December 30 , 2021.
La Réunion Island , Piton de la Fournaise :
Press release of December 30, 2021 – 10:00 a.m.
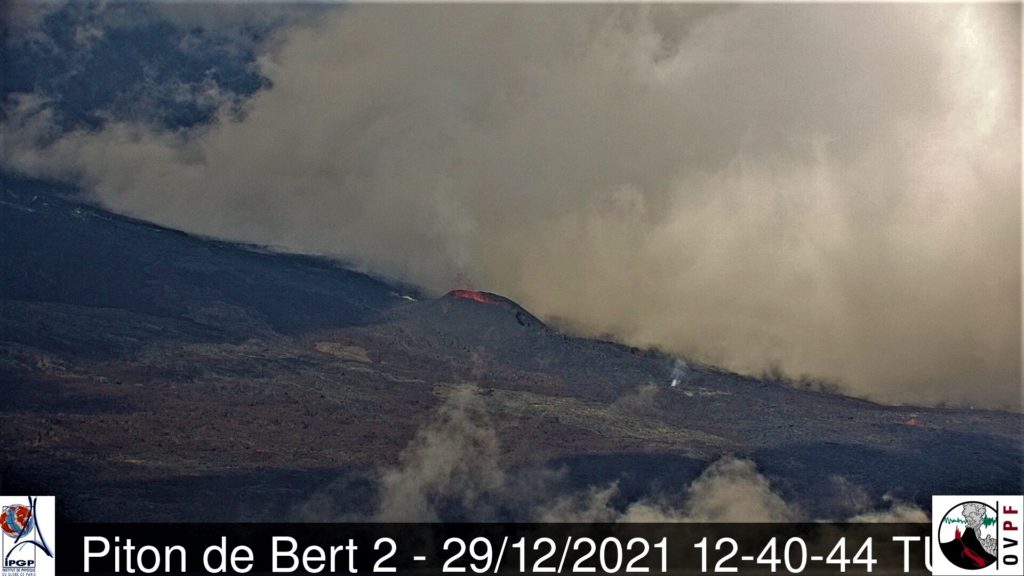
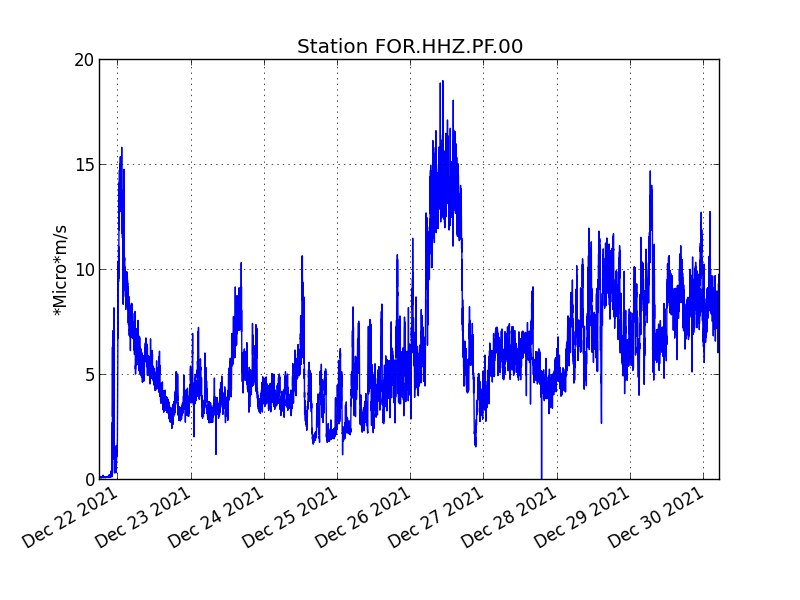
The eruption that began on December 22, 2021 at around 3:30 a.m. local time continues. Over the last 24 hours the amplitude of the eruptive tremor (indicator of an emission of lava on the surface) still shows fluctuations. The fluctuations observed can be linked either to:
– the cone under construction which undergoes construction and dismantling phases, thus influencing the speed of the lava flows at the level of the vent;
– or to punctual releases of pockets of gas trapped in the supply ducts which can be released suddenly leading to an increase in the tremor.
