January 19 , 2022 .
Italy , Stromboli :
WEEKLY BULLETIN, from January 10, 2022 to January 16, 2022. (issue date January 18, 2022)
ACTIVITY STATUS SUMMARY
In the light of the surveillance data, it is highlighted:
1) VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS: Explosive volcanic activity of the Strombolian type coupled with splashing activities, with a total frequency of events at a low level and with an intensity of explosions between low to medium in the North zone and low in the Center- South.
2) SEISMOLOGY: The seismological parameters monitored do not show any significant variations.
3) GROUND DEFORMATIONS: Ground deformation monitoring networks have not detected any significant variations
4) GEOCHEMISTRY: SO2 flux at an average level
CO2 flux in the crater area on high values
C/S ratio on mean values
There are no updates on the isotope ratio of helium in groundwater
5) SATELLITE OBSERVATIONS: The thermal activity observed by satellite was at a low level.
VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS
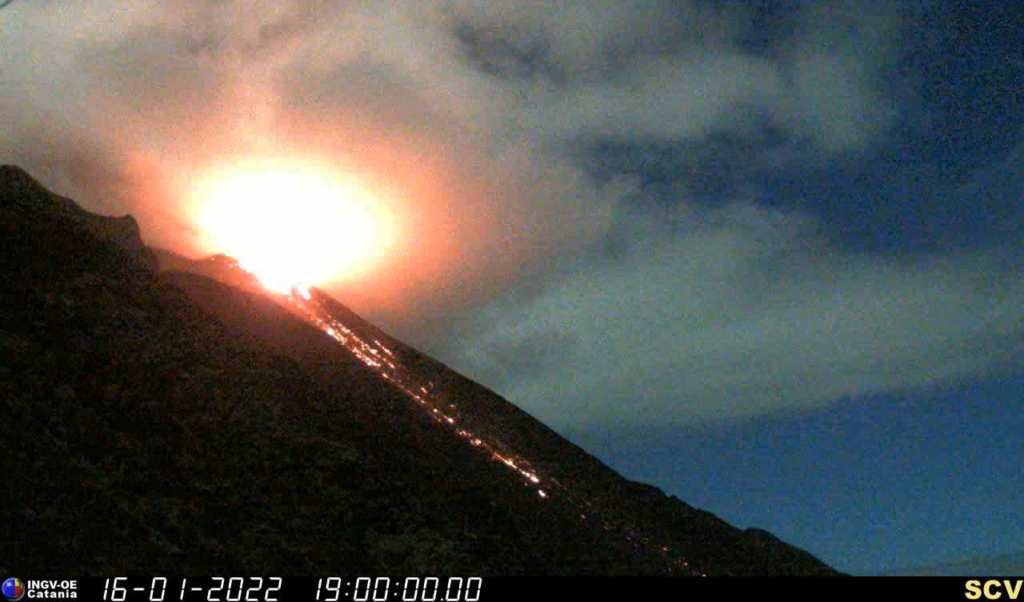
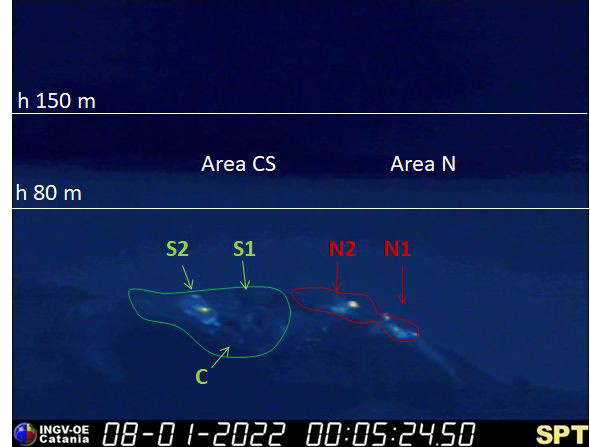
During the observation period, the eruptive activity of Stromboli was characterized by analyzing the images recorded by the INGV-OE surveillance cameras (altitude 190 m, Punta Corvi, altitude 400 m and Pizzo). The explosive activity was produced by 5 eruptive vents located in the North crater area and by 2 located in the Center-South crater area; all eruptive vents are located within the depression that occupies the crater terrace.
