July 03 , 2021.
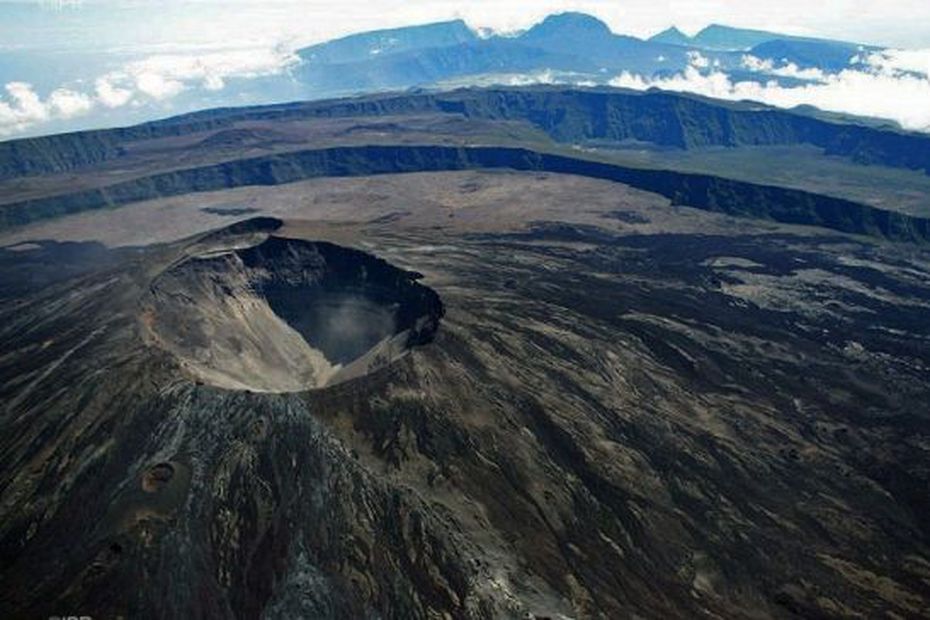
Philippines , Taal :
TAAL VOLCANO BULLETIN 02 July 2021 8:00 AM
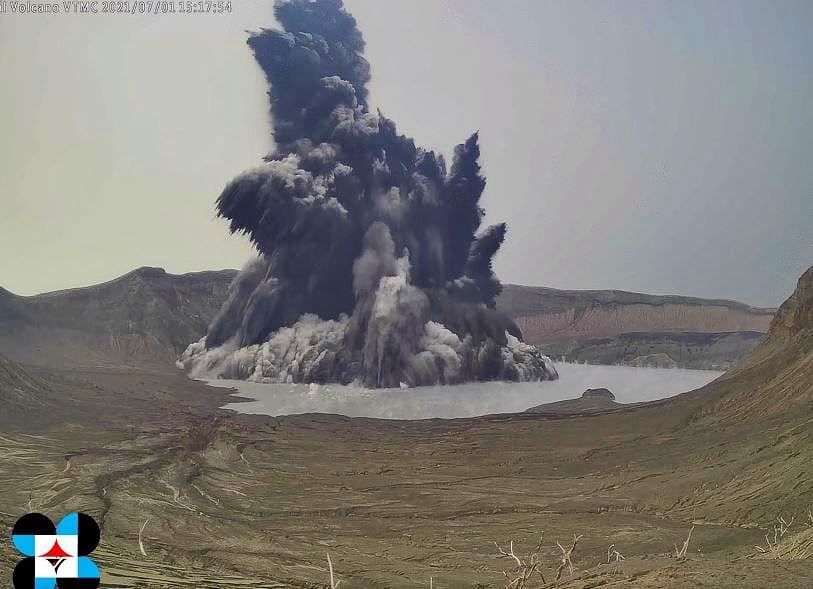
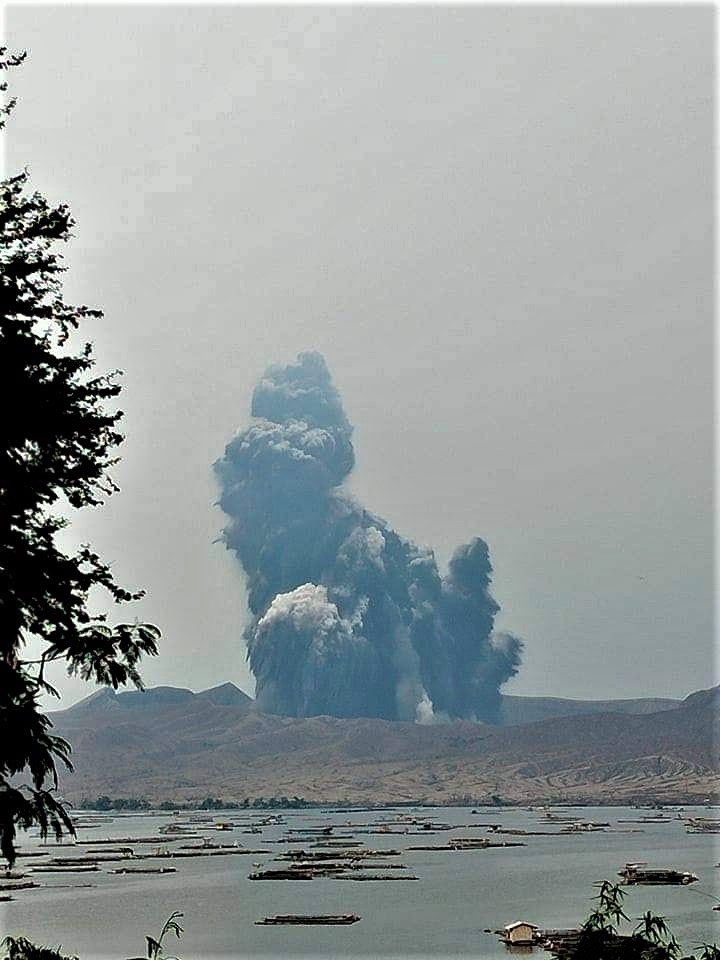
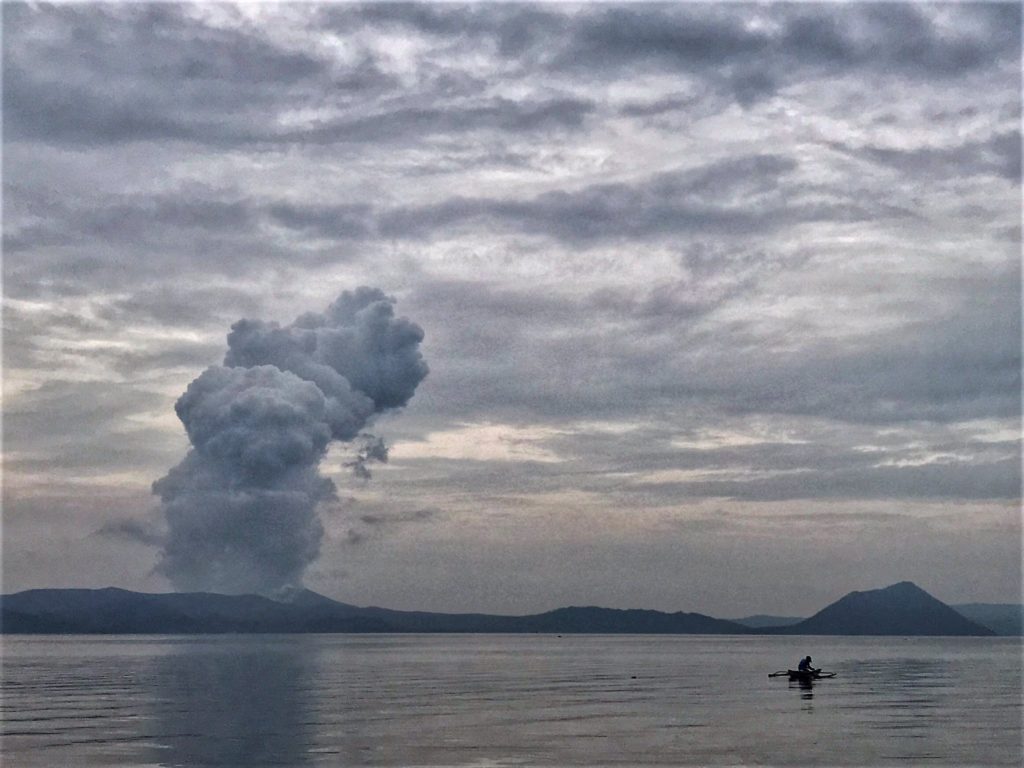
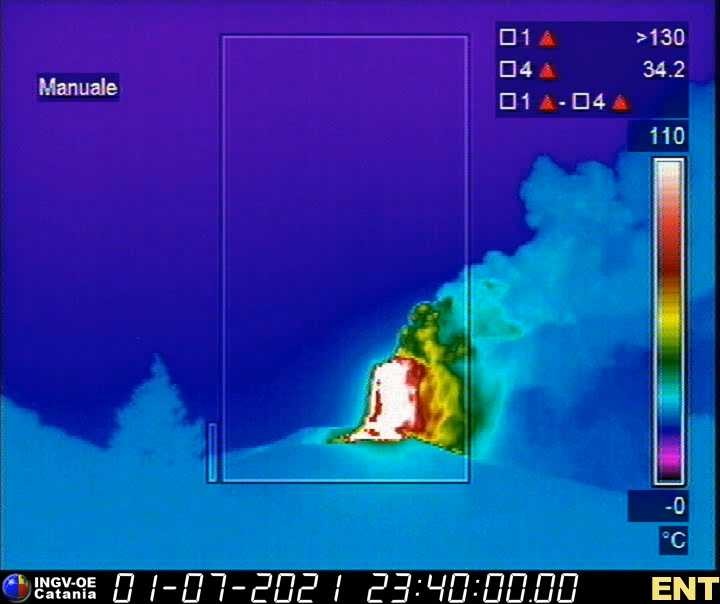
At 3:16 PM on July 02, a short-lived phreatomagmatic eruption occurred at Main Crater and generated a dark grayish plume that rose 1000 meters. This was followed by four (4) short phreatomagmatic bursts that occurred at 6:26 PM, 7:21PM, 7:41PM and 8:20 PM that lasted not longer than two (2) minutes each and produced short jetted plumes that rose 200 meters above the Main Crater Lake.
