September 16 , 2020.
Italy / Sicily , Etna :
Weekly bulletin from September 07, 2020 to September 13, 2020
(issue date September 15, 2020)
SUMMARY OF THE STATE OF ACTIVITY
In the light of the surveillance data, it is highlighted:
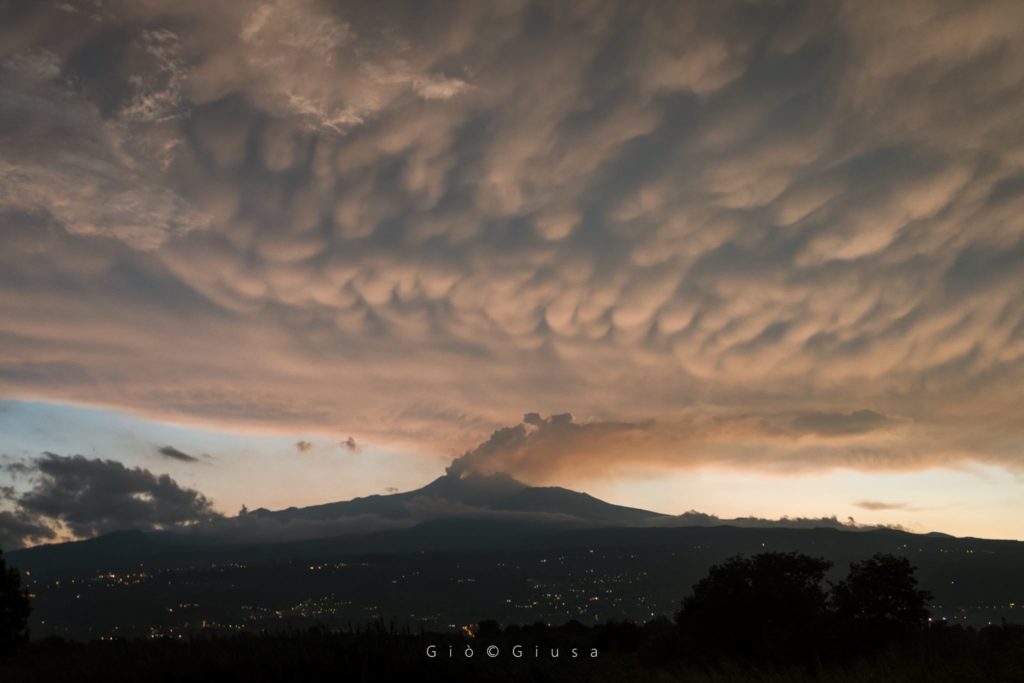
1) VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS: Strombolian activity alternating with emission of ash at the New Southeast Crater. Strombolian intracrater activity at the Northeast Crater. Degassing activity at the Voragine and Bocca Nuova craters
2) SEISMOLOGY: seismic activity due to weak fracturing; mean amplitude of volcanic tremor fluctuating in the range of mean values.
3) INFRASON: moderate infrasound activity.
4) DEFORMATIONS: The Etna soil deformation monitoring networks have not shown any significant changes over the past week. The inflationary tendency of the whole volcanic building remains.
5) GEOCHEMISTRY: The flow of SO2 occurs at a medium-low level
HCl flow occurs at a medium level.
The flow of CO2 emitted by the soil remains at a low level.
The partial pressure of dissolved CO2 in groundwater is at average values.
There are no new measures relating to the C / S ratio (last measure dated 17/07/2020)
Helium isotope ratio measurements show a slight increasing trend (last measurement dated 08/31/2020)
6) SATELLITE OBSERVATIONS: The thermal activity in the summit area is at a medium-low level.
