September 13 , 2018.
Sicily / Italy , Etna :
37.748°N, 14.999°E
Elevation 3295 m
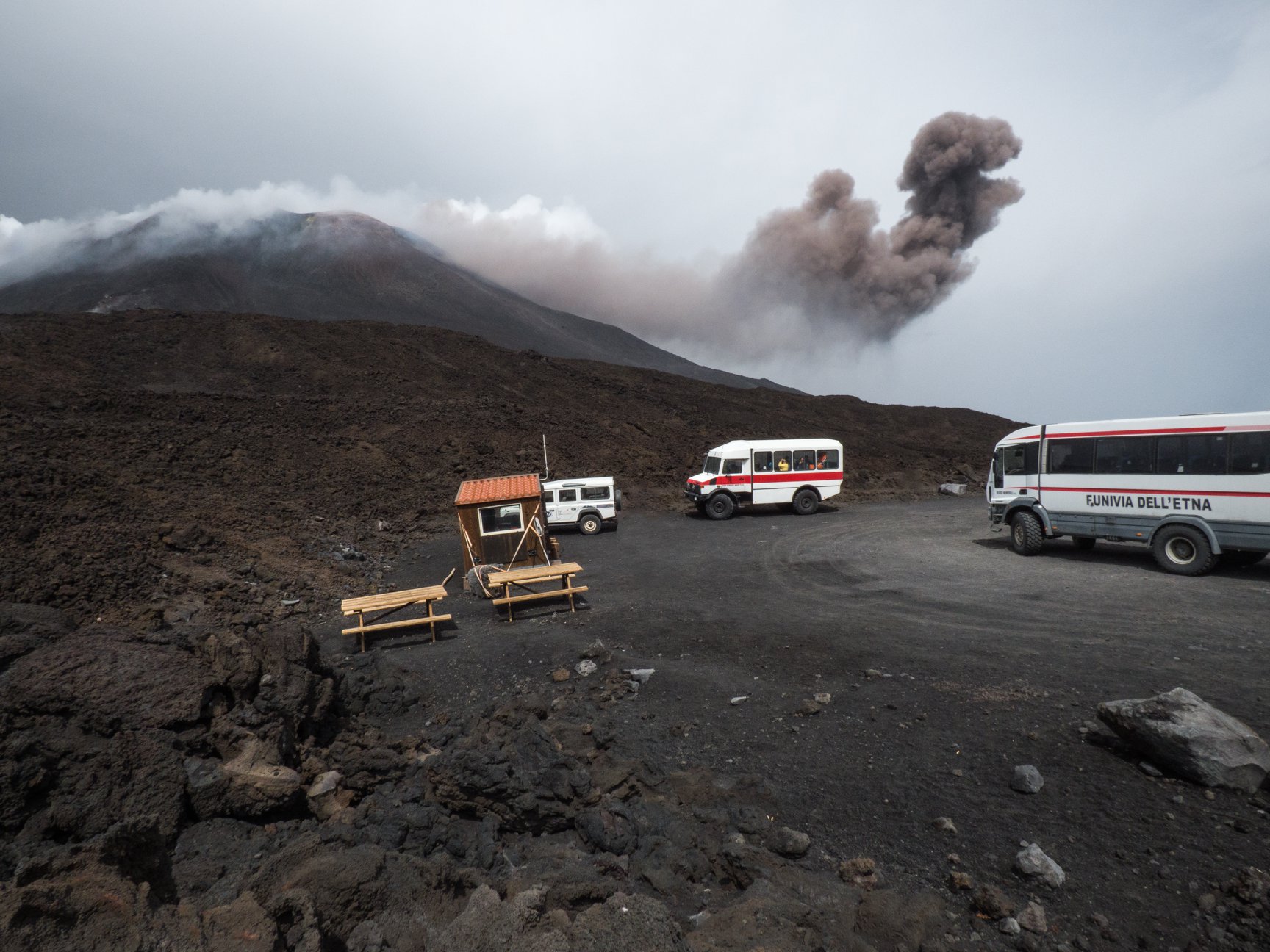
INGV reported that during 3-9 September activity at Etna was characterized by gas emissions at the summit craters, with periodic Strombolian activity from vents in Bocca Nuova, Northeast Crater (NEC), and New Southeast Crater (NSEC). A few Strombolian explosions at NSEC were recorded on 5 September; an explosion at 0536 generated an ash plume that produced local ashfall around the vent and in the Valle del Bove, and quickly dispersed.
