January 20 , 2021 .
Italy , Stromboli :
Weekly bulletin from January 11, 2021 to January 17, 2021, (publication date January 19, 2021)
SUMMARY OF THE STATE OF ACTIVITY
In the light of surveillance data, it is highlighted:
1) VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS: Normal explosive volcanic activity of Strombolian type with projection activity in the North zone. The total frequency of events showed values between average levels (12 events / h) and medium-high levels (17 events / h). The intensity of the explosions was mainly medium-low in the North crater area and medium-high in the Center-South area.
2) SEISMOLOGY: The seismological parameters do not show significant variations.
3) DEFORMATIONS: No significant change recorded by the tilt and GNSS networks.
4) GEOCHEMISTRY: SO2 flux: medium level
C / S Ratio – There is no updated data to date: the last available values referring to 06-12-2020 are at average levels (C / S = 12.1).
The isotopic ratio of helium is at fairly high values (R / Ra = 4.4 compared to the sampling of December 21).
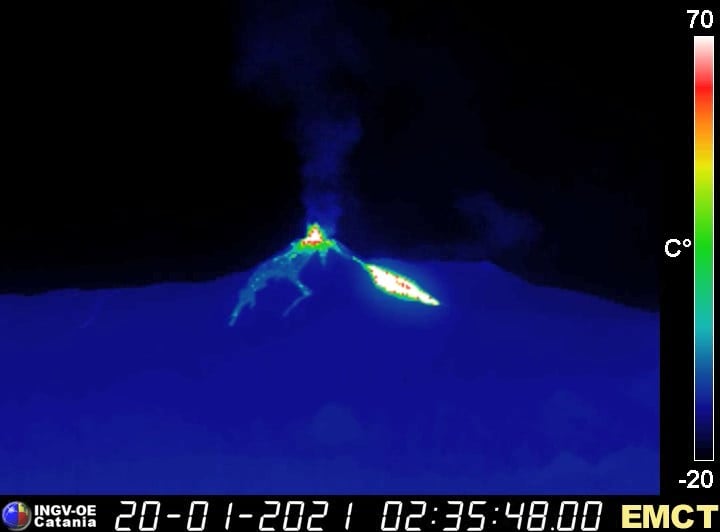
5) SATELLITE OBSERVATIONS: The thermal activity in the summit area is at a low level.
VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS
During the period under observation, the eruptive activity of Stromboli was characterized by the analysis of the images recorded by the surveillance cameras INGV-OE located at 190 m altitude, Punta Corvi and 400 m.
Due to the unfavorable weather conditions, the images from the surveillance cameras of January 12-14 and 16 were not sufficient for a correct description of the eruptive activity.
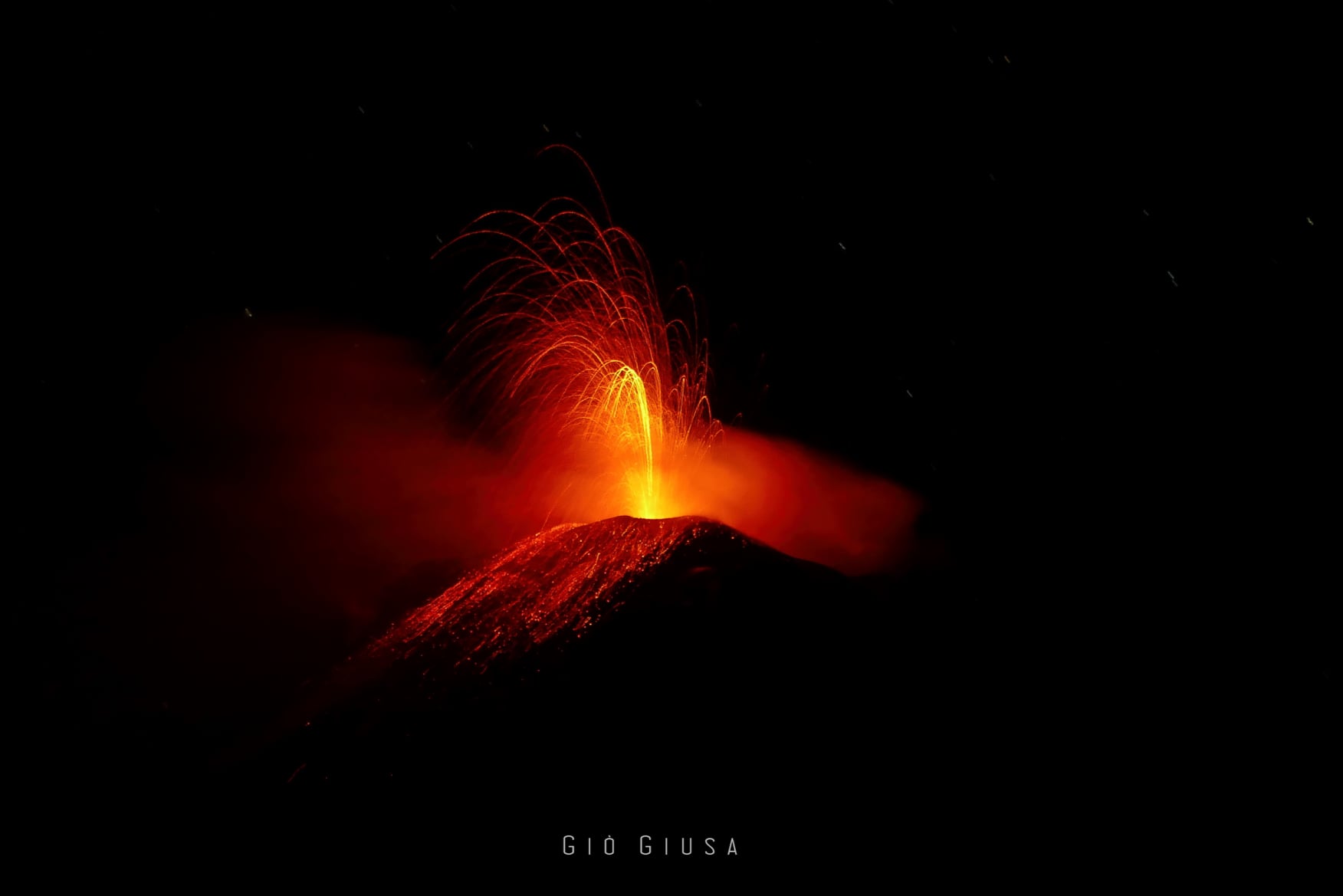