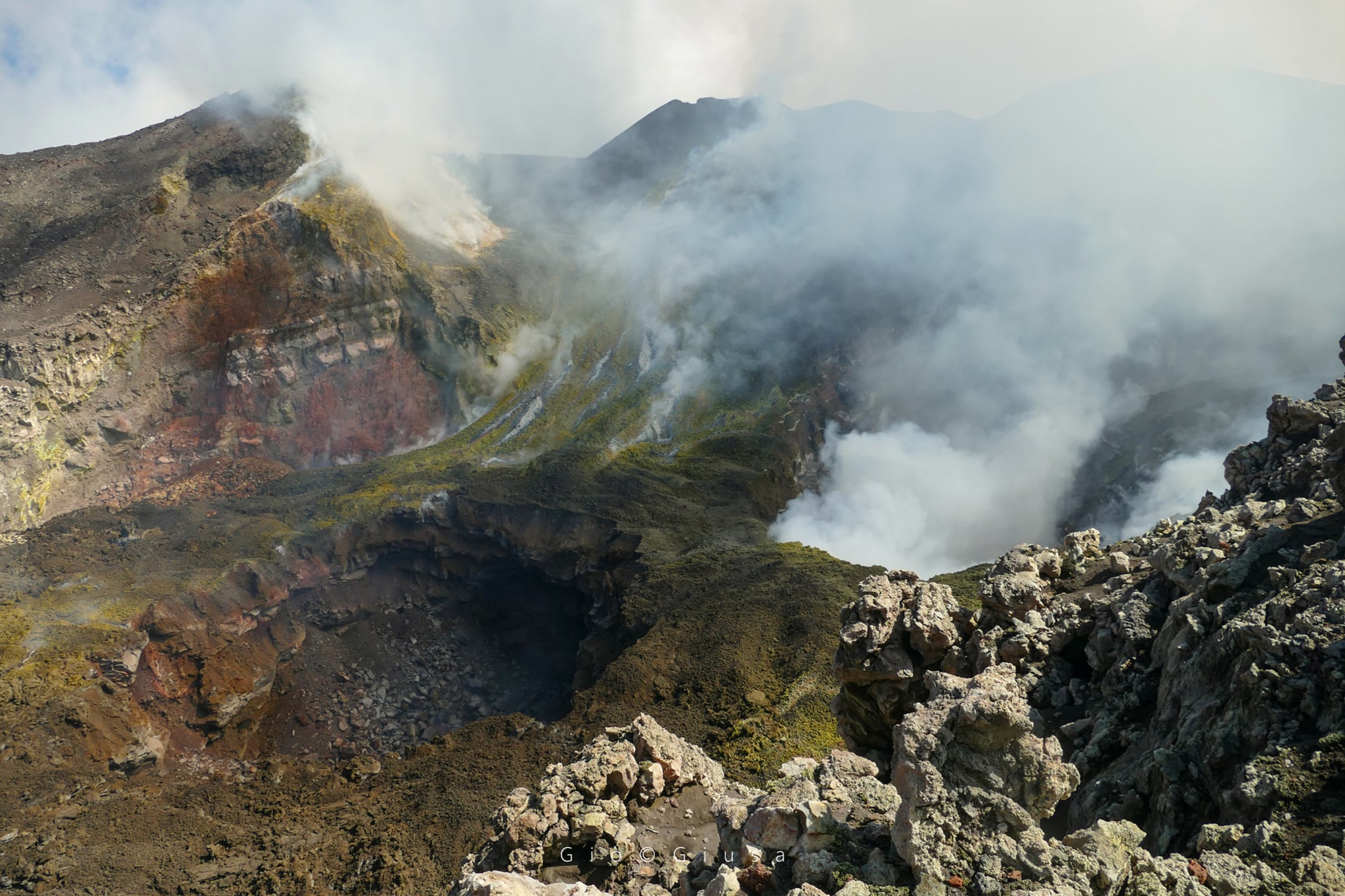
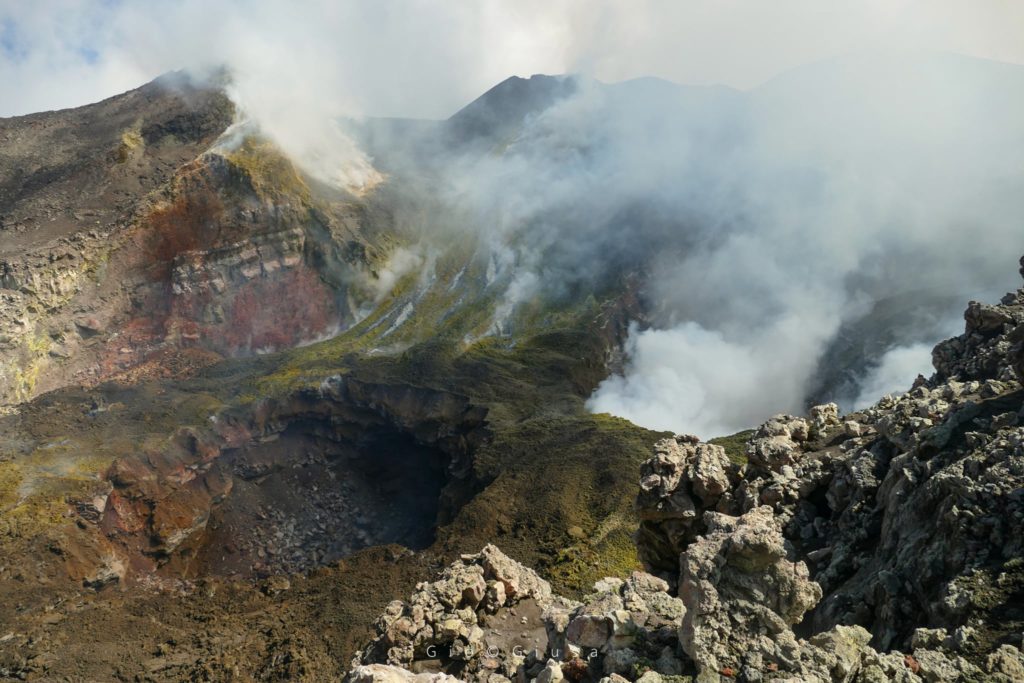
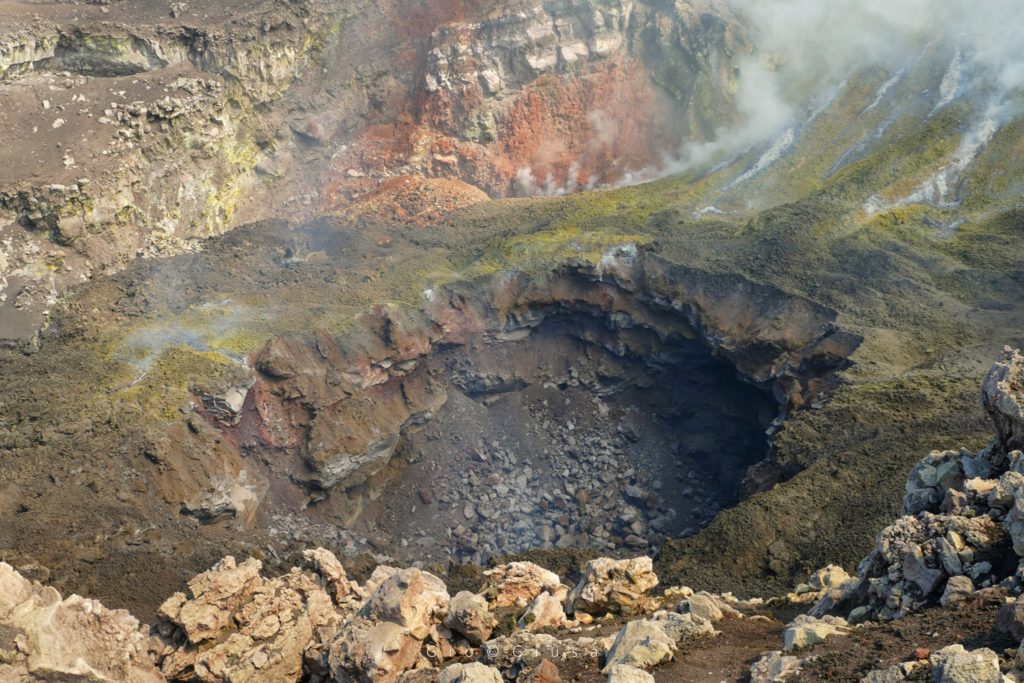
Some photos that show us the 2 » Pit » (especially the one that formed last September 3) present inside the Crater of the Bocca Nuova.
