March 04 , 2023.
Italy , Stromboli :
WEEKLY BULLETIN, from February 20, 2023 to February 26, 2023. (issue date 28 February 2023)
ACTIVITY STATUS SUMMARY
In the light of the monitoring data, it is highlighted:
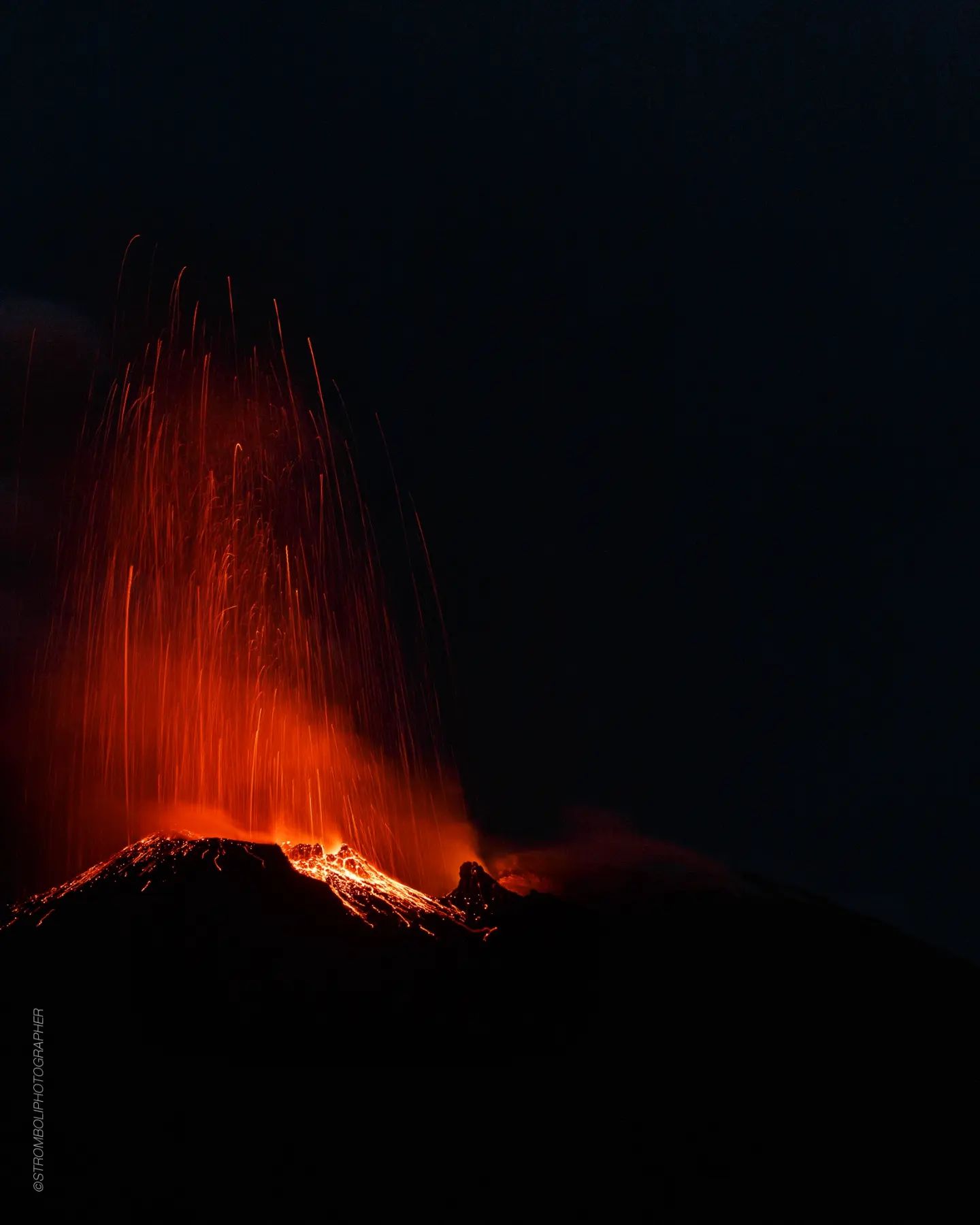
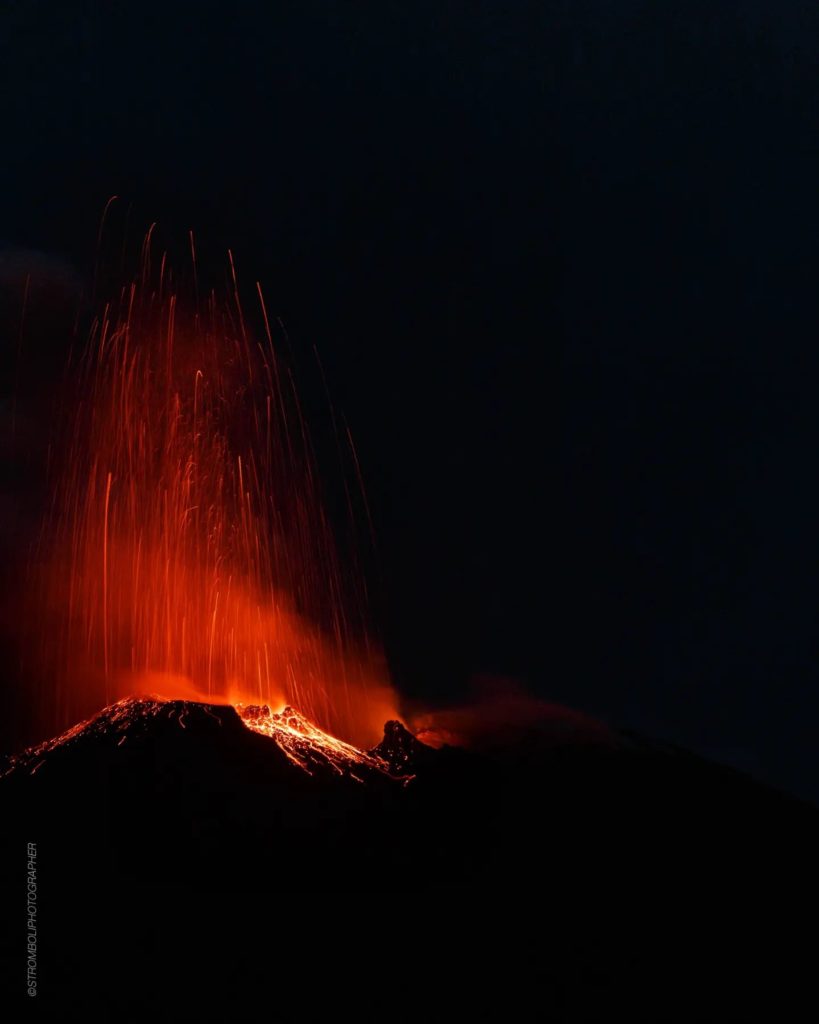
1) VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS: During this period, normal Strombolian activity was observed with spattering activity in the North Crater area. The total hourly frequency fluctuated between low (4 events/h) and average (11 events/h) values. The intensity of the explosions was mainly medium and low in the North crater area and medium-high in the Center-South crater area.
2) SEISMOLOGY: The seismological parameters monitored do not show any significant variations.
3) GROUND DEFORMATIONS: Data from ground deformation networks do not show substantial variations
4) GEOCHEMISTRY: The flow of SO2 at an average level
The CO2 flux values show average values without significant changes compared to the previous week.
The C/S values are at average values.
5) SATELLITE OBSERVATIONS: The thermal activity observed by satellite was generally low level, however on February 27, 2023 moderate values of thermal flow were recorded in correspondence with an overflow of lava in the summit area.
VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS
During the observation period, the eruptive activity of Stromboli was characterized by the analysis of the images recorded by the surveillance cameras of the INGV-OE at an altitude of 190 m (SCT-SCV), Punta dei Corvi, while 400m and Pizzo cameras are currently unavailable. The explosive activity was mainly produced by 2 (two) eruptive vents located in the North crater area and by at least 2 (two) vents located in the Center-South area. In detail, the mouths of the North crater area are located one in sector N1 and the other in sector N2.
Observations of explosive activity captured by surveillance cameras
From the two mouths of sectors N1 and N2, an explosive activity of variable intensity from low (less than 80 m in height) to medium (less than 150 m in height) emitting coarse materials (bombs and lapilli) was observed .
In addition, spattering activity was observed, intense for short periods until February 24. The average frequency of explosions varied from 2 to 7 events/h.
In the Center-South zone (CS) only from sector S2 was observed an explosive activity of medium and high intensity (sometimes the products exceeded 150 in height) emitting coarse materials mixed with fine material (ash).
The frequency varied between 1 and 7 events/h.
Source : INGV.
Photo : Stromboli stati d’animo.