A similar but less intense event occurred earlier that day, at 0316. Similar Strombolian events continued during 6-9 September, at intervals of a few hours. Strombolian activity at the N vent (BN-1) in Bocca Nuova occurred at 3-5-minute intervals, ejecting incandescent material that fell within the crater confines. Gas emissions were sometimes punctuated with ash emissions. Intense degassing was characteristic of the second vent (BN-2). Strombolian activity occurred at NEC, and a few times explosions were accompanied by ash emissions.
Source: Sezione di Catania – Osservatorio Etneo (INGV) , GVP.
Photo : Gio Giusa
Iceland , Öræfajökull :
Iceland’s second deadliest volcano stirs: A sharp earthquake swarm detected in Öræfajökull
Several relatively strong earthquakes have been detected in one of the most powerful volcanoes in Iceland sinc yesterday. A total of 15 quakes have been recorded in the volcano in the past 48 hours, including two significant 2+ quakes: A 2.7 magnitude quake yesterda, Tuesday evening, at 20:13 and a second 2.6 magnitude quake today Wednesday at 12:45.

According to the Seismic Monitoring System of the IMO the epicenter of yesterday’s 2.7 magnitude quake was in the Southeastern part of the volcano’s caldera at a depth of only 100 m (330 ft), while today’s 2.6 magnitude tremor had an epicenter in the norther edge of the caldera at a depth of 2.2 km (7,200 ft) below the surface. Historically earthquakes have been extremely rare in Öræfajökull. Recently the volcano has been showing significantly greater levels of activity.
Öræfajökull is the southernmost part of Vatnajökull glacier. Its summit, Hvannadalshnjúkur, is the tallest peak in Iceland, standing at an elevation of 2,110 meters (6.920 ft). Öræfajökull glacier covers a giant volcano which last erupted in 1727. Following this eruption the volcano was completely dormant until a couple of years ago when it started to show activity again.
Öræfajökull erupts in steam-blast eruptions, also known as phreatic eruptions. In addition to the 1727 eruption it has erupted only once since Iceland was settled in the Viking Age. In 1362 Öræfajökull erupted in the second deadliest eruption in Icelandic history, destroying one of the most prosperous farmland regions in South Iceland, killing all inhabitants and livestock at 20-40 farms.
The volcano is not particularly active, erupting at an interval of several hundred years. The 1362 eruption is considered to be the largest tepthra eruption in the world in the last 1000 years.
Source : icelandmag.is
Chile, Puyehue – Cordon Caulle :
During the evaluated period, a total of 104 seismic events were recorded, of which 5 were classified as long-lived earthquakes (LPs) in relation to fluid dynamics within the volcanic edifice. The event of greater energy had a reduced displacement value (DRc) equal to 130 cm2. 99 volcano-tectonic (VT) earthquakes associated with rock fracturing processes were also recorded. The largest energy event had a local magnitude (ML) of 1.7, and was located 2.6 km north – northwest of the 2011 emission center at a depth of 4.6 km. .
The images provided by the IP cameras installed around the volcano do not show any superficial changes.
According to the data provided by three GNSS stations, we observe that the inflationary process reported previously is continuing. The maximum rate of horizontal variation recorded by the permanent network is 0.64 cm / month and the vertical rate of 0.28 cm / month for the station closest to the point of maximum deformation.
No sulfur dioxide (S02) emissions have been reported in the area’s atmosphere near the volcanic building, according to data published by the Ozone Observatory Sulfur Dioxide Group (http: // mon2.gsfc.nasa.gov/). ) and the National Information and Satellite Data Service on the Environment (NESDIS) (http://satepsanoine.nesdis.noaa.gov).
No thermal warning was reported in the area associated with the volcanic complex during the period, according to data processed by the mean infrared observation of volcanic activity (MIROVA) (http://www.mirovaweb.it /) and Temporal Thermal Monitoring of global hot spots (MODVOLC) (http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/).
