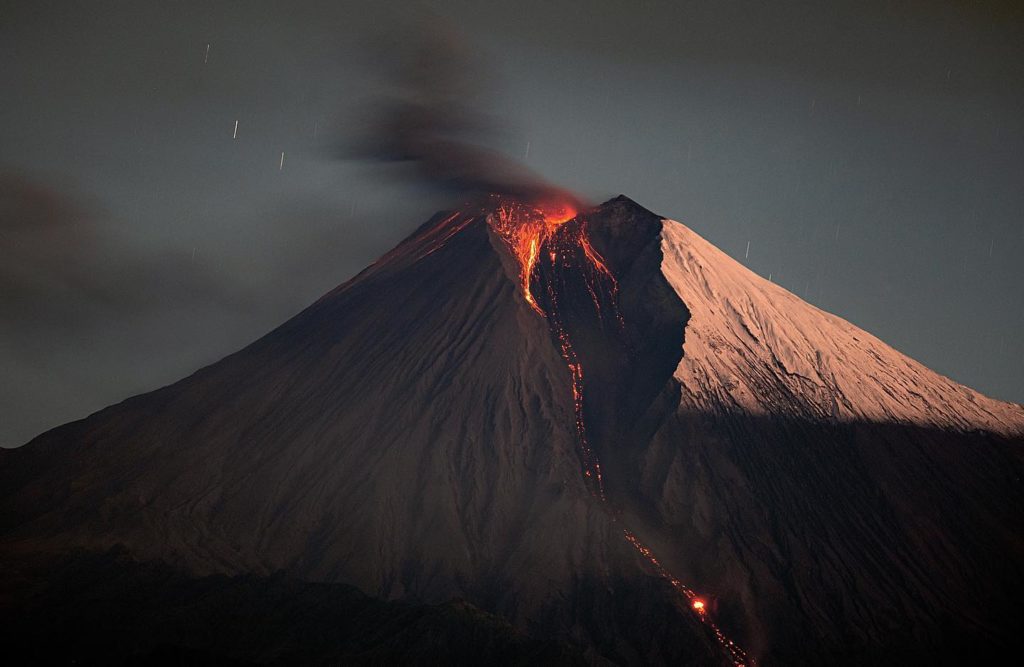
March 22, 2023.
Italy , Stromboli :
WEEKLY BULLETIN from March 13, 2023 to March 19, 2023 (issue date March 21, 2023)
ACTIVITY STATUS SUMMARY
In the light of the monitoring data, it is highlighted:
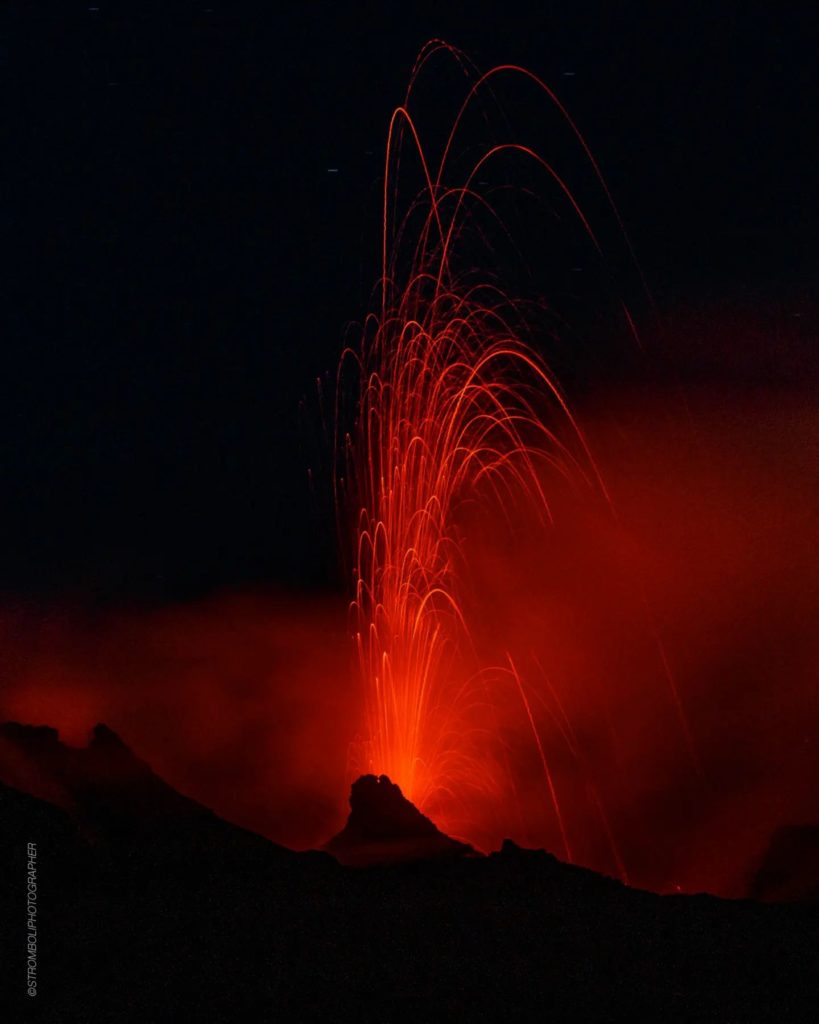
1) VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS: During this period, normal Strombolian activity was observed with splash activity from the N crater area. The total hourly frequency fluctuated between medium-low values (6 events/h) and medium-high values (18 events \h ). The intensity of the explosions was mainly medium and low in both the North Crater area and the Center-South Crater area.