In the area of the North crater, the N1 crater, with two emission points, produced low intensity explosions (less than 80 m high) emitting coarse materials (lapilli and bombs) sometimes mixed with fine materials (ash ). The N2 vent, at four emission points, showed mainly low and medium intensity explosive activity (less than 150 m in height) emitting coarse materials. In addition, projection activity was observed at the mouth of the N2 which for long periods was intense, reaching its peak on January 11 and 17. The average frequency of the explosions varied from 7 to 9 events / h.
In the Center-South area, the explosions were produced by at least two vents, one of which produced only ash emissions and the other only produced large volumes of medium to high intensity coarse incandescent material (the products reached 250 m high). The explosive activity showed hourly frequency values ranging from 7 to 8 events / h.
PRESS RELEASE ON STROMBOLI’S ACTIVITY [UPDATE n. seven]
The National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology, Osservatorio Etneo, reports that the monitoring networks recorded the return of parameters to normal activity at 09:35 (08:35 UTC).
Further updates will be communicated shortly.
Source : INGV.
Photos : INGV , Webcam.
Italy / Sicily , Etna :
Weekly bulletin from January 11, 2021 to January 17, 2021, (publication date January 19, 2021)
SUMMARY OF THE STATE OF ACTIVITY
In the light of surveillance data, it is highlighted:
1) VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS: Strombolian activity of variable intensity associated with splashing, the emission of lava by overflow and the production of ash from the Southeast Crater. Intra-crater strombolian activity at the Northeast crater, at the Voragine and at the Bocca Nuova with rare and diluted ash emissions.
2) SISMOLOGY: Moderate fracturing activity, medium to high tremor amplitude.
