January 17 , 2024 .
Iceland , Reykjanes Peninsula :
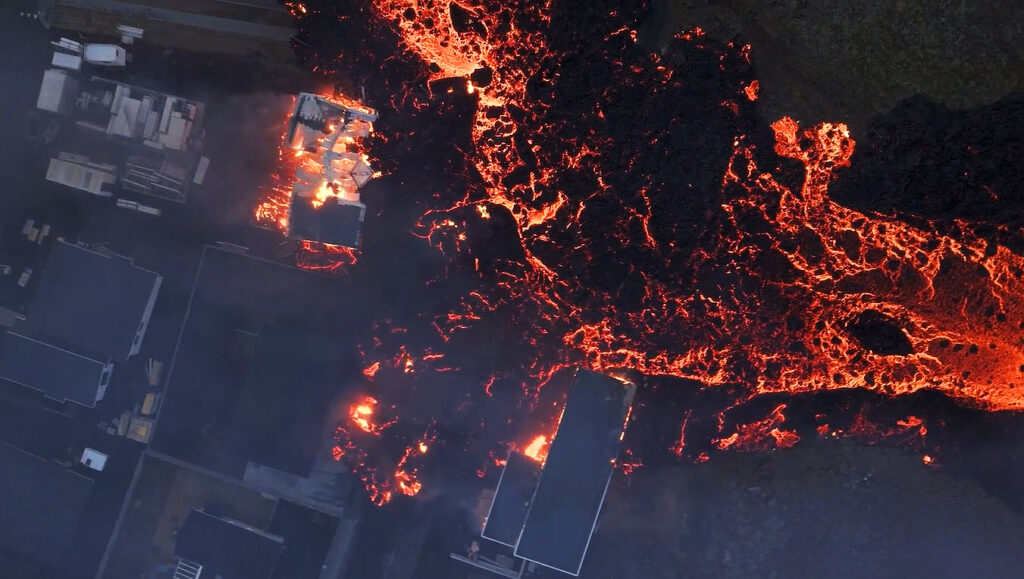
No volcanic activity visible . Fissures continue to emerge within Grindavík .
Updated 16 January at 11:45 UTC
There is currently no visible activity within the eruptive fissures, with the most recent lava observed emanating from the northern fissure shortly after 1 am last night. Seismic activity continues to decrease, signifying that the area is stabilizing. Approximately 200 small earthquakes were recorded near the magma conduit since midnight, indicating that magma is still migrating. Most seismic activity is located near Hagafell, close to the first eruptive fissure that opened on Sunday morning. At this point, it is premature to declare that the eruption is over.
GPS sensors continue to detect ground deformation in and around Grindavík, illustrating that the magma conduit beneath Grindavík is still causing expansion in the area. Thermal images from a drone last night show that fissures previously mapped southwest of Grindavík have significantly enlarged. Considerable hazards persist in the area.
Source : IMO
Photo : Rafn Sig Photography via Sherine France.
