March 29 , 2025.
Alaska , Spurr :
Volcanic unrest continues at Mount Spurr volcano and is characterized by ongoing earthquake activity, surface deformation, and volcanic gas emissions. Seismicity remains elevated with about 68 located earthquakes last week. While this is lower than previous weeks, earthquake rates have gone up and down during this current period of unrest. An overflight last Friday measured gas emissions that were elevated but unchanged from previous measurements on March 7 and 11. Gas emissions from the summit were also detected several times in satellite data. Steaming from the summit was observed during clear weather throughout the week and was robust at times. Increased steam observations on Wednesday evening were not associated with any detectable change in seismicity or gas emissions and are attributed to favorable atmospheric conditions. AVO released an Information Statement on March 12 that provides a summary of the current unrest.
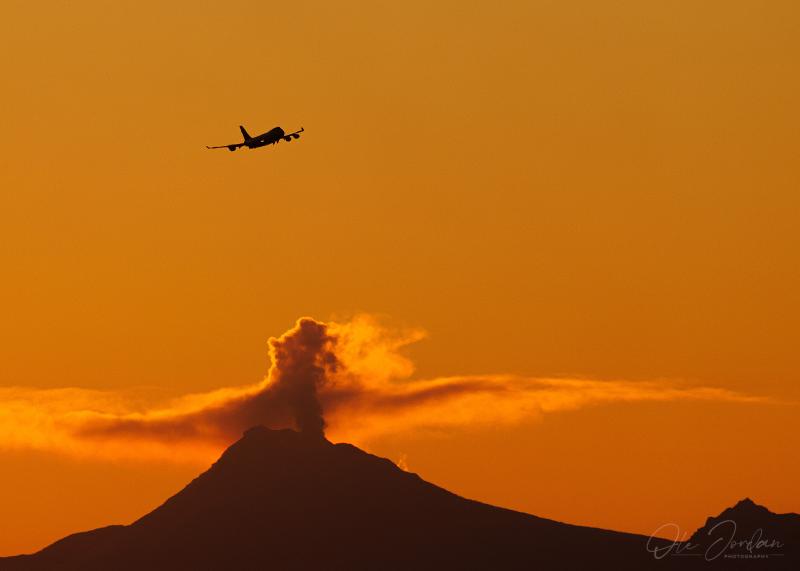
Photo of steam emissions from the summit of Mount Spurr with a departing 747 aircraft in the foreground. Mount Spurr is located about 80 miles west of Anchorage, Alaska and is the 4th busiest air cargo airport in the world.
The Mount Spurr monitoring network is functioning well, and a new web camera was recently installed.
AVO continues to closely monitor activity at Mount Spurr for signals indicating the volcano is moving closer to an eruption using local seismic, infrasound, and GNSS stations, web cameras, regional infrasound, lightning networks, and satellite data. Based on previous eruptions, additional changes in earthquakes, ground deformation, the summit lake, and fumaroles would be expected if magma moves closer to the surface. Therefore, if an eruption occurred, it would be preceded by additional signals that would allow advance warning.
Source : AVO
Photo : Jordan, Ole
Indonesia , Merapi :
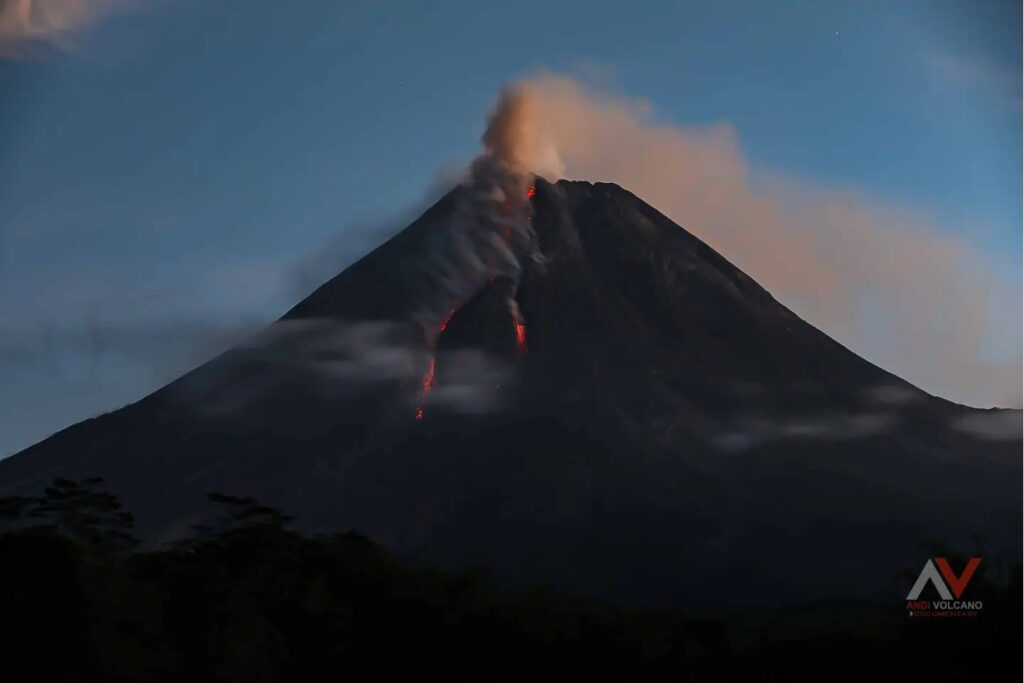
MOUNT MERAPI ACTIVITY REPORT, March 21–27, 2025
OBSERVATION RESULTS
Visual
The weather around Mount Merapi is generally sunny in the morning and evening, while it is hazy during the day. White smoke, thin to thick, low to moderate pressure, with a smoke height of 50 m, was observed from the Mount Merapi observation post in Kaliurang on March 26, 2025, at 8:00 a.m. WIB.
