January 06 , 2019.
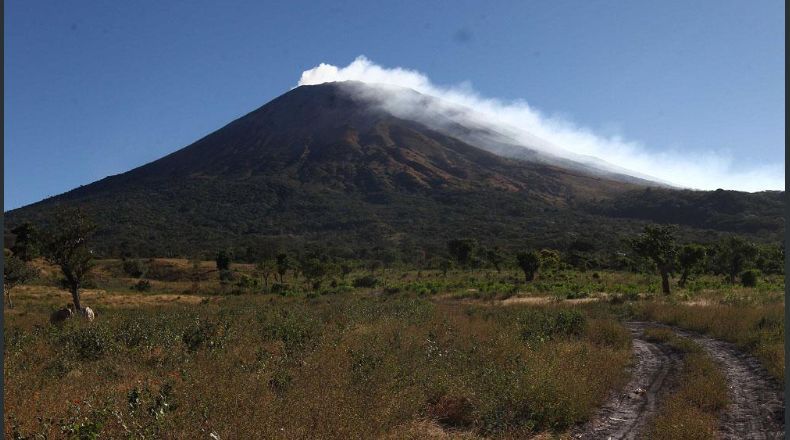
El Salvador , San Miguel ( Chaparrastique ) :
Special file n ° 4: The Chaparrastique volcano maintains an intense degassing.
There is intense degassing of the Chaparrastique volcano (Figure 1) associated with gas pressurization processes of the internal system of the volcano. This degassing forms a sustained column which sometimes reaches a kilometer above the edge of the crater.
During the past 27 hours, the amplitude of the seismic signal of the volcano has shown fluctuations, with highs and lows in the released energy related to changes in the pressure of the internal system and the passage of fluids to the surface. During this period, the local observers network (ROL) did not report a fall of fine materials in the area.
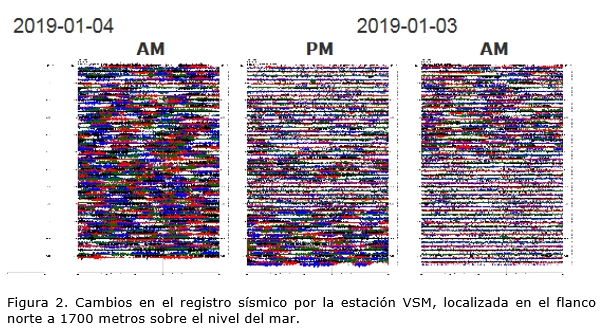
These facts allow us to interpret the appearance of sudden and periodic changes in the internal pressure of the volcanic system (Figure 2).
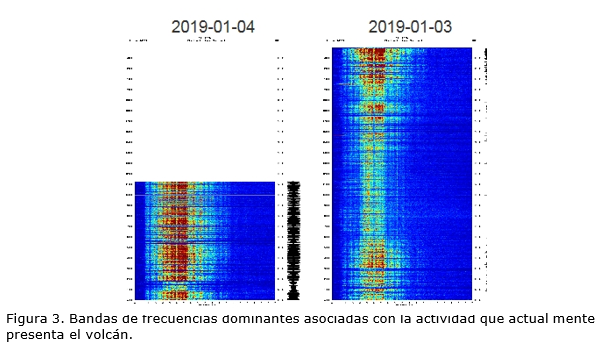
The spectral analysis of seismicity (Figure 3) from Thursday, January 3, 2018 and today, Friday, January 4, 2018, shows a predominance of high frequencies (4.5 to 7.5 Hz). A future change to frequencies below 5 Hz would be indicative of a depressurization process and could be the premonition of high energy eruptive activity. These changes on the Chaparrastic volcano can occur suddenly.
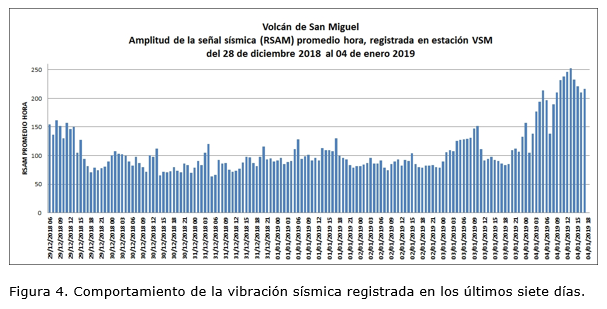
The parameters of the seismic vibration (RSAM) recorded between 08:00 on Thursday, January 3, 2018 and 11:00 on Friday, January 4, 2018, fluctuated between 84 and 252 units (with an hourly average of 156 units), considered as higher than normal values. (Figure 4).