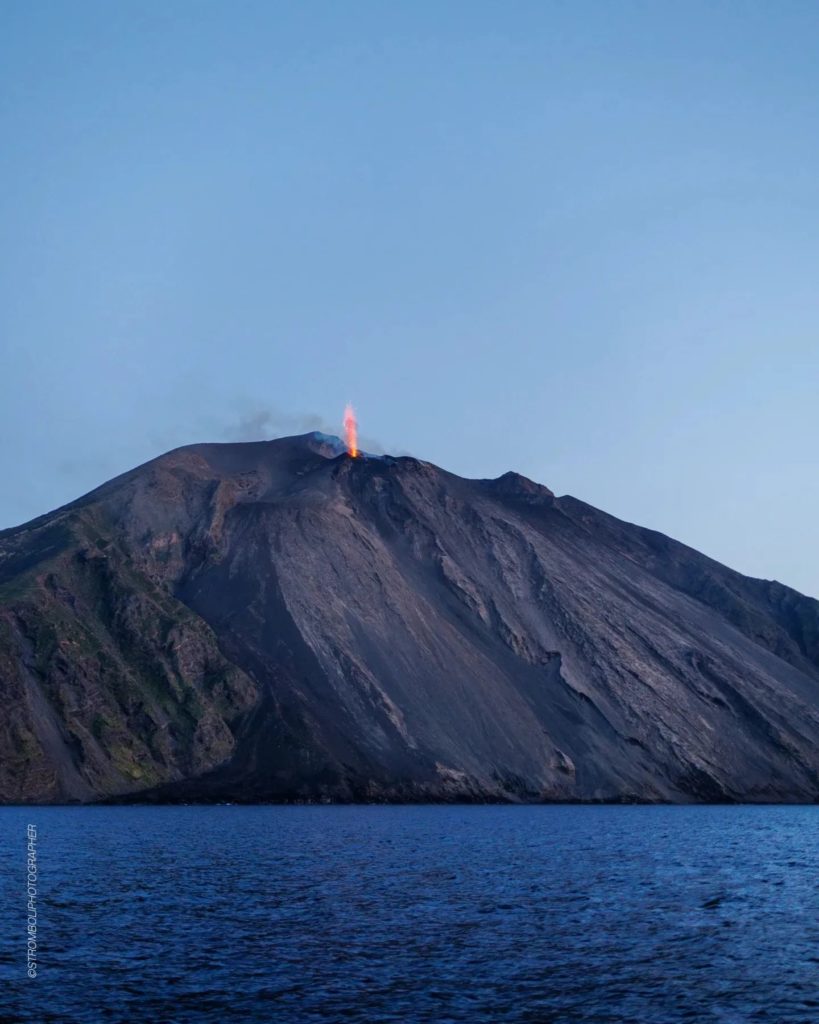
Italy , Stromboli :
WEEKLY BULLETIN, from January 8, 2024 to January 14, 2024. (issue date January 16, 2024)
SUMMARY STATEMENT OF ACTIVITY
In light of the monitoring data, it appears:
1) VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS: Due to technical problems with the monitoring cameras during the period in question, it was not possible to characterize the explosive activity of Stromboli.
2) SISMOLOGY: The monitored seismological parameters do not show significant variations.
3) GROUND DEFORMATIONS: Ground deformation monitoring networks do not show significant variations.
4) GEOCHEMISTRY: SO2 flux at medium level
CO2 flux in the summit zone: reached very high values at the start of last week, but quickly returned to average values in recent days.
C/S ratio in the plume: there are no updates.
Helium Isotope Ratio in Thermal Aquifer: There are no updates.
CO2 flux in Scari: stable data at average values
5) SATELLITE OBSERVATIONS: Thermal activity observed by satellite was generally weak.
VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS
Due to technical problems with surveillance cameras during the period in question, it was not possible to characterize the explosive activity of Stromboli. The only functional camera was the one located at Punta dei Corvi (SPCT), which however does not allow an exhaustive characterization of the volcano’s activity.
Recovery interventions are underway to restore video surveillance service to other cameras.
