July 28 , 2023.
Kamchatka , Sheveluch :
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION (VONA)
Issued: July 28 , 2023
Volcano: Sheveluch (CAVW #300270)
Current aviation colour code: RED
Previous aviation colour code: orange
Source: KVERT
Notice Number: 2023-87
Volcano Location: N 56 deg 38 min E 161 deg 18 min
Area: Kamchatka, Russia
Summit Elevation: 3283 m (10768.24 ft), the dome elevation ~2500 m (8200 ft)
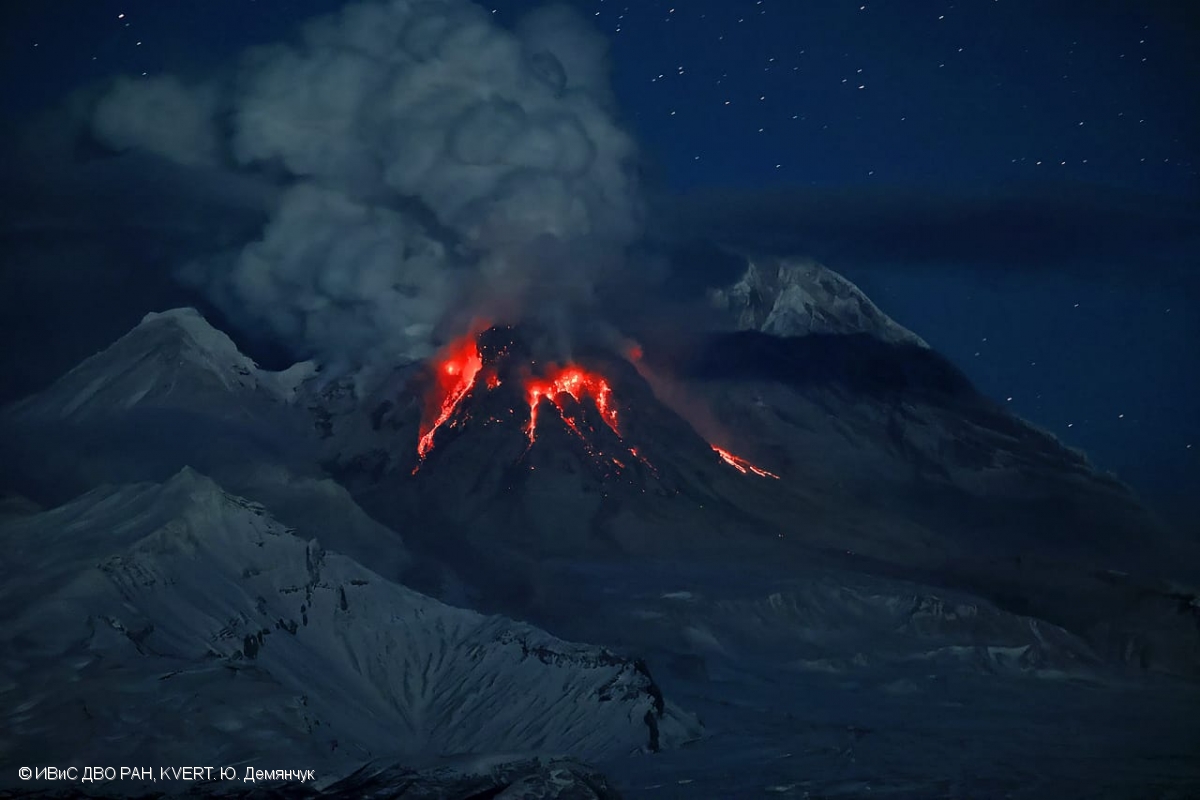
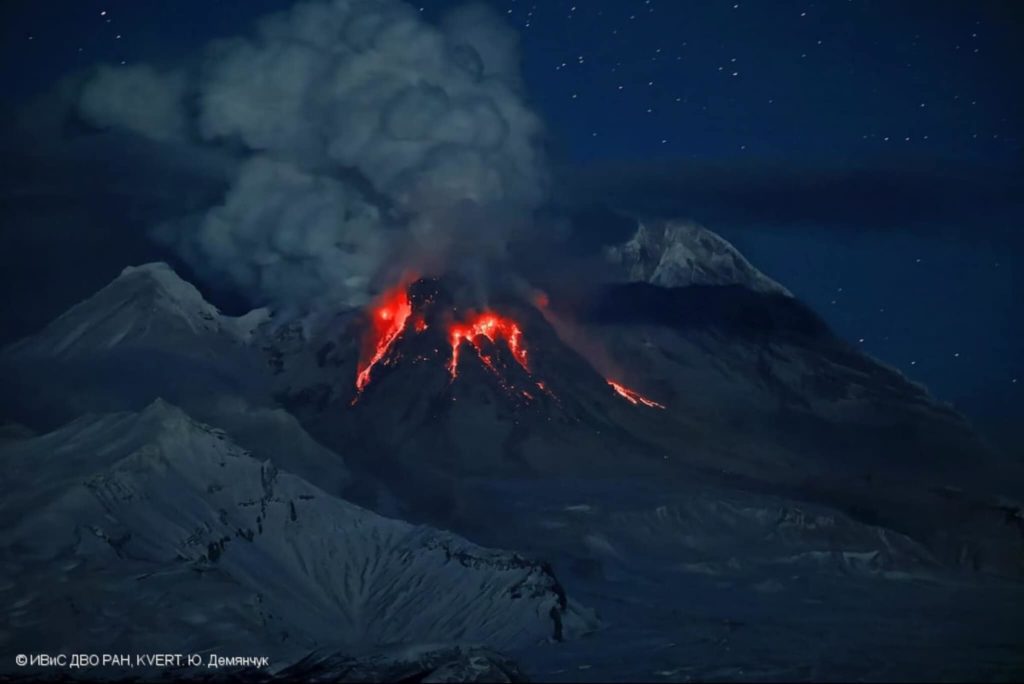
Powerful gas-steam activity and hot avalanches crash from the top of Sheveluch Volcano’s lava dome on November 29, 2022.
Volcanic Activity Summary:
An extrusive-effusive eruption of the volcano continues. Satellite data by KVERT showed explosions sent ash up to 4.5 km a.s.l. at 02:00 UTC on 28 July; and explosions sent ash up to 7.7-8 km a.s.l. at 04:10 UTC on 28 July. Ash plume is extending to the northeast of the volcano.
An extrusive-effusive eruption of the volcano continues. A danger of ash explosions up to 10 km (32,800 ft) a.s.l. is remains. Ongoing activity could affect international and low-flying aircraft.
Volcanic cloud height:
7700-8000 m (25256-26240 ft) AMSL Time and method of ash plume/cloud height determination: 20230728/0410Z – Himawari-9 14m15
Other volcanic cloud information:
Distance of ash plume/cloud of the volcano: 26 km (16 mi)
Direction of drift of ash plume/cloud of the volcano: E / azimuth 86 deg
Time and method of ash plume/cloud determination: 20230728/0410Z – Himawari-9 14m15
Source : Kvert
Photo : Yu. Demyanchuck / IVS FEB RAS KVERT . ( Archive)
Alaska , Trident :
Summary
• The unrest detected over the past five months is a result of magma intrusion beneath Trident Volcano.
• The elevated earthquake rate is also observed at neighboring volcanoes of the Katmai volcanic cluster, including Katmai, Martin, Mageik and the Novarupta vent.
• Some magma intrusions do not result in eruptions, and sometimes the unrest can persist for months or years prior to an eruption.
• If an eruption were to occur, the primary hazard would be from volcanic ashfall and drifting ash clouds, which could disrupt air and marine travel and impact local communities and infrastructure.
• The Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO) continues to monitor the volcanoes of the Katmai volcanic cluster and will issue further updates as needed.