The average amplitude of the tremor is this morning at about 50% of its initial amplitude.
The bad weather conditions on the volcano make it difficult to observe the eruption. Thus, no information relating to on-site activity can be given this morning.
However, the latest observation, made yesterday at 4:40 p.m. local time, shows:
. low lava fountain activity, with fountains rarely exceeding the height of the cone;
. mostly tunnel lava flow activity downstream of the cone;
. the small mouth located at the foot of the cone on the downstream side (and coming from the opening in the lava tunnel) still showed degassing, but much weaker than the day before.
Over the last 24 hours:
– A single volcano-tectonic earthquake under the summit was recorded.
– Surface deformations no longer show significant deformation.
In view of the bad weather conditions on site:
– No estimate of lava flow could be established by satellite method with the HOTVOLC platform (OPGC – Clermont Auvergne University).
– No assessment of the position of the flow front could be made.
Alert level: Alert 2-1 (eruption in the Enclos )
Source et photos : OVPF/IPGP.
Iceland , Reykjanes Peninsula :
Update on the earthquake swarm in Geldingadalir
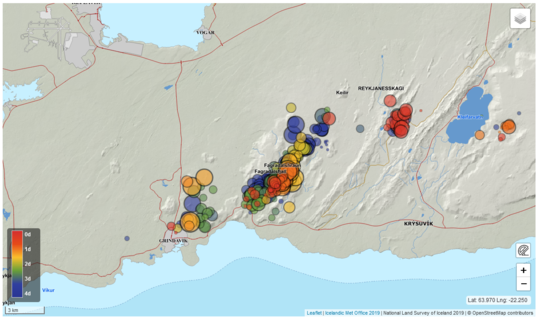
Latest information on seismic activity. Update on 29.12. at 11:53
Since midnight around 90 earthquakes have been detected. Yesterday there were around 1300 earthquakes detected in the Reykjanes peninsula as a whole. This is a lot less than the day before when around 2300 earthquakes were detected.
The scientific Advisory board for the civil protection services met on the 27th of December to go over the situation near Fagradalsfjall. GPS instruments and satellite interferograms show that the magmatic intrusion is limited to a dike intrusion by Fagradalsfjall, similarly as in February and March 2021 before the eruption onset on the 19th of March. In the event of a new eruption an onset time and location are highly uncertain, therefore it is not recommended to enter the area close to the previous eruption, until further developments.
In these circumstances there is more possibilities of falling rocks in the area and people are advised to be careful in steep hills and stay away from areas where there is a possibility of fallen rocks.
Yesterday around 400 earthquakes were detected. The seismic swarm is decreasing, the day before yesterday around 1300 earthquakes were detected on the Reykjanes peninsula. Yesterday at 10:22 a earthquake was detected east of Kleifarvatn, it was M3.7 and was felt in the capital area.