This week, lava avalanches were observed 23 times upstream of the Bebeng River, reaching a maximum elevation of 1,900 m, 20 times upstream of the Krasak River, reaching a maximum elevation of 2,000 m, and 26 times westward upstream of the Sat/Putih River, reaching a maximum elevation of 2,000 m.
The morphology of the southwest dome has undergone slight changes due to lava flow activity. No significant morphological changes were observed for the central dome. According to an analysis of aerial photos dated March 11, 2025, the volume of the southwest dome is 3,626,200 m3. Meanwhile, the volume of the central dome is measured at 2,368,800 m3.
Seismicity:
This week, Mount Merapi seismicity recorded:
13 shallow volcanic earthquakes (SV),
882 multiphase earthquakes (MP),
904 avalanche earthquakes (AV),
10 tectonic earthquakes (TT).
The intensity of earthquakes this week was higher than last week.
Deformation
Deformation of Mount Merapi monitored using EDM this week shows an average shortening rate of the thrust distance of 0.3 cm/day.
Rain and Lahars
This week, it rained at the Mount Merapi observation post, with the highest rainfall intensity of 45 mm/hour for 45 minutes at the Babadan post on March 24, 2025. There were no reports of additional discharge or lahars in the rivers originating from Mount Merapi.
Conclusion
Based on the results of visual and instrumental observations, it is concluded that:
Mount Merapi’s volcanic activity is still quite high in the form of effusive eruptions. The activity status is defined as « SIAGA » level.
Source : BPPTKG
Photo : Andi Volcanist .
Chile , Lascar :
Special Volcanic Activity Report (REAV), Antofagasta region, March 28, 2025, 6:45 a.m. local time (Continental Chile)
The National Geology and Mining Service of Chile (Sernageomin) is publishing the following information, obtained using the monitoring equipment of the National Volcanic Monitoring Network (RNVV), processed and analyzed at the Southern Andean Volcanological Observatory (OVDAS).
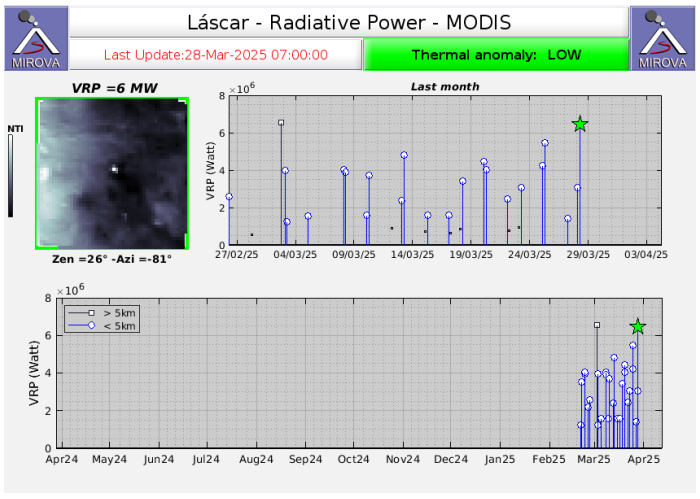
Yesterday, Friday, March 28, the MIROVA platform ( www.mirovaweb.it) reported a 6.5 MW satellite thermal anomaly, detected by the MODIS sensor, originating from the active crater. Meanwhile, Sentinel 2L2A satellite images updated through March 20, 2025, continue to record three areas of thermal radiation within the active crater, a pattern that has been occurring since February 6 of this year. Surveillance cameras installed around the volcano record visible incandescence at night.