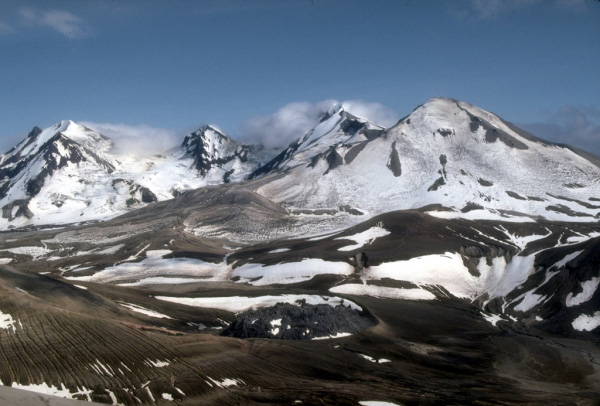
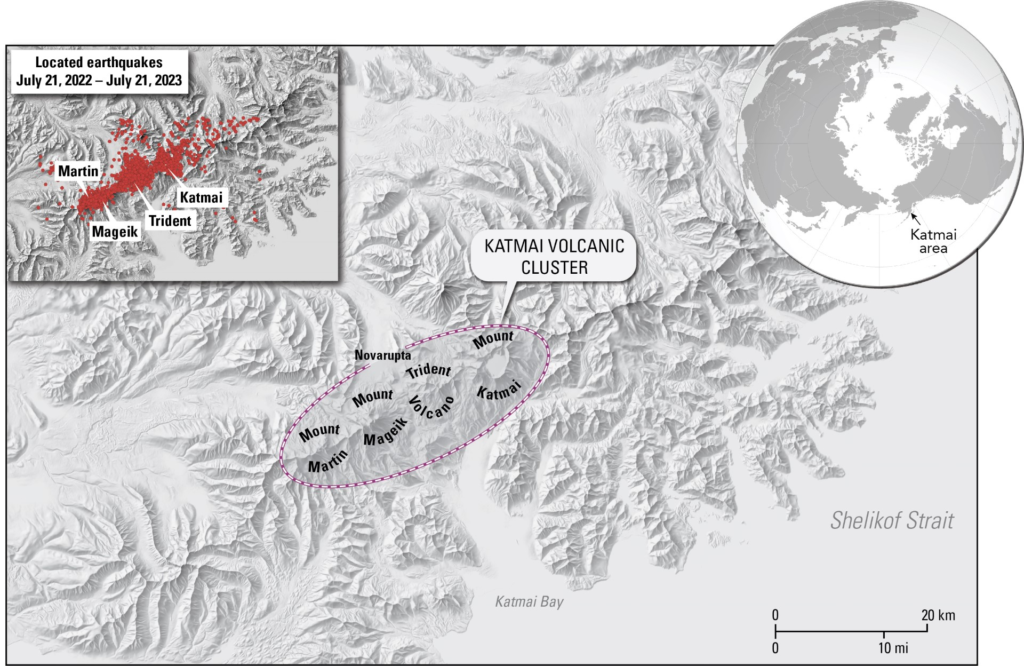
Map showing location of Mount Katmai, Trident Volcano, Mount Mageik, Mount Martin, Novarupta, and earthquakes located July 21, 2022 – July 21, 2023.
Current Observations
Rates of earthquakes
Earthquake activity at Trident Volcano has been elevated since August 2022 but has waxed and waned. The initial activity consisted of an unusual series of earthquakes beneath Trident Volcano that progressively migrated over four days from around 16 mi (25 km) below sea level to shallow depths of about 3 mi (5 km) below sea level. In response to this behavior, AVO raised the Volcano Alert Level and Aviation Color Code to ADVISORY/YELLOW on September 29, 2022. After a decrease in seismicity, AVO lowered the Alert Level and Aviation Color Code to GREEN/NORMAL on October 19, 2022.
