February 25 , 2021 .
Italy / Sicily : Etna ,
Continuation of the Etna serial ….
COMMUNICATION ON THE ACTIVITY OF ETNA, 24 February 2021, 17:12 (16:12 UTC).
The National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology, Osservatorio Etneo, reports that there is low Strombolian activity in the Southeast Crater with low ash emission.
The average amplitude of the volcanic tremor gradually increases while remaining at the current state at the average level. The sources of the tremor are located under the Southeast Crater, about 2,700 m above sea level.
The infrasound signals currently do not show significant variations.
COMMUNICATION ON THE ACTIVITY OF ETNA, 24 February 2021, 18:24 (17:24 UTC).
The National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology, Osservatorio Etneo, announces that at 6 p.m. local time, there is an increase in the intensity and frequency of Strombolian activity in the Southeast Crater, this activity affects two mouths located in the most eastern part of the Southeast Crater. A weak ash emission persists.
The phase of increasing the amplitude of the volcanic tremor continues, showing medium-high values. The springs are located under the Southeast Crater at a depth of approximately 2,500 m above sea level.
Infrasound activity is also increasing and the sources of the events are located at the Southeast Crater.
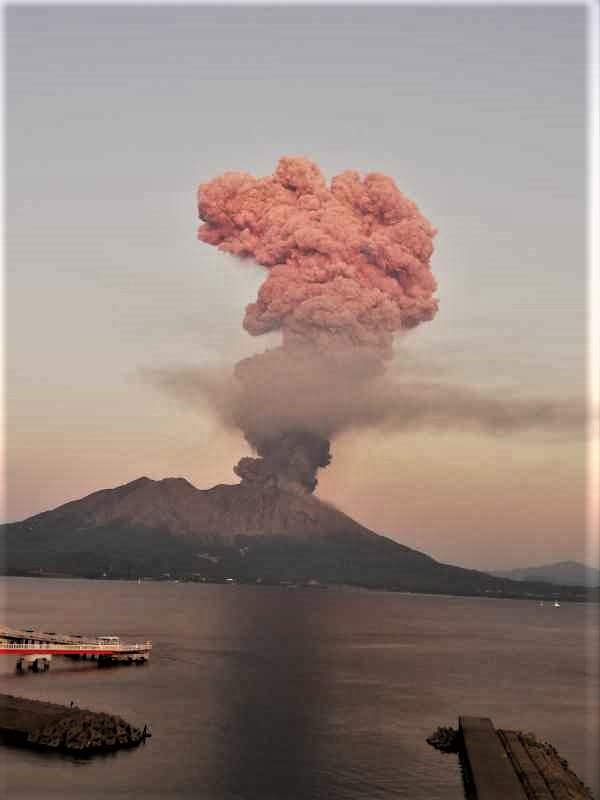
COMMUNICATION ON THE ACTIVITY OF ETNA, February 24, 2021, 20:37 (19:37 UTC).
The National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology, Osservatorio Etneo, announces that from 7 p.m. local, there is an increase in Strombolian activity at the Southeast Crater.
