October 02 , 2022.
La Réunion , Piton de la Fournaise :
Commission, Institute of Physics of the Paris Globe, Volcanological Observatory of Piton de la Fournaise, October 1, 2022 – 12:30 p.m. (local time) – 08:30 (UTC time).
Current eruption
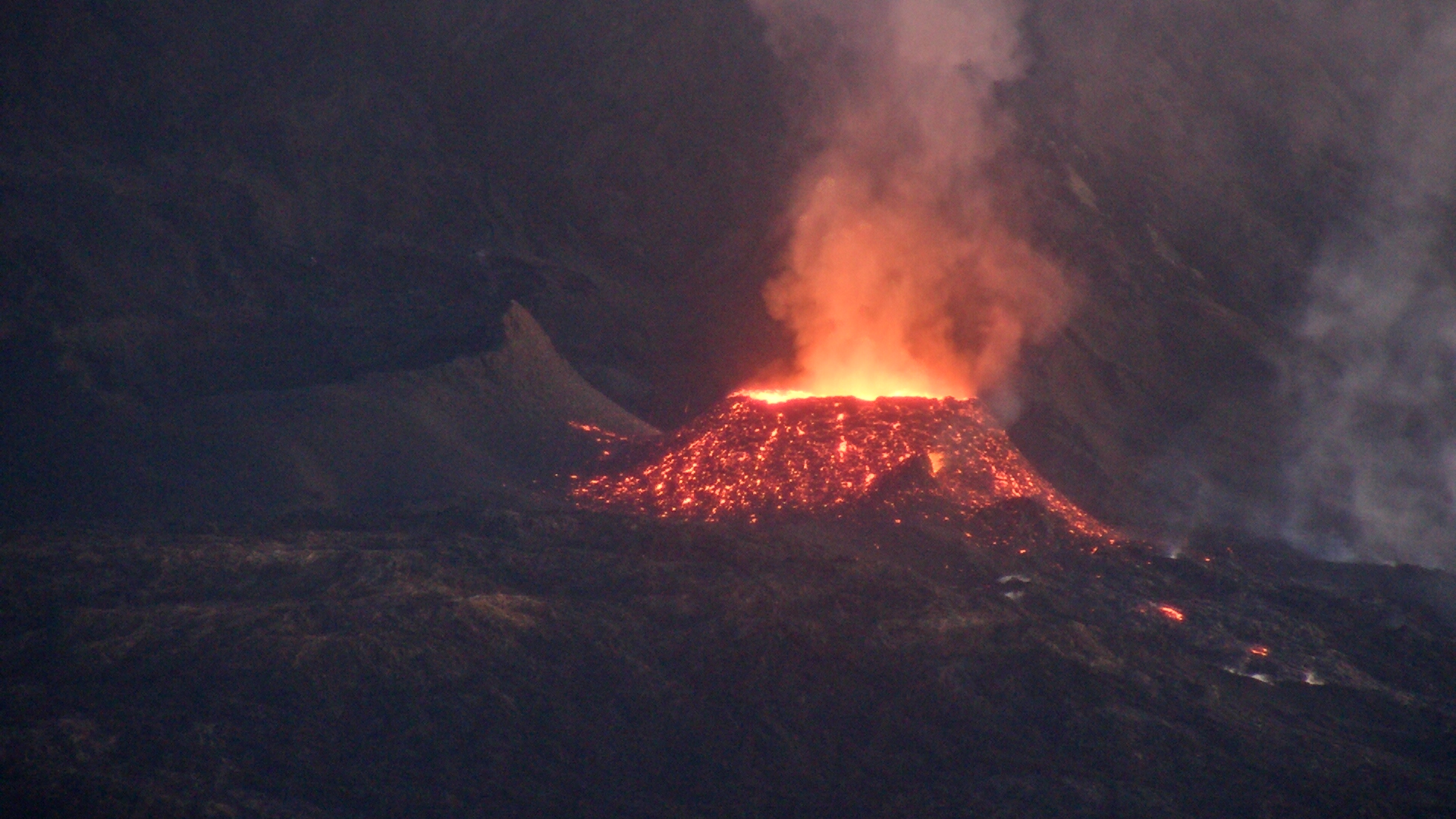
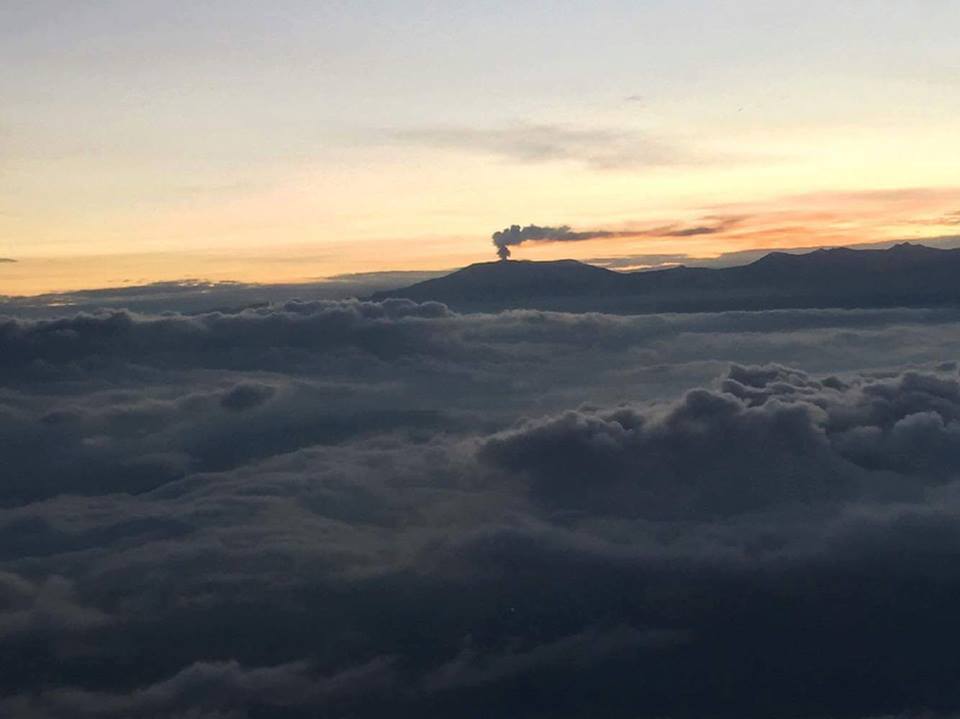
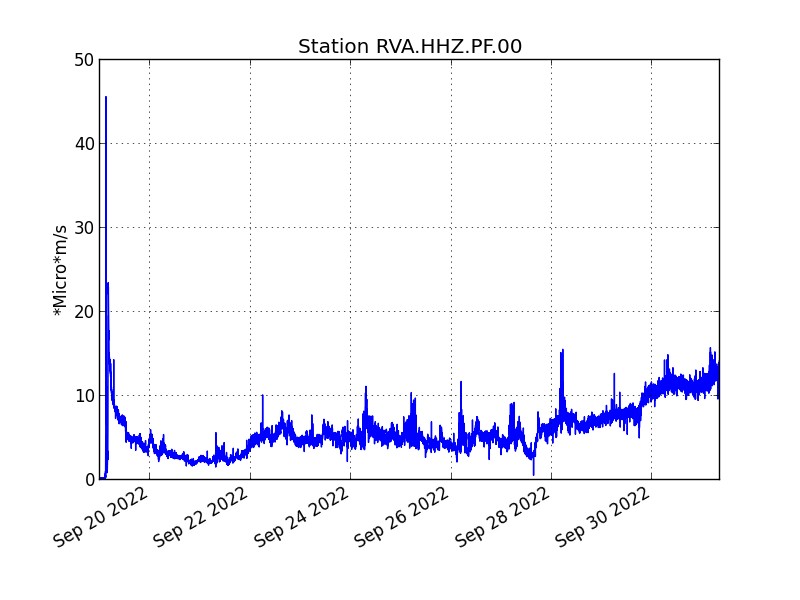
The eruption started on 09/19/2022 around 07:48 am local time continues. The amplitude of the eruptive tremor (indicator of a lava emission on the surface) has increased since 9:40 p.m. local time on September 29, 2022 (5:40 pm UTC; Figure 1). This intensification is most certainly linked to an increase in pressure within the eruptive cone which led to the widening of the opening of the main mouth yesterday. Activity at the level of the secondary mouth (south of the main cone) mentioned in the press release yesterday to greatly decreased.