The seismicity remains similar to those recorded in recent months, the vast majority being under the last active center in 2011. The general picture developed in recent months, the signs of deformation of the volcanic construction and the presence of a residual magmatic body, set up during the 2011 superficial eruption, are indicators of the development of processes that can lead to the imbalance of the volcanic system.
Because of the above, the volcanic warning is kept at the level:
YELLOW LEVEL: Changes in the behavior of volcanic activity – Probable time for an eruption: WEEKS / MONTH.
Source : Sernageomin.
Photos : Sernageomin .
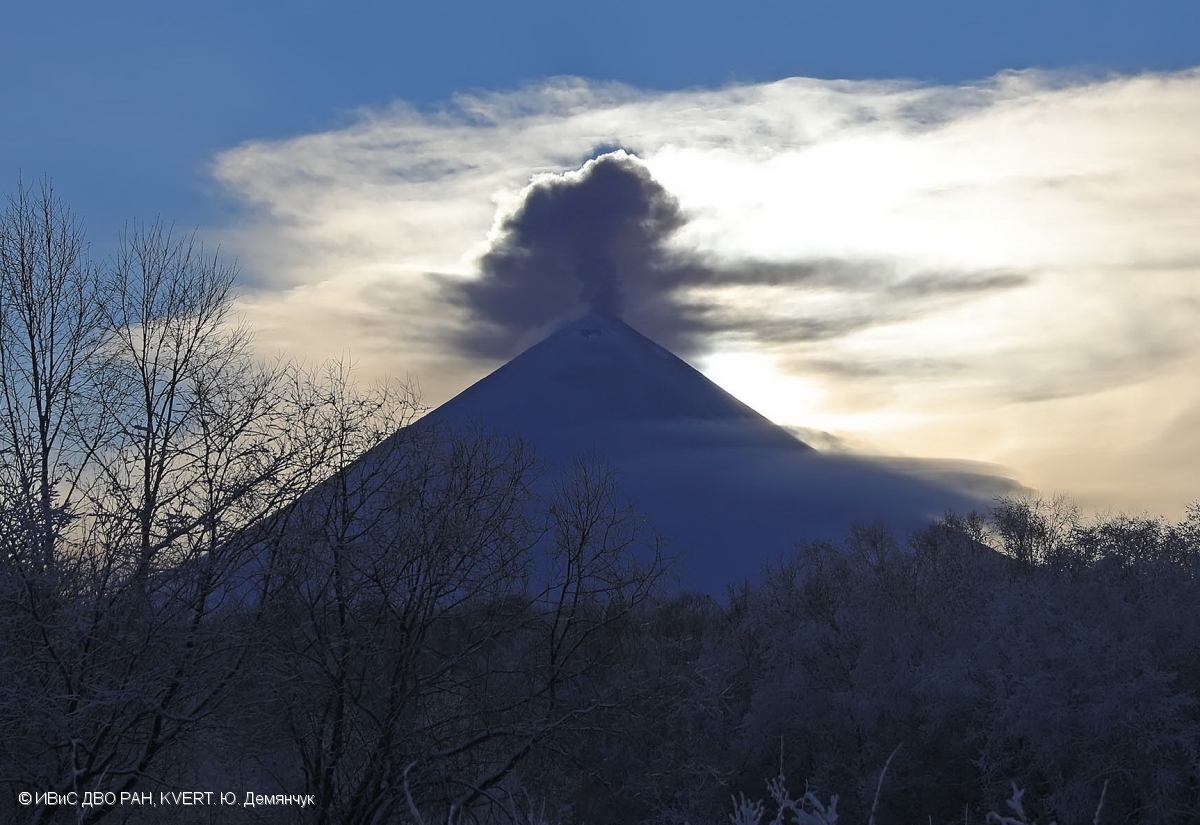
Kamchatka , Klyuchevskoy :
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION (VONA).
Issued: September 13 , 2018 .
Volcano:Klyuchevskoy (CAVW #300260)
Current aviation colour code: GREEN
Previous aviation colour code:yellow
Source:KVERT
Notice Number:2018-85
Volcano Location:N 56 deg 3 min E 160 deg 38 min
Area:Kamchatka, Russia
Summit Elevation:15580 ft (4750 m)
Volcanic Activity Summary:
According to visual and video data, a moderate gas-steam activity of the volcano continues. Satellite data by KVERT showed sometimes a weak thermal anomaly over the volcano, but the temperature of the anomaly steady decreased. Last weak ash activity of the volcano was noting on 14 July, 2018. KVERT continues to monitor Klyuchevskoy volcano.