Similarly, the seismological network installed near the volcano continues to record a decline in Long Period (LP) activity since early February. The volcano is in a state of surface activity instability that could potentially lead to the occurrence of minor explosions with limited impact to the proximal area of the active crater, and to the emission of pyroclastic material from low-energy eruptive columns.
The technical alert for this volcanic system remains at yellow alert.
Sernageomin continues its online monitoring and multiparameter tracking of the Lascar volcano, and promptly reports any significant changes in volcanic activity via official communication channels.
Source : Sernageomin
Photo : Mirova
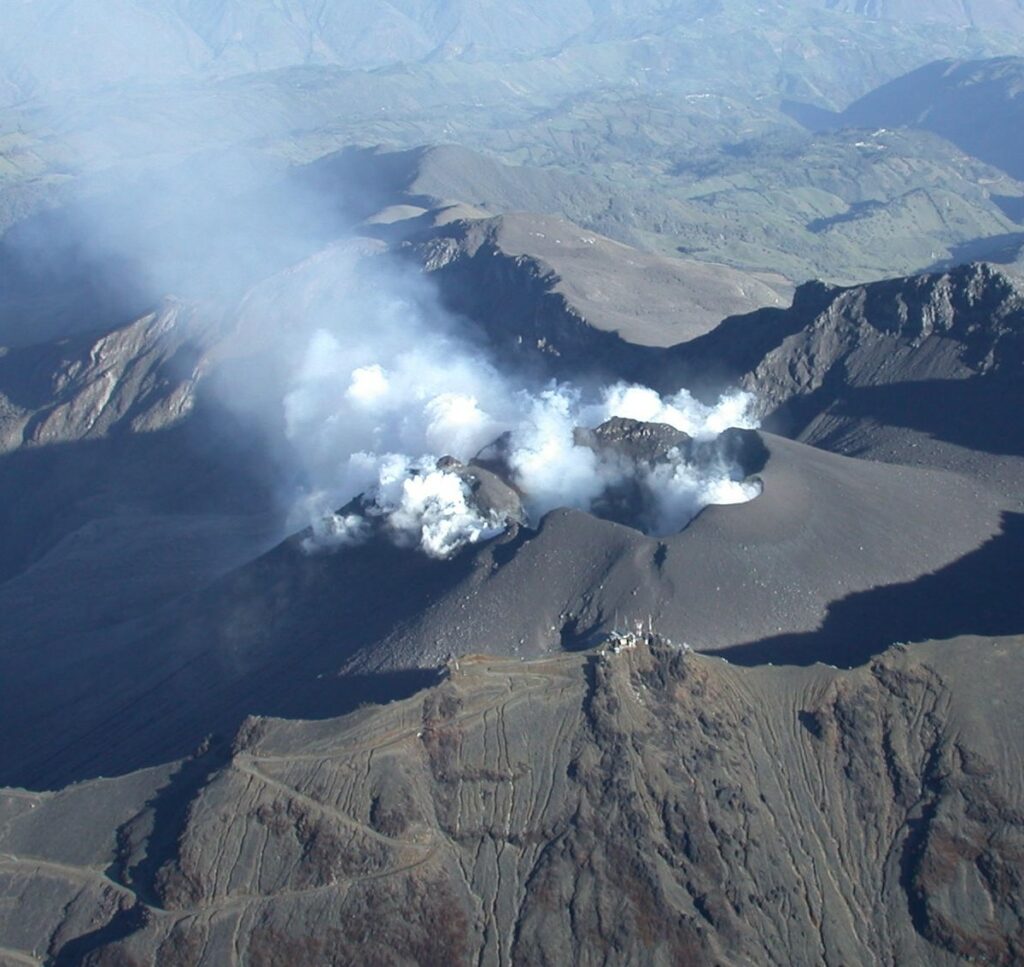
Colombia , Galeras :
San Juan de Pasto, March 25, 2025, 2:45 p.m.
Monitoring the activity of the Galeras Volcano, the Colombian Geological Survey (SGC), an entity affiliated with the Ministry of Mines and Energy, reports that:
Between March 18 and 24, 2025, volcanic activity showed a decrease in seismic activity. Compared to the previous week, the main variations in the monitored parameters were:
• A decrease in seismic activity was recorded, although the energy levels released were similar. The predominance of seismic activity associated with rock fracture processes within the volcanic system continued.