Etna Summit Craters on September 9, 2020
VOLCANOLOGICAL REMARKS
During the week, the monitoring of volcanic activity at the summit of the summit craters of Mount Etna was carried out by analyzing the images of the surveillance camera network of the INGV section of Catania, Etna Observatory (INGV-OE) and by an inspection conducted on September 9 by INGV-OE staff.
During the period under review, summit craters were primarily characterized by strombolian intracranial activity with discontinuous ash emissions in the New Southeast Crater (NSEC), and by intracranial strombolian activity in the Northeast Crater. NE). In addition, degassing activities continued from the Voragine (VOR) and Bocca Nuova (BN) craters.
In particular, the New Southeast Crater was characterized by intracranial strombolian activity, with explosions varying in intensity and frequency over time.
During the most energetic phases, the throwing of coarse materials reached heights of several tens of meters on the edge of the crater and the products sometimes fell outside the crater, depositing on the southern flank of the cone. Sporadic emissions of volcanic ash were also observed, with the formation of dilute clouds that were quickly dispersed by winds into the atmosphere.
Observations made during the inspection on September 9 showed that intense degassing was continuing from the collapse crater formed in the center of the depression of the Bocca Nuova crater. Northwest of it, a new collapse crater formed, which continued to widen due to the collapse of vertical wall materials.
During the period analyzed, the Voragine crater was affected by modest degassing of the main cinder cone and occasional, light ash emissions. Finally, during the week, Strombolian activity within the crater of the Northeast crater continued.
Volcanic Tremor: The average amplitude of the volcanic tremor showed a similar trend to that of last week, with fluctuations only in the range of average values. The source of the tremor was located between 2800 and 3000 m of altitude and in the area of the New Southeast Crater
Source : INGV .
Photos : Gio Giusa .
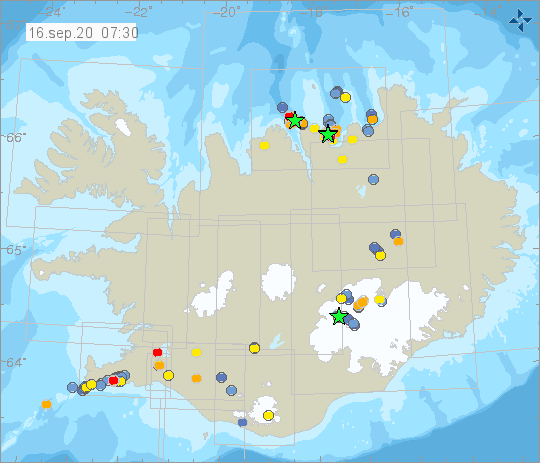
Iceland , Reykjanes Peninsula :
Just under 830 earthquakes were located by the IMO¿s SIL seismic network in week 37. This is a slight increase from the previous week, where around 750 quakes were located. Two seismic swarms are still ongoing, one on the Reykjanes peninsula where 340 earthquakes were located. Another swarm north of the country, counted additional 340 quakes. The larges earthquake of the week measured M3.3 on September 7, by Krísuvík, on the Reykjanes peninsula. The IMO received reports on earthquakes being felt by inhabitants on September 9 in the town of Ólafsfjörður and September 12. in the capital area. Twelve earthquakes were measured in Grímsvötn in week 37.
Today, September 15th at 14:51 an M 4.6 earthquake was detected around 20 km NW of Húsavík. Several reports have been received that the earthquake has been felt in North-Iceland. Several aftershocks have been detected.
At 17:06 another earthquake M4.0 was measured at the same approximate location.
Source : Vedur is.