Source et photo : Vedur is
Italy , Stromboli :
WEEKLY NEWSLETTER, from December 20, 2021 to December 26, 2021 (issue date December 28, 2021)
SUMMARY OF ACTIVITY STATUS
In view of the monitoring data, it is highlighted:
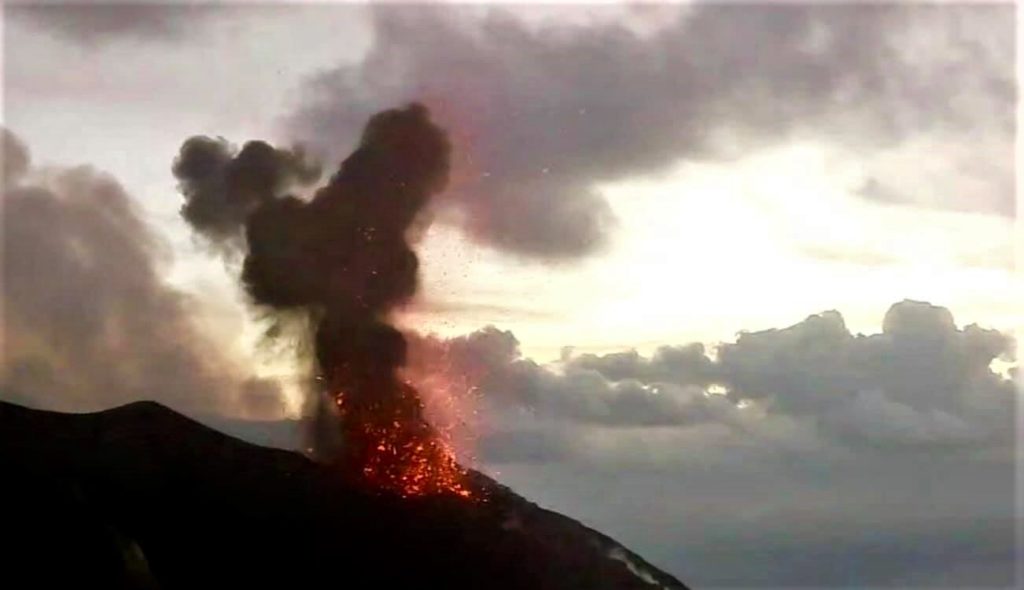
1) VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS: Explosive volcanic activity of Strombolian type coupled with splashing activity, with a total frequency of events / hour at a medium-low level and with an explosion intensity at a low and high level both at North than Center-South
2) SEISMOLOGY: The seismological parameters monitored do not show significant variations.
3) SOIL DEFORMATION: The island’s soil deformation monitoring networks did not show any significant changes to report for the period under review.
4) GEOCHEMISTRY: SO2 flux at an average level
The flux of CO2 from soils in the summit area shows a slight increase towards a level between high and very high.
The C / S value in the updated and validated plume in the plume is 18.7, settling to medium-high values.
There are no significant changes in isotope ratios compared to the previous sampling (November 15, 2021), settling on high values with an R / Ra of 4.41.
5) SATELLITE OBSERVATIONS: After the effusive event of November 26, the thermal activity observed by satellite showed low level anomalies.
VOLCANOLOGICAL REMARKS
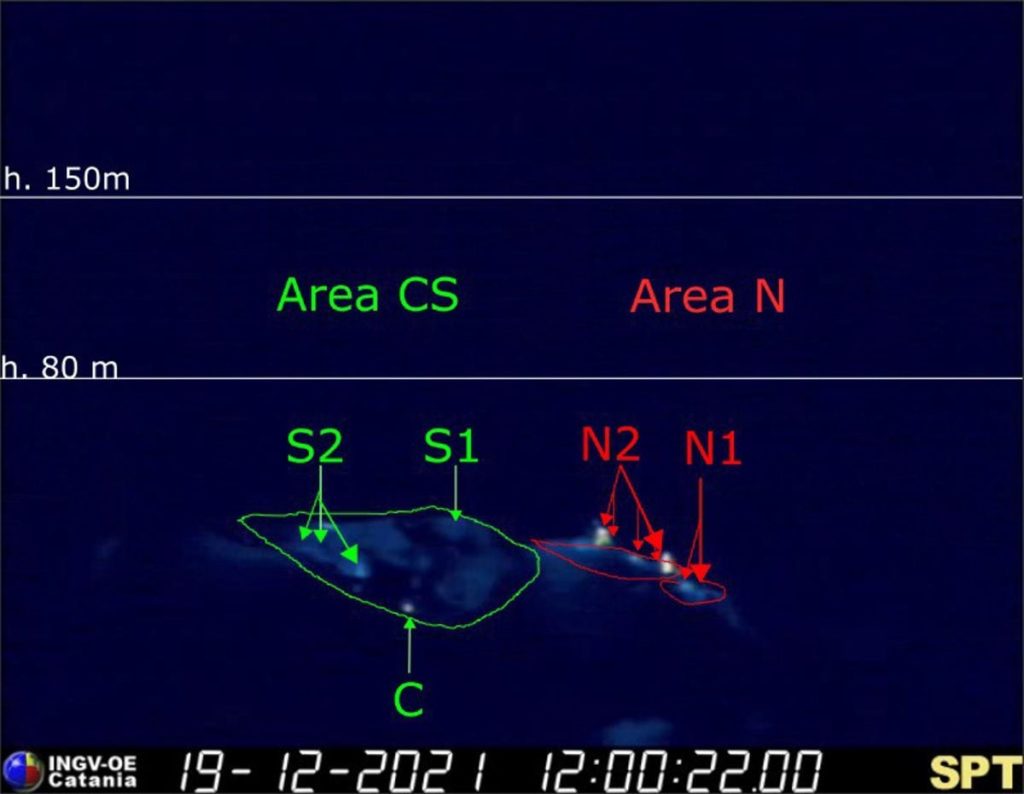
During the observation period, the eruptive activity of Stromboli was characterized by the analysis of the images recorded by the surveillance cameras of the INGV-OE (altitude 190m, Punta Corvi, altitude 400m and Pizzo). The explosive activity was mainly produced by 5 eruptive chimneys located in the area of the North crater and 3 located in the area of the Center-South crater; all the eruptive vents are located inside the depression which occupies the terrace of the crater.