Overall, the eruptive activity with respect to the frequency of explosions was at a low level with a slight prevalence of the North zone compared to that of the South Center. In detail, the North Crater area produced explosive activity with low frequency and intensity between low and medium level with products up to ~ 110 m high on the crater terrace. During the period, the spattering activity produced mainly by the N2 vent continued with variable intensity and produced episodically rheomorphic deposits in the upper part of the Sciara del Fuoco with material rolling up to the coast line (for example, January 16, 2022). Regarding the Center-South crater area, the explosive activity was placed at a low frequency level with low intensity and products emitted up to ~ 80 meters on the crater terrace. The activity was mainly produced by the S2 vent and in isolation from the S1 vent and sector C.
Source : INGV.
Photo : INGV.
Italie , Vulcano :
WEEKLY BULLETIN, from January 10, 2022 to January 16, 2022. (issue date January 18, 2022)
ACTIVITY STATUS SUMMARY.
In the light of the surveillance data, it is highlighted:
1) Temperature of the crater fumaroles: The fumarole temperatures on the edge and inside the crater are on average stable or slightly decreasing
2) CO2 flux in the crater area: The CO2 flux in the crater area remains at high values
3) SO2 flux in the crater area: SO2 flux at a high and slightly decreasing level
4) Geochemistry of fumarolic gases: No update is available.
5) CO2 fluxes at the base of La Fossa cone and in the Vulcano Porto area: CO2 fluxes at the base of the crater remain at medium-high values
6) Geochemistry of thermal aquifers: The physico-chemical parameters of the Camping Sicilia and Bambara wells remain stable
7) Local seismicity: Slight increase in the frequency of occurrence of events of lower frequency (VLP).
8) Regional seismicity: No earthquake with Ml >= 1.0 was located in the area of the island of Vulcano.
9) Deformations – GNSS: the GNSS surveillance network does not show substantial variations
10) Deformations – Clinometrics: The inclinometric network does not show any significant variations.
11) Other observations: Gravity signal: The continuous gravity stations did not record any significant variations during the period considered.
GB-RAR: The GB-RAR monitoring results referring to the period December 14, 2021 – January 17, 2022, show a general stability of the area, with deformations along the LOS of less than 1 mm. Mobile GNSS: Mobile GNSS stations show no significant changes during the reporting period.
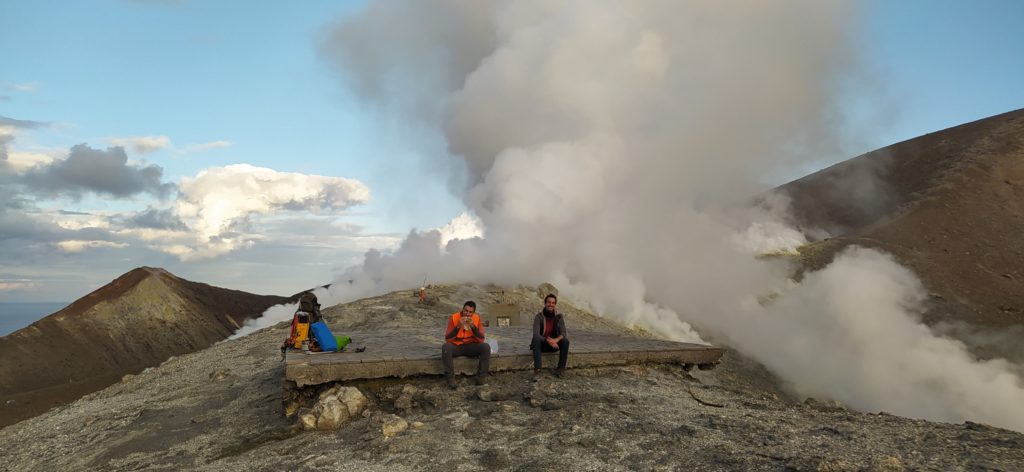
CRATER FUMAROLLES TEMPERATURE .
During the current week, the fumaroles of the summit rim and the internal slope presented a trend strongly disturbed by atmospheric phenomena. The reference temperatures are 250°C and 113°C, respectively for the edge and the internal face. The validation of the signals recorded for the fumaroles of the summit rim is awaited, by measurements to be carried out in the field in the coming days.
CO2 FLOW AT THE BASE OF THE CONE DE LA FOSSA AND IN THE VULCANO PORTO AREA:
The soil CO2 fluxes (automatically acquired by the VULCANOGAS network), during the last days of the observation period, showed a moderate downward trend in the sites of Camping Sicilia, Rimessa and P4max. On the Faraglione site, the values are comparable to those recorded the previous week.