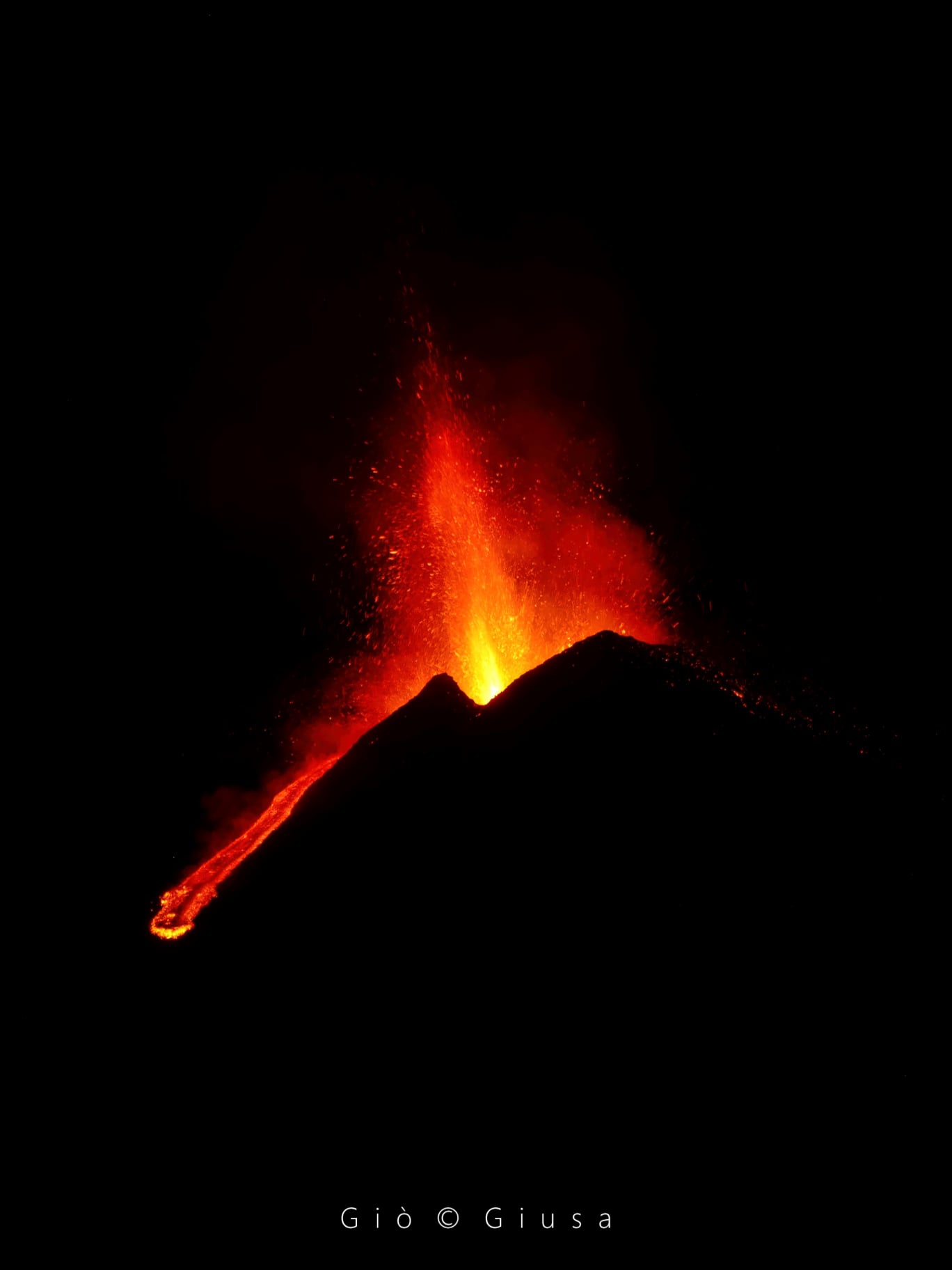
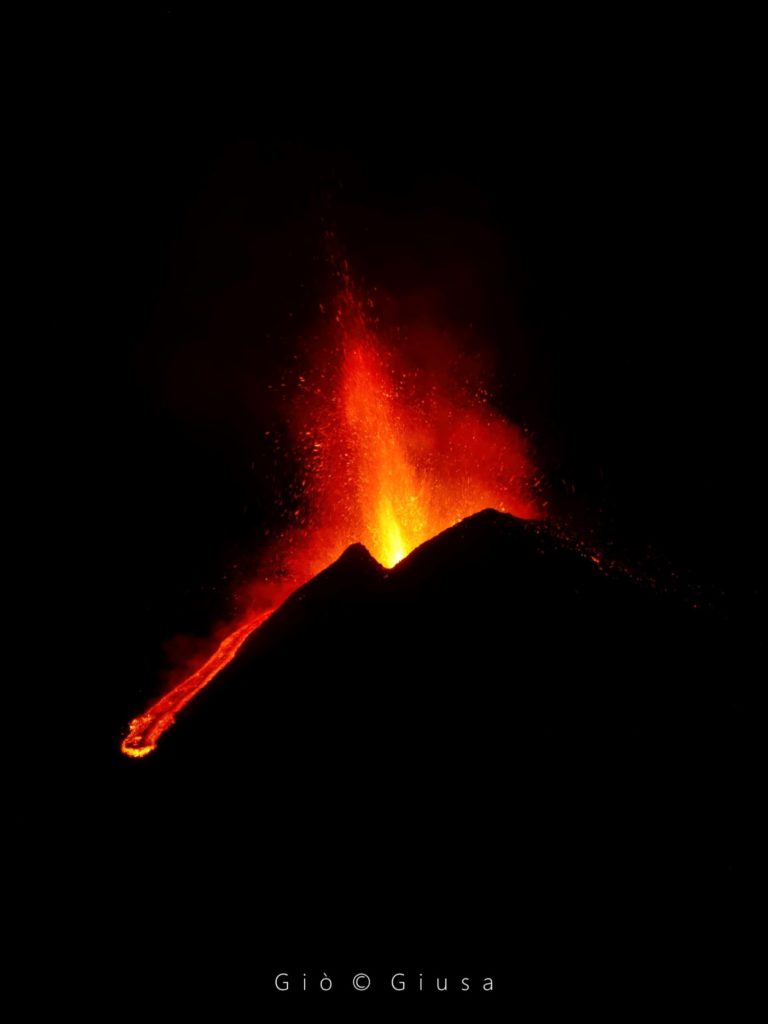
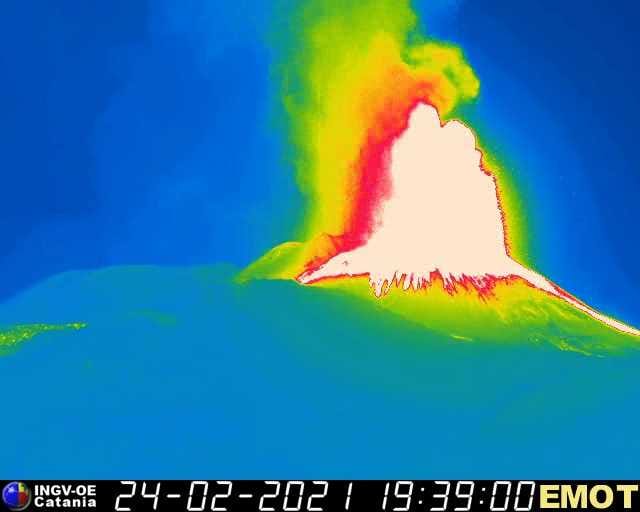
In particular, the two mouths where Strombolian activity was concentrated now produce a lava fountain, the height reached by this activity is about 400 m.
The activity of ash emission into the atmosphere above the Southeast Crater persists.
The average amplitude of the volcanic tremor shows high values with an increasing trend. The location of the source remains in the area of the Southeast Crater at a depth of about 2700 m above sea level. Infrasound activity is also quite sustained in both the rate of occurrence and in the energy of events. The location of infrasound events remains at the Southeast Crater.
COMMUNICATION ON THE ACTIVITY OF ETNA, 24 February 2021, 22:26 (21:26 UTC).
