May 31 , 2021.
Italy / Sicily , Etna :
Press release on ETNA activity, May 30, 2021, 08:35 (06:35 UTC)
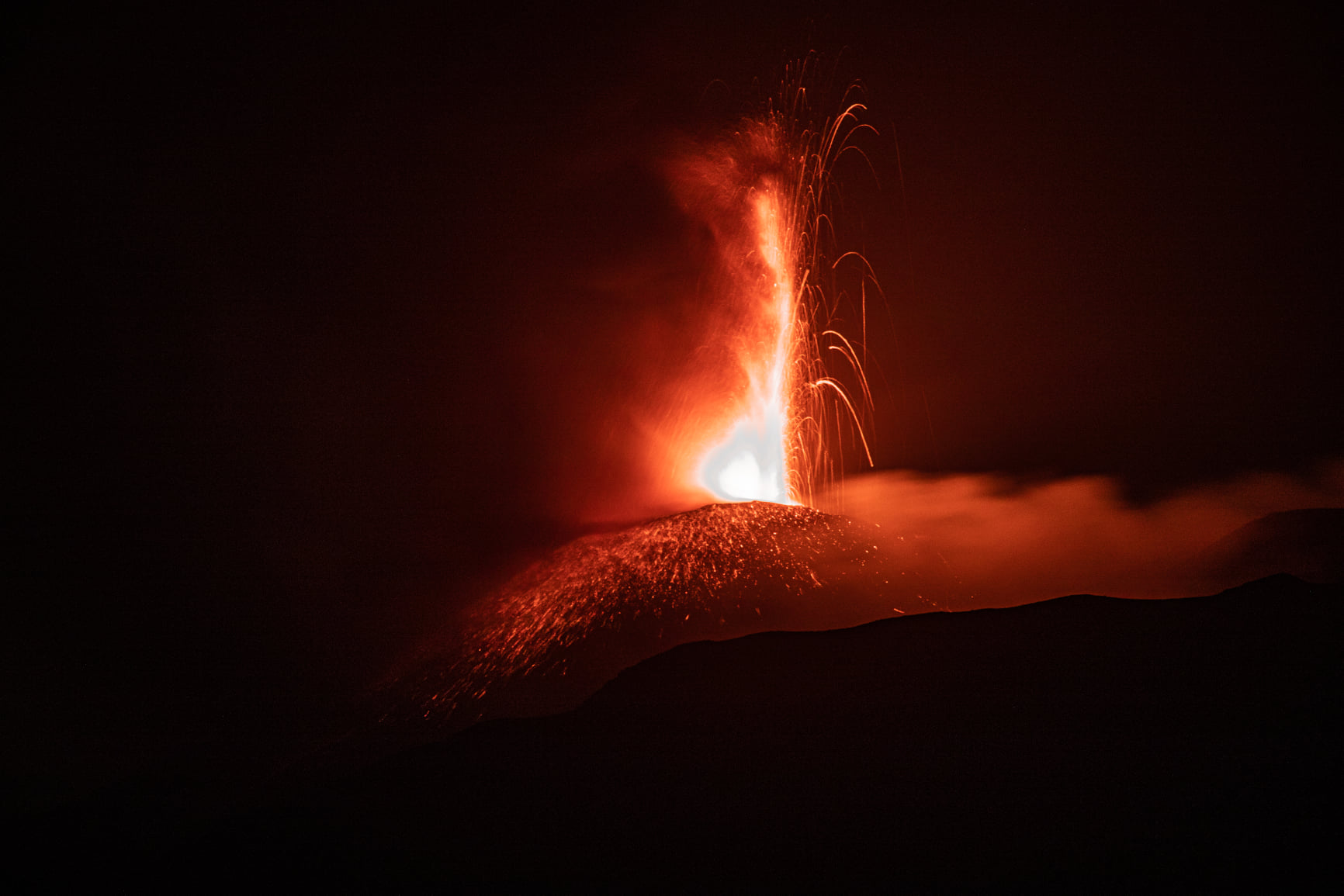
The National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology, Osservatorio Etneo, reports that as of 5:45 UTC, the lava fountain of the Southeast Crater has ceased. Due to weather conditions, the observation of the eruptive cloud was discontinuous. Where observation was possible, analysis of CCTV footage shows that the eruptive cloud reached a height of about 6.5 km above sea level. The fountain also produced an overflow of lava along from the flank of the Southeast Crater, which extended to the southwest. At the moment, there is no explosive activity at the Southeast Crater.