During the observation period, the area of the North crater produced explosions of varying intensity from low to medium with mainly coarse materials (lapilli and bombs) mixed with a fine part (ash), with an intensity of low to high and with products up to ~ 170 m in height on the terrace of the crater which, episodically, produced abundant fallout along the Sciara del Fuoco (for example, on December 25, variable intensity which, during the phases of greater vigor, produced modest rheomorphic flows, the front of which remained in the upper part of the Sciara del Fuoco). Regarding the Center-Sud crater area, the explosive activity fluctuated between low to medium-low with a level of intensity from low, and episodically, up to a high level, and with products emitted up to ~ 190 meters on the crater terrace, mainly produced by the S2 vent with mostly fine material (ash) and secondarily coarse (lapilli / bombs), the S1 vent and sector C did not show significant explosive activity.
The frequency of explosive activity with regard to the North zone fluctuated between 2 and 8 events / h with the exception of December 25 when the network of cameras recorded a number of events / hour up to 18 e / h.
In the CS zone the frequency was between 0 and 2 e / h.
Source : INGV.
Photos : INGV , webcam.
Tonga Islands , Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai :
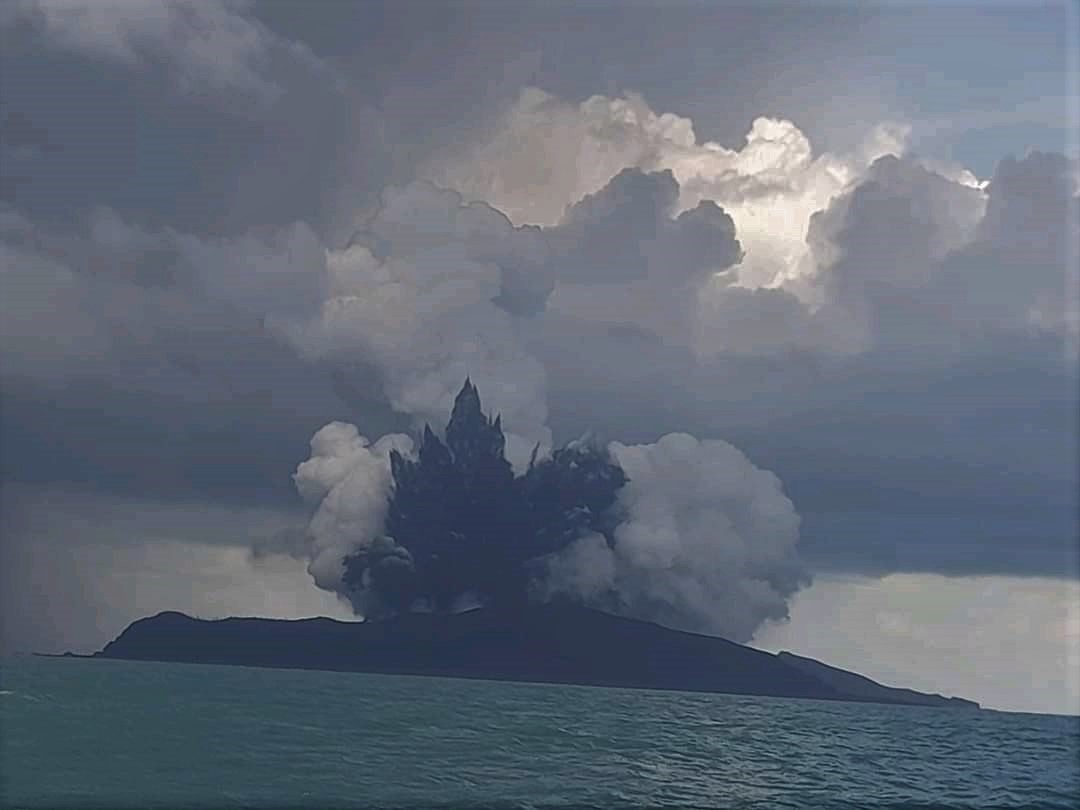
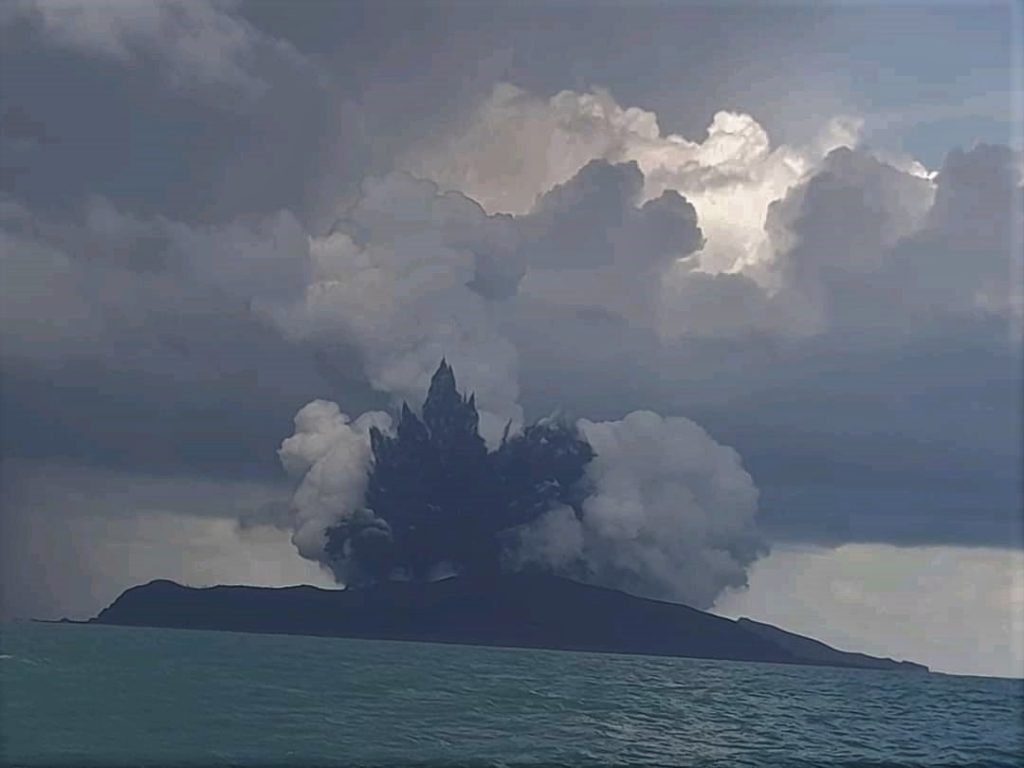
The eruption at Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai that began on 20 December continued through 28 December. According to the Wellington VAAC continuous gas-and-steam plumes with diffuse ash rose 6.1-12.2 km (20,000-40,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted NE and NNE during 22-23 December, based on pilot observations, satellite images, information from the Tonga Meteorological Office, and weather models. On 22 December Tonga Navy crew sailing near the island recorded Surtseyan explosions ejecting tephra 350 m high. The video confirmed that the vent was in the same area as the 2014 activity. According to a news article plumes of sulfur dioxide spread NNE over the Ha’apai, Vava’u, and Niuatoutapu island groups with the highest concentrations affecting the ‘Otumu‘omu‘a islands on 23 December.
