September 14 , 2021.
Canary Islands , La Palma :
The activity of the seismic series located in the south of the island of La Palma continues. September 13, 2021, 08:00 UTC.
Since the start of the seismic series at 3:18 a.m. (UTC) on the 11th, until 8:00 a.m. (UTC) today, 1,570 earthquakes have been detected in the southern area of the island of La Palma, of which a total of 354 were located. The magnitude of earthquakes has increased in recent hours with a maximum earthquake of magnitude M 3.4 that was felt by the population. The depth of the earthquakes remains between 8 and 13 km.
The IGN has stepped up the continuous monitoring of the activity.
Due to the increase in seismic activity recorded on the island of La Palma, the Regional Council of Public Administrations, Justice and Security of the Government of the Canary Islands today convened the Scientific Committee of the Special Plan of civil protection and attention to emergencies due to volcanic risk (PEVOLCA) to assess the situation. He decided to activate this plan on alert for Fuencaliente, Los Llanos de Aridane, El Paso and Mazo and to turn the light from green to yellow for these municipalities.
The scientific committee reported that since 2017, abnormal seismic activity has been recorded in the south of the island of La Palma, which since the summer of 2020 has increased with the appearance of 8 seismic swarms. The last, which began last Saturday 11, was the most intense, both in terms of the number of localized earthquakes (more than 400 until this morning), and their magnitude, the most significant having been felt by the population. In addition, the committee said that the depth of the earthquakes, which so far has been between 20 and 30 km, has fallen to 12 km during this phenomenon. Regarding the geochemical monitoring of volcanic gases, he pointed out that the recorded data of the emission of helium 3 confirms the magmatic character of this process, with the highest value observed in the last 30 years.
Source : IGN , Jean-Guy Le Roux.
Photo : Involcan
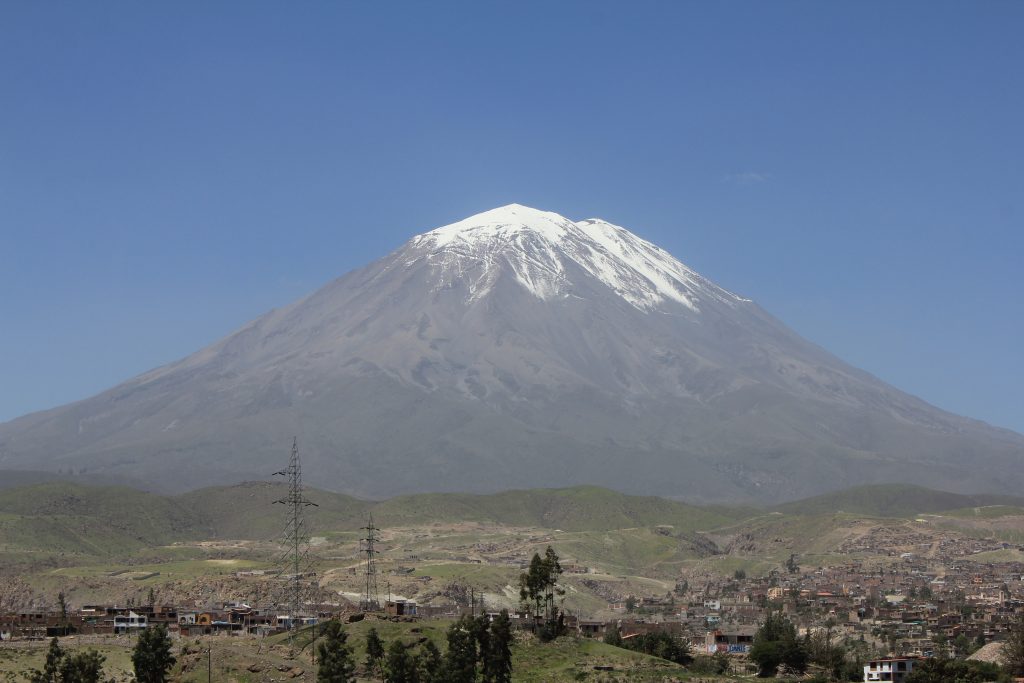
Peru , Sabancaya :
Analysis period: from September 06, 2021 to September 12, 2021, Arequipa, September 13, 2021.
Alert level: ORANGE
The Geophysical Institute of Peru (IGP) reports that the eruptive activity of the Sabancaya volcano remains at moderate levels, that is to say with the recording of an average of 31 daily explosions, with columns of ash and gas up to 4 km altitude above the summit of the volcano and their consequent dispersion. Therefore, for the following days, no significant change is expected in eruptive activity.
The IGP recorded and analyzed the occurrence of 1326 earthquakes of volcanic origin, associated with the circulation of magmatic fluids within the Sabancaya volcano. An average of 31 explosions was recorded daily. During this period, Volcano-Tectonic (VT) earthquakes associated with rock fractures were located mainly in the North and North-West of Sabancaya and presented magnitudes between M2.5 and M3, 5.
The monitoring of the deformation of the volcanic structure using GNSS techniques (processed with fast orbits) does not present any significant anomalies. However, in general, an inflation process was observed in the northern sector (around the Hualca Hualca volcano). Visual surveillance identified columns of gas and ash up to 4 km altitude above the summit of the volcano, which were scattered towards the southern, southeast, eastern and southwestern sectors of Sabancaya. Satellite recordings identified the presence of 6 thermal anomalies (maximum value of 56 MW) associated with the presence of a lava body on the surface of the volcano’s crater.