At Camping Sicilia and Rimessa, the current values remain high, although lower than those reached at the height of the current crisis.
Source : INGV.
Photo : INGV.
Peru , Ubinas :
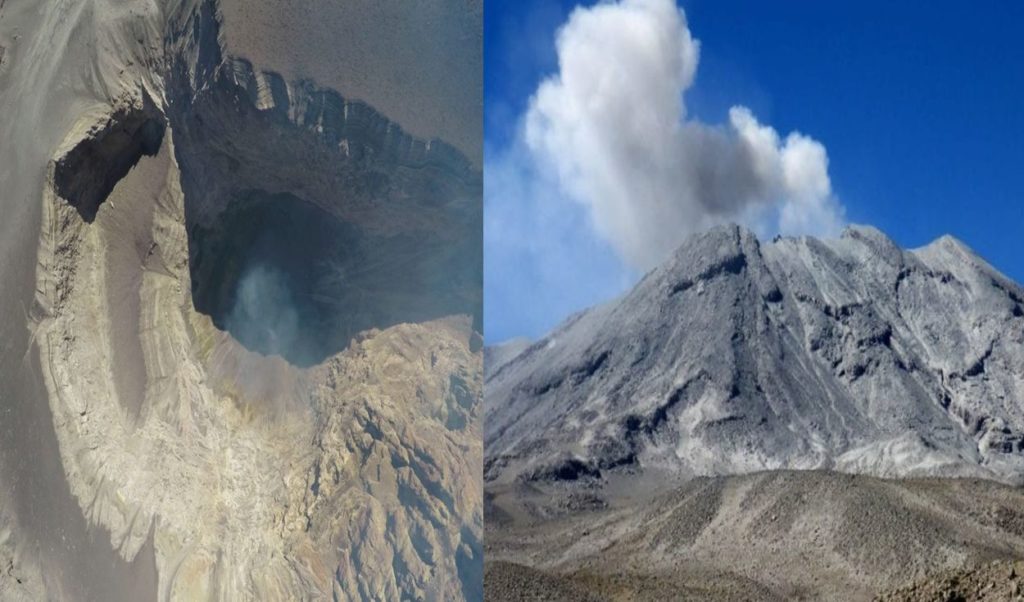
The IGP warns of the imminent danger of collapse of the flank of the Ubinas volcano.
An avalanche would affect four populated centers. Specialists have found that the massif has a network of vertical fractures. The Moquegua authorities have already been notified.
An alert to a possible collapse of the southeast flank of the volcanic wall of Ubinas has been issued by the Geophysical Institute of Peru (IGP). The notification was registered with the Civil Protection Institute (Indeci).
According to IGP specialists, this area of the massif is unstable due to slopes of 1.2 to 1.4 kilometers in height; weathering, hydrothermalization and a network of vertical fractures. The crater of this volcano contains 2,640,000 cubic meters of material accumulated by ash, lava fragments and volcanic lava sandstone.
Therefore, a collapse occurring that would descend through the Volcamayo Gorge towards the Ubinas Valley, affecting the populated centers located downstream. The avalanche would mainly affect the populated centers of Querapi, Ubinas, Tonohaya and San Miguel.
According to scientific calculations, these landslides could be due to heavy rains or a probable volcanic eruption, which would wash away large amounts of rocks and mud.
In this regard, the regional head of Civil Defense, Eduardo Quelopana, told a local radio station that the area of possible landslide had been visited in order to establish the emergency measures to be taken in case of risk. « Prevention is a joint effort between local authorities and institutions, » he said.
Source and photo : larepublica.pe
Colombia , Nevado del Ruiz :
Bulletin Activity level of the Nevado del Ruiz volcano.
The activity level continues at: Yellow activity level or (III): changes in the behavior of volcanic activity.