In November 2022, activity again escalated and consisted of shallow earthquakes less than 5 mi (8 km) below sea level. Most quakes were less than magnitude 1, but dozens of magnitude 2 and 3 earthquakes have occurred. The largest earthquake so far reached a magnitude near 4 on November 20, 2022. The earthquake rate averaged between 10 to 20 daily earthquakes, occasionally reaching rates several times higher. This level of seismicity persisted into February 2023, prompting AVO to raise the Aviation Color Code to YELLOW and the Volcano Alert Level to ADVISORY on February 22, 2023.
The multiple peaks of Trident Volcano as viewed from the top of Baked Mountain in the Valley of Ten Thousand Smokes, Alaska. Trident Volcano is composed of a cluster of andesite and dacite cones and is the only Katmai group volcano other than Katmai and Novarupta to have had historical activity. The Novarupta lava dome is visible at bottom, center.
Low-frequency earthquakes under Trident
In May 2023, AVO began detecting a marked increase in low-frequency earthquakes—in addition to regular earthquakes—at shallow and deep levels in the region between Trident and Novarupta, which lies 3 mi (5 km) to the northwest. These types of earthquakes often indicate the movement of magma or magmatic fluids within the Earth’s crust. The shallow, low-frequency events occur about 2.5 mi (4 km) north of Trident Volcano at the same depths as the regular earthquakes, around 3 mi (5 km) below sea level. The deep, low-frequency events span a broader area between Trident and Novarupta and occur 18.5 to 22 mi (30 to 35 km) below sea level. These deep low-frequency earthquakes are often accompanied by longer-duration bursts of continuous tremor, indicating deep fluid movement.
Other monitoring data
Ground uplift at Trident Volcano has also been detected in satellite radar data. Snow cover prohibits winter observations, which limits our ability to provide precise timing, but data from June 3, 2023, indicates that about 2 in (5 cm) of ground uplift has occurred since October 6, 2022. Uplift is most significant on the volcano’s south flank.
There have been no visual changes to the ground surface or hydrology. No gas emissions or temperature changes have been observed.
Source : AVO
Photos : AVO , McGimsey, R. G./ Alaska Volcano Observatory/U.S. Geological Survey .
La Réunion , Piton de la Fournaise :
Press release from the Institute of Earth Physics in Paris, Volcanological Observatory of Piton de la Fournaise. July 27, 2023 – 10:00 – 06:00 UTC
Ongoing eruption
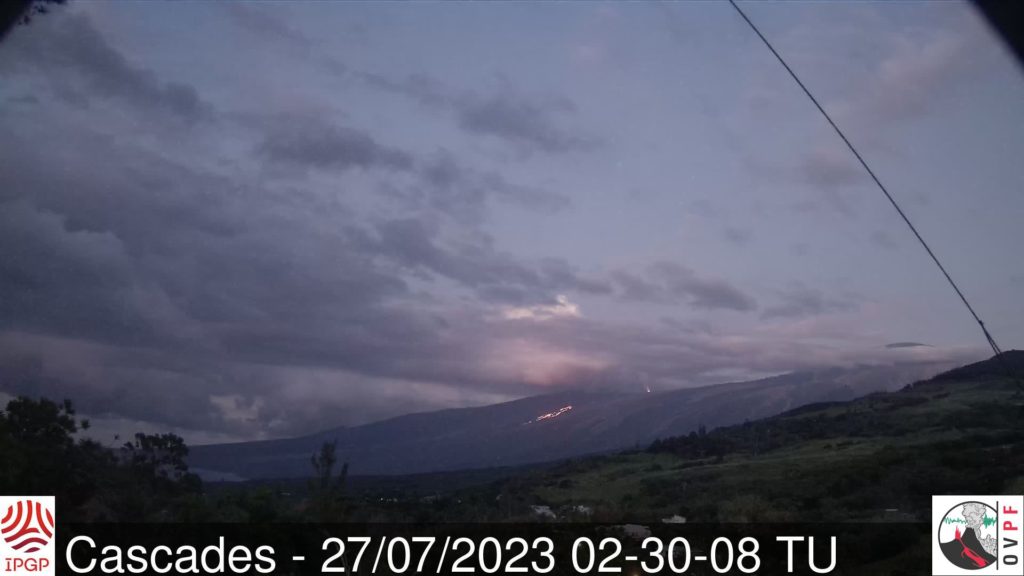
The eruption started on 02/07/2023, around 08:30 local time continues. The amplitude of the volcanic tremor (indicator of an emission of lava and gas on the surface) remains very low compared to the start of the eruption and still shows fluctuations.