Evolution of the RSAM (indicator of a lava emission on the surface) since 09/19/2022 00h00 UTC time (04:00 local time) on the RVA seismological station located at the level of the rival crater (© OVPF/IPGP).
– Three volcano-tectonic earthquakes have been recorded at the component of the summit zone over the last 24 hours.
– The resumption of a slight inflation (swelling) on the entire volcano (summit and enclosure) is confirmed but remains of very low intensity for the moment (<1 cm).
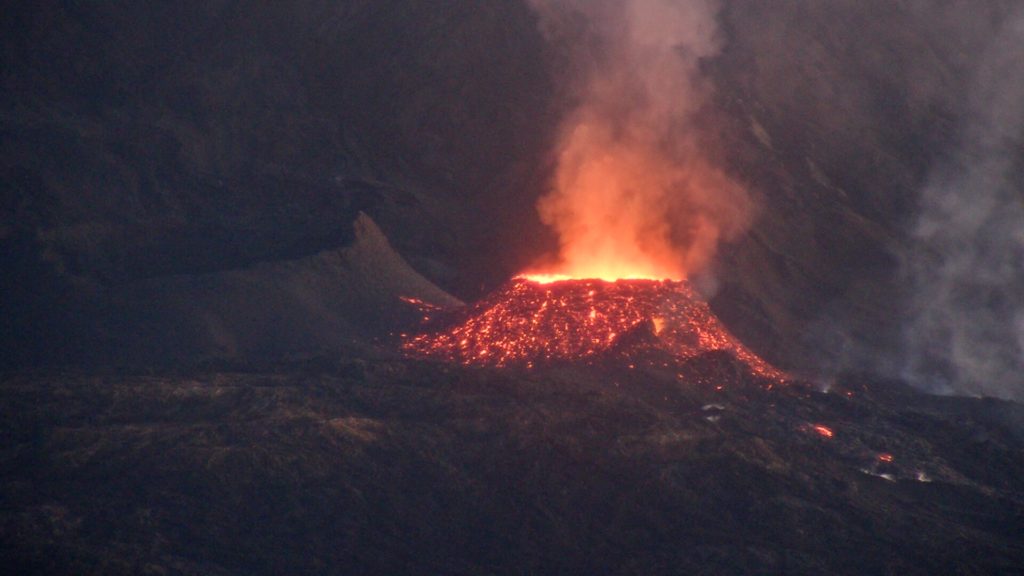
The images of the OVPF-IPGP webcam located at the Piton de Bert show that the larger lava projection activity observed yesterday at the level of the eruptive site is maintained. On the other hand, the secondary eruptive mouth mentioned in the previous press release, gradually ceased its activity during yesterday.
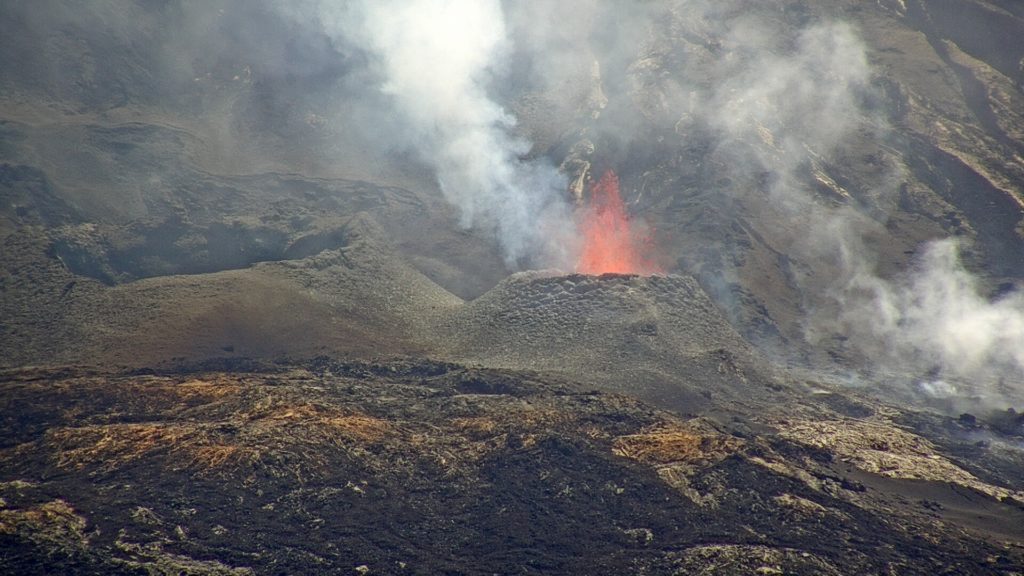
– a degassing is always observed at the level of the eruptive site;
– The majority of lava flows are always made by lava tunnels in which many resurgences are visible;
– Lave flows are also made directly from the secondary mouth.