Regarding the monitoring of the activity of the Nevado del Ruiz volcano, the COLOMBIAN GEOLOGICAL SERVICE reports that:
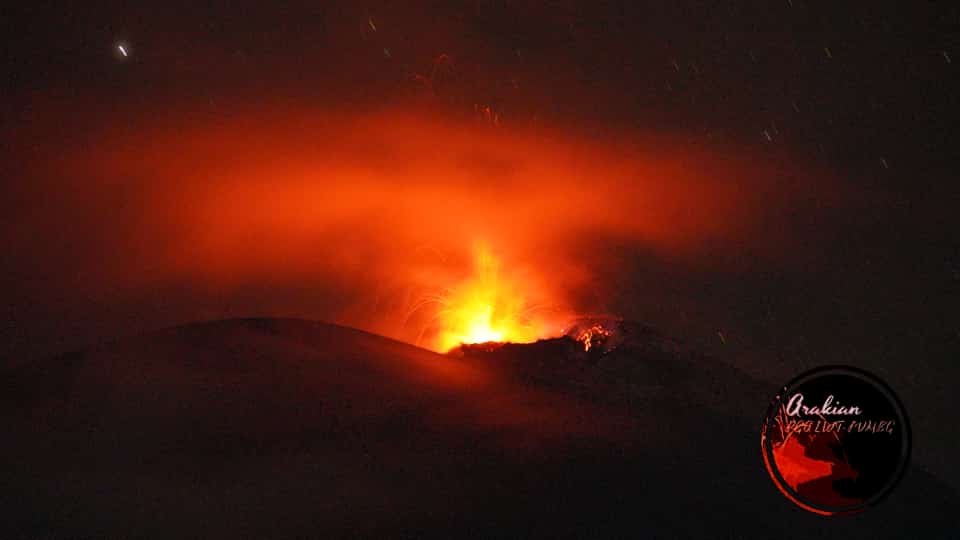
Seismicity related to fluid dynamics inside volcanic conduits showed a decrease in the number of earthquakes recorded and an increase in seismic energy released, compared to the immediately previous week. This seismic activity was characterized by the occurrence of continuous volcanic tremors, seismic pulses, long and very long period earthquakes, which had moderate energy levels and variable spectral content. These earthquakes were located mainly in the Arenas crater. Some of these signals were associated with ash emissions, confirmed by cameras installed in the volcano area.

The seismicity generated by the fracturing of the rock decreased in number of earthquakes and released seismic energy, compared to the previous week. This seismic activity was located mainly in the Northeast, East, Southeast, Southwest sectors and in the Arenas crater. The depth of the earthquakes ranged from 0.1 to 5.0 km. The maximum magnitude recorded during the week was 0.3 ML (Local Magnitude) corresponding to an earthquake recorded on January 16 at 06:39 (local time), located 1.2 km northeast of the Arenas crater, at a depth of 3.9 km.
Source : SGC.
Photo : Ingemmet.
Indonésie , Ili Lewotolok :
Le volcan est clairement visible jusqu’à ce qu’il soit couvert de brouillard . La fumée issue du cratère est blanche / grise avec une intensité faible, moyenne à épaisse, à environ 50-500 mètres au dessus du sommet. Le temps est ensoleillé à nuageux, le vent est faible à l’Est.
L’éruption s’est accompagnée d’un grondement et d’un bruit d’explosion faible à modéré .
Les tremblements de terre volcaniques sont liés à l’activité magmatique ainsi qu’à l’activité tectonique. On note :
– 17 tremblements de terre d’éruptions/explosions
– 60 tremblements de terre d’émissions
– 4 tremors harmonique
– 16 tremors non harmonique
– 1 tremblement de terre hybride/multi-phase
– 4 tremblements de terre tectoniques lointains
– Tremor continu, amplitude 0,5-2,8 mm (1 mm prédominant).
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION – VONA
Issued : January 19 , 2022
Volcano : Ili Lewotolok (264230)
Current Aviation Colour Code : ORANGE
Previous Aviation Colour Code : orange
Source : Ili Lewotolok Volcano Observatory
Notice Number : 2022LEW02
Volcano Location : S 08 deg 16 min 19 sec E 123 deg 30 min 18 sec
Area : East Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia
Summit Elevation : 4554 FT (1423 M)
Volcanic Activity Summary :
Eruption with volcanic ash cloud at 00h48 UTC (08h48 local). Eruption and ash emission is not continuing.
Volcanic Cloud Height :
Best estimate of ash-cloud top is around 6794 FT (2123 M) above sea level, may be higher than what can be observed clearly. Source of height data: ground observer.
Other Volcanic Cloud Information :
Ash-cloud moving to east
Remarks :
Seismic activity is dominated by Hembusan (gas emission earthquake)
Source : PVMBG.
Photos : InfoBencan/twitter / volcanodiscovery , Magma Indonésie .