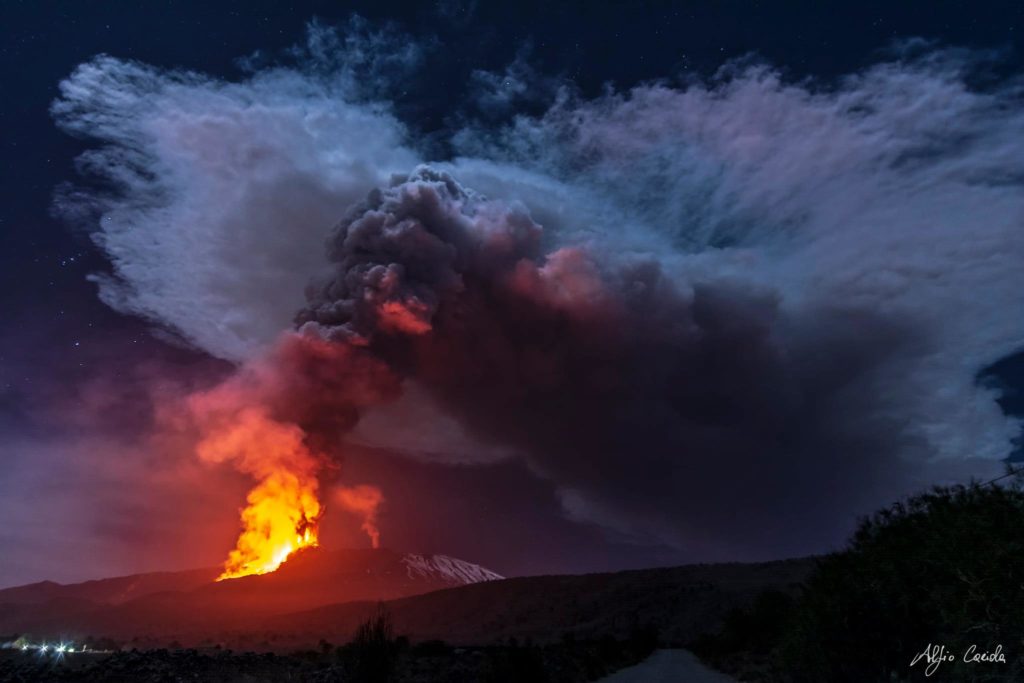
The National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology, Osservatorio Etneo, announces that at 10 p.m. local time the lava fountain has reached the height of about 500 m from the edge of the crater, the eruptive column expands vertically for several kilometers.
In the southwest sector of the Southeast Crater, a well-fed lava overflow is in progress. The stream flowing in Valle del Bove is always fed.
The average amplitude of the volcanic tremor shows high values with a tendency to increase more. The source location remains in the Southeast Crater area at a depth of about 2800 m above sea level. Infrasound activity is also high in both the rate of occurrence and the energy of events. The location of infrasound events remains at the Southeast Crater.
COMMUNICATION ON THE ACTIVITY OF ETNA, 24 February 2021, 23:35 (22:35 UTC).
The National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology, Osservatorio Etneo, announces that the activity of the lava fountains in the South-East Crater has ceased, the lava flows remain active in the South-West sector and in the East zone.
As for the average amplitude of the volcanic tremor, after a phase of increase to very high values, at 21:20 UTC, it showed a sharp drop reaching the average level, where it is still found. The source of the tremor is located in the area of the Southeast Crater at a depth of about 2900 m above sea level. At the same time, the infrasound activity also suffered a sharp decrease in both the rate of occurrence and energy of events, which are located at the Southeast Crater.
Further updates will be communicated shortly.
Source : INGV.
Photos : INGV , Alfio Cariola via Sherine France , Gio Giusa.
Iceland , Reykjane Peninsula :
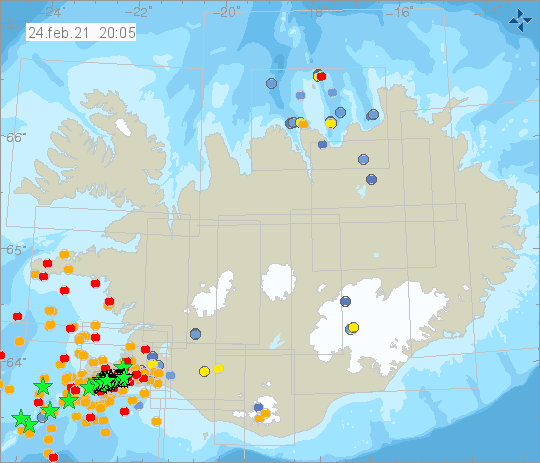
Nearly 1100 earthquakes were detected by the IMO’s SIL seismic network this week, considerably more than during previous week when around 800 earthquakes were detected. The most activity was in the Reykjanes Peninsula and a minor earthquake swarm NE of Grimsey. Around 200 earthquakes were detected near Eiturhóll at Mosfellsheidi. The largest earthquake of the week was M2.9 by Núpshlíðarháls in Reykjanes peninsula, on the 18th of February at 08:10.