RECOMMENDATIONS
• Keep the volcanic alert level in orange.
• Do not approach within a radius of 12 km from the crater.
Source : IGP.
Photo : Ingemmet .
Iceland , Geldingadalur / Fagradalsfjall :
Pulsating activity that has not been seen since this spring
The volume of magma was significant both in the Fagradalsfjall lava flows today and in the large crater. Salóme Jórunn Bernharðsdóttir, nature conservation specialist at the Icelandic Meteorological Bureau, says that at 3:45 p.m., pulsating activity resumed, as seen in April and May. The pulses then lasted ten minutes and dropped to five, with lava flows visible.
Such pulses have not been observed for several months.
Salóme says it is difficult to discern the significance of these changes, that there is some sort of phase shift going on and the question is how long they will last. The nine-day outage may have had an effect on the « plumbing » and made these pulses appear. When asked if it was possible to predict the spectacle during tonight’s eruptions, Salóme said showers could be expected later in the evening, but there could be good visibility.
Source : RUV.
Photo : Donatas Arlauskas
New Zealand , White Island :
Whakaari/White Island: Intermittent weak ash emissions continue . Published: Tue Sep 14 2021 3:00 PM
Intermittent ash emissions continued last week, and further occasional emissions are expected to occur in the coming weeks. Small amounts of ash were carried by the vigorous degassing a few hundred metres into the atmosphere near the volcano, and further activity of this type is unlikely to affect the mainland. The volcano remains in a state of moderate to heightened unrest and the Volcanic Alert Level remains at Level 2.
Over the past week, we observed ash being carried within emissions from vigorous fumaroles within the active vent area at Whakaari/White Island. Observations of ash has been intermittent, and the amount of ash carried in the plume is small. When we have observed ash in the plume, these periods were not accompanied by impulsive or explosive seismic or acoustic signals, hence showing no evidence of eruption. Instead, this suggests that the activity is still passively driven by weak wall fragments falling into the gas stream through the active vents.
Ash and gas emissions remain confined to low altitudes and a small dusting of ash sometimes gets deposited on the island. Over the last few days, ash has adhered to our island-based webcam lenses, which has severely obscured our view of the vent area.
Ash emissions are passive and weak in intensity, which means that ash is unlikely to reach high in the atmosphere to then be transported onto the mainland. However, in case of strong northerly winds and more intense ash emissions, a fine dusting of ash could potentially be recorded along the Bay of Plenty coastline.
The seismic activity remains similar to last week, with low levels of volcanic tremor and occasional volcanic earthquakes. Continued subsidence around the active vents, measured by satellite remote sensing techniques, shows a similar pattern to the last couple of weeks. We infer that gas release from depth is responsible for this deformation signal.
The current level of activity is consistent with moderate to heightened levels of unrest. As such the Volcanic Alert Level remains at 2 and the Aviation Colour Code remains at Yellow.
Equipment that provides real-time monitoring on the island is currently degraded and we are continuing to work on restoration options.
Source : Geonet / Geoff Kilgour / Duty Volcanologist.
Photos : Brad Scott , Geonet .
Indonesia , Ibu :
The level of activity is at level II (WASPADA) since December 10, 2013. The Ibu volcano (1340 m above sea level) has been in continuous eruption since 2008. The eruption produces rocks that accumulate in the crater.
The volcano was clearly visible until it was covered in fog. The smoke from the crater, of low to moderate pressure was observed to be white / gray with low to medium intensity and a height of 200 to 800 m above the summit. An eruption was observed at a height of 200-800 m, the color of the smoke was white / gray. The weather is sunny to cloudy, the winds are weak to moderate in the south and west.
According to the seismographs of September 13, 2021, it was recorded:
70 eruption earthquakes / explosions
56 avalanche earthquakes
40 emissions earthquake
16 harmonic tremors.
VONA:
The last VONA message was sent with the color code ORANGE, published on September 6, 2021 at 09:16:00. Volcanic ash had been observed at a height of about 1725 m above sea level or 400 m above the peak moving north.
Source : PVMBG.
