November 25 , 2023 .
Chile , Villarica :
Seismology
The seismological activity of the period was characterized by the recording of:
A continuous tremor signal associated with the fluid dynamics inside the volcano, which during the period presented an energy variation, evaluated with the RSAM parameter, between 0.8 and 1.6 µm/s, values considered above their base level.
6 seismic events of type VT, associated with the fracturing of rocks (Volcano-Tectonics). The most energetic earthquake had a Local Magnitude (ML) value equal to 2.2, located 8.1 km east-southeast of the volcanic edifice, at a depth of 7.0 km relative to to the crater.
17,158 LP-type seismic events, associated with fluid dynamics inside the volcanic system (Long Period). The size of the largest earthquake evaluated from the Reduced Displacement (RD) parameter was equal to 50 cm2.
2045 seismic events of type TR, associated with the dynamics maintained over time of fluids inside the volcanic system (TRemor). The size of the largest earthquake evaluated from the Reduced Displacement (RD) parameter was equal to 29 cm2.
Fluid geochemistry
The sulfur dioxide (SO2) emissions data obtained by the differential optical absorption spectroscopy (DOAS) equipment, corresponding to the Los Nevados and Tralco stations, installed respectively at 10 km in an East-North-East direction and 6 km East-South-East of the active crater, presented an average value of 816 ± 159 t/d, a value higher than that reported for the previous period and which is within the usual values of this volcanic system. The maximum daily value was 1,668 t/d on November 2.