From around 05:40 UTC, we observe a rapid decrease in the average amplitude of the volcanic tremor whose values around 06:20 UTC have returned to average levels. The center of gravity of the sources of the volcanic tremor is located in the region of the Southeast Crater at an altitude of about 2900 m above sea level.
At around 5:40 am UTC, a decrease in infrasound activity located at the Southeast Crater was also observed. Analysis of the soil deformation data shows stabilization of the inclinometric signals from around 06:00 UTC, after the disturbance which reached a maximum amplitude of about 0.3 microradians around 05:40 UTC. There are no significant variations from the signals from GNSS network stations.
Further updates will be communicated shortly
Source : INGV.
Photo : Guide Alpine Vulcanologiche Etna
Alaska , Semisopochnoi :
51°55’44 » N 179°35’52 » E,
Summit Elevation 2625 ft (800 m)
Current Volcano Alert Level: WATCH
Current Aviation Color Code: ORANGE
Low-level ash emissions resumed today around 1745 UTC (0945 AKDT) and were accompanied by an increase in seismic tremor (continuous shaking). They are visible in geostationary satellite data and are continuing through 2050 UTC (1250 AKDT), Seismic tremor remains elevated at present and intensity varies. The ash cloud is moving towards the south over Amchitka Island at an altitude of about 5000 ft asl, This height is based on wind trajectory and on observations from field crews yesterday during similar periods of ash emission. High-spatial resolution data from yesterday afternoon show strongly elevated surface temperatures in the active (northernmost) vent of Mount Cerberus. Infrasound data show no evidence of strong explosive events. Seismicity over the past day has been characterized by periods of elevated tremor that has waxed and waned over periods of hours, interspersed with times of much lower amplitude.
Semisopochnoi, view of Cerberus from the south. Image courtesy of Ian L. Jones, Department of Biology, Memorial University
Small eruptions producing minor ash deposits within the vicinity of the active north crater of Mount Cerberus and ash clouds under 10,000 ft above sea level are typical of recent activity at Semisopochnoi. Small explosions may occur undetected by regional infrasound sensors and cloudy weather conditions.
Semisopochnoi is monitored by a local seismic network, satellite data, regional infrasound, and lightning detection instruments. An infrasound array on Adak Island may detect explosive emissions from Semisopochnoi with a slight delay (approximately 13 minutes) if atmospheric conditions permit.
Source : AVO
Photo : Ian L. Jones, Département de biologie, Université Memorial .
Italy , Stromboli :
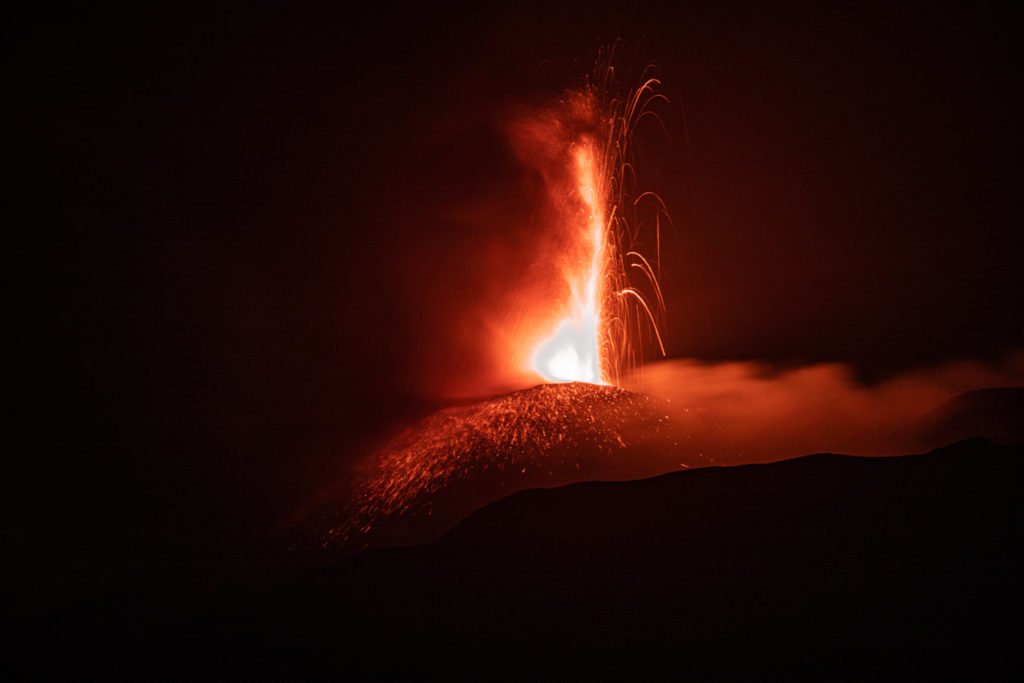
Press release on the activity of Stromboli, May 31, 2021, 00:14 (22:14 UTC).