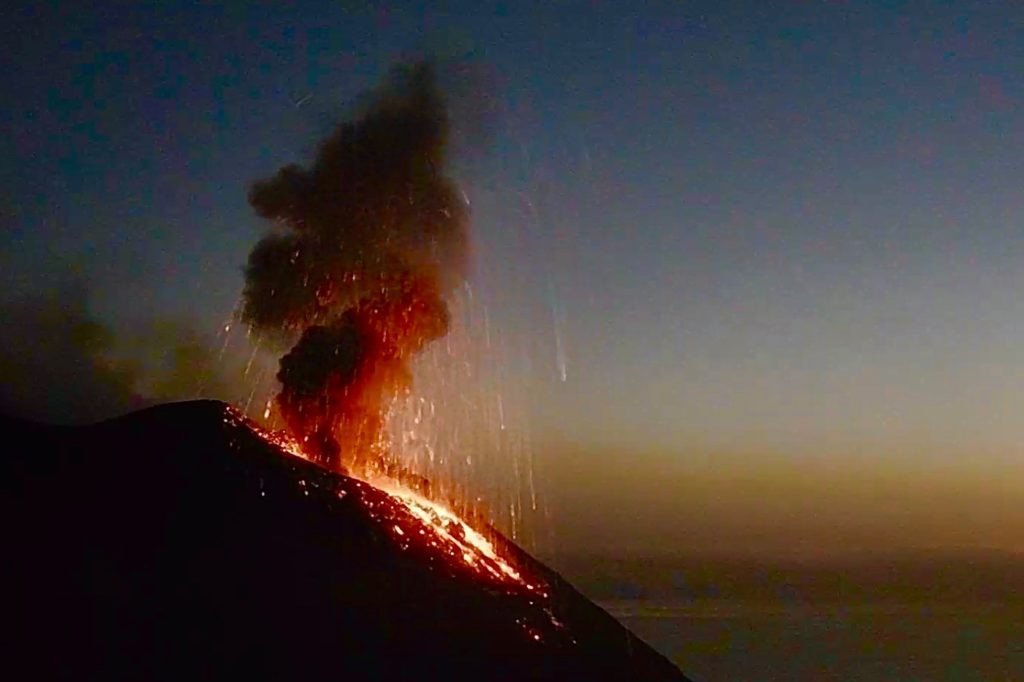
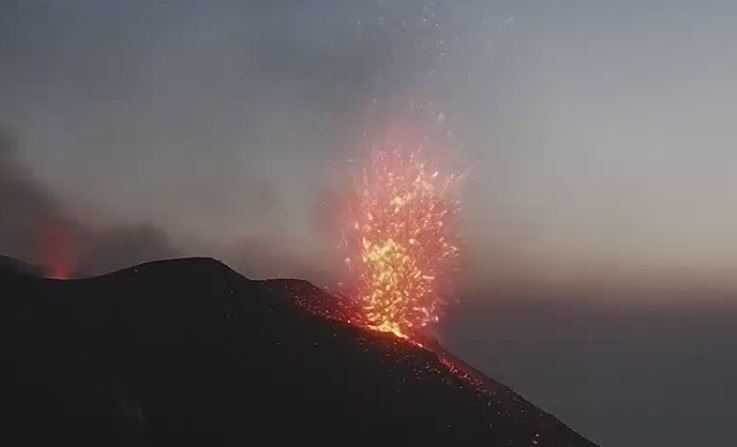
Italy , Stromboli :
Weekly bulletin from September 07, 2020 to September 13, 2020
(issue date September 15, 2020)
SUMMARY OF THE STATE OF ACTIVITY.
In the light of surveillance data, it is highlighted:
1) VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS: Normal explosive volcanic activity of Strombolian type on medium-low to medium levels (9-14 events / h) with the sole exception of September 11 on medium-high levels (16 events \ h) and with intensity medium-low in the North crater area and medium-high intensity in the Center-South area.
2) SEISMOLOGY: The seismological parameters do not show significant variations.