2) SEISMOLOGY: The seismological parameters monitored do not show any significant variations.
3) GROUND DEFORMATIONS: The ground deformation monitoring networks did not show any significant variations during the week.
4) GEOCHEMISTRY: the flow of SO2 is at an average level
The CO2 streams show average degassing values.
The C/S values are at average values.
The isotopic ratio of helium dissolved in the heat sinks is at average values with R/Ra equal to 4.24
5) SATELLITE OBSERVATIONS: The thermal activity observed from the satellite was generally weak.
VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS
During the observation period, the eruptive activity of Stromboli was characterized by the analysis of the images recorded by the surveillance cameras of the INGV-OE at an altitude of 190 m (SCT-SCV), Punta dei Corvi, while the Pizzo’s infrared camera was restored on March 16, providing stable images as of 12:22 UTC. The explosive activity was mainly produced by 3 (three) eruptive vents located in the North zone of the crater and by 4 (four) vents located in the Center-South zone.
Due to the unfavorable weather conditions of March 15, the visibility of the crater area was insufficient for a correct description of the eruptive activity.
Observations of explosive activity captured by surveillance cameras
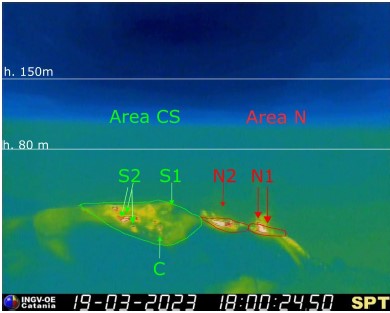
In the area of the North crater (N), with two vents located in the N1 sector and one in the N2 sector, an explosive activity varying from low (less than 80 m in height) to medium (less than 150 m in height) has been observed, emitting coarse materials (bombs and lapilli)). In addition, splashing activity was observed that was intense for long periods on March 19 from sector N1. The average frequency of explosions varied from 3 to 10 events/h.
In the Center-South zone (CS), sector S2, with three active vents, showed explosive activity of low and medium intensity (less than 150 in height) emitting coarse materials. Sector C, during the day on March 17, showed occasional pressurized gas jetting activity and low-intensity explosive activity. Sector S1 showed no activity. The frequency varied between 1 and 9 events/h.
Inspection of the summit area on March 16, 2023.
On the occasion of the restoration of the SPT camera, an inspection was carried out in the summit area that rises from the Labronzo slope and descends along the Rina Grande.
Along the climb, the collapse niche present on the edge of the Sciara at the foot of the N1 and N2 craters is clearly visible. From the Pizzo, one can see the jagged edge of the N2 crater and the presence of various vents in the Center-South zone. In particular, the formation of an outgassing vent in the central area is evident, with a hint of agglomerated slag cone. By observing in an East-West orientation, one can distinguish, in order, at least one vent site of occasional Strombolian activity with emission of ash and lapilli, a small hornito and a large slightly accentuated intra-crater cone whose activity and number of mouths it was not possible to assess.
During the observation period from 11:00 a.m. to 1:30 p.m., the activity appeared equally distributed between the North and Center-South zones, with activity of low to medium intensity and frequency. In sector N1: emission of ash, in sector N2: ash and coarse materials; the Center-South zone alternated energetic detonations with rare explosions and emissions of coarse materials.
Source : INGV.
Photos : INGV , Stromboli stati d’animo .