In the past 24-hour period, the Taal Volcano Network recorded twenty-nine (29) volcanic earthquakes, including one (1) explosion-type earthquake, twenty-two (22) low frequency volcanic earthquakes and two (2) volcanic tremor events having durations of three (3) minutes, and low-level background tremor that has persisted since 08 April 2021. High levels of volcanic sulfur dioxide or SO2 gas emissions and steam-rich plumes that rose as much as three thousand (3000) meters high and drifted southwest and southeast have been observed from the Taal Main Crater. Sulfur dioxide (SO2) emission averaged 13,287 tonnes/day on 01 July 2021. In addition, vog was observed over Taal Volcano and vicinity. Based on ground deformation parameters from electronic tilt, continuous GPS and InSAR monitoring, Taal Volcano Island has begun deflating in April 2021 while the Taal region continues to undergo very slow extension since 2020.
03 July 2021 8:00 AM
A series of three (3) short phreatomagmatic bursts occurred at 10:25 AM, 10:47 AM, 11:01 AM yesterday and produced short jetted plumes that rose 100 meters above the Main Crater Lake. Active upwelling of hot volcanic fluids of the Taal Main Crater Lake followed in the afternoon.
In the past 24-hour period, the Taal Volcano Network recorded forty-eight (48) volcanic earthquakes, including two (2) volcano-tectonic earthquakes, forty (40) low frequency volcanic earthquakes, six (6) volcanic tremor events having durations up to four (4) minutes, and low-level background tremor that has persisted since 08 April 2021.