4) DEFORMATIONS: The island’s soil deformation monitoring networks did not show any significant changes during the period under review.
5) GEOCHEMISTRY: Medium-low SO2 flux
There are no updates on the soil CO2 flux data.
The CO2 / SO2 ratio measurement station, restored on 02/09/2020, has carried out confirmed measurements of medium-low values.
The isotopic values of Helium (last update on 08/24/2020) are at medium-low values.
6) SATELLITE OBSERVATIONS: The thermal activity in the summit area is at a medium-low level.
VOLCANOLOGICAL REMARKS:
In the period under observation, the eruptive activity of Stromboli was characterized by the analysis of the images recorded by the surveillance cameras INGV-OE located at an altitude of 190 m, in Punta dei Corvi and at 400 m. The Pizzo camera was damaged during the event of July 19, 2020 and the station is being restored in the INGV-OE laboratories.
Referring to observations made by INGV-OE staff during the August 22 inspection, the morpho-structural arrangement of the crater terrace consists of three eruptive vents located in the North crater area and at least three eruptive vents located in the South Center Crater area. All the vents are placed inside the depression which occupies the terrace of the crater.
In the area of the North crater, the N1 crater, with three emission points, produced low to high intensity explosions (the products of some explosions exceeded 200 m in height) emitting coarse materials (lapilli and bombs) sometimes mixed to fine materials (ash) which have fallen abundantly with a radial distribution. Vent N2 showed low intensity explosive activity (less than 80m in height) emitting coarse materials. The average frequency of the explosions varied from 4 to 11 events / h.
In the Center-South zone, the explosions emitted mainly fine materials sometimes mixed with coarse materials, with a medium-high intensity (the products emitted often exceeded 250 m in height).
The frequency of the explosions varied from 3 to 10 events / h.
The amplitude of the volcanic tremor generally had values between low and medium-low.
Source : INGV .
Photos : Webcam .
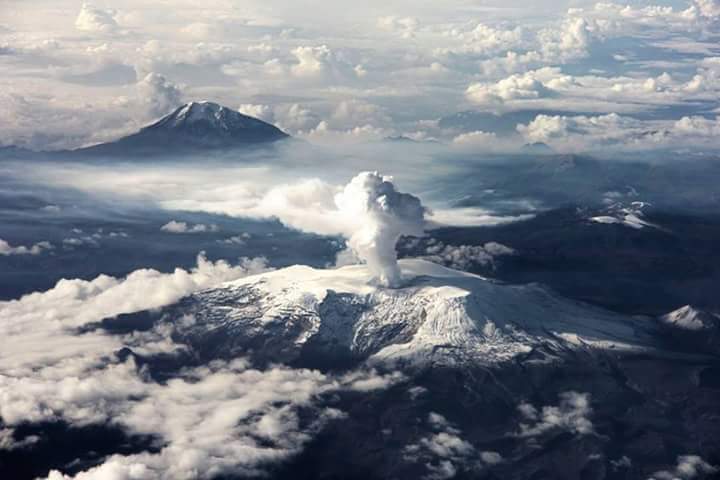
Colombia , Nevado del Ruiz :
Nevado del Ruiz volcano activity bulletin.
The activity level continues at the yellow activity level or (III): changes in the behavior of volcanic activity.
Regarding the monitoring of the activity of the Nevado del Ruiz volcano, the COLOMBIAN GEOLOGICAL SERVICE reports that:
The seismicity generated by rock fracturing showed a slight increase in the number of earthquakes and a decrease in the seismic energy released, compared to the previous week. This type of seismicity was located mainly in the Arenas crater and in the North-East and East sectors, and to a lesser extent in the South, South-East and South-West of the volcano. The depth of the earthquakes varied between 0.2 and 6.2 km. The maximum magnitude recorded during the week was 1.4 ML (local magnitude) corresponding to the earthquake recorded on September 14 at 8:35 p.m. (local time), located 2.5 km south of the Arenas crater, at a depth of 3 , 2 km.