The volcanologists of the MARN continue in the region of the volcano to evaluate the activity and carry out gas measurements with the station DOAS MOVIL.
The trend of the volcano’s behavior indicates that it will continue to degas. This can be accompanied by emissions of fine materials that can be transported in the direction of the prevailing wind and reach the populated areas to the south and west of the volcano and make the sulfur feel in the area between El Carreto and Piedra Azul.
In the event of a sudden increase in activity, the most likely scenario is the generation of an eruptive column whose ashes could fall in the municipalities of San Rafael Oriente, San Jorge and Chinameca. Given this scenario, the emission of ballistic missiles is not excluded, up to three kilometers around the crater. However, the possible production of lava flows from the flanks of the volcano currently has a lower probability of existing.
The Ministry calls on the general public not to approach the upper part of the volcano because of the high degree of danger it presents and asks the inhabitants of the region to be attentive to the information provided by the official means. avoid rumors of unofficial sources.
In the event of a material change, an advance special report will be published.
Source : Marn
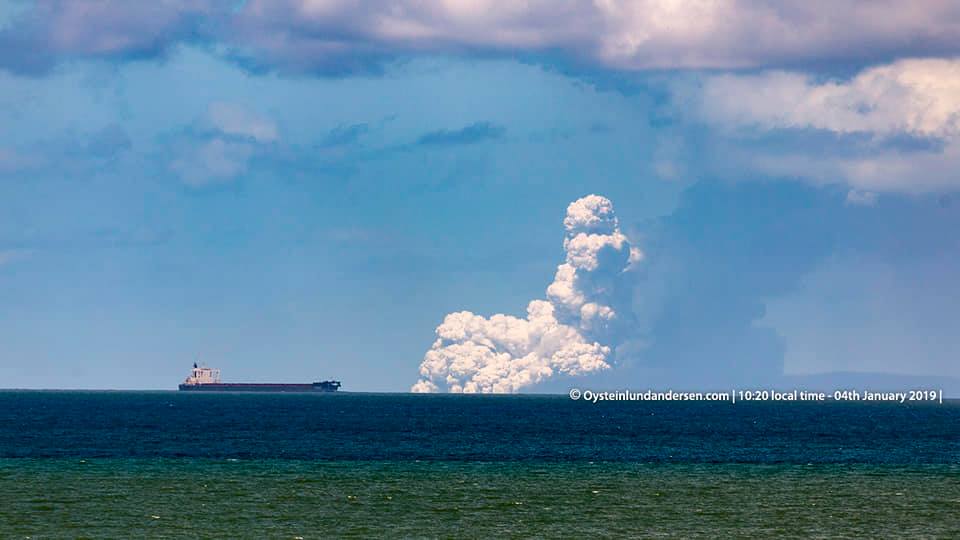
Indonésie , Anak Krakatau :
Level of activity level III (SIAGA) since December 27, 2018. The Anak Krakatau volcano (110 m altitude) has increased its volcanic activity since June 18, 2018.
Since yesterday and until this morning, the volcano was clearly visible then covered with fog. The smoke from the crater was observed at a height of about 300-1500 meters above the volcano, thin, of a gray / white color. The wind is blowing moderately from the Northeast and East.
The seismographs, January 5, 2019, recorded:
79 eruptions / explosions
24 earthquakes
A continuous tremor of amplitude 1 to 17 mm (dominant value of 7 mm)
Recommendation:
People / tourists are not allowed to approach the crater within 5 km.
https://www.facebook.com/sherinefrance/videos/2052222594842926/
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION – VONA.
Issued: January 06 , 2019
Volcano: Anak Krakatau (262000)
Current Aviation Colour Code: ORANGE
Previous Aviation Colour Code: orange
Source: Anak Krakatau Volcano Observatory
Notice Number: 2019KRA12
Volcano Location: S 06 deg 06 min 07 sec E 105 deg 25 min 23 sec
Area: Lampung, Indonesia
Summit Elevation: 352 FT (110 M)
Volcanic Activity Summary:
Eruption with ash clouds at 04:44 UTC (11:44 local time). The eruption lasted for 20 seconds
Volcanic Cloud Height:
Best estimate of ash-cloud top is around 3552 FT (1110 M) above sea level, may be higher than what can be observed clearly. Source of height data: ground observer.