The National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology, Osservatorio Etneo, announces that a projection activity continues from the active vents in the area of the North crater. Analysis of the CCTV images shows a slight decrease in this activity from around 9:00 p.m. UTC. No change in Strombolian activity is observed in the areas of the North and Center-South craters.
The trend of the mean amplitude of the volcanic tremor remains at medium-low values comparable to those of the previous press release. The frequency and amplitude of transients attributable to explosive events do not show significant variations.
The analysis of the deformations of the ground does not show any significant changes on the stations of the inclinometric and GNSS networks.
Further updates will be communicated shortly
Source : INGV.
Photo : Viaggi e Vulcani
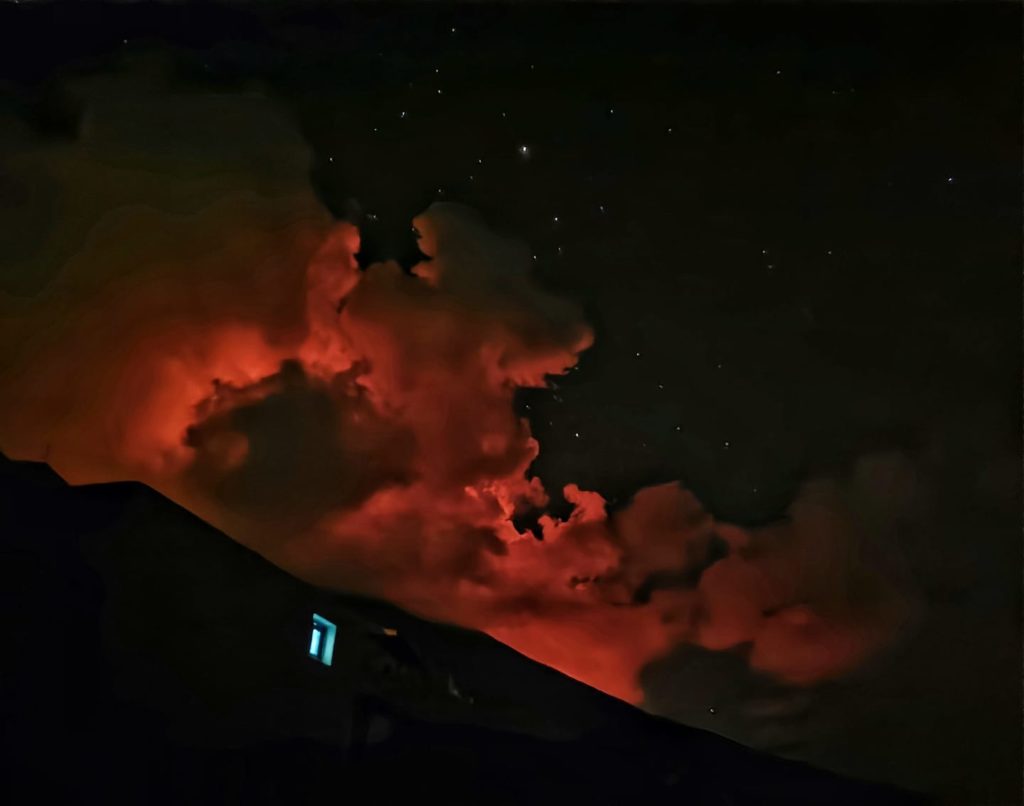
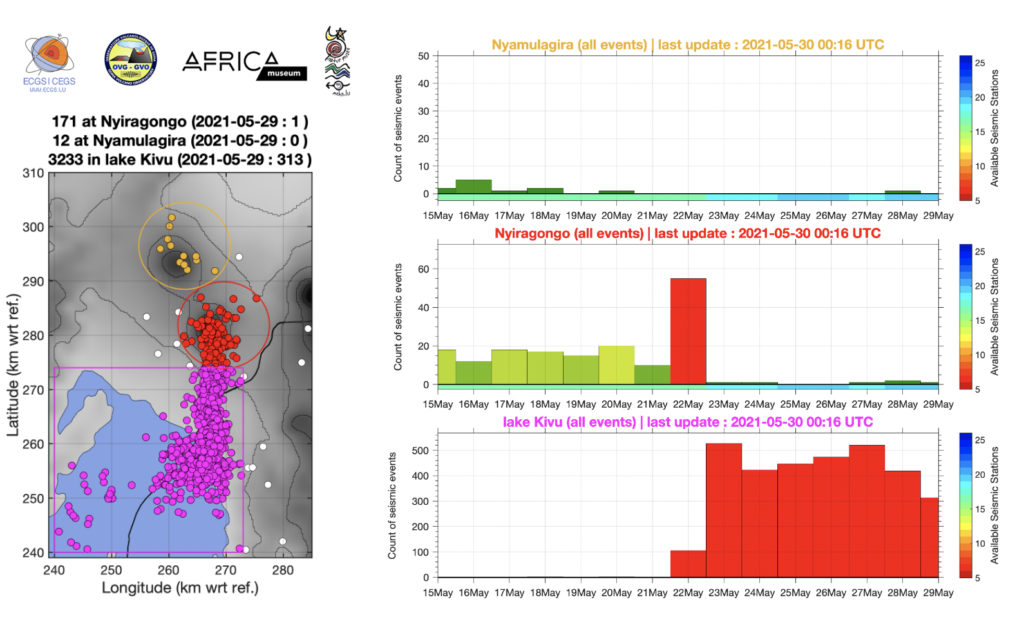
Democratic Republic of Congo , Nyiragongo :
2021-05-29:
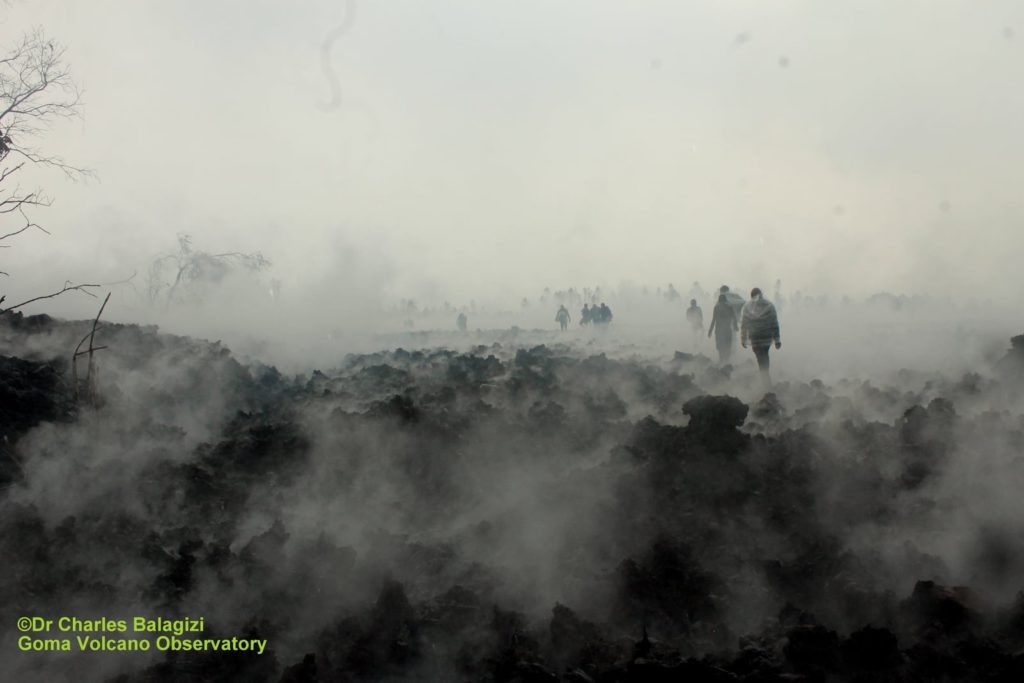
Current seismicity and ground deformation data continue to indicate the presence of magma under the urban area of Goma with an extension under Lake Kivu. Seismicity and deformation continue. The number of earthquakes detected in 24 hours decreases slightly, as do the deformation rates. However, this decrease in the phenomenology at this stage cannot yet be interpreted as the end of activity. During phases of volcanic activity, periods of higher seismic activity often alternate with phases of lower seismicity. seismic activity often alternate with phases of lower seismicity. Seismicity above the baseline is always recorded. These observations are always consistent with the presence of magma at depth. Ash fallout may occur as a result of the collapse of parts within the crater. The data on the stability of Lake Kivu do not currently show any significant The stability data for Lake Kivu do not currently show any significant change (the latest available data is from 27 May 2021).