Seismicity related to fluid dynamics inside volcanic conduits increased in the number of events, compared to the previous week, and showed similar levels of seismic energy released. This seismic activity was characterized by the appearance of continuous volcanic tremors, tremor pulses, earthquakes of long and very long period type, which presented variable energy and spectral levels. This seismicity was localized around the Arenas crater.
The recording of new seismic signals of this type, which may be associated with emissions of gases and ash, which will be dispersed according to the prevailing wind regime at the time of transmission, is not excluded.
Source : SGC .
Photo : Auteur inconnu .
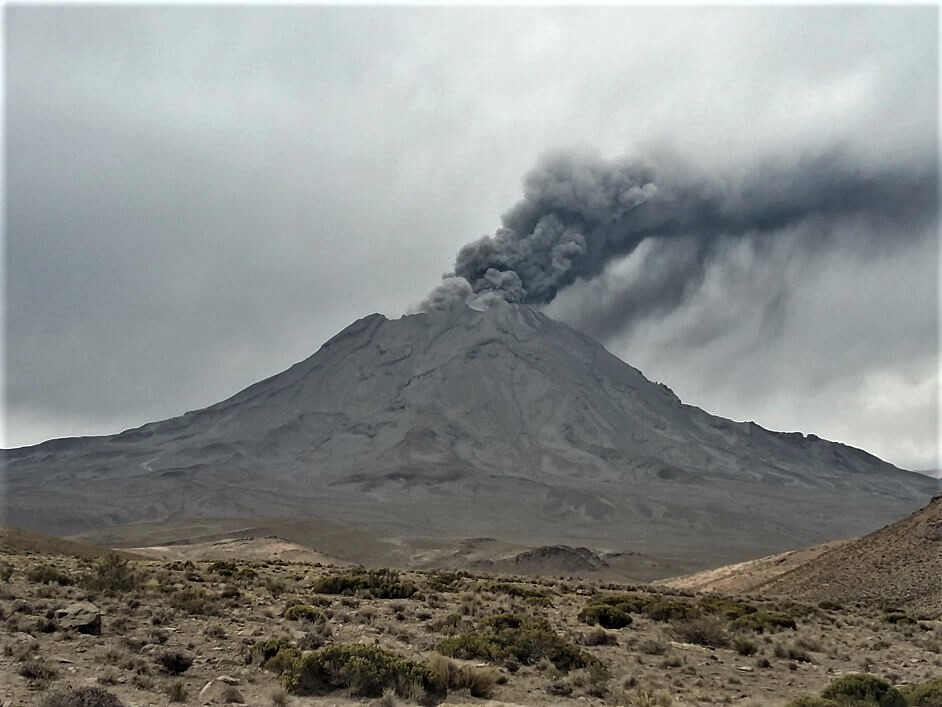
Peru , Ubinas :
Analysis period: September 7 to 13, 2020, Arequipa, September 14, 2020
Alert level: YELLOW
The Geophysical Institute of Peru (IGP) reports that the Ubinas volcano (Moquegua region) continues to record a slight increase in seismic activity during the analysis period; therefore, it is suggested that the authorities and the public pay attention to the bulletins published by the IGP.
During the period of analysis, the occurrence of 27 volcano-tectonic (VT) earthquakes with a magnitude less than M1.2 was identified, associated with rock fracturing processes occurring inside the volcano. .
On average, 4 earthquakes were recorded per day. Likewise, 6 seismic signals were recorded, associated with movements of volcanic fluids (water vapor and gas), including 2 of the « Tornillo » type.
Surveillance cameras recorded columns of gas and water vapor that reached heights of up to 700 m above the summit of the volcano. These emissions were dispersed towards the South-East and North-West sectors of the volcano.
Monitoring the deformation of the volcanic structure, using GNSS equipment (processed with fast orbits), shows no signs of deformation. Satellite monitoring, carried out through the SENTINEL, OMI-NASA (SO2 volcanic gas) and MIROVA (thermal anomalies) systems, did not record any anomalies.
Source : IGP .
Photo : archive ingemmet.