Due to the low surface activity and the cloudy passages on the eruptive site, no estimate of the lava flows could be made over the last 24 hours.
With the low surface activity, the morphology of the active volcanic cone – located southeast of the Enclos Fouqué at 1720 m altitude – hardly changes and the flow of the lava takes place mainly in lava tunnels. , even if flows are still visible at resurgence points and feed flows extending to distances of 1200 to 2000 m from the eruptive cone, i.e. up to 1000-1100 m altitude.
Low inflation of the summit area is still recorded, indicating a re-pressurization of the volcano’s feeder system with possible transfer of deep magma to the latter.
The seismic activity recorded under the summit zone remains weak. Thus over the last 24 hours, no superficial volcano-tectonic earthquake has been recorded. This low seismic activity leads to a reduction in the risk of the appearance of a new crack and/or collapse in the crater, but does not mean that it can be excluded, as shown by the continuation of the summit inflation and the fluctuations in the amplitude of the tremor.
Alert level: Alert 2-1 (eruption in the Enclosure without any particular threat to the safety of people, property or the environment).
Source et photo : OVPF
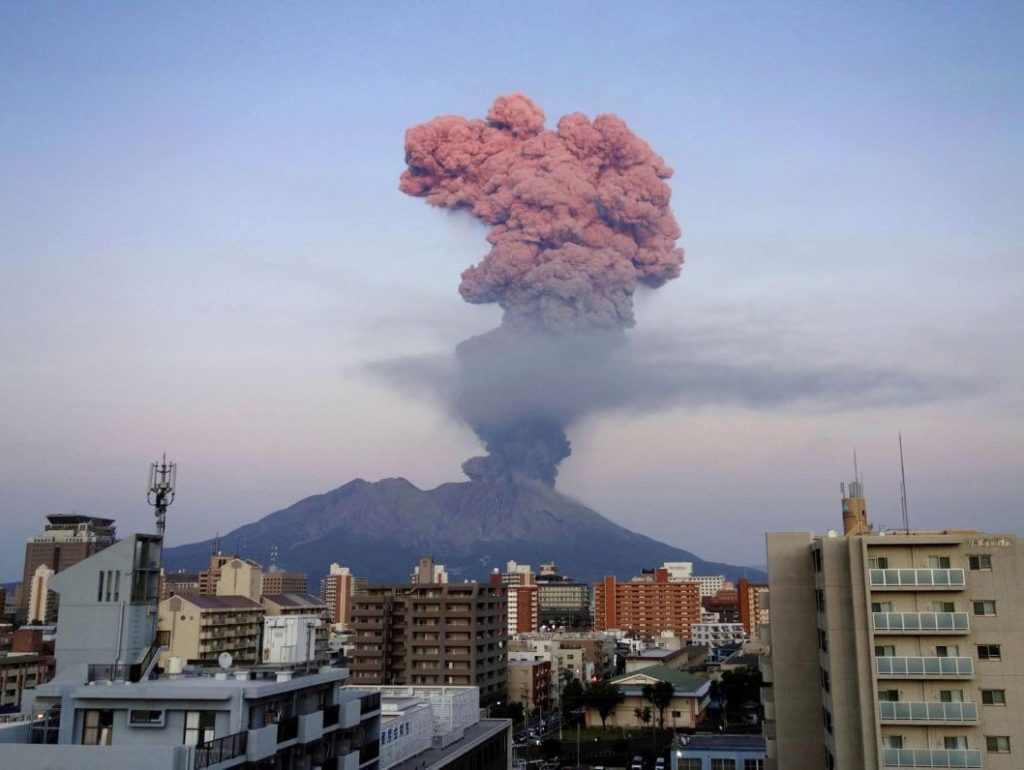
Japon , Sakurajima :
JMA reported ongoing activity at both Minamidake Crater and Showa Crater (Aira Caldera’s Sakurajima volcano) during 16-24 July. Very small eruptive events occasionally occurred at Minamidake and incandescence was observed at night. An eruptive event at Showa on 16 July produced an ash plume that rose 1.2 km above the crater rim and drifted N. An explosion at the same crater at 23h14 produced an ash plume that rose 1.8 km above the crater rim and drifted N, and also ejected blocks 300-500 m from the vent. Explosions at 12h24 and 12h32 on 17 July generated ash plumes that rose 2-2.5 km and drifted N, with blocks ejected 500-800 m from the vent. At 20h44 on 17 July an ash plume from an explosion rose 1.2 km and drifted N. Sulfur dioxide emissions were very high, averaging 3,200 tons per day on 20 July. The Alert Level remained at 3 (on a 5-level scale), and the public was warned to stay 2 km away from both craters.