Shots of the eruptive site on October 1, 2022 at 01:44 am UTC (05:44 local time, above) and at 06:54 UTC (10:54 am local time , below) from the camera of the OVPF-IPGP-Irt located at Piton de Bert (© OVPF-IPGP-IRT).
The lava flow estimates established by satellite method on Hotvolc (OPGC – Clermont Auvergne University) and Mirova (University of Turin) platforms an average speed over the last 24 hours relatively stable around 4-6 m3/s with a peak recorded at 16 m3/s today at the end of the morning. These measures have been showing since September 28, a gradual increase in estimated flow. The lava flow activity is now mainly in tunnel, these estimates are minimum values.
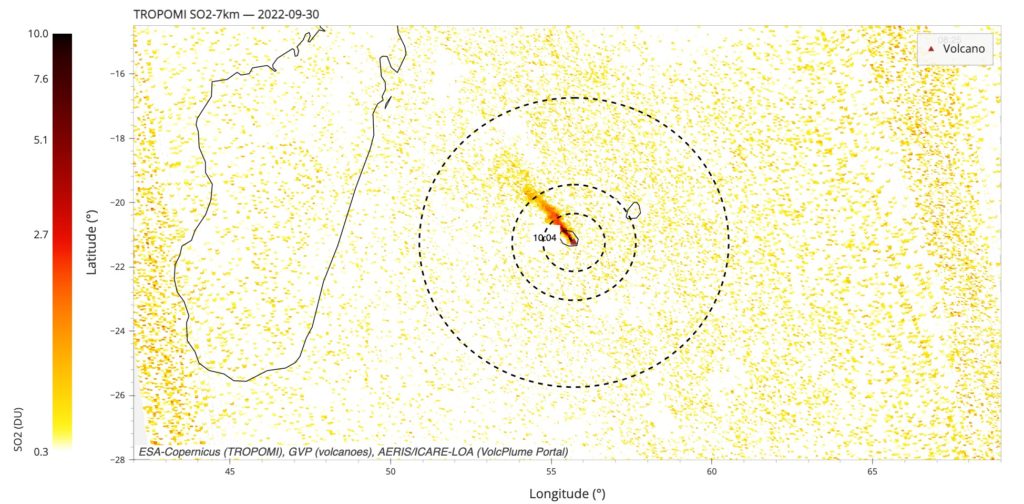
The acquisitions of the Copernicus program developed by the European Commission provide images of the tropom instrument intended to observe the composition of the atmosphere, and in particular SO2 concentrations. The image of September 30 (around 10:00 am UTC;) shows a very well marked plume, denser than the previous days, and which extends over a distance of 300 km, towards the northwest, coherent with an increase in the ‘activity. Wind fields from ECMWF/ERA5 data indicate that volcanic plume seems to be transported at an altitude of approximately 3km. The mass of SO2 integrated on a 300 km radius disc around the Piton de la Fournaise (only taking into account the pixels associated with a column integrated in SO2> 0.3 of) amounts to 0.8 KTON (produced 7 km) and 5.8 KTON (produces 1 km). Note that we have reached significant peaks in air pollution in SO2 at the Bourg-Murat station, with hourly values which exceeded 330 UG/m3.