Photo : Martin Rietze
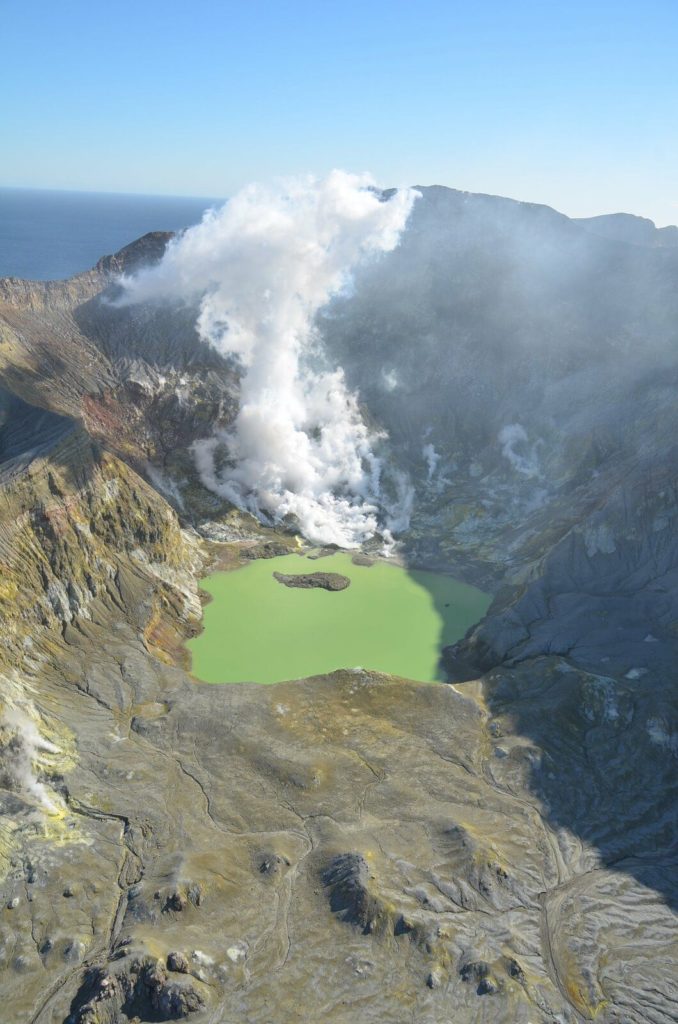
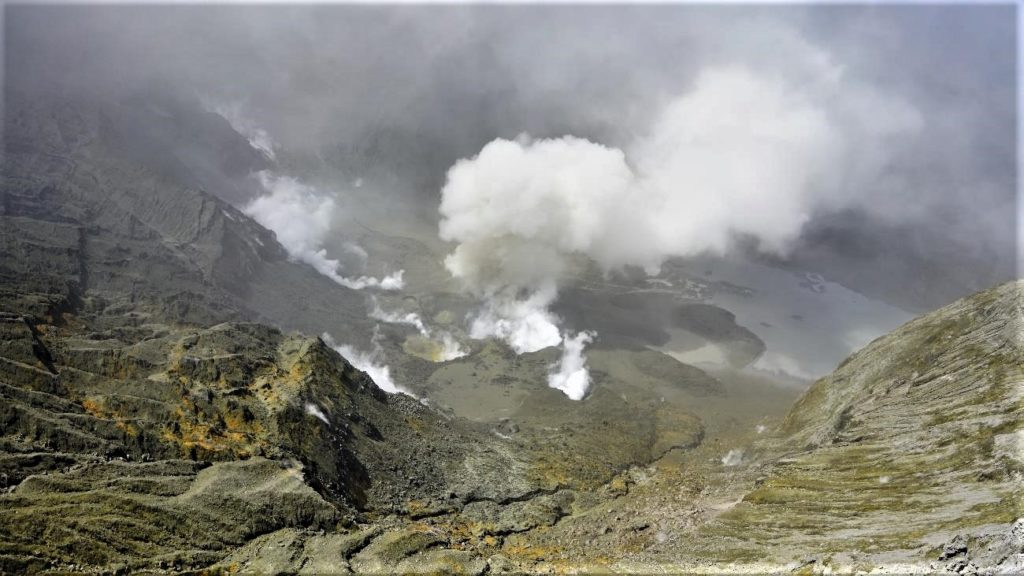
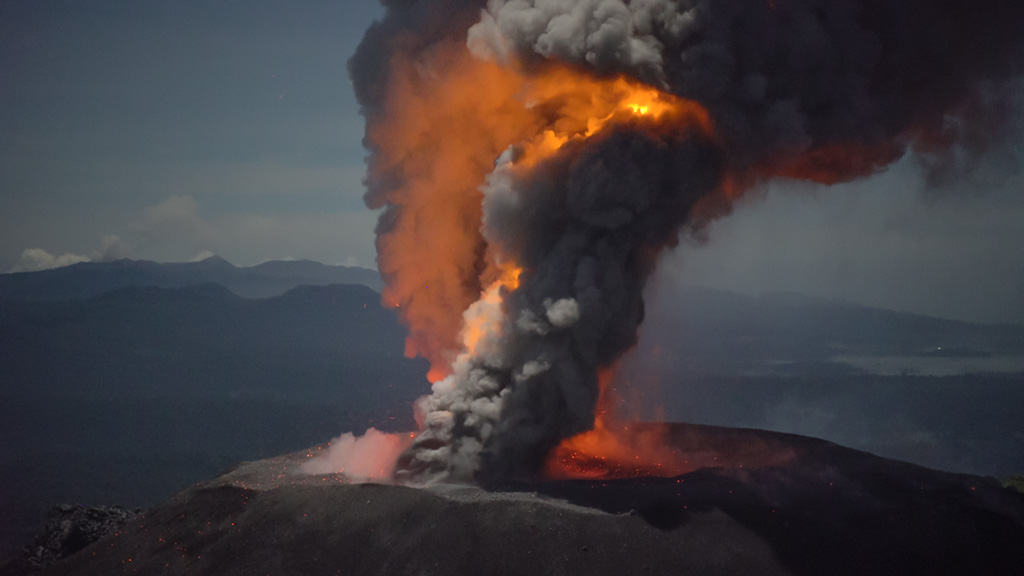
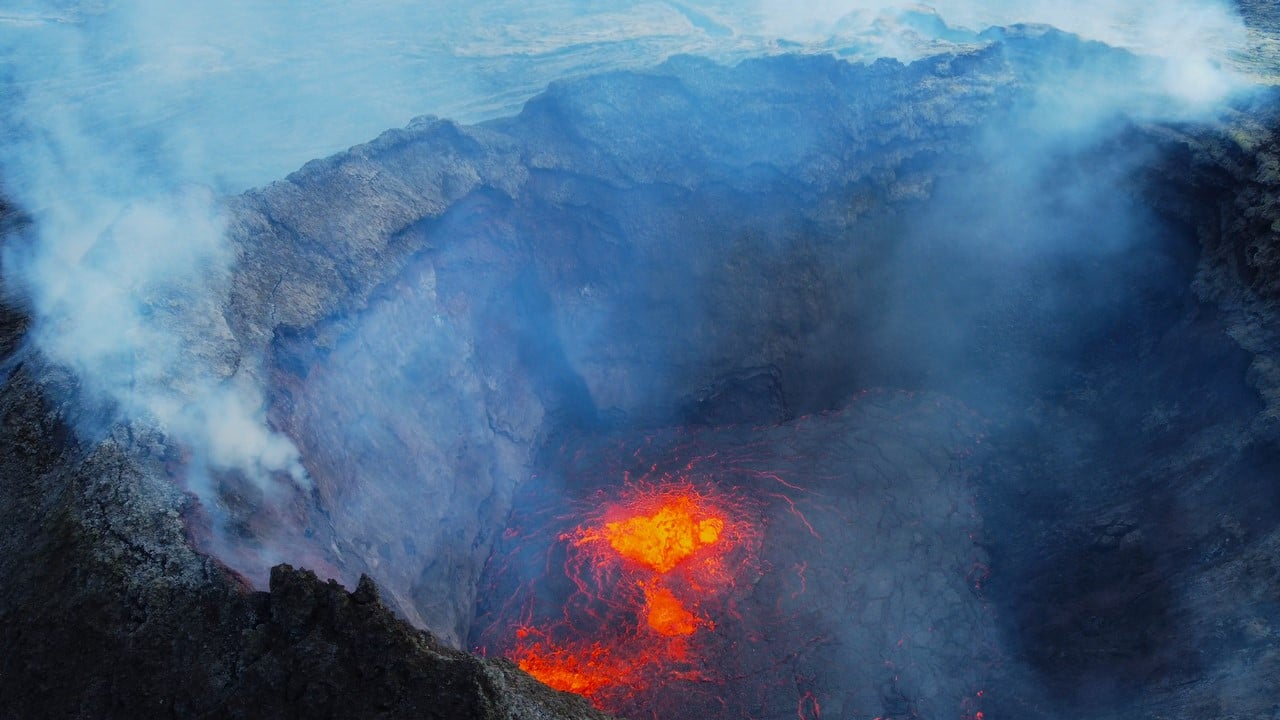