Satellite anomalies were reported in atmospheric sulfur dioxide (SO2) emissions in the area near the volcano between November 8 and 12.
Thermal anomalies by satellites
During the period, 15 thermal alerts were recorded in the area associated with the volcano, with a maximum volcanic radiative power (VRP) of 45 MW on November 12, a value considered low according to data processed by Activity Observation volcanic in the mid-infrared (MIROVA). Thanks to the analysis of Sentinel 2-L2A satellite images, 3 radiance anomalies were detected in the area associated with the crater. The NHI tools platform detected a maximum area of anomalous radiation in the crater area of 42,300 m2 on November 10.
The volcanic system remains in a context of high seismic productivity of LP events and continuous seismic energy values close to 1 um/s. At the same time, Strombolian explosions are still recorded which disperse pyroclastic materials in the zone of influence of the active crater, mainly gaseous emissions, nocturnal incandescence and considerable thermal anomalies. Based on the above, it is determined that the volcanic system presents internal and surface activity linked to the dynamics of an active lava lake, however, the surface activity remained limited to the main crater, it is why potential hazard zoning is suggested. of 500 meters measured from the center of the crater and its technical alert is maintained at:
YELLOW TECHNICAL ALERT: Changes in the behavior of volcanic activity
Source : Sernageomin
Photo : auracaniadiario
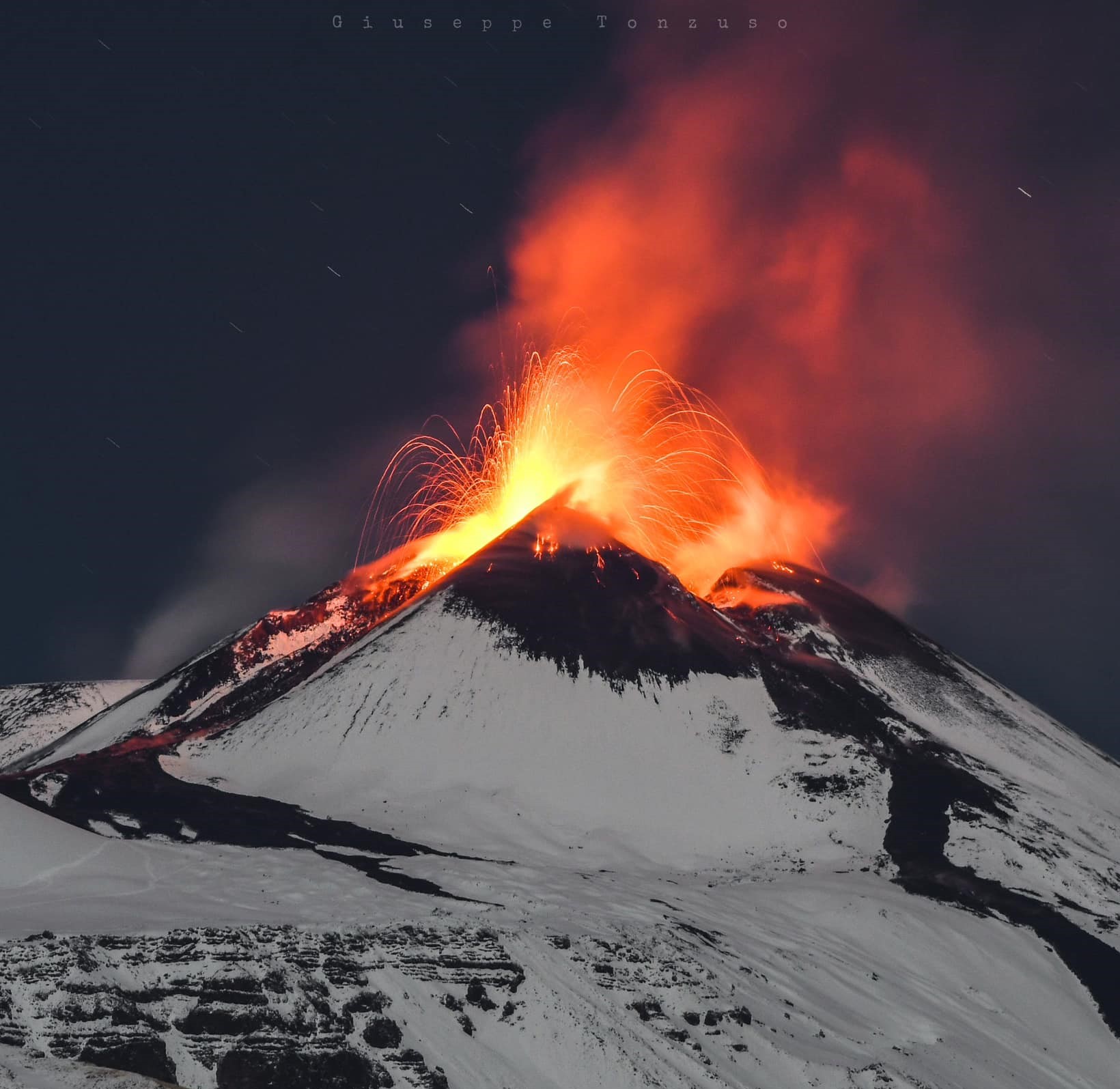
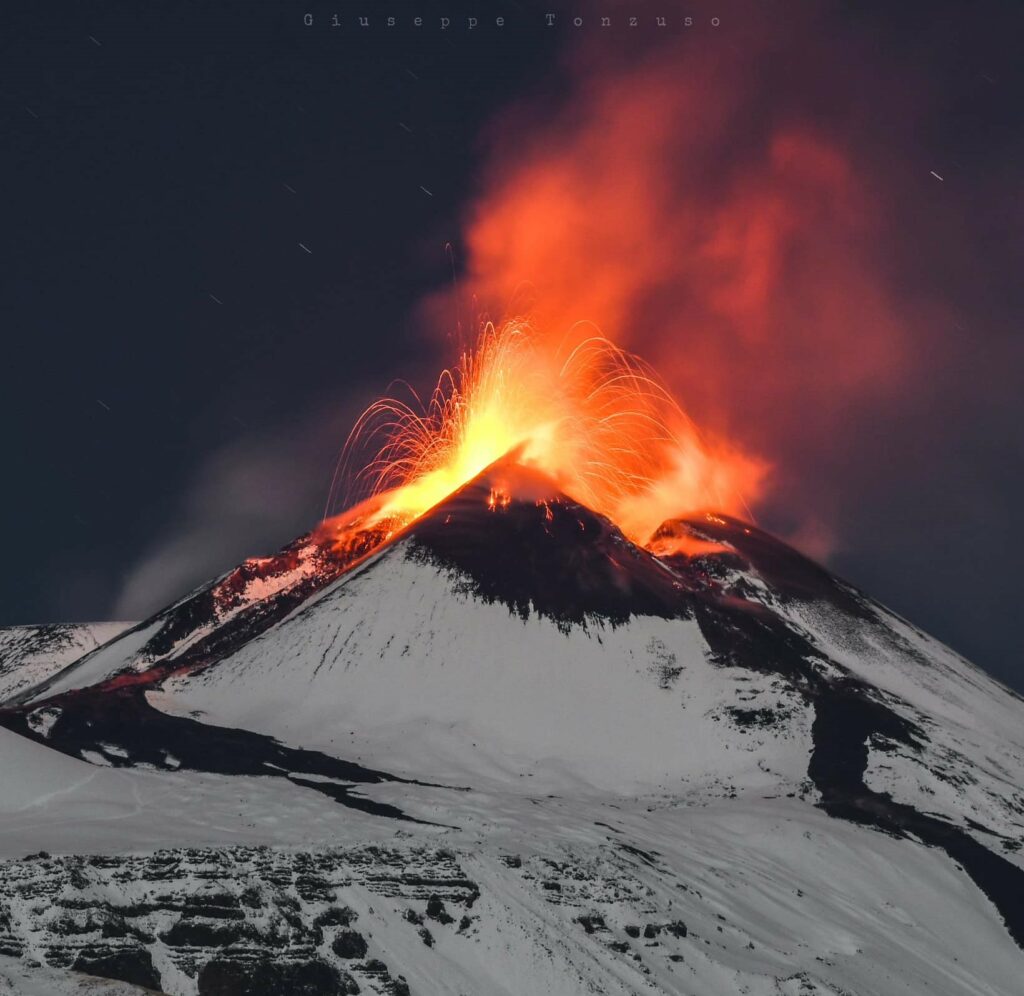
Italy / Sicily, Etna :
Waiting for the INGV press release.