Today two earthquakes above M5.0 have been detected in the ongoing earthquake swarm on Reykjanes peninsula. One at 10:05 am of M5.7 and M5.0 at 10:30 am. At 12:37 pm an earthquake of M4.8 was detected near Kleifarvatn. The IMO’s SIL system has detected 10 eartquakes over M4.0 and many of M3.0. More info will be updated as soon as the activity has been reviewed further. Please note that the activity is within the Reykjanes peninsula. Other locations of large earthquakes are unreliable.
IMO raised the Aviation Color Code for Krýsuvík to Yellow on 24 February based on recent increased seismicity. Intense seismic activity had been detected for the previous few days and since midnight through the generation of the report at 1107 more than 500 earthquakes had been recorded. At 1005 a M 5.7 earthquake occurred 5 km W of Krýsuvík and at 1027 a M 4.2 was located in Nupshlidarhals, less than 1 km NW of Krýsuvík. The seismic unrest was unusual for the area in the context of the unrest in the Reykjanes peninsula that began in January 2020.
Source : Vedur is , GVP .
Philippines , Taal :
TAAL VOLCANO BULLETIN 25 February 2021 08:00 A.M.
In the past 24-hour period, the Taal Volcano Network recorded sixty-nine (69) volcanic tremor episodes having durations of one (1) to sixty-one (61) minutes. Despite these, only weak steam-laden plumes were emitted by fumarolic activity at the vents of the Main Crater.
Temperature highs of 74.6°C and pH of 1.59 were last measured from the Main Crater Lake respectively on 18 and 12 February 2021. Ground deformation parameters from continuous electronic tilt on Volcano Island record a slight deflation around the Main Crater since October 2020 but overall, very slow and steady inflation of the Taal region has been recorded by continuous GPS data after the eruption.
Source : Phivolcs .
Photo : Raffy Tima .
Indonesia , Sinabung :
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION – VONA .
Issued : February 25 , 2021
Volcano : Sinabung (261080)
Current Aviation Colour Code : ORANGE
Previous Aviation Colour Code : orange
Source : Sinabung Volcano Observatory
Notice Number : 2021SIN09
Volcano Location : N 03 deg 10 min 12 sec E 98 deg 23 min 31 sec
Area : North Sumatra, Indonesia
Summit Elevation : 7872 FT (2460 M)
Volcanic Activity Summary :
Eruption with volcanic ash cloud at 03h08 UTC (10h08 local)
Volcanic Cloud Height :
Best estimate of ash-cloud top is around 12672 FT (3960 M) above sea level, may be higher than what can be observed clearly. Source of height data: ground observer.
Other Volcanic Cloud Information :
Ash-cloud moving to southeast – east.
Remarks :
Seismic activity is characterized by eruption volcanic event.
The activity level has been at level III (Siaga) since May 20, 2019 at 10:00 a.m. WIB. Mount Sinabung (2460 m above sea level) has been erupting since 2013.
The volcano was clearly visible until it was covered in fog. The crater emits white smoke with a strong thickness, rising about 100 to 500 meters above the summit. The weather is sunny to cloudy, light to moderate winds from the east, southeast, southwest and west. The air temperature is around 17-25 ° C.