Recent high-resolution INSAR radar images showed that the ground south of the volcano had risen several centimeters during or since the eruption. Vertical displacement is highest in the Goma city area, where numerous cracks in the ground have become visible.
This raises concerns that a possible (not necessarily the most likely) scenario is the formation of a new dyke – or lava-filled fissure – which could open up in this area and produce a potentially catastrophic second flank eruption.
It is hoped that it will be the same this time around and that the seismic activity will gradually decrease and not be followed by further eruptions of lava at low altitude.
Source : georiska.africamuseum.be , OVG .
Photos : Georiska , Charles Balagizi .
Iceland , Geldingadalur :
The fissure eruption in the W part of the Krýsuvík-Trölladyngja volcanic system, close to Fagradalsfjall on the Reykjanes Peninsula, continued during 19-25 May. Lava fountains rose from the fifth vent and continued to feed the lava flows. According to news sources, lava during 20-21 May overtook the eastern earthen dam that had been constructed at the head of Nátthaga valley in an attempt to prevent flows from descending towards Highway 427 (Suðurstrandarvegur) to the S, and burying fiber optic cables. By 22 May the lava was about 2.5 km from the road. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange due to the lack of ash and tephra emissions. Authorities warned of increased gas emissions hazards.
The lava flow has passed the dam and is heading towards the Nátthaga valley – RUV photo
Lava cools quickly and solidifies in open channels
Lava flows in Meradali, much in Geldingadalur and then in Syðri-Meradalur. From Syðri-Meradälar, which has been called the Anonymous Valley, it flows into Nátthaga through open, incandescent canals. Under these conditions, the heat loss is very important. For every mile the lava travels, it loses 100 to 300 degrees Celsius and doesn’t go far before solidifying. For this reason, the progress of the lava in Nátthaga has been slow. But Þorvaldur says that by combining the open channels into one or two closed channels, the heat loss would be less than one degree per kilometer. If this were to happen, the lava would pass through Nátthaga relatively quickly.
Source : GVP , RUV.
Photo : RUV.
Ecuador , Sangay :
Sunday May 30, 2021
A high energy tremor continues to be recorded at the SAGA seismic station. This type of signal is similar to that observed during the most active pulses of the current eruptive period of the volcano. According to our simulations, in addition to the province of Chimborazo, the ash cloud could reach the provinces of Bolívar, Los Ríos and Guayas and there is a possibility of ash fall in these provinces. Macas residents continue to report window vibrations due to the current eruptive process. The IG-EPN continues to monitor the event and will notify in a timely manner if any changes in the seismic signals are detected. The Institute of Geophysics is monitoring and any news will be reported.
DAILY REPORT ON THE STATE OF SANGAY VOLCANO.
Surface activity level: High, Surface trend: No change.
Internal activity level: High, Internal trend: No change.
Seismicity: From May 29, 2021, 11:00 a.m. to May 30, 2021, 11:00 a.m .:
Explosion (EXP) 2
Long period (LP) 74
Tremors of emission (TREMI) 4
Lahars: 1
Emission column / ash:
There are no reports.
Rains / Lahars:
During the night, several episodes of rain were recorded which generated a slight increase in the amplitude of the signal from the reference station. ** In the event of heavy rains, these could re-mobilize the accumulated material, generating mudslides and debris that would descend on the sides of the volcano and flow into the adjacent rivers. *
Other monitoring parameters:
FIRMS recorded 10 thermal alerts on the Sangay in the last 24 hours. MIROVA has recorded 1 low thermal alert on the Sangay during the last 24 hours.
Observation:
Yesterday afternoon, the volcano partially cleared, however, no gas and ash emissions were observed. Until the close of this bulletin, no ash fall report has been recorded.
Alert level: yellow.
Source et photo : IGEPN.