Italy / Sicily , Etna :
WEEKLY BULLETIN, from February 20, 2023 to February 26, 2023. (issue date 28 February 2023)
ACTIVITY STATUS SUMMARY
In the light of the monitoring data, it is highlighted:
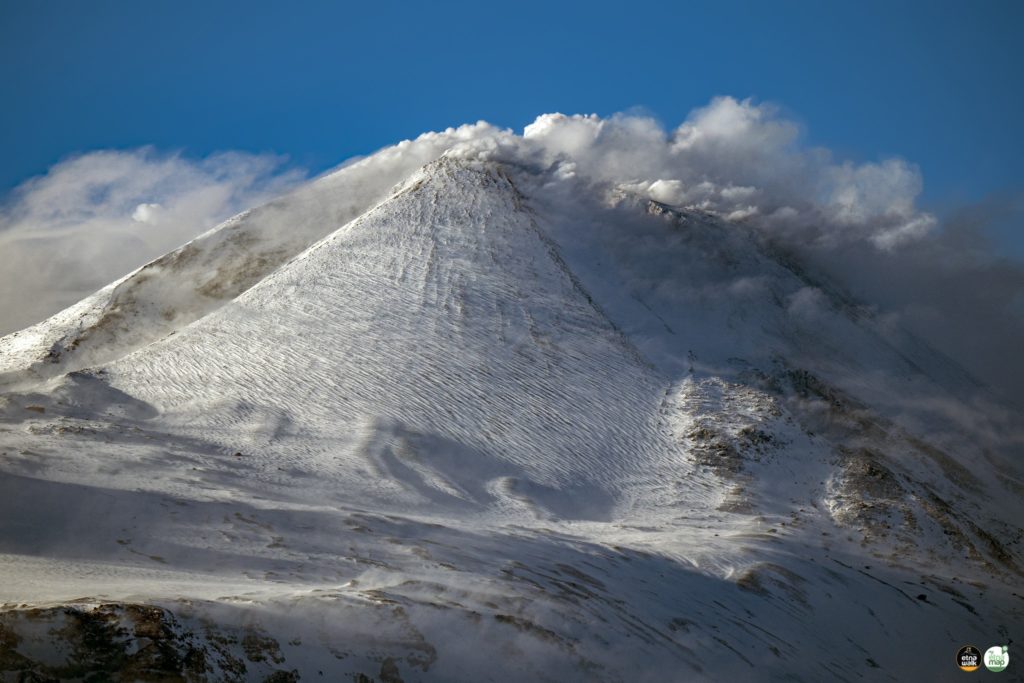
1) VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS: Degassing activity at the summit craters, in particular continuous degassing of the Bocca Nuova crater (BN) and at the Southeast crater (SEC).
2) SEISMOLOGY: Absence of seismic activity of fracturing with Ml>=2.0; average amplitude of the volcanic tremor in the average level.
3) INFRASOUND: Weak infrasonic activity.
4) GROUND DEFORMATIONS: No significant variation was observed in the data from the ground deformation monitoring networks.
5) GEOCHEMISTRY: SO2 flux at an average level
CO2 circulates in average values.
Helium isotopic data do not show any significant variations, remaining however at high values.
Partial pressure of dissolved CO2: no significant variation
6) SATELLITE OBSERVATIONS: Thermal activity observed from the satellite was generally weak.
VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS
The monitoring of Etna’s volcanic activity was carried out through the analysis of images from the network of INGV surveillance cameras, Osservatorio Etneo (INGV-OE) and an inspection carried out on February 24, 2023 in the area Summit. Observations of activity at the summit craters have been erratic at times due to the presence of cloud cover.
During the week, the activity of the summit craters of Etna was characterized by intense and continuous degassing at the level of the crater of Bocca Nuova (BN); sometimes modest emissions of reddish ash were observed which were quickly dispersed by the winds in the summit area.
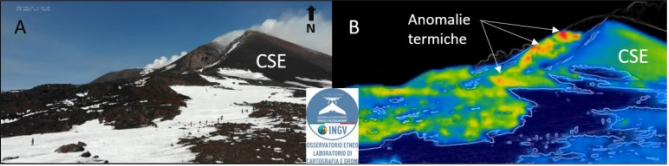
The Southeast Crater (CSE) was characterized by intense degassing produced by the eruptive vent of May-June 2022 and by the fumaroles which are present along the rim of the crater, the sides of the cone and the walls of the niche produced by the flank collapse of February 10, 2022; in particular along the walls there are areas of thermal anomalies, as evidenced by the observations made during the control of February 24, 2023.
Finally, images from surveillance cameras show that the Northeast Crater (NEC) is affected by weak degassing.