Plumes became intermittent by 24 December rising to 10.4 km (34,000 ft) a.s.l. and occasionally as high as 12.2 km. Tonga Geological Services warned the public to stay outside of a 5 km radius of the vents. According to Tonga’s Lead Geologist, satellite images from 25 December showed that the island had grown 300-600 m on the E side, and ash was falling within a 10 km radius. During 25-28 December the gas-and-steam plume rose 9.1-12.2 km (30,000-40,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted N and NE; the lower part of the plume contained ash and rose as high as 3 km (10,000 ft) a.s.l.
Ashfall was confined to the vicinity of the volcano. Tonga Geological Services reported that during 27-28 December clouds of gas and steam drifted E across the ‘Otu Mu’omu’a Islands of Ha’apai at altitudes of 1-18 km (3,300-59,000 ft) a.s.l.; they warned residents to protect water reservoirs because rain may be acidic or contain traces of ash, though the plumes were predominantly drifting at high levels. One flight to Tonga was canceled on 28 December, for the second time since the eruption started.
Sources : GVP .
Photos : Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai /Ioana Kalo Sugar via Wulkany świata
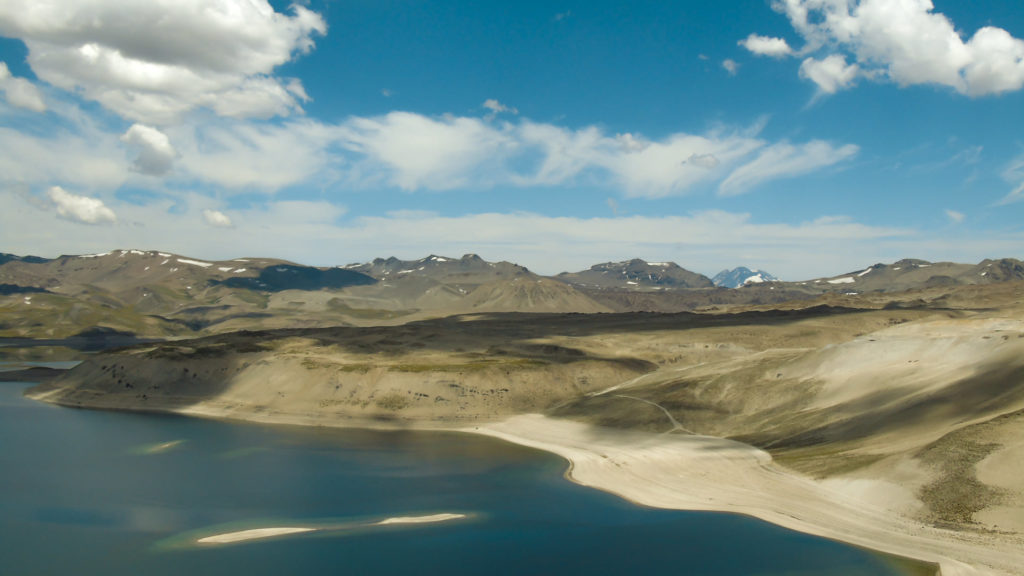
Chile , Laguna Del Maule :
SERNAGEOMIN reported that inflation at Laguna del Maule continued in an area SW of the lake during 1-15 December, though deformation had been decreasing since October with a with a maximum rate of 1.88 centimeters per month. Deformation rates during November and December were comparable to those recorded prior to 2019. The number of volcano-tectonic events had also decreased; the largest event was a M 2.3 located 4.1 km ESE from the center of the lake at a depth of 6.1 km. The Alert Level for Laguna del Maule was lowered to Green, the lowest level on a four-color scale, on 24 December. ONEMI canceled the Yellow Alert for San Clemente, and reminded the public to stay 1 km away from the area producing anomalous carbon dioxide emissions, about 5 km SW of the lake’s shore.