Alert Level 3 (Magmatic Unrest) now prevails over Taal Volcano. At Alert Level 3, magma extruding from the Main Crater could drive explosive eruption. The public is reminded that the entire Taal Volcano Island is a Permanent Danger Zone (PDZ), and entry into the island as well as into the high-risk barangays of Agoncillo and Laurel must be prohibited due to the hazards of pyroclastic density currents and volcanic tsunami should strong eruptions occur. All activities on Taal Lake should not be allowed at this time. Communities around the Taal Lake shores are advised to remain vigilant, take precautionary measures against possible airborne ash and vog and calmly prepare for possible evacuation should unrest intensify. Civil aviation authorities must advise pilots to avoid flying over Taal Volcano Island as airborne ash and ballistic fragments from sudden explosions and pyroclastic density currents such as base surges may pose hazards to aircraft.
DOST-PHIVOLCS maintains its close monitoring of Taal Volcano and any new development will be communicated to all concerned stakeholders.
Source : Phivolcs.
Photos : Auteur inconnu , Rizal M , Phivolcs.
Italy / Sicily , Etna :
Press release on ETNA’s activity, 02 July 2021, 00:48 (22:48 UTC).
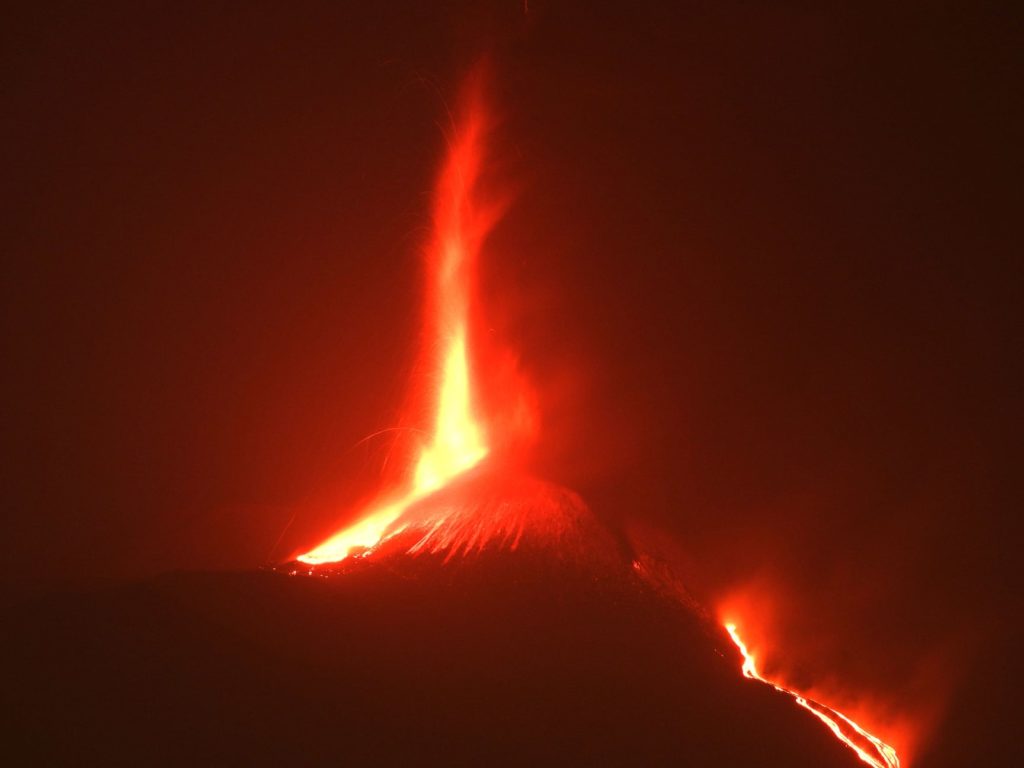
The National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology, Osservatorio Etneo, announces that a resumption of Strombolian activity at the level of the Southeast Crater is observed from 22:40 UTC.
At 22.40 UTC the amplitude of the volcanic tremor is high. The last tremor location, at 9.45pm UTC, is near the Southeast Crater at a depth of approximately 3.0 km. The number of infrasound events in the last 10 minutes is low.
The deformation networks show a slight inclinometric variation at the summit station of the ECP (Cratere Del Piano).
From 22.50 UTC, we observe the passage of Strombolian activity at the lava fountain stage at the Southeast Crater. Based on the forecast model, the eruptive cloud produced by the current activity disperses in the West-North-West direction.