3) INFRASONO: moderate infrasound activity
4) DEFORMATIONS: No significant variation to report for the deformations measured by the tilt and GNSS networks unless there is a minimum variation evident at the inclinometric station of ‘Crater del Piano’ observed in conjunction with the onset of the eruptive event at the South-East crater on January 17th.
5) GEOCHEMISTRY: SO2 flux: medium level
HCl flow occurs at an average level.
The CO2 flux from the soil is at average levels.
The partial pressure of dissolved CO2 does not show significant changes.
There are no updates for the C / S report.
The helium isotope ratio is at average values (last update 08/01/2021).
6) SATELLITE OBSERVATIONS: The thermal activity in the summit area is at a medium-low level.
VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS
The monitoring of the volcanic activity of Etna during the week in question was carried out by analyzing the images of the network of surveillance cameras of the INGV, Osservatorio Etneo (INGV-OE) and by means of an inspection carried out in the summit area by INGV-OE staff on January 14. Weather conditions during the week partly made the observation of volcanic activity discontinuous.
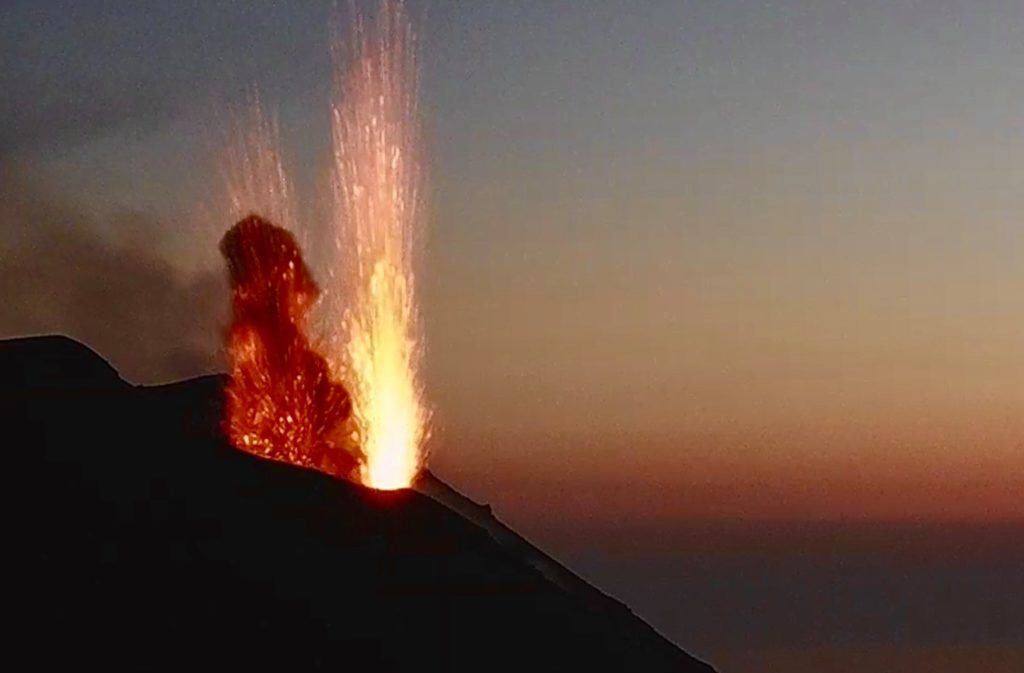
The Southeast Crater (SEC), during the whole week, did not show significant variations compared to the previous week and produced explosive activity varying in intensity and frequency with the launching of pieces of lava falling on the flanks of the crater, associated with ash emissions. This activity was mainly produced by two bites located in the East zone of the SEC complex, and marginally by one in the South zone.
The explosive activity was associated with intense and discontinuous splashing produced by the vents in the East Zone. This splash on January 17 produced an overflow of lava that moved on the eastern flank of the Southeast Crater (SEC) towards the Valle del Bove.
