July 15 , 2023.
Alaska , Shishaldin :
AVO/USGS Volcanic Activity Notice
Current Volcano Alert Level: WATCH
Current Aviation Color Code: ORANGE
Issued: Friday, July 14, 2023, 11:34 AM AKDT
Source: Alaska Volcano Observatory
Notice Number: 2023/A1050
Location: N 54 deg 45 min W 163 deg 58 min
Elevation: 9373 ft (2857 m)
Area: Aleutians
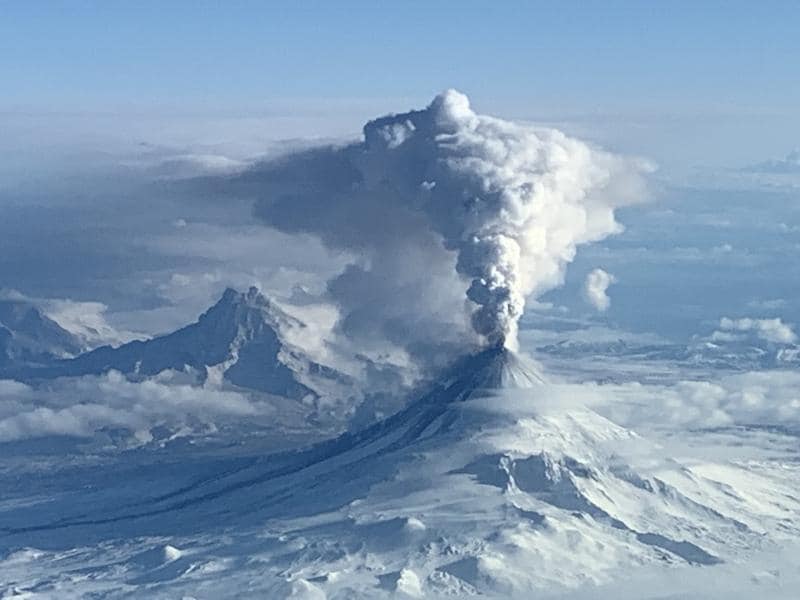
Shishaldin Volcano eruption plume, July 14, 2023. Photo of Lee Cooper, onboard the Canadian Coast Guard icebreaker Sir Wilfrid Laurie
Volcanic Activity Summary:
A significant explosion occurred at 1:09 am AKDT (9:09 UTC) this morning and produced an ash cloud that initially reached 30,000 to 40,000 ft (9–12 km) above sea level and drifted south over the Pacific Ocean. A second smaller explosion occurred at 7:10 am AKDT (15:10 UTC) and reached ~15,000 ft (4.5 km) above sea level. The National Weather Service issued a SIGMET for these events and suggested a maximum cloud height of 25,000 ft (7.6 km) above sea level for the drifting ash cloud. Web camera images and pilot reports show continued low-level ash emissions this morning including a small ash cloud near the summit around 10:30 am AKDT (18:30 UTC).
Eruptions from Shishaldin have produced minor and on occasion significant ash clouds in the past. These can occur with little warning. Shishaldin is monitored by local seismic and infrasound sensors, web cameras, and a telemetered geodetic network. The local monitoring network is partially impaired, therefore AVO is also using nearby geophysical networks, satellite data and regional infrasound and lighting data to detect activity. AVO will continue to closely monitor unrest at Shishaldin Volcano.