Source : INGV.
Photos : Etna Walk , INGV.
Alaska , Aniakchak :
56°54’21 » N 158°12’32 » W,
Summit Elevation 4400 ft (1341 m)
Current Volcano Alert Level: ADVISORY
Current Aviation Color Code: YELLOW
Earthquake activity beneath Aniakchak volcano continued over the past week, with over 120 earthquakes located. Magnitudes reached as high as M3.1 and several earthquakes had magnitudes between M2 and M3. The earthquakes are occurring at shallow depths (< 5 km) and below the southern part of the caldera and to the east of the volcano. No significant activity was observed in partly clear to cloudy web camera and satellite views.
There is no indication that an eruption of Aniakchak is imminent, or that one will occur. Increases in seismic activity have been detected previously at other similar volcanoes, with no subsequent eruptions. We expect additional shallow seismicity and other signs of unrest, such as gas emissions, elevated surface temperatures, and surface deformation to precede any future eruption, if one were to occur.
AVO monitors Aniakchak with a local network, which consists of six seismometers, a web camera, and a single infrasound sensor, as well as satellite remote sensing data and regional infrasound and lightning networks.
Aniakchak volcano, located in the central portion of the Alaska Peninsula, consists of a stratovolcano edifice with a 10 km (6 mile) diameter summit caldera. The caldera-forming eruption occurred around 3,500 years ago. Postcaldera eruptions have produced lava domes, tuff cones, and larger spatter and scoria cone structures including Half-Cone and Vent Mountain all within the caldera. The most recent eruption occurred in 1931 and created a new vent and lava flows on the western caldera floor while spreading ash over much of southwestern Alaska. Aniakchak volcano is 25 km (15 miles) southeast of the nearest community, Port Heiden, and 670 km (416 miles) southwest of Anchorage, Alaska.
Source : AVO.
Photo : Mayo, Wyatt / Alaska Volcano Observatory / Alaska Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys
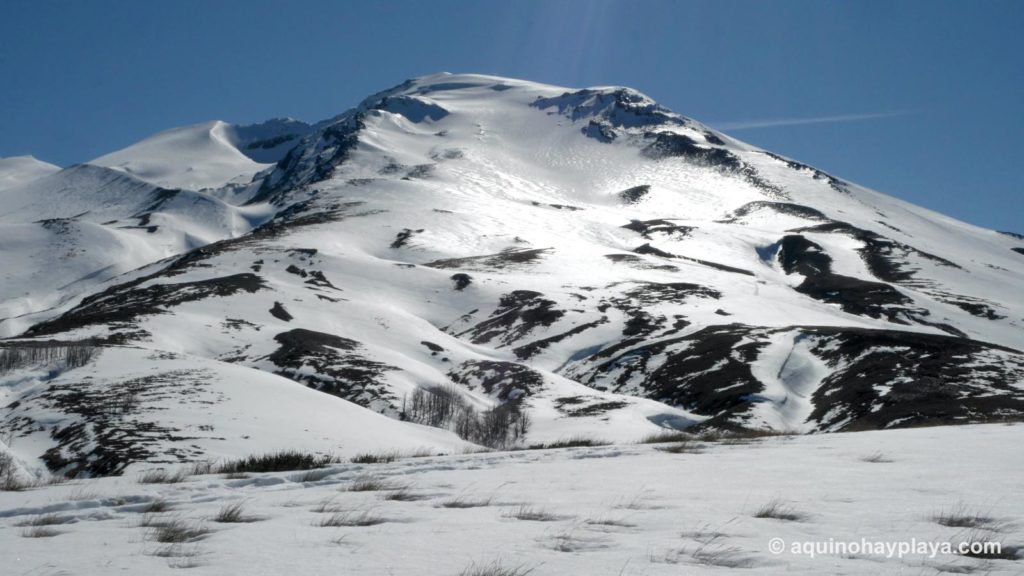
Chile , Puyehue-Cordon Caulle :
Special Report on Volcanic Activity (REAV), Los Lagos region, Puyehue-Cordon Caulle volcanic complex, March 03, 2023, 05:55 a.m. local time (mainland Chile).
The National Service of Geology and Mines of Chile (Sernageomin) publishes the following PRELIMINARY information, obtained through the monitoring equipment of the National Volcanic Monitoring Network (RNVV), processed and analyzed at the Volcanological Observatory of the Southern Andes ( Ovdas):
On Friday March 03, 2023, at 05:24 local time (08:24 UTC), the monitoring stations installed near the Puyehue-Cordon Caulle volcanic complex recorded an earthquake associated with the fracturing of rocks (volcano-tectonic type) in the volcanic system.