The amplitude of the volcanic tremor is on high values with an increasing tendency.
Press release on ETNA’s activity, 02 July 2021, 00:48 (22:48 UTC).
The National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology, Osservatorio Etneo, announces that from 00:50 UTC the lava fountain of the Southeast Crater has ceased, a weak Strombolian activity remains. As for the lava overflow, it is always fed in the southwest direction.
At 00.50 UTC the amplitude of the volcanic tremor is on high values with a decreasing trend.
The last location of the tremor, results in the proximity of the Southeast Crater at a depth of about 3.0 km. The number of infrasound events during the last 10 minutes at 23:38 UTC is low. The last infrasound event is located near the Southeast Crater.
The signal from the ECP summit inclinometer station reached a maximum variation of about 3 microradians around 00:20 UTC and then stabilized again, no significant distortion is detectable at the stations of the GNSS network
Further updates will be communicated shortly
Source : INGV.
Photos : INGV , Boris Behncke.
La Réunion , Piton de la Fournaise :
Seismicity
In June 2021, the OVPF recorded in the Piton de la Fournaise massif in total:
• 48 superficial volcano-tectonic earthquakes (0 to 2.5 km above sea level) below the summit craters;
• 1 deep earthquake (below sea level);
• 119 collapses (in the Dolomieu Crater, the ramparts of the Fouqué Enclos and Piton de Crac and the East River).
The seismicity under the Piton de la Fournaise during the month of June 2021 remained low with an average of less than two superficial volcano-tectonic earthquakes per day.
Deformation
The building’s inflation, which began in April 2021, continued throughout June 2021. This inflation showed a pressurization of the superficial magmatic reservoir located around 2 km deep.
Gas geochemistry
CO2 concentration in the soil Following the eruption of December 2020, a continuous increase in CO2 emissions from the soil was recorded at the level of the distal sites (Plaine des Cafres sectors) but also proximal (Gîte du volcan ).
At remote sites, a trend reversal (drop in CO2 emissions) occurred on February 12, 2021, witnessing a possible transfer of magma to more superficial crustal levels. A further increase followed this phase, with the largest increase recorded between April 4 and April 16.