VOLCANO OBSERVATION NOTICE FOR AVIATION (VONA)
Published: November 20, 2023
Volcano: Etna 211060
Current color code: ORANGE
Previous color code: yellow
Source: Etna Volcano Observatory
Notice number: 2023/0085/13N01
Volcano Location: 3744N 01500E
Area: Italy
Summit altitude: 3300 m.
Summary of volcanic activity:
Moderate explosive activity at the summit craters
Volcanic Cloud Height: NO ASH CLOUD ARE PRODUCED
Other information on volcanic clouds: N/A
Remarks: THE PHENOMENON IS OBSERVED BY VISIBLE AND THERMAL SURVEILLANCE CAMERAS
Source : INGV
Photo : Giuseppe Tonzuso
Iceland , Reykjanes Peninsula :
Unchanged situation based on the latest interpretation
Likelihood of Volcanic Eruption still being considered over the magma Intrusion. Today, approximately 300 earthquakes have been detected since midnight.
Updated 24. November at 13:30 UTC
Yesterday, around 650 earthquakes were measured near the dike intrusion north of Grindavík, and since midnight today, nearly 300 earthquakes have been detected. Most of the earthquakes are below M1.0, but the largest earthquake in the last two days was M2.7 near Hagafell. The seismic activity continues to decrease.
Data from GPS measurements show that deformation continues near Svartsengi, and deformation is still measured around the dike intrusion. However, there are indications that the rate of deformation has decreased based on data from the past week. Though, the interpretation of deformation data is complex at this stage. This is because other processes, such as fault movements related to earthquakes and the viscoelastic response of the Earth’s crust to unrest in the area, have an impact on the deformation signals.
