January 14 , 2024.
Iceland , Reykjanes Peninsula :
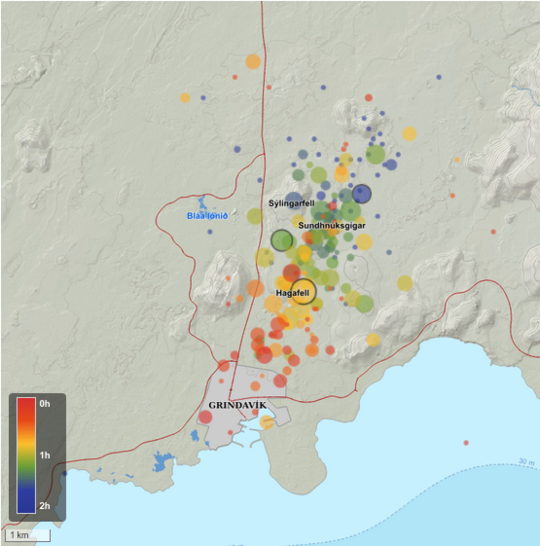
The possibility of an eruption is high in light of increased seismicity , Updated 14 January at 06:15 UTC
At around 03:00 UTC today, an intense series of earthquakes began at the Sundhnúksgígar crater row.
At the time of publication, over 200 earthquakes have been measured in the area, and the seismicity has moved towards the town of Grindavík.
So far, the largest recorded earthquake is 3.5 in magnitude, and it was measured at 04:07 UTC at Hagafell.
Both real-time GPS measurements and borehole pressure readings (from HS Orka) show major changes since the onset of today’s earthquake activity. These observations, in addition to the ongoing seismicity, confirm that magma is moving within the region.
Our assessment is that the possibility of an eruption is high, and that it could occur imminently.
Source et photo : IMO
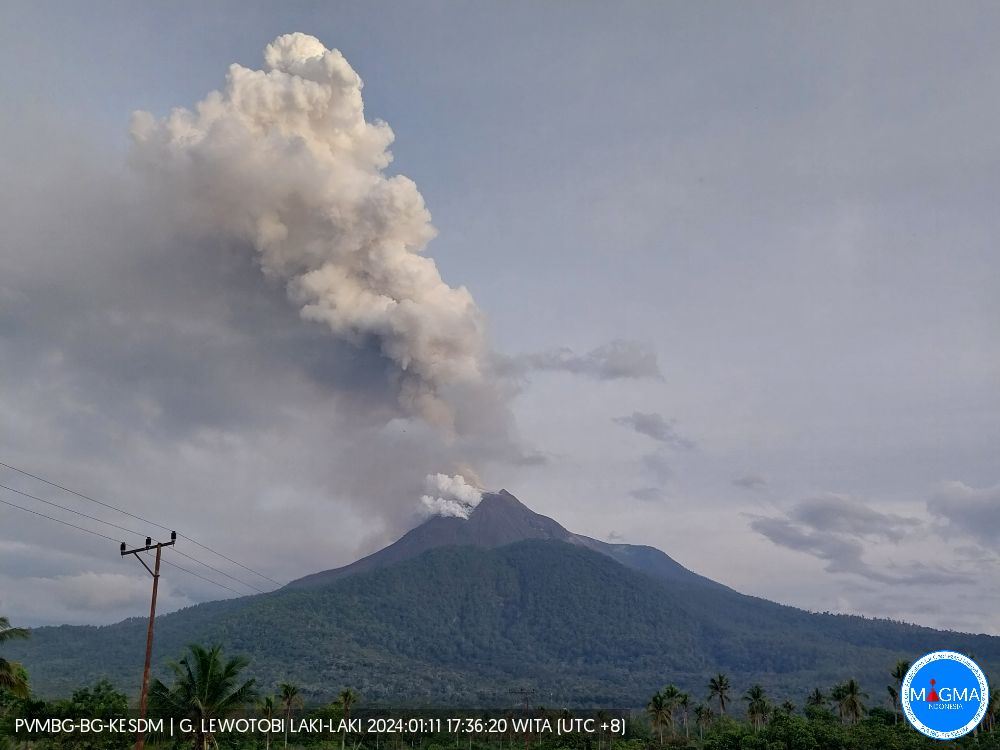
Indonesia , Lewotobi Laki Laki :
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION – VONA
Issued : January 13 , 2024
Volcano : Lewotobi Laki-laki (264180)
Current Aviation Colour Code : ORANGE
Previous Aviation Colour Code : orange
Source : Lewotobi Laki-laki Volcano Observatory
Notice Number : 2024LWK017
Volcano Location : S 08 deg 32 min 20 sec E 122 deg 46 min 06 sec
Area : East Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia
Summit Elevation : 5069 FT (1584 M)
Volcanic Activity Summary :
Eruption with volcanic ash cloud at 21h37 UTC (05h37 local).