According to the seismographs of February 24, 2021, it was recorded:
• 152 avalanche earthquakes
• 13 earthquakes of emissions
• 215 low frequency earthquakes
• 8 hybrid / multi-phase earthquakes
• 1 distant tectonic earthquake
Source : Magma Indonesie , PVMBG.
Photo : Nachelle Homestay .
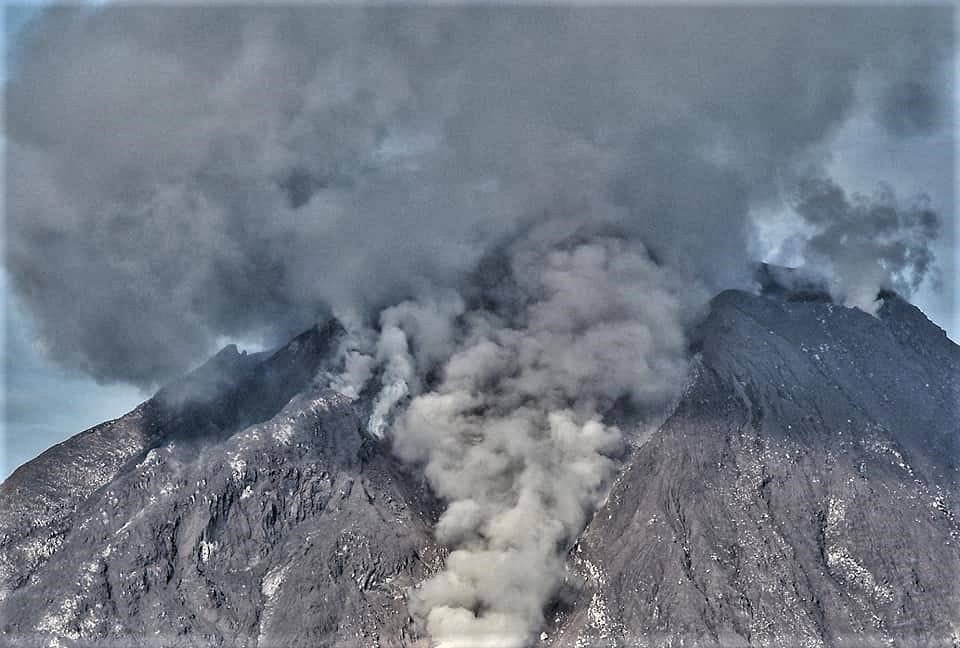
Japan , Sakurajima :
JMA reported that during 15-22 February incandescence from Minamidake Crater (at Aira Caldera’s Sakurajima volcano) was visible nightly. An explosion on 16 February generated an eruption plume that rose 1 km above the crater rim and ejected bombs 1-1.3 km away from the crater. That same day the sulfur dioxide emission rate was extremely high, at 4,300 tons per day. An ash plume from an explosion at 2253 on 21 February rose 1.6 km and entered weather clouds. Large bombs were ejected 800-1,100 m away from the crater. The Alert Level remained at 3 (on a 5-level scale).
The Aira caldera in the northern half of Kagoshima Bay contains the post-caldera Sakurajima volcano, one of Japan’s most active. Eruption of the voluminous Ito pyroclastic flow accompanied formation of the 17 x 23 km caldera about 22,000 years ago. The smaller Wakamiko caldera was formed during the early Holocene in the NE corner of the Aira caldera, along with several post-caldera cones. The construction of Sakurajima began about 13,000 years ago on the southern rim of Aira caldera and built an island that was finally joined to the Osumi Peninsula during the major explosive and effusive eruption of 1914. Activity at the Kitadake summit cone ended about 4850 years ago, after which eruptions took place at Minamidake. Frequent historical eruptions, recorded since the 8th century, have deposited ash on Kagoshima, one of Kyushu’s largest cities, located across Kagoshima Bay only 8 km from the summit. The largest historical eruption took place during 1471-76.
Sources: Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) , GVP .
Photo : @volcanohull / public domain / Volcanodiscovery