Remarks:
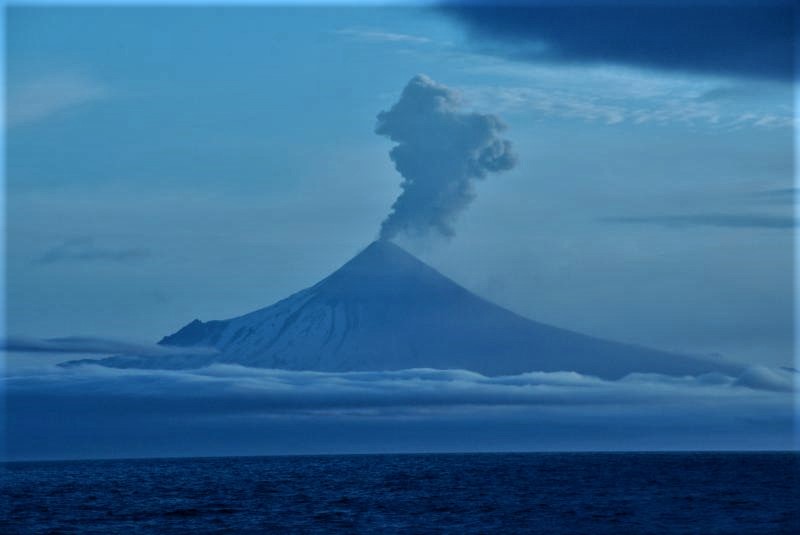
Shishaldin Volcano, located near the center of Unimak Island in the eastern Aleutian Islands, is a spectacular symmetric cone with a base diameter of approximately 16 km (10 mi). A 200-m-wide (660 ft) funnel-shaped summit crater typically emits a steam plume and occasional small amounts of ash. Shishaldin is one of the most active volcanoes in the Aleutian volcanic arc, with at least 54 episodes of unrest including over 26 confirmed eruptions since 1824. Most eruptions are relatively small, although the April-May 1999 event generated an ash column that reached 45,000 ft above sea level.
Source : AVO
Photo : Cooper, Lee , setiavan.
La Réunion , Piton de la Fournaise :
Press release from the Institute of Earth Physics in Paris, Volcanological Observatory of Piton de la Fournaise. July 14, 2023 – 9:30 a.m. – 05:30 a.m. UTC
Ongoing eruption
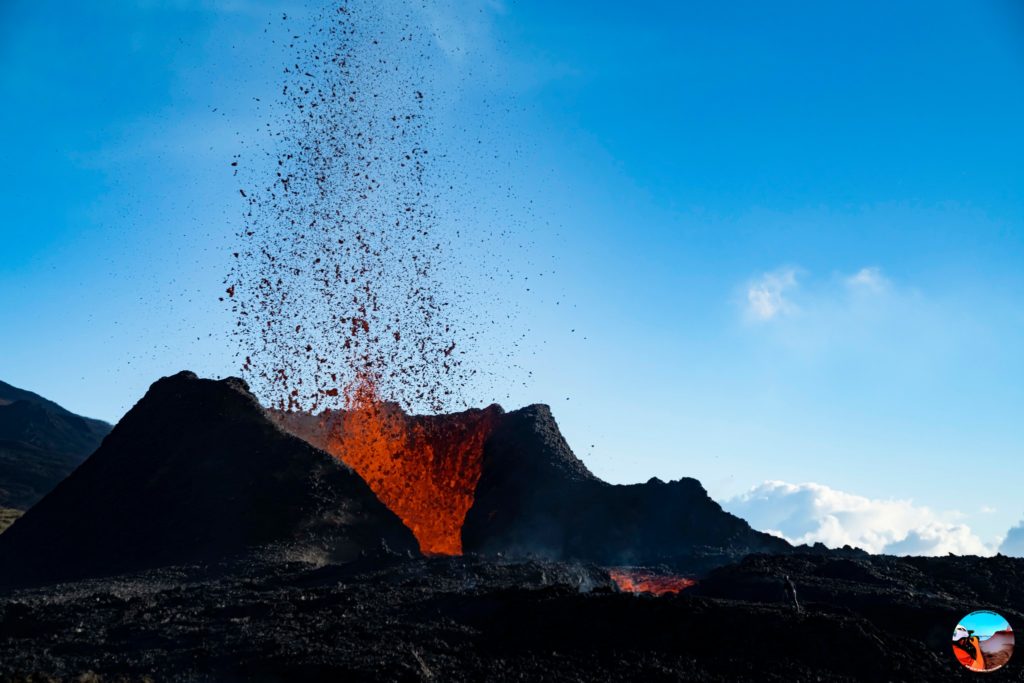
The eruption which began on July 02, 2023, around 08:30 local time continues. The amplitude of the volcanic tremor (indicator of an emission of lava and gas on the surface) is always fluctuating over time on the scale of a few tens of minutes, with phases of continuous tremor and phases of intermittent tremor. The amplitude of the tremor nevertheless remains low compared to the start of the eruption.