Volcanic Cloud Height :
Best estimate of ash-cloud top is around 8269 FT (2584 M) above sea level or 3200 FT (1000 M) above summit. May be higher than what can be observed clearly. Source of height data: ground observer.
Other Volcanic Cloud Information :
Ash cloud moving from north to northeast. Volcanic ash is observed to be white to gray. The intensity of volcanic ash is observed to be thick.
Remarks :
Eruption and ash emission is continuing. Eruption recorded on seismogram with maximum amplitude 29 mm. Tremor recorded on seismogram with maximum amplitude 3 mm.
Source et photo: Magma Indonésie .
Vanuatu , Bembow ( Ambrym) :
16°15’00”S 168°07’00”E
Summit Elevation 4377ft (1334m)
Current Vanuatu Volcano Alert Level: Level 3
Ambrym volcano has increased its activity from minor unrest to minor eruption state. The Volcanic Alert Level is raised from Level 1 to Level 3.
Ambrym Volcano is now in the minor eruption state. The volcanic eruption is happening inside the Benbow Crater. The Danger Zone for life safety is limited at the Danger Zone B which is about 2km around Benbow and 4Km around Marum craters (Including Maben-Mbwelesu, Niri-Mbwelesu and Mbwelesu)
Observations from Ambrym Volcano Webcam and seismic data analysis on 13th January 2024 confirmed an eruption inside Benbow Crater from 2217hrs (10:17PM) local time. The activity consists of strong glow, loud explosion, gas and steam. People from Ambrym and neighboring islands may view gas plumes and observe volcanic glow.
The Alert Level for Ambrym volcano has been at the Level 1 since 10th October 2019. The current activity show that Ambrym volcano is undergoing a small-scale eruption. This is consistent with the Alert Level 3 activity. Level 3 indicates ‘Minor eruption; Danger is now at 2km around Benbow and 4km around Marum’. The possibility that the Ambrym volcano activity escalate to the level of moderate eruption (Level 4) is low for now.
Source et photo : Geohazard
Colombia , Nevado del Ruiz :
Weekly bulletin on the activity of the Nevado del Ruiz volcano
From the monitoring of the activity of the NEVADO DEL RUIZ VOLCANO, the MINISTRY OF MINES AND ENERGY through the COLOMBIAN GEOLOGICAL SERVICE (SGC) reports that:
In the week of January 2-8, 2024, the volcano continued to exhibit unstable behavior with moderate activity levels, particularly evident in seismicity and the persistence of thermal anomalies at the bottom of Arenas Crater. The main variations in the monitored parameters were:
– The increase in seismic activity associated with the fracturing of rocks inside the volcanic edifice, both in the number of earthquakes recorded and in the seismic energy released. The earthquakes were located mainly in the North-West and South sectors of the volcano, at distances less than 4 km from the Arenas crater and, to a lesser extent, in the Arenas crater and in the East-South-East and North-North-East of the volcano. Depths of the events varied between 1 and 7 km from the summit. During days 3 and 5, the highest seismicity rates of the week were recorded.
On January 3, most of the seismicity was located in the northwest sector of the volcano, at depths between 3 and 6 km with a maximum magnitude of 3.9. This magnitude was the largest of the week corresponding to the earthquake recorded on January 3 at 11:03 a.m., which was reported as felt by officials of the Los Nevados National Natural Park, SGC personnel on the ground and residents of the areas of influence . near the volcano and in the town of Manizales. On January 5, the seismic activity was located mainly in the southern sector, at depths between 3 and 4 km with a maximum magnitude of 2.8, corresponding to the earthquake of January 5 at 3:03 p.m.
– The reduction in seismicity linked to pulsatile emissions of ash and gas into the atmosphere both in terms of the number of earthquakes recorded and the seismic energy released. Seismic signals of this type had low to sometimes moderate energy levels. Some of these were associated with ash emissions or changes in the relative temperature of the emitted materials.
These phenomena were confirmed mainly thanks to the cameras used to monitor the volcano.
– The variability of sulfur dioxide (SO2) degassing rates with an increasing trend. The maximum height of the gas or ash column was 800 m vertical and 1,800 m dispersed.
These values were measured at the summit of the volcano on January 6, 2024. The direction of dispersion of the column was variable towards the North-West, West and South-West flanks of the volcano, generating ash falls in areas close to the volcano and in the city of Manizales.
– The persistence of thermal anomalies at the bottom of Arenas crater with moderate energy levels, detected from satellite monitoring platforms. During the week, several reports of thermal anomalies with these values were obtained due to the good weather conditions in the region.