SO2 concentration detected by the tropomi instrument (Copernicus – ESA), on September 30, 2022, around 10:00 am UTC. The unit is the Dobson Unit (surface concentration: 1 DU = 2.69 × 10^16 molecules cm – 2). (© ESA-Copernicus (tropom), GVO (volcanoes), Aeris/Icare-Loa (Portal volcplume)).
Alert level: 2-1 alert (access to the Enclos prohibited ; eruption in the Enclo without any particular threat to the safety of people, goods or environment).
Source and photos : Direction OVPF / IPGP.
Indonesia , Marapi :
Volcanic activity of Mont Sorik Marapi September 30, 2022.
The Sorik Marapi volcano is administratively located in the regency of native mandating, in the province of Sumatra du Nord. The volcanic activity of Mont Sorik Marapi has fluctuated since January 2022, and the current level of activity is at level I (normal).
The latest developments on the activities of Mont Sorik Marapi until September 30, 2022 at 12:00 WIB are as follows:
There was an increase in the number of occurrences of deep volcanic earthquakes on September 29, 2022, up to 146 events, but there is no visual increase in activity. This shows that there is an increase in pressure that can come from hydrothermal activity and magmatic activity in the body of the volcano but still does not show an increase on the surface.
We must pay attention to potential dangers in the form of phreatic rashes, namely eruptions linked to hydrothermal activity. If a water eruption occurs, it can be accompanied by rain of ash, mudslides and ejection of materials around the crater.
In terms of level I activity (normal), it is recommended that the community around the Sorik Marapi volcano and visitors/tourists:
(a) are not allowed to approach the crater nearby
(b) immediately move away the area around the crater if an increase in the intensity/thickness of the crater smoke is observed and/or if there is a strong smell of gas to avoid the potential danger of Exposure to toxic gases or phreatic eruptions.
Based on observations, analysis of visual and instrumental data until September 30, 2022 at 12:00 WIB, the activity level of Mount Sorik Marapi is still at level I (normal).
Source et photo : PVMBG.
United-States , Yellowstone :
44°25’48 » N 110°40’12 » W,
Summit Elevation 9203 ft (2805 m)
Current Volcano Alert Level: NORMAL
Current Aviation Color Code: GREEN
Recent Work and News
September field work in Yellowstone involved numerous projects, including repair and maintenance of seismic and continuous GPS stations, study of the new thermal area that has emerged in the past two decades near Tern Lake, installation of new continuous gas-monitoring equipment near Mud Volcano, geologic mapping of units associated with Yellowstone’s most recent caldera-forming eruption 631,000 years ago, a magnetotelluric study of subsurface characteristics and fluid pathways, and investigation of the causes of hydrothermal explosions in Lower Geyser Basin. In October, YVO will close out the 2022 field season with additional field work that will include, during the first week of the month, maintenance on the Norris Geyser Basin temperature-monitoring network and the recovery of several temporary GPS stations, which are deployed every May and recovered in October before the onset of winter.
Steamboat Geyser experienced one major water eruption during the previous month, on September 18. There have been 9 major water eruptions of the geyser in 2022.
Seismicity
During September 2022, the University of Utah Seismograph Stations, responsible for the operation and analysis of the Yellowstone Seismic Network, located 678 earthquakes in the Yellowstone National Park region. The largest event of the month was a minor earthquake of magnitude 3.9 located about 14 miles south-southwest of Mammoth Hot Springs in Yellowstone National Park on September 18 at 6:55 AM MDT. This event is part of ongoing seismicity that began in the area on July 29. In September, 510 earthquakes were added to the sequence, and seismicity continued through the end of the month.
September seismicity was marked by three additional swarms:
1) A small swarm of 14 earthquakes, ~3 miles north-northeast of Lake Village in Yellowstone National Park, took place during September 9–10, with the largest earthquake (magnitude 2.0) occurring on September 9 at 7:52 PM MDT.
2) A small swarm of 16 earthquakes, ~11 miles south of West Thumb in Yellowstone National Park, occurred during August 31–September 1, with the largest earthquake (magnitude 3.3) on August 31 at 7:33 PM MDT (the quake occurred on September 1 at 01:33 AM in the UTC time zone and is therefore counted as a September earthquake).