A gas-steam activity of the volcano continues. Aerosol plumes could affect low-flying aircraft.
Volcanic cloud height:NO ASH CLOUD PRODUSED
Other volcanic cloud information:NO ASH CLOUD PRODUSED
Source : KVERT
Photo : Yu. Demyanchuk, IVS FEB RAS, KVERT ( 6/1/2018 ).
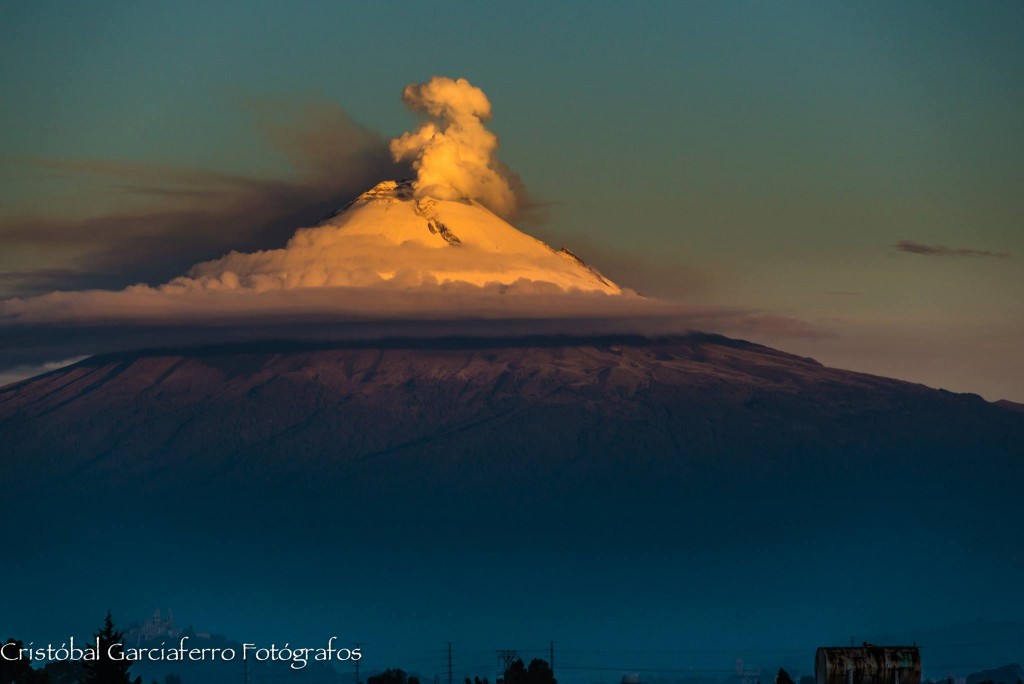
Mexico , Popocatepetl :
September 12, 11:00 am (September 12, 4:00 pm GMT)
During the last 24 hours, according to the monitoring systems of the Popocatepetl volcano, 144 exhalations accompanied by steam, gas and small amounts of ash, as well as five explosions, three yesterday at 11:27, 11:51 and 18:25, the other two appeared today at dawn at 1:12 am and 5:24 am, have been identified. In addition to seven volcano-tectonic earthquakes recorded at 15:00, 15:36, 18:16, 21:05, 21:05, 21:06 and 03:40, magnitude M 2.0, M 2,3, M 1,3, M1,7, M1,5, M1,4 and M 1,6 respectively, and 114 minutes of tremor.
During the night, an incandescence was observed which increased during certain episodes.
The time of this report, it has intermittent visibility of the volcano, it was observed that the water vapor emission and other gases are dispersed in the West-Southwest direction.
CENAPRED asked not to approach the volcano and in particular of the crater, because of the risk of falling of projectiles, and in case of heavy rain to remain far from the bottom of the ravines because of the danger of landslides and flows mud.
The warning light of the Popocatepetl volcano is located at Amarillo Phase 2.
Source : Cenapred.
Photo : Cristobal Garciaferro