Source : SGC
Photo : Julian Fernando Aranzazu Henao ( archive)
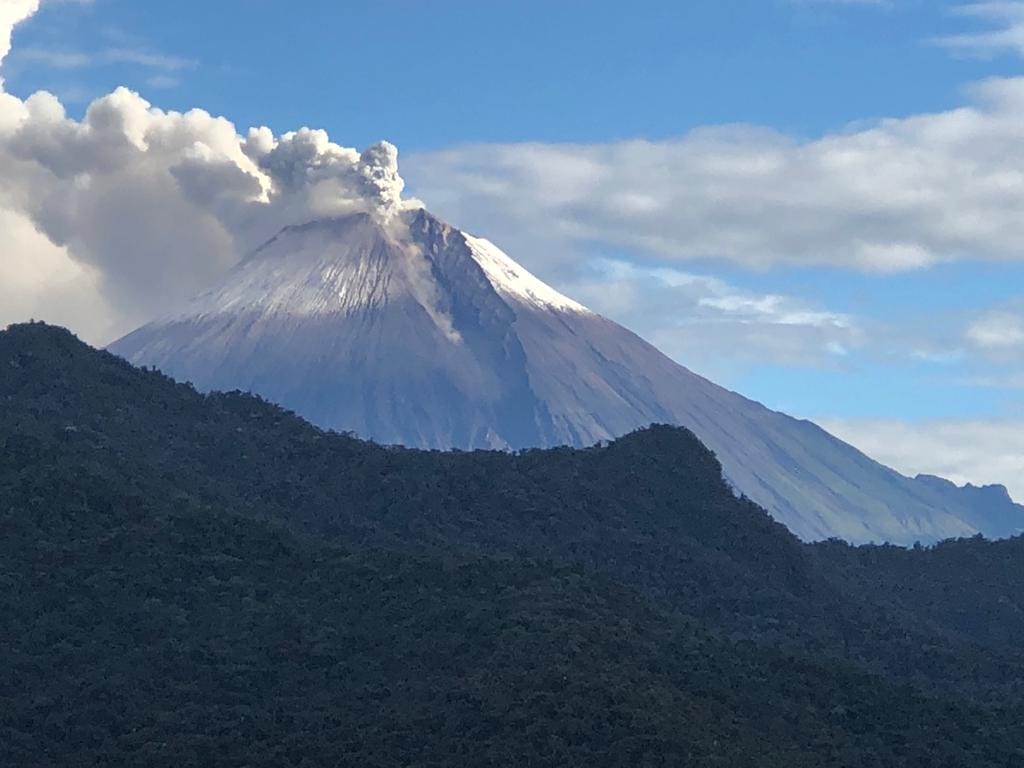
Ecuador , Sangay :
DAILY REPORT ON THE STATE OF THE SANGAY VOLCANO, Saturday January 13, 2024.
Information Geophysical Institute – EPN.
Surface activity level: High, Surface trend: No change
Internal activity level: High, Internal trend: No change
Seismicity: From January 12, 2024, 11:00 a.m. to January 13, 2024, 11:00 a.m.:
The number of seismic events recorded at the reference station over the past 24 hours is shown below. The level of seismic activity of the volcano remains high.
Explosion Event (EXP): 426
Precipitation/Lahars:
No rain was recorded in the volcano area. *In the event of heavy rains, these could remobilize the accumulated materials and generate mudflows with debris, which could descend down the sides of the volcano, flowing into adjacent rivers.
Emissions/ash column:
Thanks to the surveillance camera system and the GOES-16 satellite system, several ash emissions were observed, with heights between 500 and 1,500 meters above the level of the crater, in the southwest and west directions. South West. Likewise, this activity was reported through 4 alerts from the Washington VAAC agency, with heights of 900 meters above the level of the crater, in the West and South-West directions.
Gas:
At midday yesterday, the Mounts satellite system detected the emission of 150 tonnes of SO2 (sulfur dioxide).
Other monitoring parameters:
The FIRMS satellite system detected 25 thermal anomalies, the MIROVA-MODIS satellite system recorded 3 thermal anomalies and the MIROVA-VIIRS satellite system recorded 2 thermal anomalies.
Observation:
Since 6:10 p.m. (TL) yesterday, thanks to the IG-EPN Santa Rosa camera, a pyroclastic flow was observed in the Southeast ravine. This type of phenomenon could cause an increase in sediments in the Volcán River and consequently in the Upano River. In addition, during last night, several episodes of incandescence were recorded, with material descending to 1000 meters below the level of the crater. Until the close of this report, the volcano is cloudy.
Alert level: yellow
Source : IGEPN.
Photo : Carlos Riera