In detail, the event has evolved into three phases:
(i) at ~ 06:00 GMT, a small overflow begins which remains confined to the upper area of the cone);
(ii) at ~ 06:40 GMT the overflow appears to be well fed and the lava flow begins to expand slowly, staying near the top of the crater, with material loosened from the front of the flow reaching the base of the cone ;
(ii) at ~ 07:19 GMT an increase in the supply of the lava flow was observed, the front of which at 09:00 GMT had reached an altitude of about 3000 meters above sea level. Additionally, at 07:19 GMT, a probable ash emission associated with a breach in the rim of the crater was observed.
From ~ 12:30 GMT due to the cloud cover, it was not possible to follow the evolution of the phenomenon; the latest available data indicated that the lava front was stable at an elevation of about 3,000 meters and that the flow appeared to be poorly fed. The first data available on January 18 at 5.30 p.m. GMT shows that the lava flow was no longer fed and was cooling.
PRESS RELEASE ON ETNA’S ACTIVITY [UPDATE n. 121]
The National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology, Etneo Observatory, reports that from around 00:40 GMT a new lava overflow is observed on the north side of the Southeast crater. There is also moderate Strombolian activity still at the Southeast Crater.
With regard to the volcanic tremor, an increase in amplitude is noted which reaches high values. The infrasound activity is modest. Etna’s GPS network data does not show significant variations.
Further updates will be communicated shortly.
Source : INGV
Photos : Gio Giusa , INGV.
Iceland , Reykjanes Penisula :
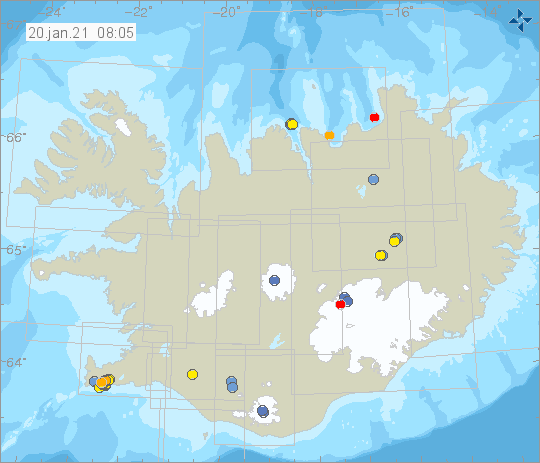
Around 570 earthquakes were detected by the IMO’s SIL seismic network this week, much fewer than the previous week when around 790 earthquakes were detected. The biggest difference between the weeks is considerably fewer earthquakes in Reykjanes peninsula this week compared to last week.
The largest earthquake of the week was M3.1 on 13. January at 15:23 on Reykjanes Ridge. Two other earthquakes M3 were also detected this week, the first at 15:34 on 13. January on Kolbeinsey Ridge and the other at 23:31 on 16. January in the Katla caldera in Mýrdalsjökull. One small earthquake was detected in Hekla volcano and five in Grímsvötn.
Source : Vedur .
Colombia , Nevado del Ruiz :
Nevado del Ruiz volcano activity level bulletin.
The activity level continues at Yellow Activity Level or (III): changes in the behavior of volcanic activity.
Regarding the monitoring of the activity of the Nevado del Ruiz volcano, the COLOMBIAN GEOLOGICAL SERVICE reports that:
Seismicity generated by rock fracturing has decreased in the number of earthquakes and in the seismic energy released, compared to the previous week. This seismic activity was located mainly in the south-eastern sector of the volcano and in the Arenas crater. To a lesser extent and in a dispersed manner, it recorded a seismicity of this type in the North, North-East, South and South-West sectors of the volcano. The depths of the earthquakes ranged from 0.7 to 7.0 km. The highest magnitude recorded during the week
was 0.6 ML (local magnitude), corresponding to the earthquake that occurred on January 15 at 4:31 p.m. (local time), located 0.6 km to the South-South-West, at a depth of 1.7 km.
Seismicity related to fluid dynamics inside volcanic conduits increased in the number of events and in the seismic energy released, compared to the previous week. This seismic activity was characterized by the occurrence of continuous volcanic tremors, tremor pulses, earthquakes of long and very long period type, which presented variable energy levels and spectral content.