Indonesia , Ili Lewotolok :
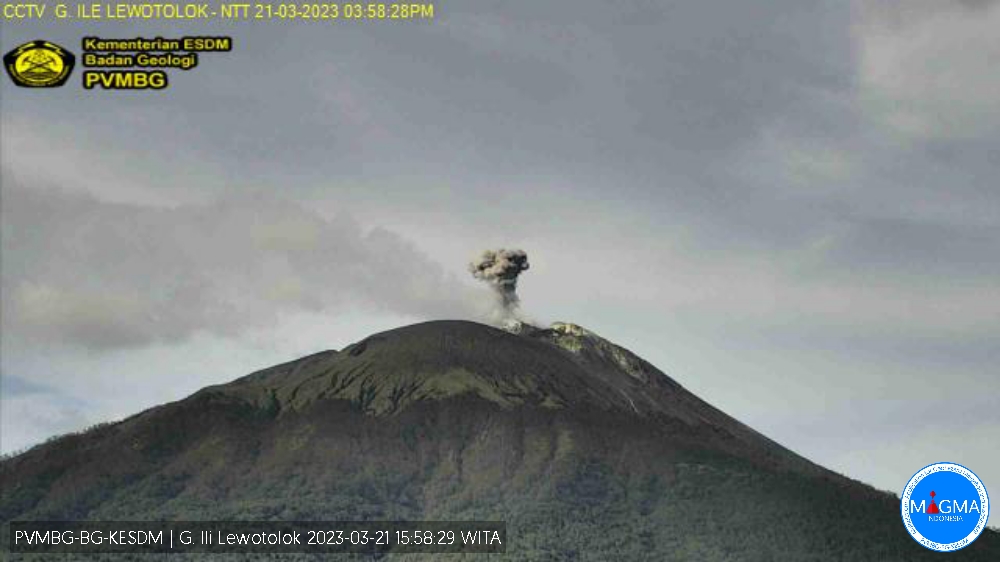
An eruption of G. Ili Lewotolok occurred on Tuesday, March 21, 2023 at 4:56 p.m. WITA with an ash column height observed at ± 400 m above the summit (± 1823 m above sea level) . The ash column was observed to be white to gray with a thick intensity, oriented northwest. This eruption was recorded on a seismograph with a maximum amplitude of 21.3 mm and a duration of 41 seconds.
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION – VONA
Issued : March 21 , 2023
Volcano : Ili Lewotolok (264230)
Current Aviation Colour Code : ORANGE
Previous Aviation Colour Code : orange
Source : Ili Lewotolok Volcano Observatory
Notice Number : 2023LEW005
Volcano Location : S 08 deg 16 min 19 sec E 123 deg 30 min 18 sec
Area : East Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia
Summit Elevation : 4554 FT (1423 M)
Volcanic Activity Summary :
Eruption with volcanic ash cloud at 08h56 UTC (16h56 local).
Volcanic Cloud Height :
Best estimate of ash-cloud top is around 5834 FT (1823 M) above sea level or 1280 FT (400 M) above summit. May be higher than what can be observed clearly. Source of height data: ground observer.
Other Volcanic Cloud Information :
Ash cloud moving to northwest. Volcanic ash is observed to be white to gray. The intensity of volcanic ash is observed to be thick.
Remarks :
Eruption recorded on seismogram with maximum amplitude 21.3 mm and maximum duration 41 second.
Source : Magma Indonésie.
Colombia , Nevado del Ruiz :
Bulletin of activity level of the Nevado del Ruiz volcano.
The activity level continues at the yellow activity level or (III): changes in the behavior of volcanic activity.
Regarding the monitoring of the activity of the Nevado del Ruiz volcano, the COLOMBIAN GEOLOGICAL SERVICE reports that:
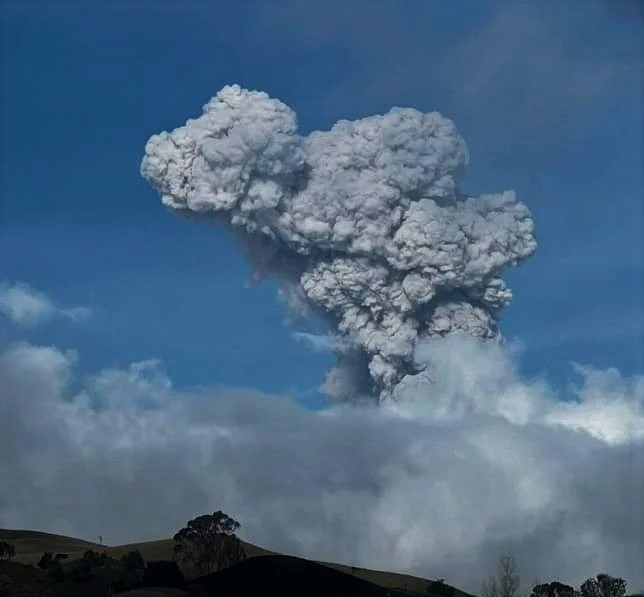
Seismic activity related to the movement of fluids inside volcanic conduits has increased in the number of events recorded and in the seismic energy released compared to the previous week. The continuity in the recording of volcanic tremors with moderate energy levels and gas and ash emissions stands out. Through images captured by conventional and thermographic (FLIR) cameras installed in the volcano area, several gas and ash emissions and temperature changes of the emitted material were confirmed, both phenomena were related to some of the seismic signals recorded.