Source : INGV
Photo : Stromboli stati d’animo
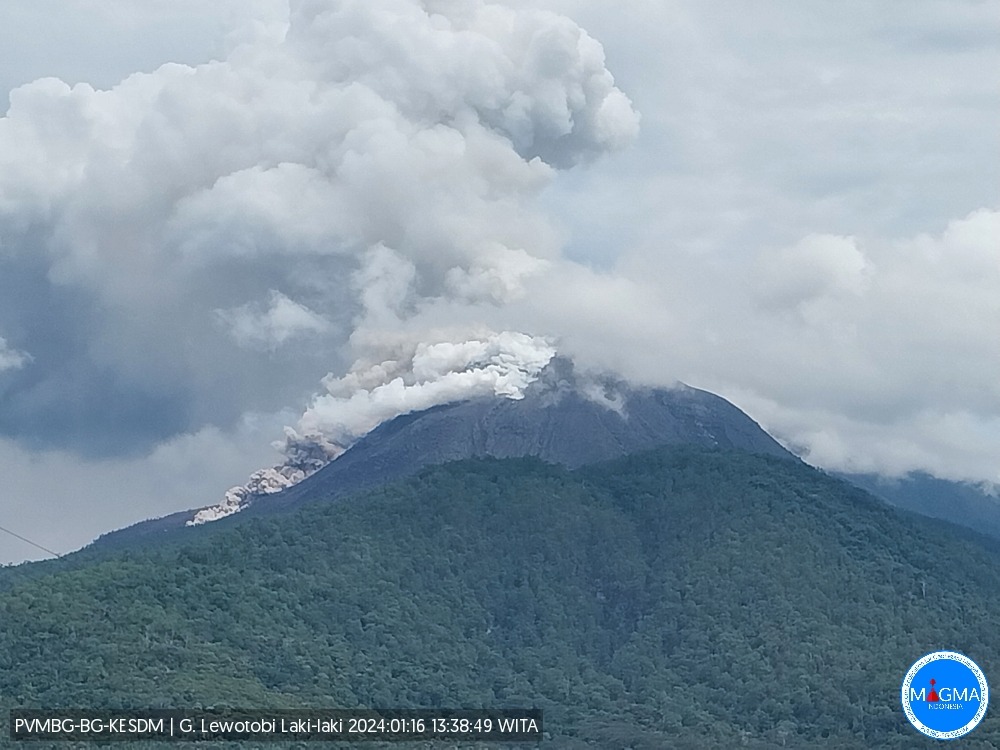
Indonesia , Lewotobi Laki Laki :
Press release on CHANGES IN RECOMMENDED SAFE DISTANCE for G. LEWOTOBI AT ACTIVITY LEVEL IV (AWAS)
Mount Lewotobi is a twin volcano located in the southeastern part of the island of Flores, Indonesia. This mountain is located in East Flores Regency, East Nusa Tenggara Province. Mount Lewotobi consists of two peaks, namely Mount Lewotobi Men and Mount Lewotobi Women.
On January 9, 2024 at 11:00 p.m. WITA, G. Lewotobi’s activity level was increased from level III (Siaga) to level IV (Awas). Seismic monitoring shows a significant increase in the number of eruptions, avalanches and hot cloud avalanches. Visual monitoring also showed lava flows to the northeast up to 3 km, lava avalanches to the north-northeast up to 1,500 meters and hot cloud avalanches up to 2 km to the North-Northeast.
The latest developments in the activities of G. Lewotobi until January 16, 2024 at 24:00 WITA are as follows:
On January 16, 2024 at 8:58 p.m. WITA, an eruption occurred with the height of the eruptive column reaching 600 meters above the peak, white to gray in color, thick, oriented to the North and Northeast. This eruption was accompanied by avalanches of incandescent lava in the southwest-west direction up to 2 km from the center of the eruption.
Earthquake monitoring shows that on January 16, 2024 between 00:00 and 24:00 WITA there was a significant increase in seismicity, namely 13 hot cloud avalanche earthquakes, 108 hot cloud avalanche earthquakes, eruption, 92 emissions earthquakes, 172 low frequency earthquakes, 10 harmonic tremors and 1 deep volcanic earthquake. From 8:58 p.m. WITA to 9:24 p.m. WITA, an earthquake was recorded with a maximum amplitude of 47 mm (off-scale).
Seismic data from G. Lewotobil Laki shows a significant increase in low frequency earthquakes, which shows that the movement of magma towards the surface becomes more intense in a fairly short time, so it is estimated that this will increase the volume of lava in the crater area, leading to a sliding distance of lava flows as well as the appearance of hot cloud avalanches, which will also increase. The presence of lava flow descending in a new direction, namely South-West-West with a sliding distance of 2 km, shows that lava flows can currently occur in all directions given the very intense movement of the magma towards the surface. Apart from this, the emergence of harmonic tremors shows that the formation of gas in the magma conduit is increasing, so it is feared that this could increase the explosiveness of the eruption.
Based on the results of a comprehensive analysis and evaluation of visual and instrumental monitoring data, it shows that there has been a significant increase in visual activity and seismicity on Mt. Lewotobi Male, so the recommended distance needs to be changed to Level IV (AWARE). status as follows:
Communities around Mount Lewotobi Laki and visitors/tourists do not carry out any activities within a radius of 5 km around the center of the eruption of Mount Lewotobi Laki and within a radius of 6 km in the north-northeast direction.