• The vast majority of earthquakes were located in the area near the main crater, at distances of less than 1 km and at depths that did not exceed 3 km from the Galeras summit (4,200 m altitude); Some events were located scattered throughout the volcanic region, at distances of up to 15 km, with depths between 5 and 14 km and with a maximum magnitude of 1.4.
• Gas emissions were observed coming from the floor of the main crater and from the fumarole fields of El Paisita to the north and Las Chavas to the west of the active cone, with low white columns and variable dispersion depending on the wind direction.
• Other volcanic monitoring parameters showed stability.
Based on the above, the SGC recommends closely monitoring developments through weekly bulletins and other information published through our official channels, as well as instructions from local and departmental authorities and the National Disaster Risk Management Unit (UNGRD).
Volcanic activity remains on alert status. Yellow: active volcano with changes in the baseline level of monitored parameters and other manifestations.
Source et photo : SGC
Costa Rica , Poas :
OVSICORI-UNA Statement on Poás Volcano, Updated March 28, 2025.
OVSICORI-UNA observes:
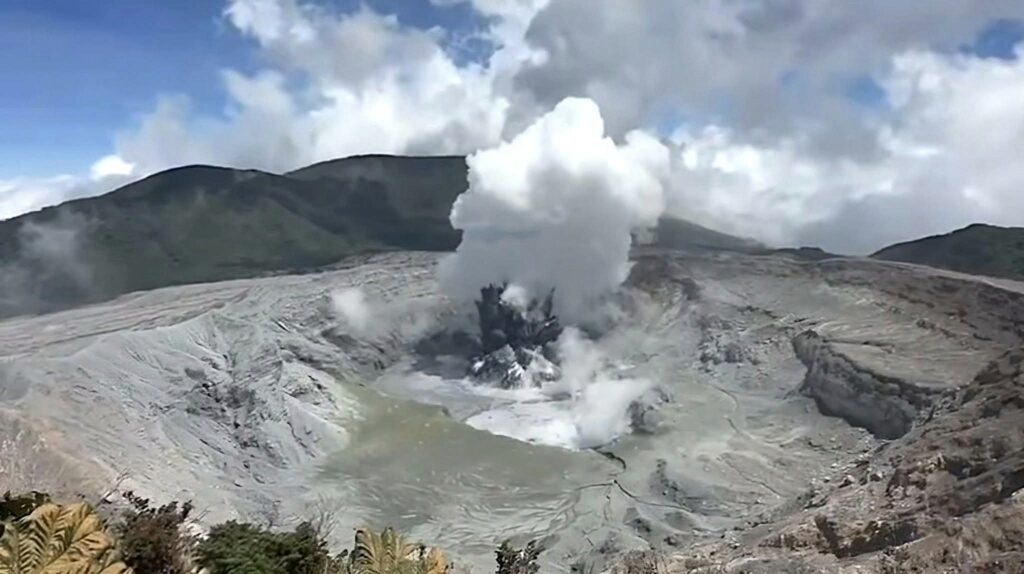
● Continuous eruption with very frequent explosions (every two minutes), with ash columns reaching 400 m at the vent C fumarole.
● Intense seismic tremors.
● Vertical deformation of crustal uplift.
● Gas compositions and fluxes related to surface magma.
● The hyperacid lake is dry. The eruptions are phreatomagmatic in nature, with a moderate amount of ash in the plume. ● Ash with a juvenile glass content of approximately 10%
Since Sunday, March 23, a new phase of this eruptive cycle has been observed, characterized by almost continuous phreatomagmatic explosions of moderate energy.
The volcano’s activity level is at WARNING level 3 out of 4.
Eruptive Activity
An eruption began on Sunday, March 23rd, and is still ongoing at the time of writing. Between March 23rd and 26th, the eruption was continuous with few interruptions but with variations in amplitude. Starting on the 27th, eruptive activity began to show interruptions of a few minutes between each pulse. Currently, activity remains very frequent.
Seismic and Acoustic Activity:
After the banded tremor sequence of March 20th, a slight increase in distal volcano-tectonic seismicity was observed. Since then, the tremor amplitude has shown a general upward trend. On Sunday, March 23rd, during the night, a major increase in tremor amplitude was noted, corresponding to the eruptive activity. Then, the amplitude of the tremor increased, reaching levels higher than those of previous years, during the climax of the 2024 eruption. From March 27, the amplitude of the tremor decreased. Since then, it has remained very variable, and even with strong amplitudes.
Source: Ovsicori .
Photo : Rod Cortes / FB