The Laguna del Maule volcanic complex includes a 15 x 25 km caldera with a cluster of small stratovolcanoes, lava domes, and pyroclastic cones of Pleistocene-to-Holocene age. The caldera lies mostly on the Chilean side of the border, but partially extends into Argentina. Fourteen Pleistocene basaltic lava flows were erupted down the upper part of the Maule river valley. A cluster of Pleistocene cinder cones was constructed on the NW side of Maule lake in the northern part of the caldera. The latest activity produced an explosion crater on the E side of the lake and a series of Holocene rhyolitic lava domes and blocky lava flows that surround it.
Sources : GVP , Sernageomin.
Photo : Franco Vera.
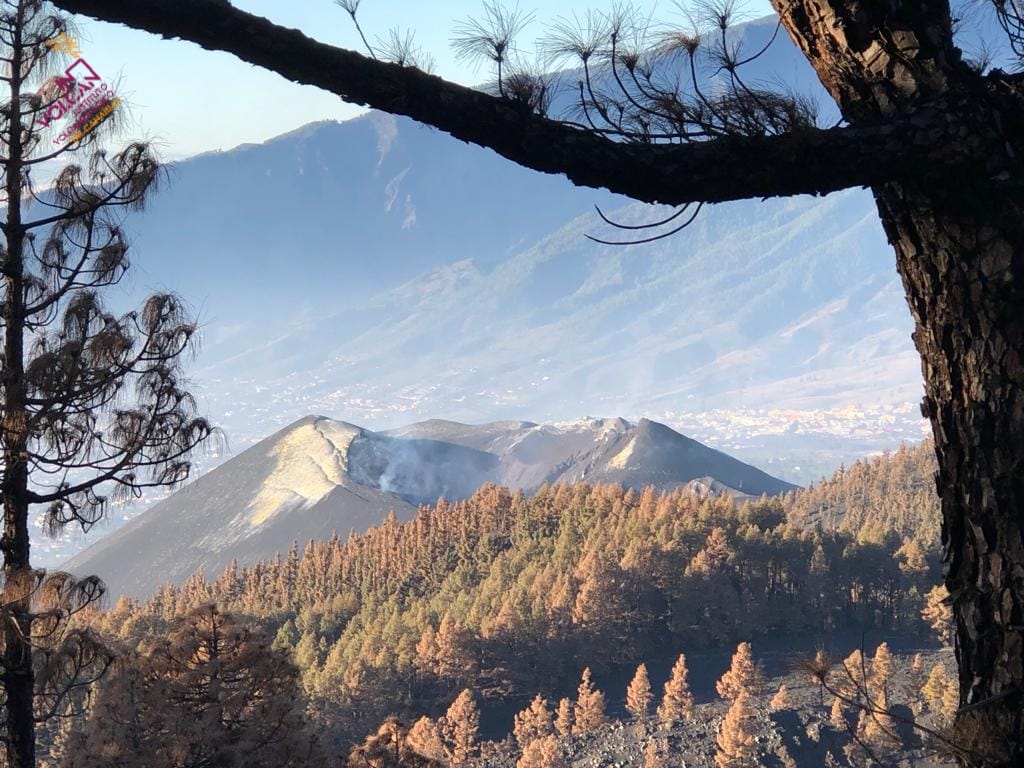
Spain / Canaries , Cumbre Vieja :
December 29, 2021 09:00 UTC. Post-eruptive activity on Cumbre Vieja, La Palma.
Since the last press release (the 27th at 9:00 UTC), 14 earthquakes have been located on the island of La Palma, none of them have been felt by the population.
The magnitudes are between 0.9 and 2.3 (mbLg).
The localization of hypocenters continues under the central area of Cumbre Vieja in the same areas as the previous days. 7 earthquakes were located at depths between 11 and 16 km and 7 earthquakes at depths less than 5 km. No earthquake was located at depths greater than 16 km.
The island’s network of permanent GNSS stations does not show significant deformations that could be associated with volcanic activity.
Yesterday, the height of the cone was measured, obtaining a value of 1,121 m on the sea level.
Source : IGNes.
Photo : Involcan.