The public should remain calm and follow the instructions of the regional government and not believe rumors whose origin is unclear.
Communities around Mount Lewotobi Laki are wary of the risk of lahar flooding in the rivers that originate at the summit of Mount Lewotobi Laki during heavy rains.
Source et photo : PVMBG
Colombia , Puracé – Los Coconucos Volcanic Range :
Weekly bulletin of the activity of the Puracé volcano – Los Coconucos volcanic chain
From the monitoring of the activity of the VOLCANIC CHAIN PURACE VOLCANO – LOS COCONUCOS, the MINISTRY OF MINES AND ENERGY, through the COLOMBIAN GEOLOGICAL SERVICE (SGC), reports that:
During the week of January 9-15, 2024, seismic activity decreased in number of earthquakes and seismic energy released compared to the previous week. The fracture earthquakes were mainly located less than 3 km deep between the Puracé and Piocollo volcanoes, with low magnitudes; while those associated with fluids were mainly located less than 1 km on the western flank of the Puracé volcano, with very low magnitudes.
Likewise, localized deformations continued to be recorded between the Puracé and Curiquinga volcanoes. Carbon dioxide (CO2) values have decreased compared to those previously recorded; However, they remain higher than the reference values in this volcano. On the other hand, stable values were recorded in the sulfur dioxide (SO2) flux.
The images obtained using the installed cameras show that high degassing of the volcanic system is maintained, both inside the crater and in the external lateral fumarole.
(Northwest flank of the volcanic edifice).
The other parameters measured and used for the diagnosis of volcanic activity showed no notable changes during the period evaluated.
The alert status for volcanic activity remains at: YELLOW ALERT: ACTIVE VOLCANO WITH CHANGES IN THE BEHAVIOR OF THE BASE LEVEL OF MONITORED PARAMETERS AND OTHER MANIFESTATIONS.