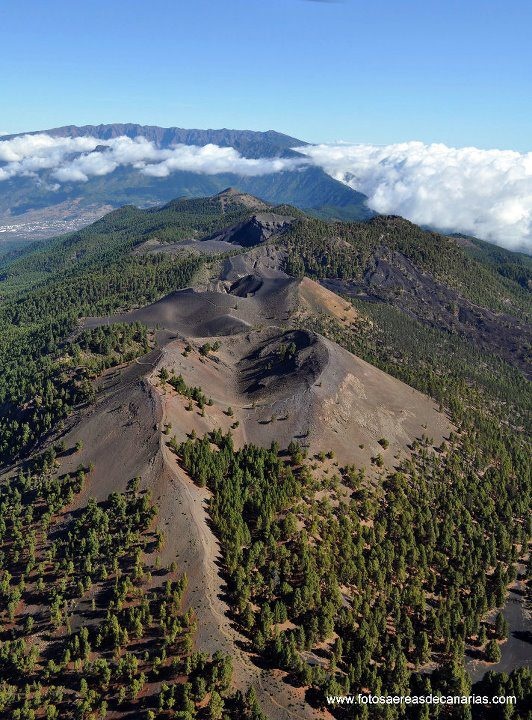
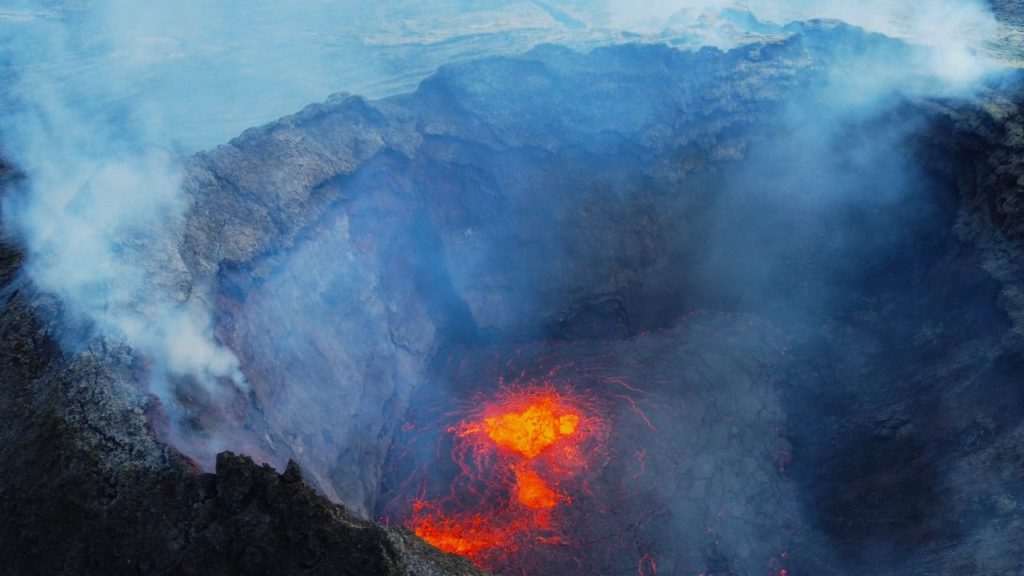
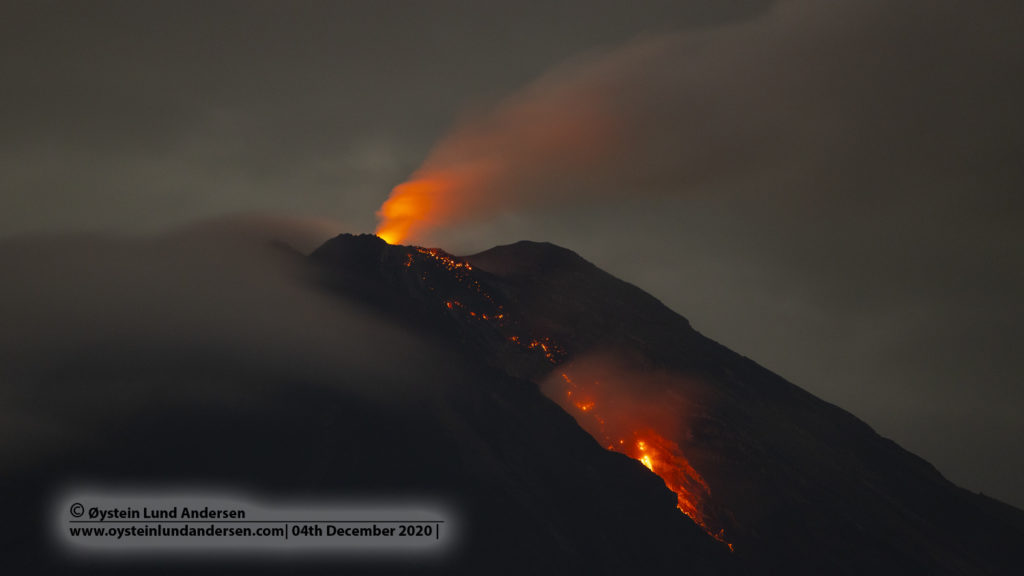
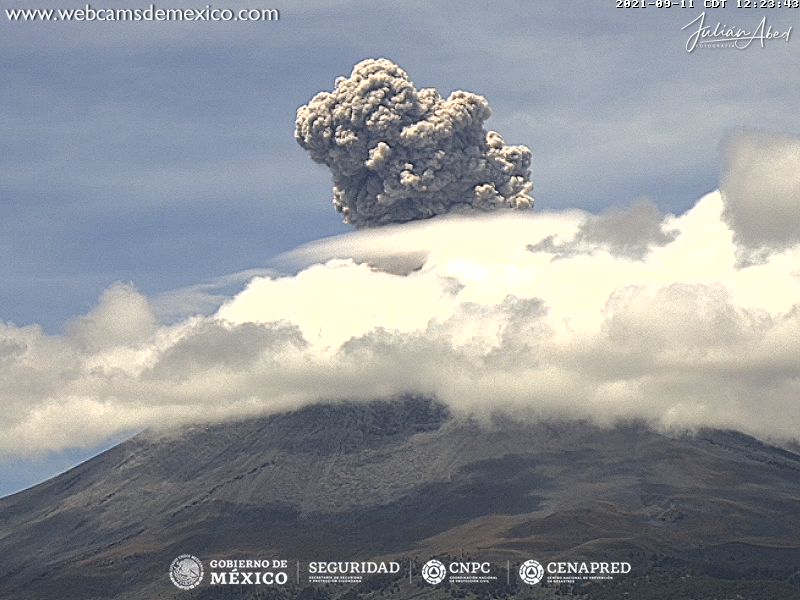
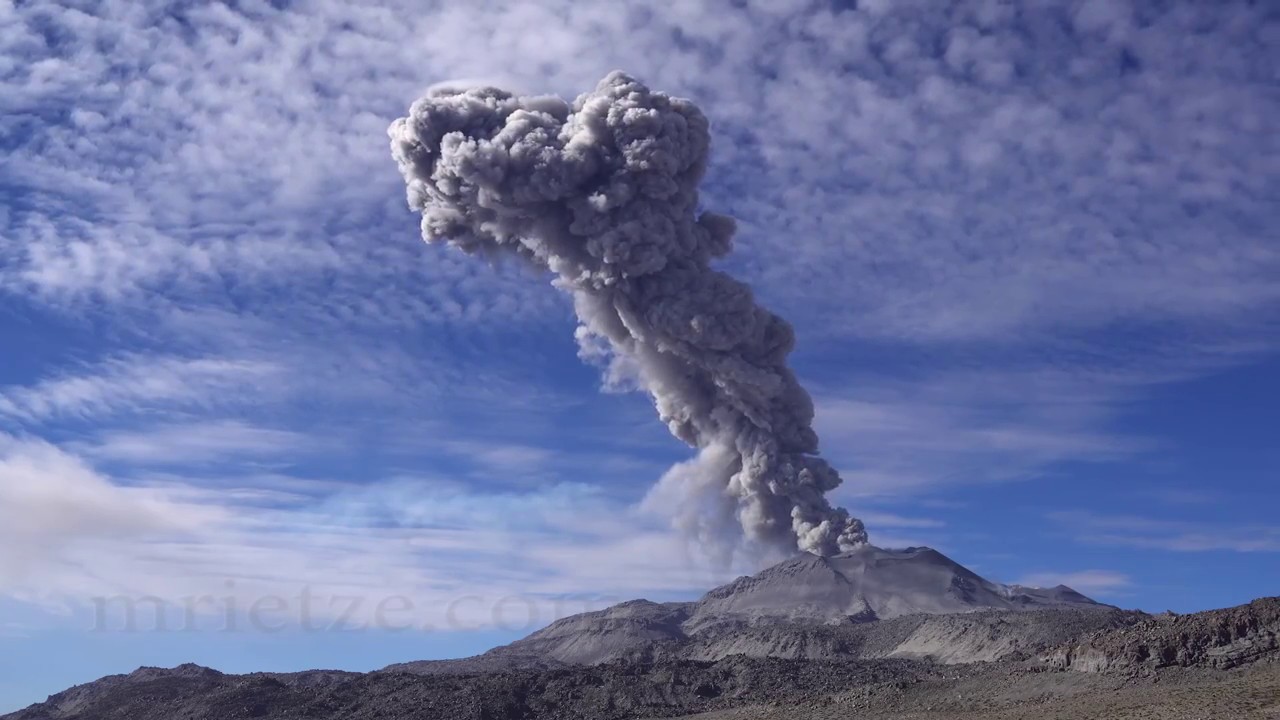