The characteristics of earthquakes after their analysis are as follows:
ORIGINAL TIME: 05:24 local time (08:24 UTC)
LATITUDE: 40.556°S
LONGITUDE: 72.157°E
DEPTH: 5.8 km
LOCAL MAGNITUDE: 3.5 (ML)
COMMENTS:
Following the occurrence of the event, no changes in volcanic activity were observed.
The volcanic technical alert remains at the Green level.
Sources : Sernageomin.
Photo : wikiloc.
Ecuador , Cotopaxi :
DAILY REPORT OF THE STATE OF COTOPAXI VOLCANO, Friday March 03, 2023.
Information Geophysical Institute – EPN.
Surface Activity Level: Moderate, Surface Trend: Unchanged.
Internal activity level: Moderate, Internal trend: No change.
Seismicity: From March 02, 2023, 11:00 a.m. to March 03, 2023, 11:00 a.m.:
For seismicity statistics, there are 24 hours of transmission from the reference station.
Emission Tremor (TREMI) 25
Long Period (LP): 20
Rains / Lahars:
No rain was recorded.
Emission / Ash Column:
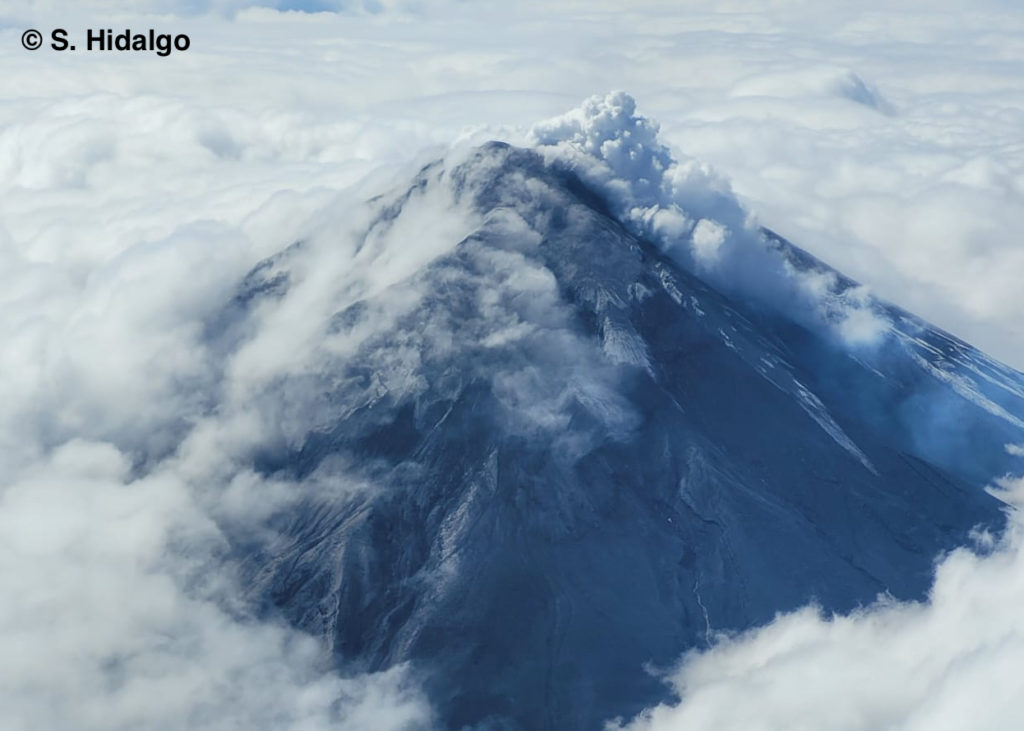
The Washington VAAC for the past 24 hours has issued an ash emission alert 800 meters above crater level in a northwesterly direction. In the afternoon and last night, ash emissions up to 1200 m were observed by IGEPN cameras.
Gas:
The MOUNTS satellite system recorded 612.6 tons of sulfur dioxide (SO2), measured on 2023-03-02 at 2:08 p.m. TL.
Observation:
The volcano was cloudy most of the time but between the clouds an emission could be observed with a height of 1200 meters above the summit heading northwest. In the morning today, it appeared partially clear, observing a steam emission 300 meters high above the level of the crater to the southwest. Thereafter the volcano darkened until now.
Alert level: Yellow.
Source : IGEPN
Photo : Silvana Hidalgo IGEPN