S 06 deg 06 min 07 sec E 105 deg 25 min 23 sec
Area: Lampung, Indonesia
Summit Elevation: 502 FT (157 M)
Volcanic Activity Summary:
recorded eruption at 05:28 UTC (12:28 local )
Volcanic Cloud Height:
Best estimate of ash-cloud top is around 1142 FT (357 M) above sea level, may be higher than what can be observed clearly. Source of height data: ground observer.
Other Volcanic Cloud Information:
Ash cloud is moving to North
Remarks:
Eruption recorded on seismogram with maximum amplitude 38 mm and duration 223 second.
Source : Magma Indonésie .
Photo : Detik.com
Alaska , Cleveland :
52°49’20 » N 169°56’42 » W,
Summit Elevation 5676 ft (1730 m)
Current Volcano Alert Level: ADVISORY
Current Aviation Color Code: YELLOW
A few small earthquakes were noted on the local seismic network. No eruptive activity was detected in regional infrasound data or in cloudy satellite images. A steam plume, common at Cleveland, was observed in clear web camera images.
Episodes of lava effusion and explosions can occur without advance warning. Explosions from Cleveland are normally short duration and only present a hazard to aviation in the immediate vicinity of the volcano. Larger explosions that present a more widespread hazard to aviation are possible, but are less likely and occur less frequently.
Cleveland volcano is monitored by only two seismic stations, which restricts AVO’s ability to detect precursory unrest that may lead to an explosive eruption. Rapid detection of an ash-producing eruption may be possible using a combination of seismic, infrasound, lightning, and satellite data.
Source : AVO .
Photo : Dave Clum.
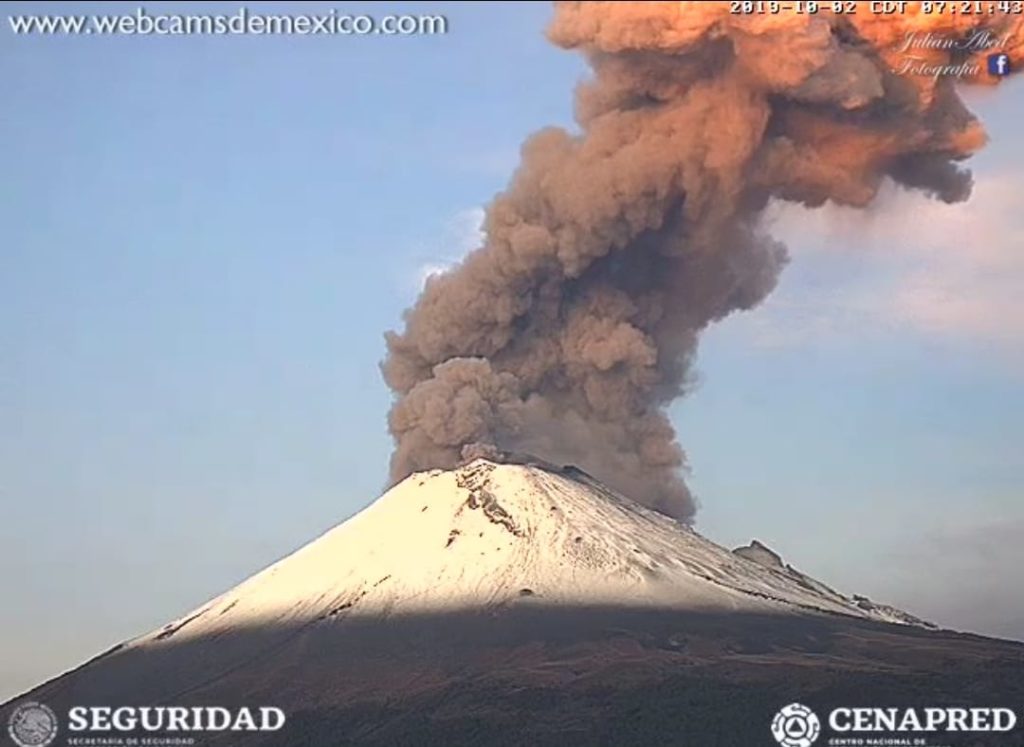
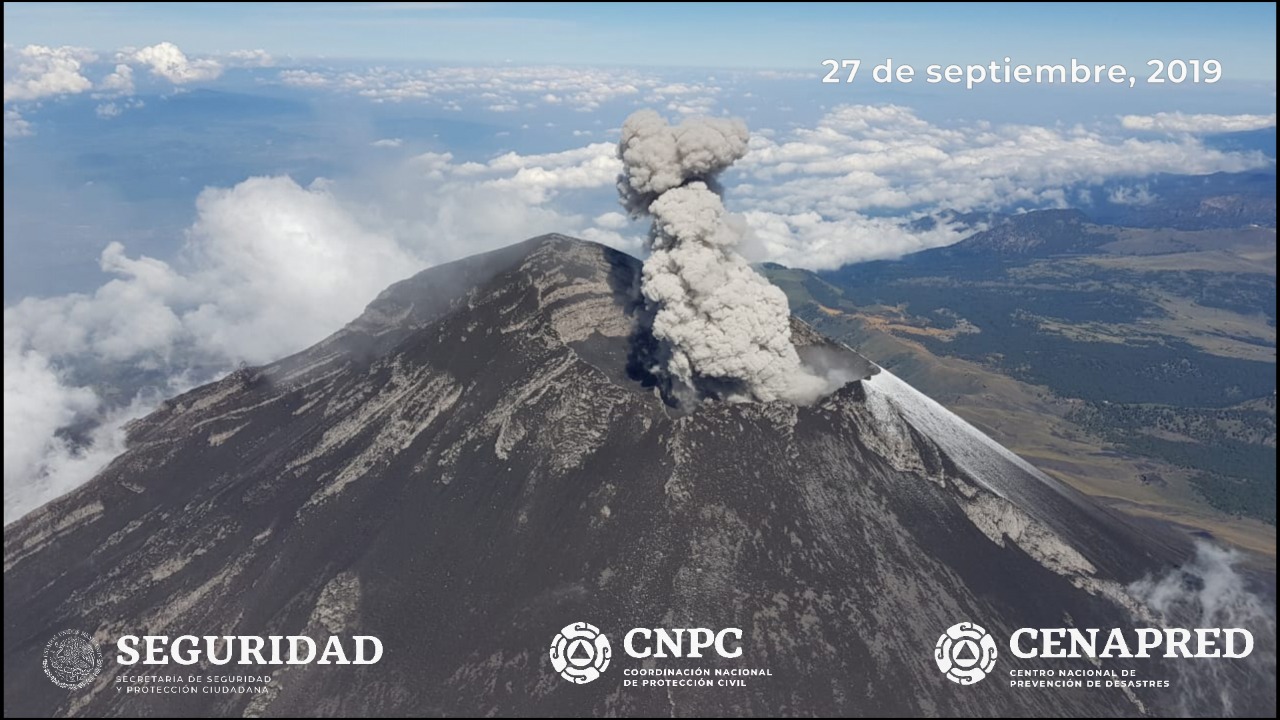
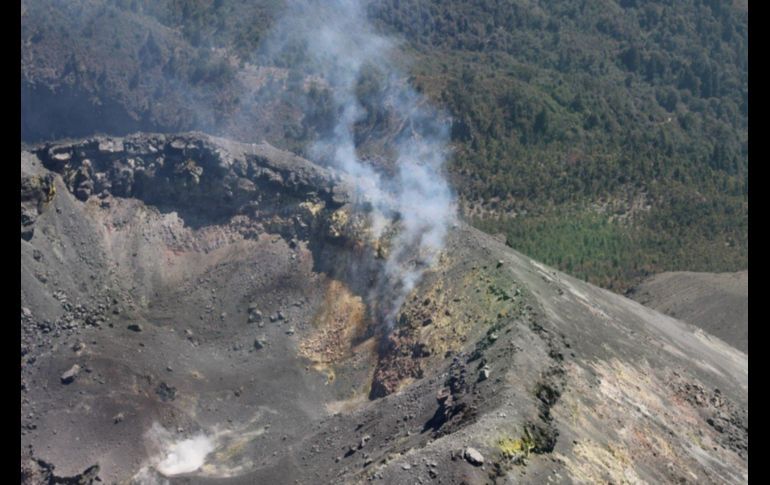
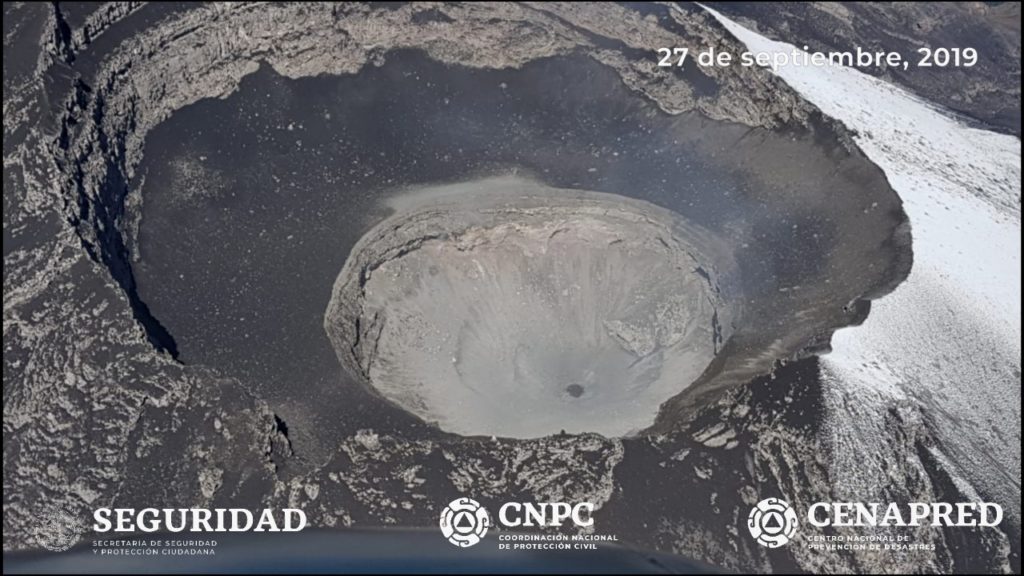