The fluctuations observed in the tremor are reflected at the level of the eruptive site by variations in intensity in the activity, with projections of lava fountains at the level of the more or less intense eruptive cone.
Given the bad weather conditions currently on site:
– no visual feedback on the eruptive site and the lava field could be made today and tonight,
– nor any estimate of lava flows by satellite method.
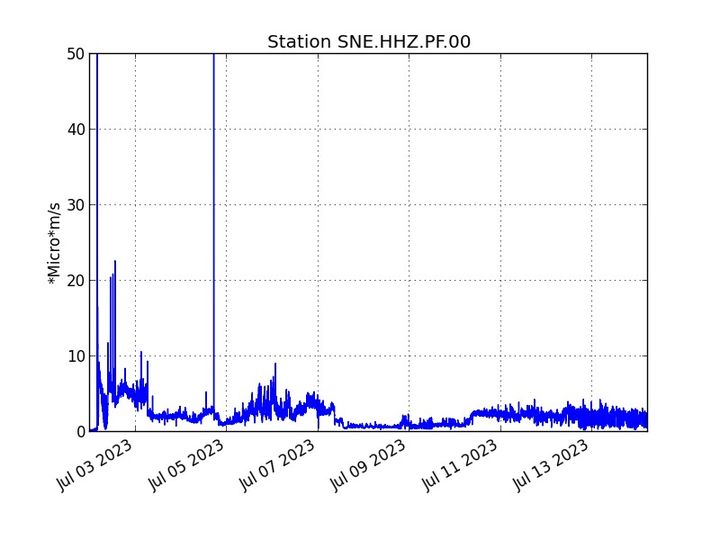
Evolution of the RSAM and the amplitude of the tremor (indicator of an emission of lava and gas on the surface) since
July 02, 2023 00:00 UTC time (04:00 local time) on the SNE seismological station located at the top of the volcano (©
OVPF-IPGP)
No significant deformation of the building is recorded except for a slight deflation of the summit area.
The seismic activity recorded under the summit zone remains weak. Thus over the last 24 hours, no superficial volcano-tectonic earthquake has been recorded. This low seismic activity leads to a reduction in the risk of the appearance of a new crack and/or collapse in the crater, but does not mean that it can be excluded.
Alert level: Alert 2-1 (eruption in the Enclos without any particular threat to the safety of people, property or the environment)
Source : OVPF
Photos : Tunnels de lave Réunion : Rando-Volcan/Vincent Cheville , OVPF.
Italy / Sicily : Etna :
Statement on the activity of Etna, July 14, 2023, 21:29 (19:29 UTC).
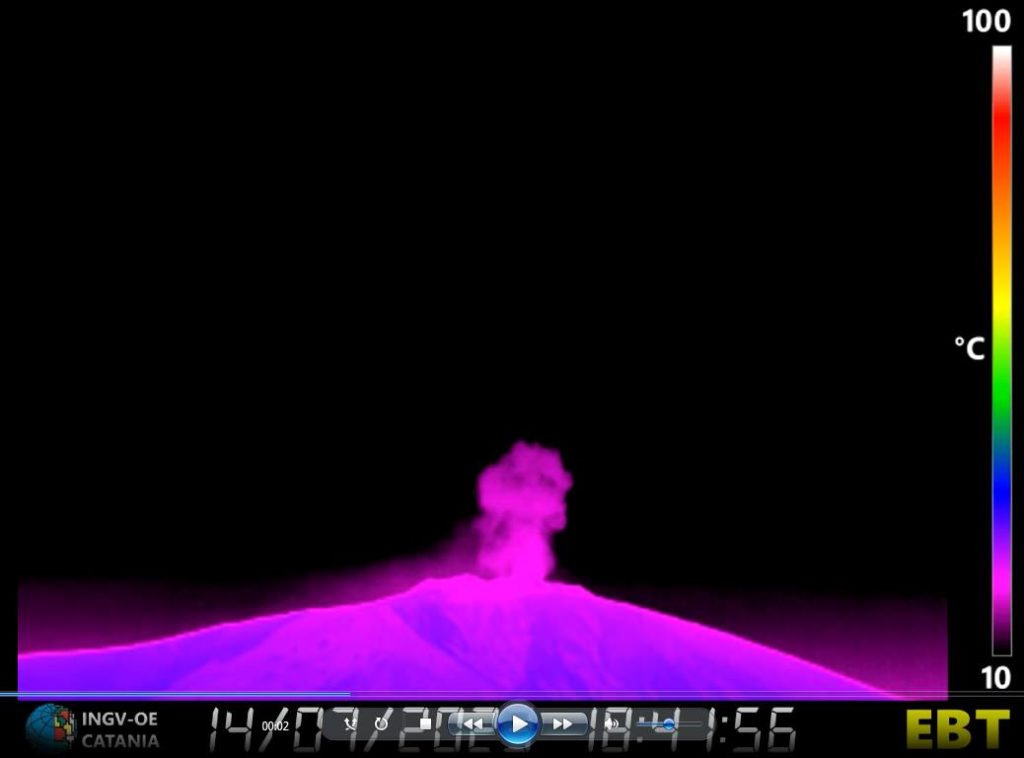
The National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology, Osservatorio Etneo, announces that light Strombolian activity began at the Southeast crater from 18:52 UTC.
Further updates will be communicated soon.
Communique on the activity of Etna, July 14, 2023, 21:59 (19:59 UTC).
The National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology, Osservatorio Etneo, reports that modest Strombolian activity at the Southeast Crater has been observed by surveillance cameras since 18:40 UTC. The activity was preceded by an emission of ash with rapid dispersion in the atmosphere.