Seismic activity associated with rock fracturing increased both in the number of earthquakes recorded and in the seismic energy released compared to the previous week. The earthquakes were located mainly in the North-North-East sectors and in the Arenas crater. Depths ranged from 0.8 to 8.0 km. The maximum magnitude calculated during the week was 2.8 ML (Local Magnitude) corresponding to the earthquake recorded on March 13 at 02:30 (local time), located 1.3 km northeast of the Arenas crater, at 3, 7 km deep. This earthquake was part of a slight increase that occurred in this area between 2:27 a.m. and 3:55 a.m. that same day.
Source : SGC.
Photo : Entérate Ciénaga
Chile , Lascar :
Volcanic Activity Report (RAV), Volcanological Observatory of the Southern Andes – Ovdas.
Seismic activity:
The seismicity of the last 24 hours continues to show the characteristics of a discrete activity with a predominance of volcano-tectonic events (VT, linked to rock material rupture processes), and the isolated recording of long-type events period (LP) and « tornillos » (TO), associated with fluid dynamics inside conduits or volcanic fractures.
Observations:
The VT-type earthquake with the highest energy was located 0.6 km in an East-South-East direction and at a depth of 1.6 km from the active crater.
No apparent surface activity in viewing windows. Partial visibility due to heavy cloud cover.
Other Notes:
Position variations are recorded at GNSS stations, both in the length of the survey line and in the vertical components. The QUEB-PUNA line maintains a shortening trend with an average of 0.52 cm/month, mainly caused by the displacement of the PUNA station, recording a variation rate of 0.83 cm/month towards the North-West in the horizontal direction and 0.01 cm/month of vertical variation. Using the satellite analysis technique (InSAR), no representative indication of deformation is detected, showing only areas of weak coherence in the upper part of the volcanic building, allowing to deduce that the activity associated with the deformation would relate to very superficial changes and/or limited to the areas of instrumental monitoring and does not represent changes in the internal dynamics of the volcano.
No new satellite thermal anomaly was detected (date of last image: March 21). No new satellite anomaly of SO2 emissions has been detected (latest image: March 20).
The average flow of SO2 gas was 509 t/d on March 18 (latest data available). These values were measured with a device based on Sernageomin differential optical absorption spectrometry (DOAS).
Source : Sernageomin
Photo : Vulcanopro.
Ecuador , Sangay :
DAILY REPORT OF THE STATE OF SANGAY VOLCANO, Tuesday March 21, 2023.
Information Geophysical Institute – EPN.
Surface Activity Level: High, Surface Trend: Unchanged
Internal activity level: High, Internal trend: No change
Seismicity: From March 20, 2023, 11:00 a.m. to March 21, 2023, 11:00 a.m.:
There were no interruptions in the transmission of data from the reference station.
Explosion (EXP) 136
Emission Tremors (TREMI ) 34
Rains / Lahars:
There was light rain in the area. **In the event of heavy rains, these could remobilize the accumulated materials, generating mudslides and debris that would descend the flanks of the volcano and flow into the adjacent rivers.**
Emission / Ash Column:
The Washington VAAC reported 2 ash emissions, which were recorded by satellite, one reached 860 meters above the crater, in a southeasterly direction and the other had a height of 1,100 meters above from the crater, heading south.
Other Monitoring Parameter:
The FIRMS system records 16 thermal anomalies, the MIROVA-MODIS system records 1 moderate thermal anomaly, the MIROVA-MODIS system records 2 strong thermal anomalies (133 and 251 MW) on the Sangay during the last 24 hours.
Observation:
Most of the time the volcano was cloudy.
Alert level: Orange.
Source : IGEPN
Photo : Eqphos_fotografía