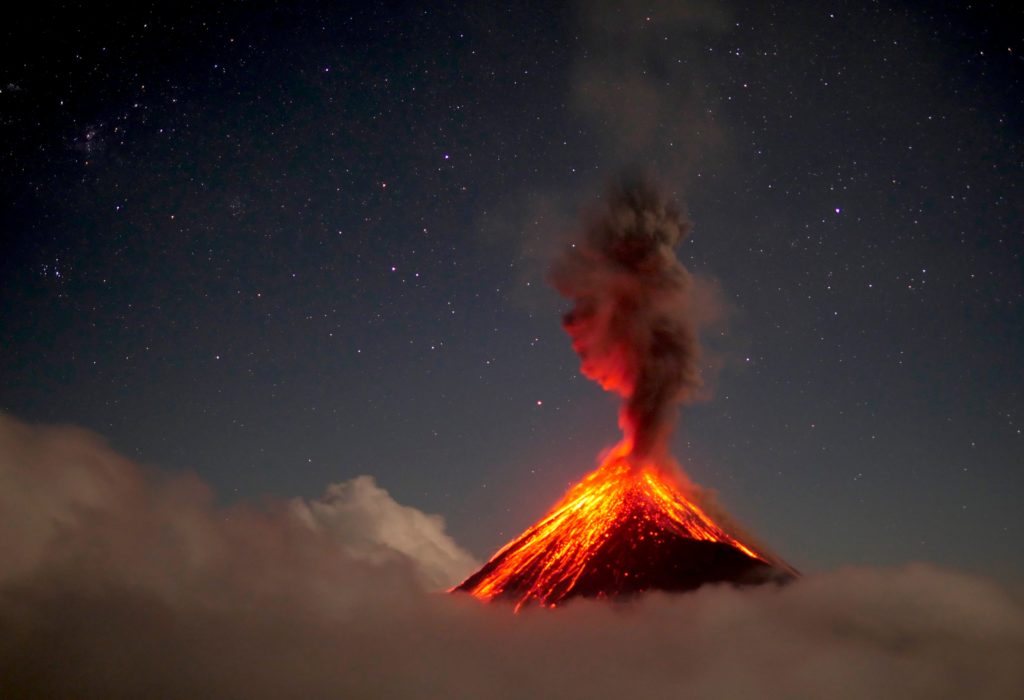
Mexico , Popocatepetl :
October 13, 11:00 am (October 13, 16:00 GMT)
According to the monitoring systems of the Popocatépetl volcano, 117 exhalations have been identified, accompanied by gas and light amounts of ash. In addition, a moderate explosion was identified yesterday at 10:27 and that, for meteorological reasons, could not be observed. In addition, 709 minutes of tremor were recorded.
This morning and at the time of this report, there is a visibility towards the volcano, any emission will be dispersed in the North-West direction.
CENAPRED urges NOT to approach the volcano and in particular the crater, because of the risk of falling ballistic fragments, and in case of heavy rains, to stay far from the bottom of the ravines because of the risk of mudslides and debris.
The warning light of Popocatépetl is in YELLOW PHASE 2.
Source : Cenapred.
Photo : Cenapred.