Other Volcanic Cloud Information:
Ash cloud is moving to east
Remarks:
Eruption recorded on seismogram with maximum amplitude 12 mm and maximum duration 20 second
Source : PVMBG , Magma Indonesia.
Video : Via Sherine France.
Photo : Øystein Lund Andersen
Guatemala , Fuego :
Type of activity: Vulcanian
Morphology: Composite Stratovolcano
Geographical location: 14 ° 28’54˝ N Latitude; 90 ° 52’54˝ Longitude W.
Height: 3,763 meters above sea level
Weather conditions: Clear weather.
Wind: north.
Precipitation: 0.0 mm.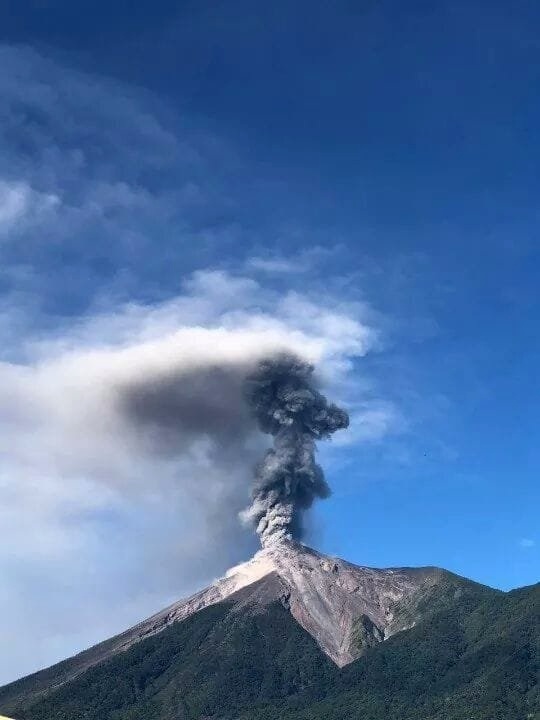
Activity:
The observatory of the Fuego volcano (OVFGO) reports that the crater is observed with white fumaroles. At night, there were light to moderate explosions in a range of 8 to 15 per hour, accompanied by gray ash, with heights of 4400 and 4700 m (14435 to 15419 feet) that are scattered west of the volcanic complex , over a distance of 15 kilometers. Ash is reported on the villages of Santa Sofia, Panimache, Morelia and others in this region. The explosions generate low rumblings and sounds similar to locomotives. At night, it is possible to observe an incandescence in the crater at 150 meters altitude, generating avalanches of blocks around the crater. The strong wind in the volcanic area raises ash curtains, mainly in the ravines.
Source : Insivumeh
Photo : Edilverto Santos
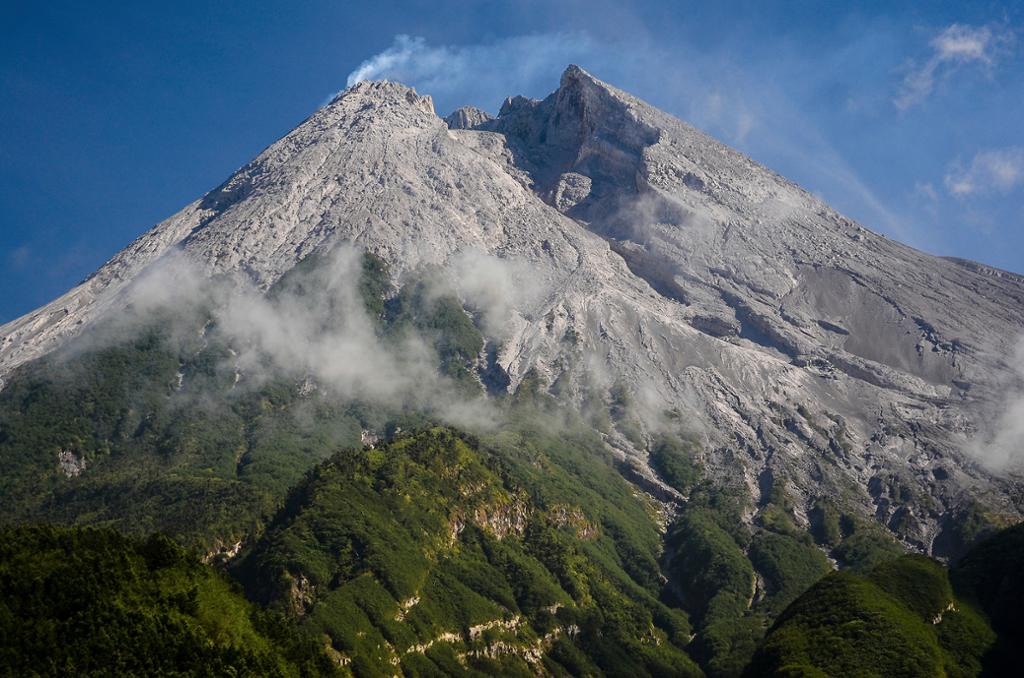
Indonésie , Merapi :
Mount Merapi eruption triggers ash fall in Klaten .