At the proximal sites, the increase was continuous until early May, heralding the onset of the long-lasting eruption from April 9 to May 24, 2021.
Since June 7, 2021, a new trend of increasing CO2 fluxes has been recorded both in the far field, and to a lesser extent in the near field. The rates of increase are similar to those recorded at the start of the year
Source : OVPF.
Read the article: https://www.ipgp.fr/sites/default/files/ovpf_20210702_bullmensu.pdf
Photo : Imaz Press .
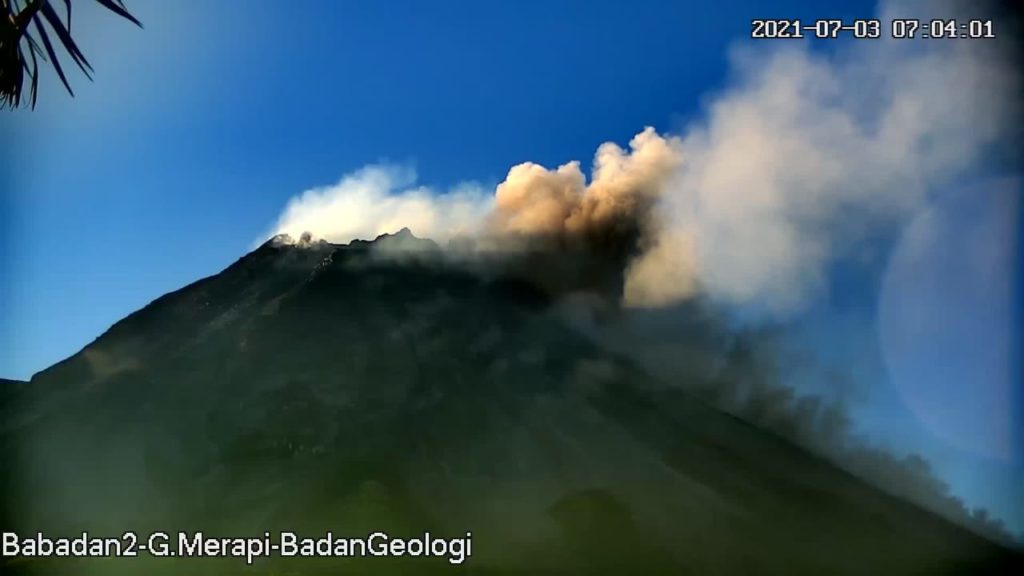
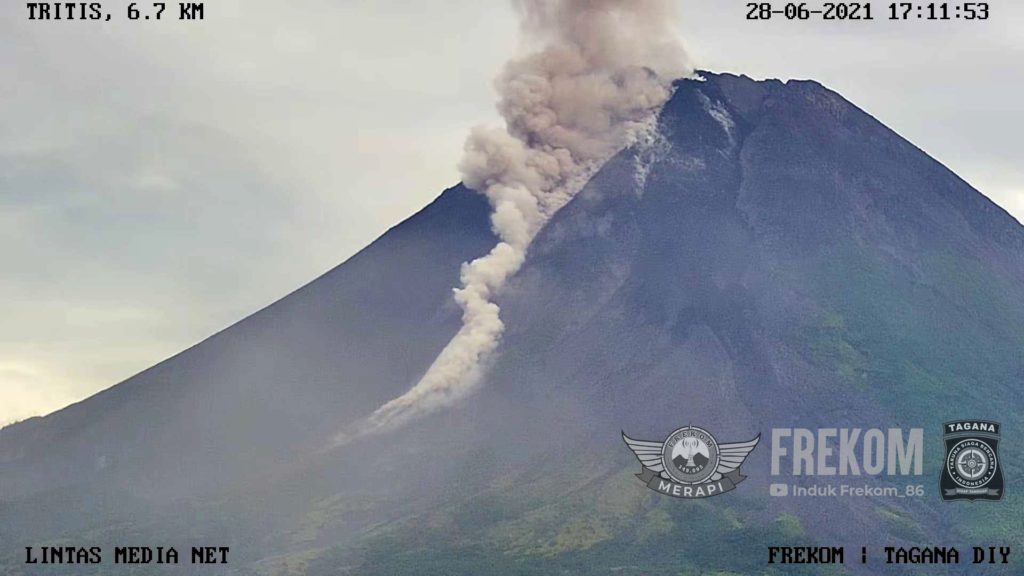
Indonesia , Merapi :
Mount Merapi Activity Report, June 25 to July 1, 2021
OBSERVATION RESULT
Visual
The weather around Mount Merapi is generally sunny in the morning and evening, while it is foggy in the afternoon. White, weak to thick, low pressure, 200m high smoke was observed from the Mount Merapi observation post in Kaliurang on June 30, 2021 at 07:17 WIB.
This week, hot cloud avalanches have occurred 10 times to the southwest with a maximum slide distance of 2000 m and 29 times to the southeast with a maximum slide distance of 3000 m. Ash rains were reported in several areas of the southeastern sector of Mount Merapi on June 25, 2021. Lava avalanches were observed 100 times to the southwest with a maximum slide distance of 2,000 m and 26 times to the south-east with a maximum sliding distance of 1,200 m.
The volume of the lava dome in the southwest sector is 1,680,000 m3 with a growth rate of 11,800 m3 / day. Morphological analysis of the summit area based on photos of the southeast sector on July 1 shows a change in height of the central dome 0.5 m lower than that of June 24, 2021. The increasing number of cloud avalanches Hot and lava avalanches observed that the central dome was lower than the previous week.
Seismicity
This week, the seismicity of Mount Merapi showed:
39 hot cloud avalanches (AP)
21 shallow volcanic earthquakes (VTB),
141 multi-phase earthquakes (MP),
1,824 avalanche earthquakes (RF),
143 emission earthquakes (DG)
4 tectonic earthquakes (TT).
On June 28, 2021 at 5:15 am WIB, there was a tectonic earthquake that was felt at all observation posts of Mount Merapi. External seismicity (AP, RF and DG) this week is higher than last week.
Deformation
The deformation of Mount Merapi, which was monitored using EDM this week, showed a distance shortening rate of 0.7 cm / day.