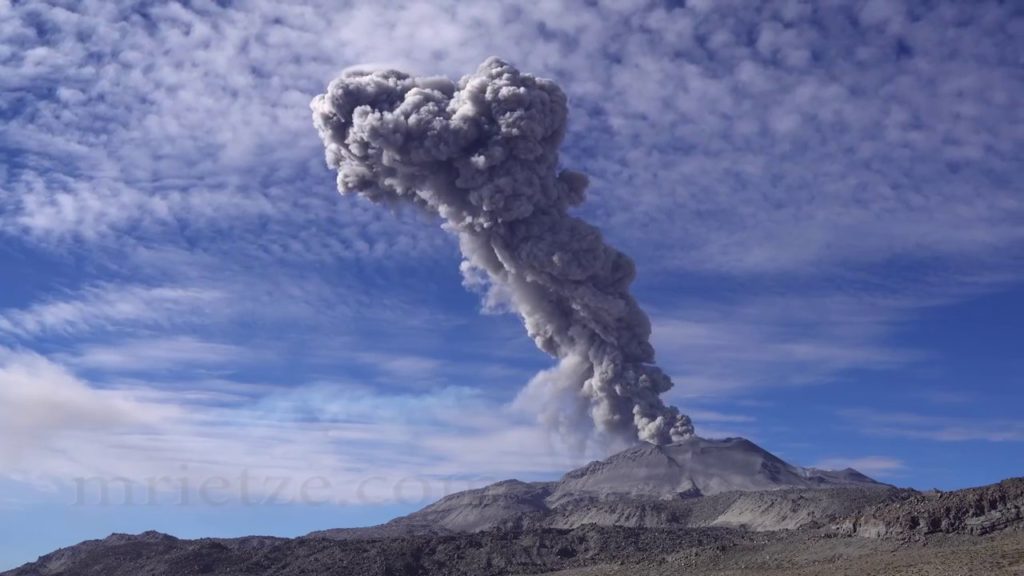
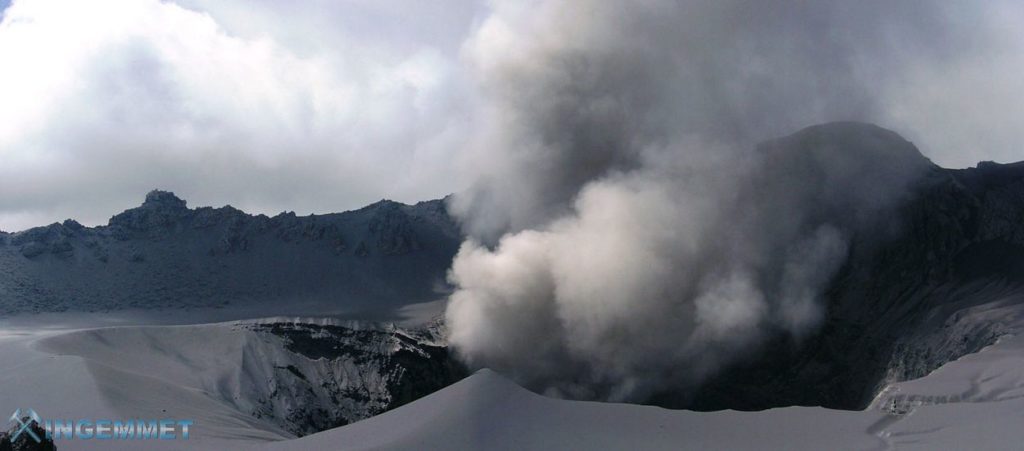

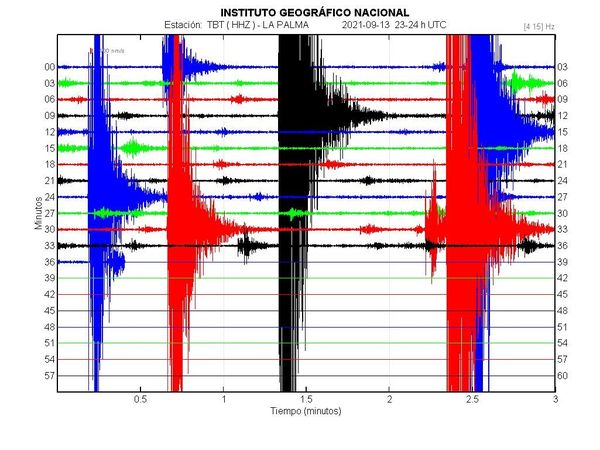















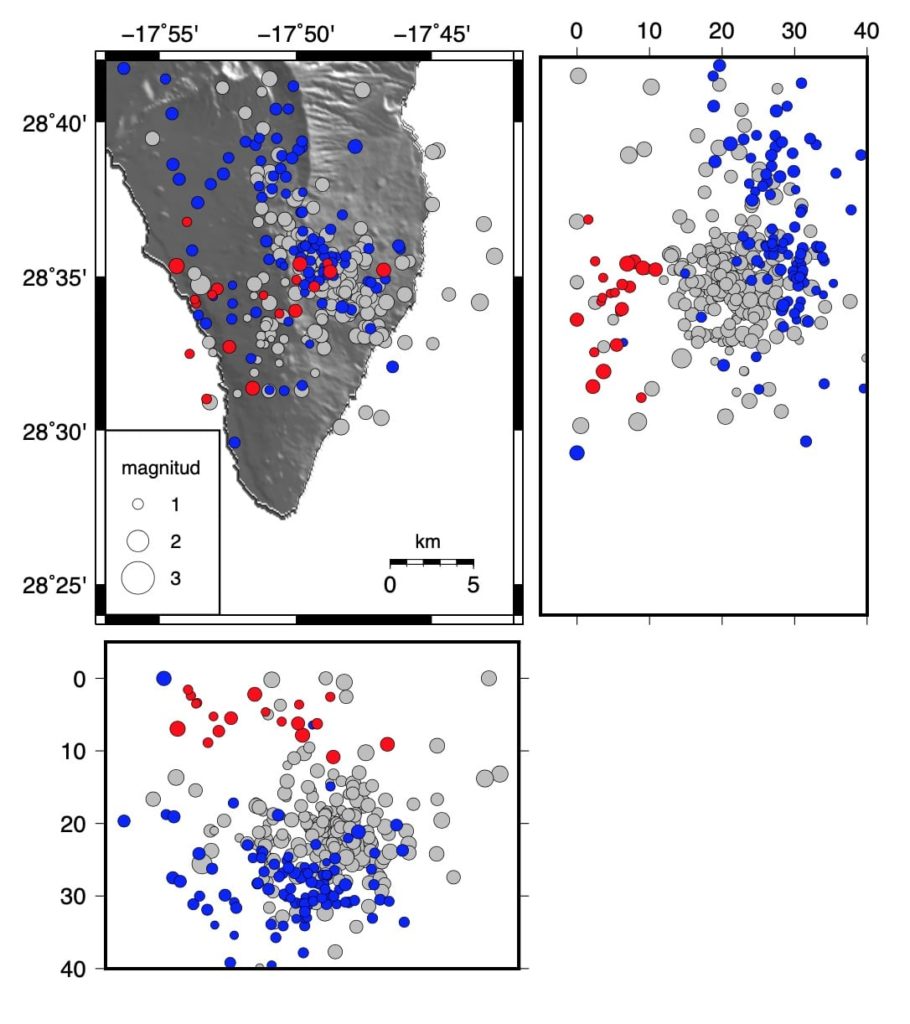