In the past week, the MIROVA portal reported a low-energy thermal anomaly on the volcano.
Source : SGC .
Photo : Auteur inconnu .
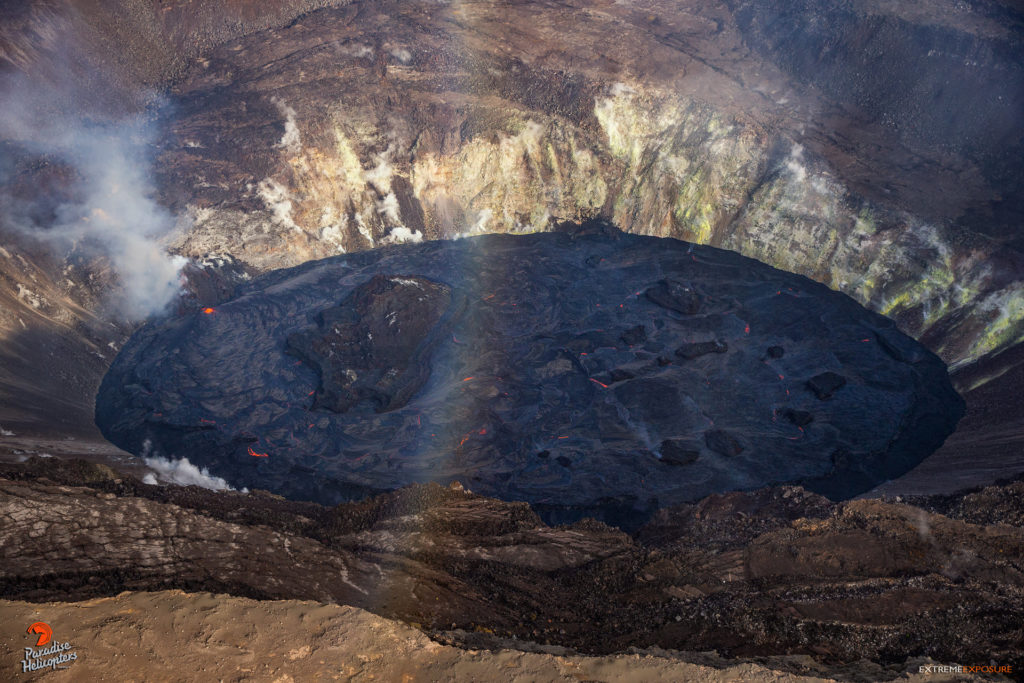
Hawaii , Kilauea :
19°25’16 » N 155°17’13 » W,
Summit Elevation 4091 ft (1247 m)
Current Volcano Alert Level: WATCH
Current Aviation Color Code: ORANGE
Activity Summary:
Kīlauea Volcano is erupting. Lava activity is confined to Halemaʻumaʻu with lava erupting from a vent on the northwest side of the crater. Yesterday evening, January 18, the lava lake was about 202 m (663 ft) deep and remains stagnant over its eastern half. SO2 emission rates remain elevated.
Summit Observations:
The most recent sulfur dioxide emission rate measurements from January 14, show an increase to about 4,700 t/d—within the range of emission rates from the pre-2018 lava lake (3,000–6,500 t/d). The summit tiltmeters recorded neither inflation or deflation over the past few days. Seismicity remains elevated but stable, with steady elevated tremor and a few minor earthquakes.
Halemaʻumaʻu lava lake Observations:
Low fountaining from the west vent supplies a channel of lava which is pouring into the lava lake within Halema‘uma‘u crater.
The active western half of the lava lake was about 202 m (663 ft) deep yesterday evening (Jan. 18) while the stagnant eastern half of the lake remains several meters (yards) lower. The whole lava lake—including the stagnant eastern half—is perched at least 1–2 m (yards) above the crust between the perched lake and the crater wall.
All of the islands have been stationary over the past week, frozen in the eastern stagnant portion of the lava lake. On January 12, the west end of the island was measured as 8 m (26 ft) above the lava lake surface, with the highest point at 23 m (75 ft) above the surface.
Source : HVO.
Photo : Bruce Omori .