From a seismic perspective, volcanic tremor remains at average levels, with a source located under the Southeast crater at a depth of approximately 2700 above sea level. As of 17:40 UTC, there is had an increase in the occurrence of infrasonic events whose location appears to be under the Southeast crater.
The soil deformation networks at present do not show significant variations.
Further updates will be communicated promptly and in any case within 3 hours of this press release.
Source et photo : INGV.
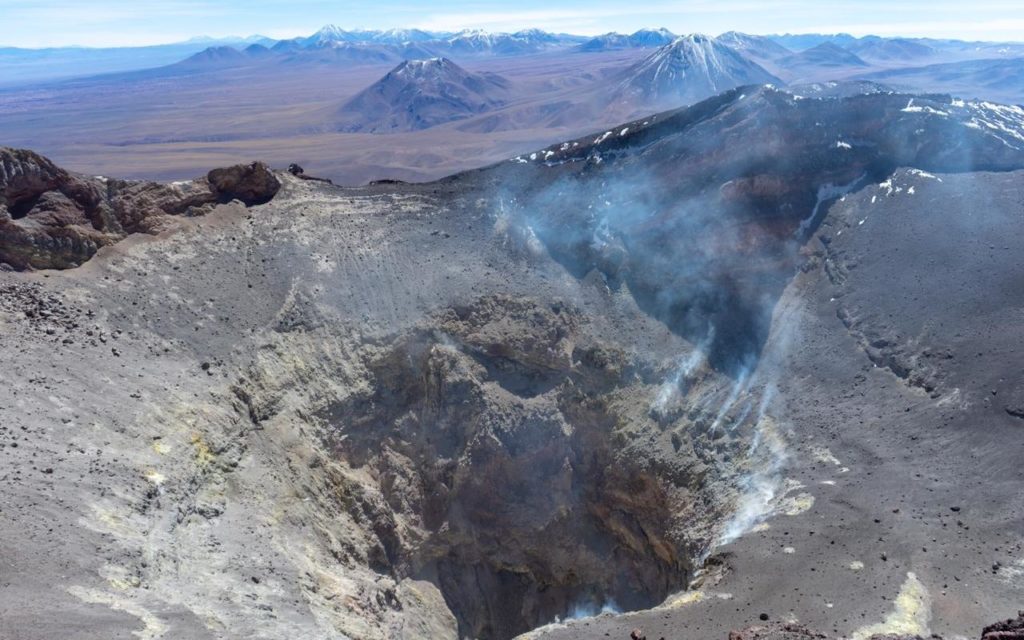
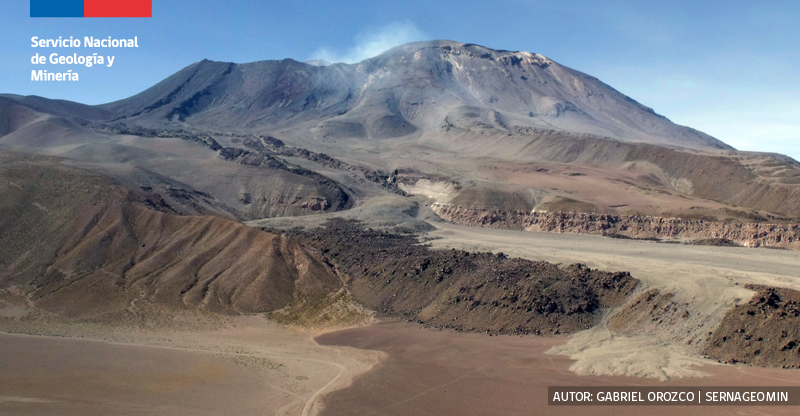
Chile , Lascar :
Seismology
The seismological activity of the period was characterized by the recording of:
146 VT-type seismic events, associated with rock fracturing (Volcano-Tectonics). The most energetic earthquake presented a value of local magnitude (ML) equal to 2.7, located 1.2 km south-southeast of the volcanic edifice, at a depth of 4.2 km by relative to the crater.
45 LP-type seismic events, associated with fluid dynamics within the volcanic system (Long Period). The size of the largest earthquake assessed from the Reduced Displacement (DR) parameter was equal to 49 cm2.
2 seismic events of the TR type, associated with the dynamics maintained over time of the fluids within the volcanic system (TRemor). The size of the largest earthquake assessed from the Reduced Displacement (DR) parameter was equal to 1 cm2.
2 TO-type seismic events, associated with fluid dynamics within the volcanic system characterized by its particular waveform (TOrnillo). The size of the largest earthquake (DR) was equal to 1 cm2.
Fluid Geochemistry
The sulfur dioxide (SO2) emission data obtained by the Differential Absorption Optical Spectroscopy (DOAS) equipment, corresponding to the Emú station, located 6 km in an East-South-East (ESE) direction from the active crater, presented an average value of 358 ± 85 t / d, with a maximum daily value of 1086 t / d on June 19.
Geodesy