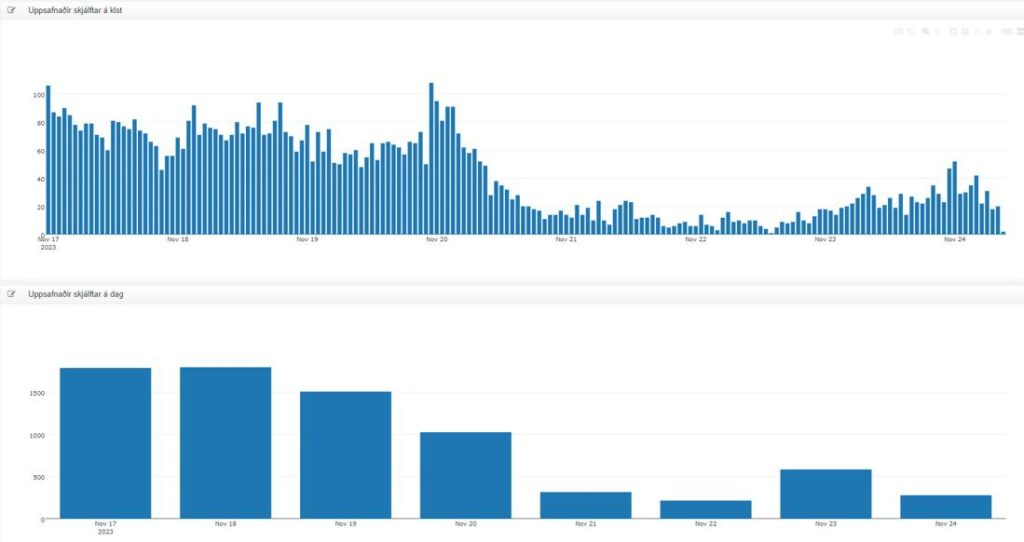
Overview of seismic activity from Friday, November 17th. The upper graph shows the number of earthquakes per hour, and the lower graph shows the number of earthquakes per day. The effects of strong wind and heavy sea swell on the Reykjanes Peninsula on November 21st and 22nd are evident in fewer recorded earthquakes due to reduced sensitivity of the seismic network during that time.
Considering the latest interpretation of all data, the likelihood of a volcanic eruption at some location along the length of the magma intrusion persists. It is possible that magma could emerge in the area between Hagafell and Sýlingarfell. However, as crustal relaxation continues to occur and seismicity decreases, along with a decrease in magma inflow to the intrusion, the likelihood of an imminent volcanic eruption diminishes with time.
Source et photo : IMO
Alaska , Bogoslof :
53°55’38 » N 168°2’4″ W,
Summit Elevation 492 ft (150 m)
Current Volcano Alert Level: UNASSIGNED
Current Aviation Color Code: UNASSIGNED
Following the seismic swarm that began near Bogoslof around October 22, 2023, the frequency of earthquakes has now subsided to background levels. During the swarm 5 to 10 events per hour and up to a total of ~1,100 earthquakes were recorded in one week. The decline in seismicity has been observed over the past 3 weeks, with the last moderate earthquake (M2.7) recorded on November 9. No other signs of volcanic unrest have been detected. In response, AVO lowered the Aviation Color Code and Volcano Alert Level to UNASSIGNED earlier this morning.
Bogoslof volcano is monitored using a single local seismic station, distant seismic and infrasound instruments, satellite data, and lightning networks.
At least nine historical eruptions have been documented at Bogoslof volcano. The most recent occurred from December 2016 to August 2017 and produced seventy main explosive events that generated volcanic ash clouds that rose as high as 42,500 ft (13 km) above sea level, and greatly modified the topography of Bogoslof Island. Previous eruptions of the volcano have lasted weeks to months and have on occasion produced ash fall on the community of Unalaska. Eruptions of the volcano are often characterized by multiple explosive ash-producing events as well as the growth of lava domes.