Rain and lahars
This week, it rained at the Mount Merapi observation post with an intensity of 123 mm / hour for 70 minutes at Kaliurang post on June 28, 2021. There were no reports of lahars or additional flow in the mountains. rivers that originate from Mount Merapi.
Conclusion
Based on the results of visual and instrumental observations, it is concluded that:
The volcanic activity of Mount Merapi is still quite high in the form of effusive eruption activity. The status of the activity is defined in the “SIAGA” level.
Source : BPPTKG.
Photos : BPPTKG, Frekom .
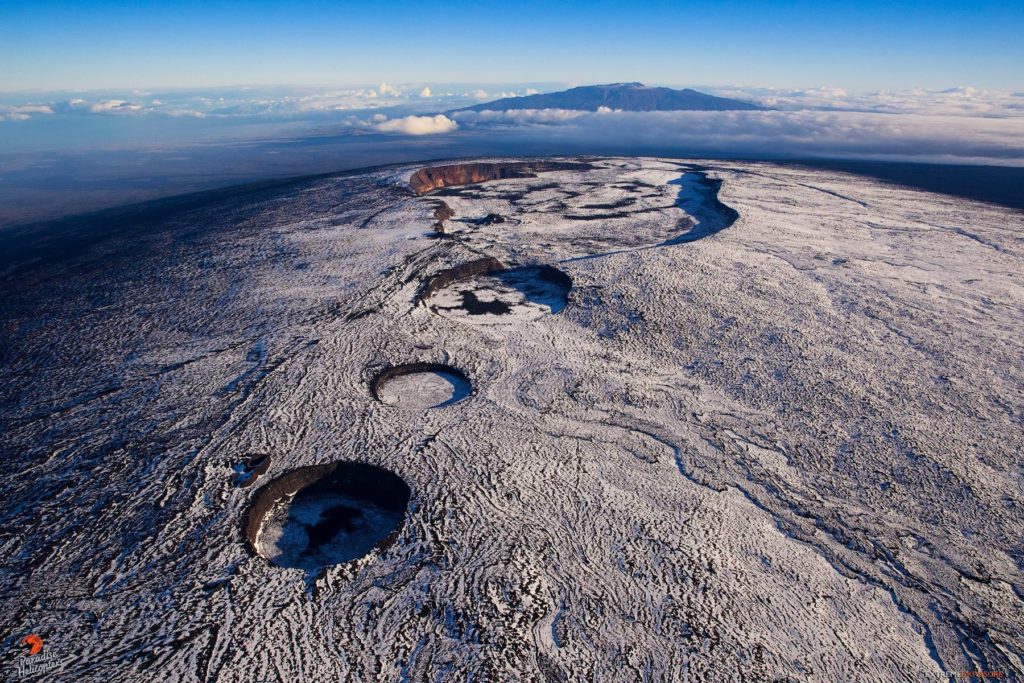
Hawaii , Mauna Loa :
19°28’30 » N 155°36’29 » W,
Summit Elevation 13681 ft (4170 m)
Current Volcano Alert Level: ADVISORY
Current Aviation Color Code: YELLOW
Activity Summary:
Mauna Loa Volcano is not erupting. Rates of seismicity at the summit remain slightly elevated and above long-term background levels. Other Mauna Loa monitoring data streams show no significant changes that would indicate increased volcanic hazard at this time.
Observations:
During the past week, HVO seismometers recorded approximately 172 small-magnitude earthquakes below Mauna Loa. 79 of these occurred below the summit and upper-elevation flanks of the volcano, and 92 were located under the southeast flank. All earthquakes over the past week were less than M3 and occurred mostly at depths of less than 8 km (5 mi) below ground level.
Global Positioning System (GPS) measurements show low rates of deformation in the summit region continuing through the past week.
At both the summit instrument site and at Sulphur Cone on the Southwest Rift Zone, gas concentrations remain stable at below 2 ppm SO2 and fumarole temperatures are also stable at below 100°C (212°F).
Webcam views have shown no changes to the volcanic landscape on Mauna Loa over the past week.
Source : HVO
Photo : Bruce Omori