5 JANUARY 2019. Light ash fall was noticed in Tegalmulyo and Tlogowoatu villages, Klaten, Central Java, after Mount Merapi spewed lava toward Kali Gendol Sleman in Yogyakarta on Friday night.
Klaten Disaster Mitigation Agency head Bambang Giyanto said the ash fall occurred at around 9.30 p.m. and lasted for 20 minutes.
« Last night we noticed a thin ash fall in Tegalmulyo and Tlogowatu in Kemalang district, » Bambang said, as reported by kompas.com on Saturday
The agency then headed to the two villages to distribute around 5,000 masks to the residents.
“Based on our monitoring, there is no rain from the ash anymore this morning. It only happened last night, » Bambang said.
The lava dome of the volcano continues to grow steadily, at rates of 3800 cubic meters per day. On 3 Jan 2019, PVMBG estimated it to have reached 415,000 cubic meters volume.
For now, its position is stable, and alert level is kept at 2 (on a 1-4 scale). An exclusion zone of 3 km around the summit is in place.
Source : The Jakartapost , Volcanodiscovery.
Photo : Azimuth Adventure Travel
United-States , Yellowstone :
Wednesday, January 2, 2019, 4:13 PM MST (Wednesday, January 2, 2019, 23:13 UTC)
44°25’48 » N 110°40’12 » W,
Summit Elevation 9203 ft (2805 m)
Current Volcano Alert Level: NORMAL
Current Aviation Color Code: GREEN
Recent work and news
In December, Steamboat geyser experienced three water eruptions, on December 8, 17, and 25. There were 32 Steamboat water eruptions in 2018, which breaks the record of 29, set in 1964, for the most eruptions in a calendar year.
Seismicity
During December 2018, the University of Utah Seismograph Stations, responsible for the operation and analysis of the Yellowstone Seismic Network, located 121 earthquakes in the Yellowstone National Park region. The largest event was a minor earthquake of magnitude 3.1 located 19 miles west-northwest of West Yellowstone, MT, on December 20 at 09:36 AM MST.
December seismicity in Yellowstone concluded with a swarm of 53 located earthquakes on December 31 (additional earthquakes that were too small to be located but can be seen on webicorders are not included in this count). The largest swarm event, a minor earthquake of magnitude 2.8, was located 5 miles west-northwest of Lake, WY, on December 31 at 03:21 AM MST.
Earthquake swarms like this are common and account for roughly 50% of the total seismicity in the Yellowstone region.
Yellowstone earthquake activity remains at background levels.
Ground deformation
There were no significant changes in surface deformation at Yellowstone as recorded by GPS stations. Ground subsidence of Yellowstone caldera continues, as it has since 2015, with about 2 cm of subsidence occurring during 2018. In the area of Norris Geyser Basin, GPS data indicate a minor amount of uplift over the past few months, with a total uplift of about 2 cm during 2018, also continuing the trend that has been ongoing since 2015.
The Yellowstone Volcano Observatory (YVO) provides long-term monitoring of volcanic and earthquake activity in the Yellowstone National Park region. Yellowstone is the site of the largest and most diverse collection of natural thermal features in the world and the first National Park. YVO is one of the five USGS Volcano Observatories that monitor volcanoes within the United States for science and public safety.
Source : YVO
Photos : PNY