From the geodetic data obtained during the period, slight changes in the vertical displacements of low amplitude can be observed.
Surveillance cameras
Thanks to the cameras installed on the volcano, a passive and diffuse degassing is identified during the evaluated period, which reached a maximum height of 820 m above the level of the crater, recorded on June 25. No pyroclastic emission, ash or nocturnal incandescence was identified.
Satellite geomorphological analysis
By observing the Planet Scope, Sentinel 2-L2A and Landsat satellite images, it is observed that areas of degassing remain in the main active crater and the inner wall. No changes are observed in the morphology of the main crater or in the flanks of the volcano which are attributed to the development of volcanic processes during the evaluated period. However, from the analysis of the digital elevation models on May 29, 2023, an increase in the local volume at the base of the crater of 58,000 m3 was identified, caused by the contribution of deposits of gravitational origin and the fluctuating overpressure processes due to gaseous activity.
During the fortnight assessed, changes in volcanic activity were observed. On the one hand, an increase in the productivity and energy of the signals associated with the fracturing of the fragile material was observed, recording an earthquake of ML 2.7 and some seismic swarms, the events were located in the zone of influence of the active crater at shallow depth. In turn, thanks to the processing of high-resolution satellite images of May 29, a change in the internal morphology of the crater was observed, with an increase in the level of its bottom. Finally, although even at low levels, discharges continue to be recorded in SO2 at the surface. Deformation data from the volcanic edifice show no significant changes. Based on the above, it is concluded that the process of shallow volcanic activity continues to evolve above its base threshold, thus maintaining its technical alert in yellow and its possible assignment radius at 3 km.