3) A swarm of 34 earthquakes, ~12 miles northeast of Old Faithful in Yellowstone National Park, occurred during September 4–5, with the largest earthquake (magnitude 2.6) taking place on September 4 at 8:10 PM MDT.
Earthquake sequences like these are common and account for roughly 50% of the total seismicity in the Yellowstone region.
Yellowstone earthquake activity is currently above background levels.
Ground Deformation
Continuous GPS stations in Yellowstone Caldera and near Norris Geyser Basin recorded a transition from slight uplift to slight subsidence (0.5-1 cm, or a fraction of an inch) in mid-September. This style of deformation occurs every summer. The overall trend of of caldera subsidence has been ongoing since 2015, but during summer months is interrupted by a pause or slight uplift as snowmelt percolates into the ground and causes the surface to swell slightly, like a sponge. The pause or slight uplift begins in late spring or early summer, and by late summer or early fall the deformation style returns to subsidence. The overall rate of caldera subsidence since 2015 is a few centimeters (1–2 inches) per year.
Source : YVO
Photos : Daisy geyser / Yelowstone National Park, Pat Shanks (Imperial geyser).
Colombia , Nevado del Ruiz :
Activity bulletin of the Nevado del Ruiz volcano.
The activity level continues at the level of yellow activity, (III): changes in the behavior of volcanic activity.
Regarding monitoring the activity of the Nevado del Ruiz volcano, the Colombian geological service informs that:
The seismicity linked to the dynamics of fluids inside the volcanic conduits presented a slight increase in the number of earthquakes recorded and a reduction in released seismic energy, compared to the previous week. Through the cameras installed in the volcano area and the report of civil servants of the Natural Park Los Nevados in the region, gas emissions and ash emissions have been confirmed associated with some of these seismic signals. Likewise, changes in the relative temperature of the material observed in the gases and columns of ash were appreciated.
The seismicity associated with fracturing has increased slightly in the number of earthquakes recorded and decreased in released seismic energy, compared to the previous week. Earthquakes were located in the northern, southeast, south and east sectors of the volcano and in the Arenas crater. The depth of earthquakes varied between 0.3 and 9.0 km. The maximum magnitude recorded during the week was 1.3 ml (local magnitude), corresponding to the earthquake of September 20 at 9:37 p.m. (local time), located 2.3 km south-south east Arenas crater, 3.8 km deep.
During the week, there was a seismicity linked to the process of growth and evolution of a lava dome in the Arenas crater.
In monitoring the thermal activity of the volcano, web portals have reported thermal anomalies in the Arenas crater for this week.
Source : SGC.
Photo : Diana M Bustamante.
La Martinique , Mount Pelée :
Weekly assessment of the activity of the Mount Pelée for the period from September 23, 2022 to September 30, 2022.
Between September 23, 2022 at 4 p.m. (UTC) and September 30, 2022 at 4 p.m. (UTC), the OVSM recorded at least 9 earthquakes of volcano-technical type of magnitude less than 0.1. 4 of these low energy earthquakes could be located. These are earthquakes identical to those of families well known on the peeled which are located inside the volcanic building around 0.4 km deep above sea level or about 1 km under the top. This superficial seismicity of volcano-tectonic type is associated with the formation of micro-fractures in the volcanic building.
None of these earthquakes were felt by the population.
During the volcanic reactivation phases of volcanoes similar to the Pelée Mountain, periods of stronger seismic activity often alternate with lower seismicity phases. Since the reactivation of the Hydrothermal-Magmatic system (late 2018), several periods of zero or weak seismicity have been recorded by the OVSM, for example May 2019 (5 earthquakes), October 2019 (3 earthquakes), August 2020 (1 earthquake) , and only 8 earthquakes between June 24 and August 8, 2022 (period of 2 months).
The degraded vegetation zones located between the dreary plum and the hot river was noted during a helicopter overflow carried out on February 9 and May 5, with the support of the Dragon 972, and confirmed by analysis of satellite images and drone (overview of May 11) and satellite analysis (June 2022). A new degraded vegetation area, located just north of the hot river was found from August 26.
The alert level remains yellow: vigilance.
Source : OVSM-IPGP.
Photo : Antilles prestige