Source : AVO
Photo : Read, Cyrus / Alaska Volcano Observatory / U.S. Geological Survey. ( 2018)
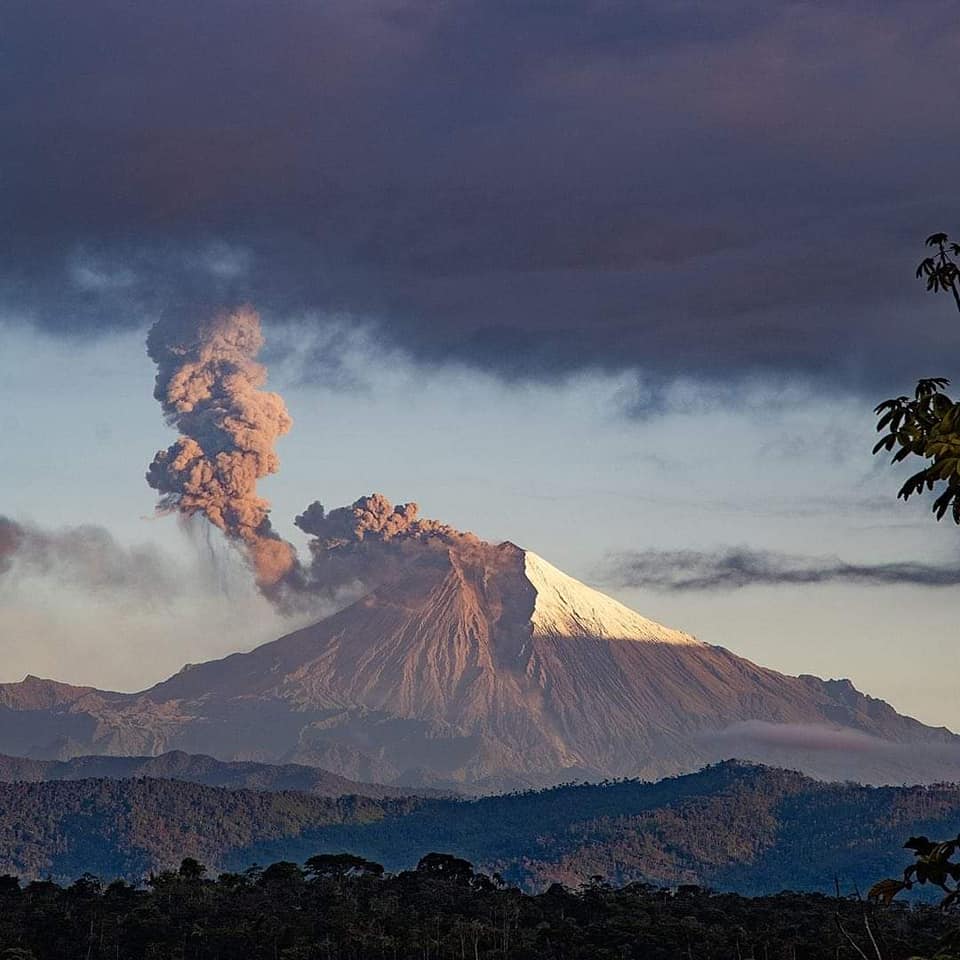
Ecuador , Sangay :
DAILY REPORT ON THE STATE OF THE SANGAY VOLCANO, Friday November 24, 2023.
Information Geophysical Institute – EPN.
Surface activity level: High, Surface trend: No changes
Internal activity level: High, Internal trend: No changes
Seismicity: From November 23, 2023, 11:00 a.m. to November 24, 2023, 11:00 a.m.:
The number of seismic events recorded at the reference station over the past 24 hours is shown below. The level of seismic activity of the volcano remains high.
Explosion Event (EXP): 442
Precipitation/Lahars:
Rain fell in the volcano area, without generating mudslides and debris.
**In the event of heavy rains, these could remobilize the accumulated volcanic material, generating mud and debris flows which would descend down the sides of the volcano and flow into adjacent rivers.
Emissions/ash column:
Due to weather conditions, it was not possible to observe gas and ash emissions via the surveillance camera network or via the GOES-16 satellite system.
Other monitoring parameters:
The FIRMS satellite system has detected 4 thermal anomalies over the last 36 hours.
Observation:
Since yesterday afternoon until the closing of this report, the volcanic sector remained cloudy.
Alert level: yellow
Source : IGEPN.
Photo : volcan sangay FB