The Aira caldera in the northern half of Kagoshima Bay contains the post-caldera Sakurajima volcano, one of Japan’s most active. Eruption of the voluminous Ito pyroclastic flow accompanied formation of the 17 x 23 km caldera about 22,000 years ago. The smaller Wakamiko caldera was formed during the early Holocene in the NE corner of the Aira caldera, along with several post-caldera cones. The construction of Sakurajima began about 13,000 years ago on the southern rim of Aira caldera and built an island that was finally joined to the Osumi Peninsula during the major explosive and effusive eruption of 1914. Activity at the Kitadake summit cone ended about 4850 years ago, after which eruptions took place at Minamidake. Frequent historical eruptions, recorded since the 8th century, have deposited ash on Kagoshima, one of Kyushu’s largest cities, located across Kagoshima Bay only 8 km from the summit. The largest historical eruption took place during 1471-76.
Source : Agence météorologique japonaise (JMA), GVP.
Photo : Deniss García Mendoza
Indonesia , Ili Lewotolok :
An eruption of G. Ili Lewotolok occurred on Thursday, July 27, 2023 at 10:02 p.m. WITA with the height of the ash column observed at ± 500 m above the summit (± 1923 m above sea level) . The ash column was observed to be gray with moderate intensity, oriented northwest. This eruption was recorded on a seismograph with a maximum amplitude of 36.9 mm and a duration of 73 seconds.
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION – VONA
Issued : July 27 , 2023.
Volcano : Ili Lewotolok (264230)
Current Aviation Colour Code : ORANGE
Previous Aviation Colour Code : orange
Source : Ili Lewotolok Volcano Observatory
Notice Number : 2023LEW041
Volcano Location : S 08 deg 16 min 19 sec E 123 deg 30 min 18 sec
Area : East Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia
Summit Elevation : 4554 FT (1423 M)
Volcanic Activity Summary :
Eruption with volcanic ash cloud at 14h02 UTC (22h02 local).
Volcanic Cloud Height :
Best estimate of ash-cloud top is around 6154 FT (1923 M) above sea level or 1600 FT (500 M) above summit. May be higher than what can be observed clearly. Source of height data: ground observer.
Other Volcanic Cloud Information :
Ash cloud moving to northwest. Volcanic ash is observed to be gray. The intensity of volcanic ash is observed to be medium.
Remarks :
Eruption recorded on seismogram with maximum amplitude 36.9 mm and maximum duration 73 second.
Source : Magma Indonésie
Photo : Jeffry Pugel /PVMBG – Magma Indonesia ( archive).