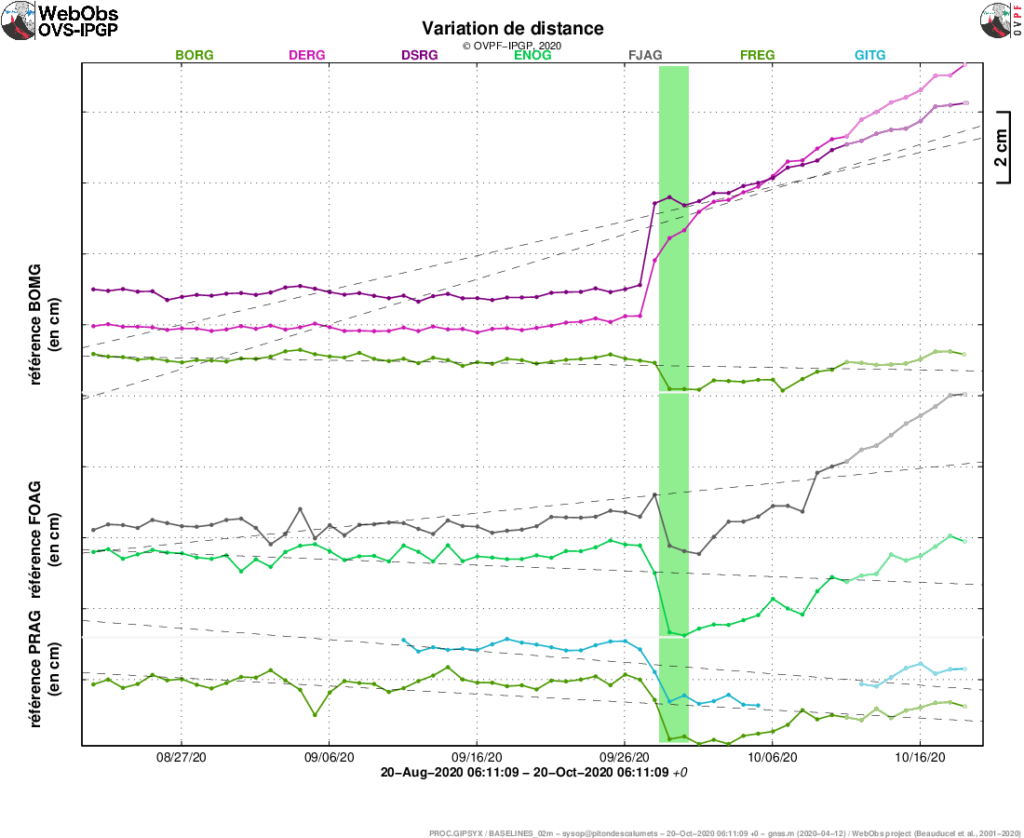

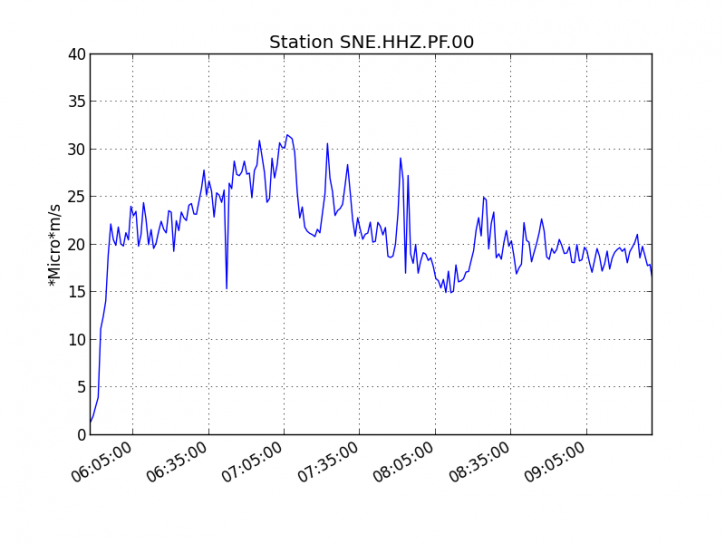

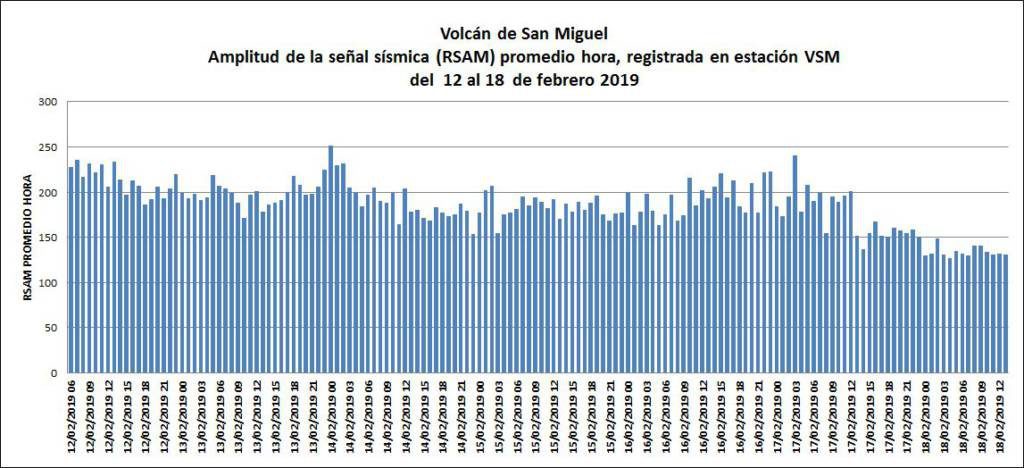
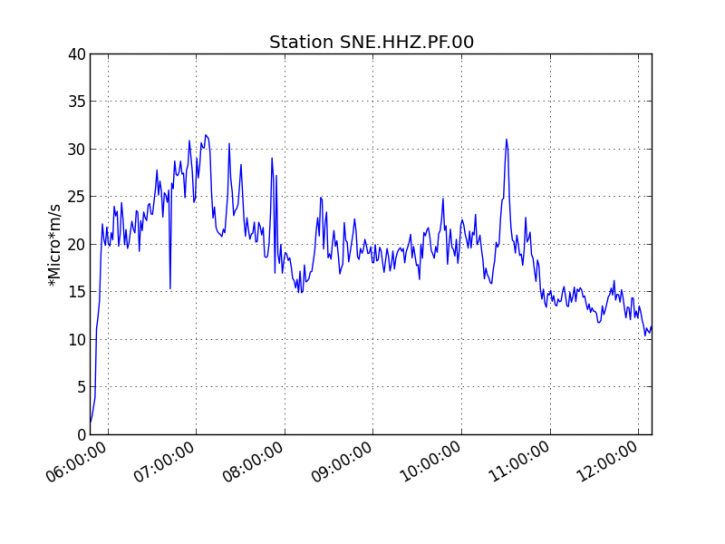 Figure 1: Evolution of the RSAM (indicator of the volcanic tremor and the intensity of the eruption) between 09h48 (05h48 UTC) and 16h15 (12h15 UTC) on 18 February on the seismic station of SNE. (© OVPF / IPGP)
Figure 1: Evolution of the RSAM (indicator of the volcanic tremor and the intensity of the eruption) between 09h48 (05h48 UTC) and 16h15 (12h15 UTC) on 18 February on the seismic station of SNE. (© OVPF / IPGP)