Source : SGC
Photo : José María Arboleda C / Flickr .
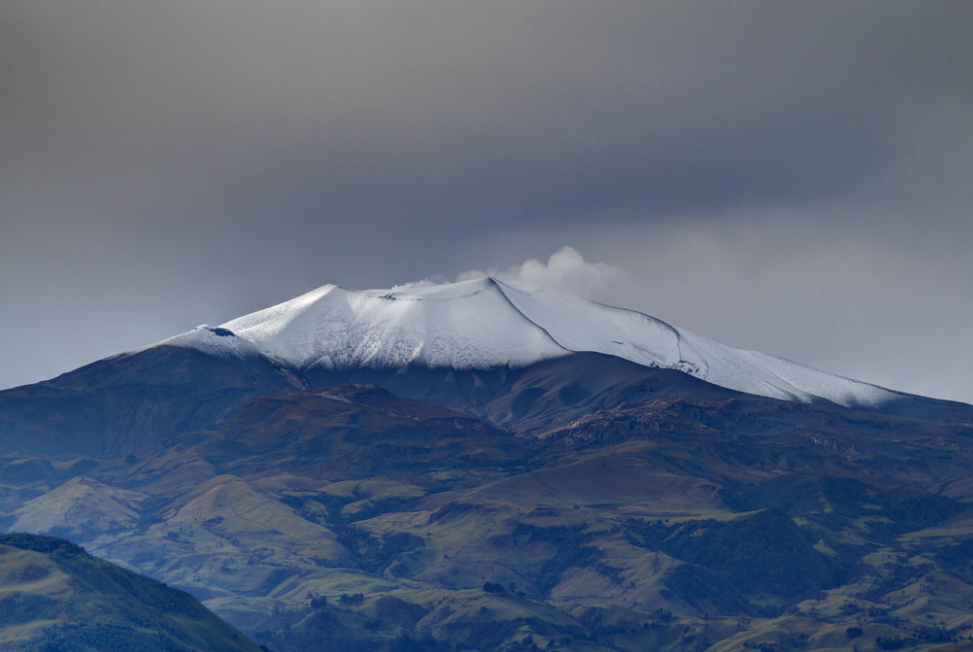
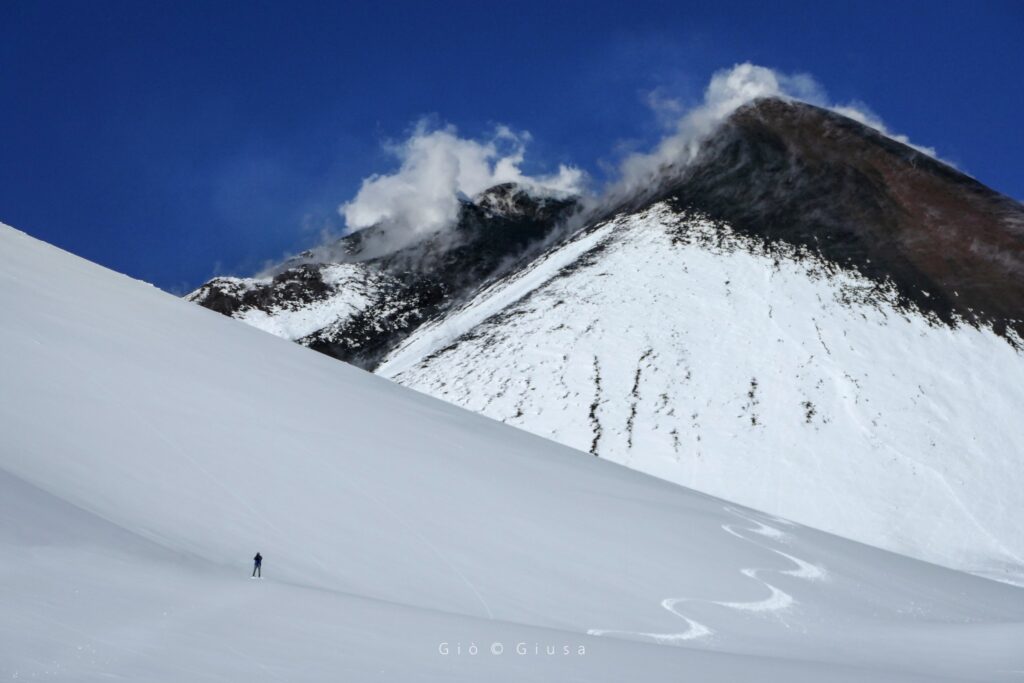
Italy / Sicily , Etna :
WEEKLY BULLETIN, from January 8, 2024 to January 14, 2024. (issue date January 16, 2024)
SUMMARY STATEMENT OF ACTIVITY
In light of the monitoring data, it appears:
1) VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS: Degassing activity at the Bocca Nuova Crater (BN) and at the South-East Crater (CSE).
2) SEISMOLOGY: Low seismic activity due to fracturing; Stationarity of volcanic tremor parameters.
3) INFRASOUND: Low level infrasound activity. Sources located at the Bocca Nuova crater.
4) GROUND DEFORMATIONS: Ground deformation monitoring networks do not show significant variations.
5) GEOCHEMISTRY: SO2 flux at medium level
The CO2 fluxes emitted by the ground are at average values.
The partial pressure of CO2 dissolved in groundwater presents values included in seasonal variability.
Helium isotope ratio: there are no updates
6) SATELLITE OBSERVATIONS: Thermal activity observed by satellite was generally weak.
VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS
The monitoring of the volcanic activity of Etna was carried out through the analysis of images from the INGV surveillance camera network, Osservatorio Etneo (INGV-OE). Observations of activity at the summit craters (Fig. 3.1) were limited to a few hours, or even impossible throughout the day, due to poor weather conditions.
During the period considered, the activity of Etna was characterized by variable degassing activity at the Bocca Nuova crater (BN) and the Southeast crater (CSE), while the crater of North-East (CNE) and Voragine (VOR) present degassing coming from fumarolic activity
Source : INGV.
Photo : Gio Giusa