YELLOW TECHNICAL ALERT: Changes in volcanic activity behavior
Source : Sernageomin
Photos : Vulcanopro. Sernageomin / Gabriel Orozco.
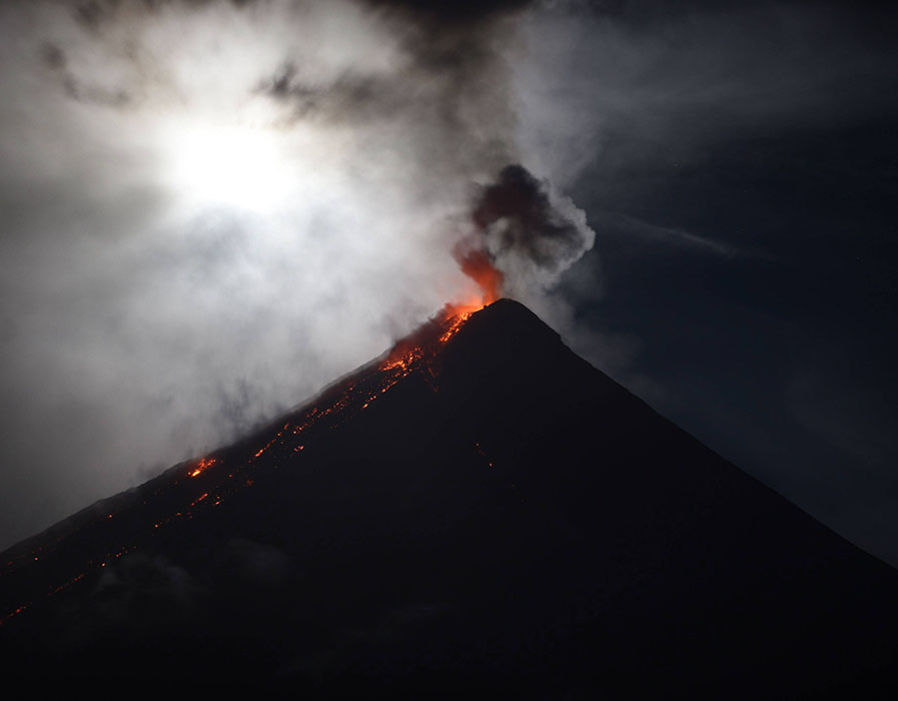
Philippines , Mayon :
MAYON VOLCANO BULLETIN 15 July 2023 8:00 AM
In the past 24-hour period, very slow effusion of lava from the summit crater of Mayon Volcano continued to feed lava flows and collapse debris on the Mi-isi (south) and Bonga (southeastern) gullies as well as rockfall and PDCs on these and the Basud (eastern) Gullies. The lava flows have advanced to approximate lengths of two thousand eight hundred (2800) meters and one thousand four hundred (1400) meters along Mi-isi and Bonga gullies, respectively, from the summit crater while collapse debris has deposited to four thousand (4000) meters from the crater along the Basud channel. Five (5) pyroclastic density currents (PDC) generated by dome-collapse, three hundred sixty-two (362) rockfall events, and thirty-nine (39) volcanic earthquakes were recorded by the Mayon Volcano Network.
Sulfur dioxide (SO2) emission averaged 2,132 tonnes/day on 14 July 2023. Short-term observations from EDM and electronic tiltmeter monitoring show the upper slopes to be inflating since February 2023. Longer-term ground deformation parameters based on EDM, precise leveling, continuous GPS, and electronic tilt monitoring indicate that Mayon is still inflated, especially on the northwest and southeast.
Alert Level 3 is maintained over Mayon Volcano, which means that it is currently in a relatively high level of unrest and hazardous eruption within weeks or even days could still be possible.
Source : Phivolcs.
Photo : Auteur inconnu ( archive).