October 19 , 2022.
Italy , Stromboli :
WEEKLY BULLETIN, from October 10, 2022 to October 16, 2022, (issue date October 18, 2022)
ACTIVITY STATUS SUMMARY
In the light of the surveillance data, it is highlighted:
1) VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS: During this period, normal explosive activity of the Strombolian type was observed with spattering and lava flows from the area of the N crater. The total hourly frequency and intensity of the explosions were low in the North crater area while no explosive activity was observed in the Center-South crater area.
2) SEISMOLOGY: The seismological parameters do not show significant variations.
3) GROUND DEFORMATIONS: In the period under review, the island’s ground deformation monitoring networks recorded some variations probably related to the eruptive activity that occurred during the week.
4) GEOCHEMISTRY: SO2 fluxes at an average level with intraday values are at a high level.
CO2 fluxes in the crater area showed significant growth last week, settling at high values.
The C/S ratio in the plume is at average values (C/S = 8.4).
The isotope ratio of helium in groundwater shows high values (4.41 Ra).
5) SATELLITE OBSERVATIONS: The thermal activity observed by satellite in the summit area was moderate.
VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS
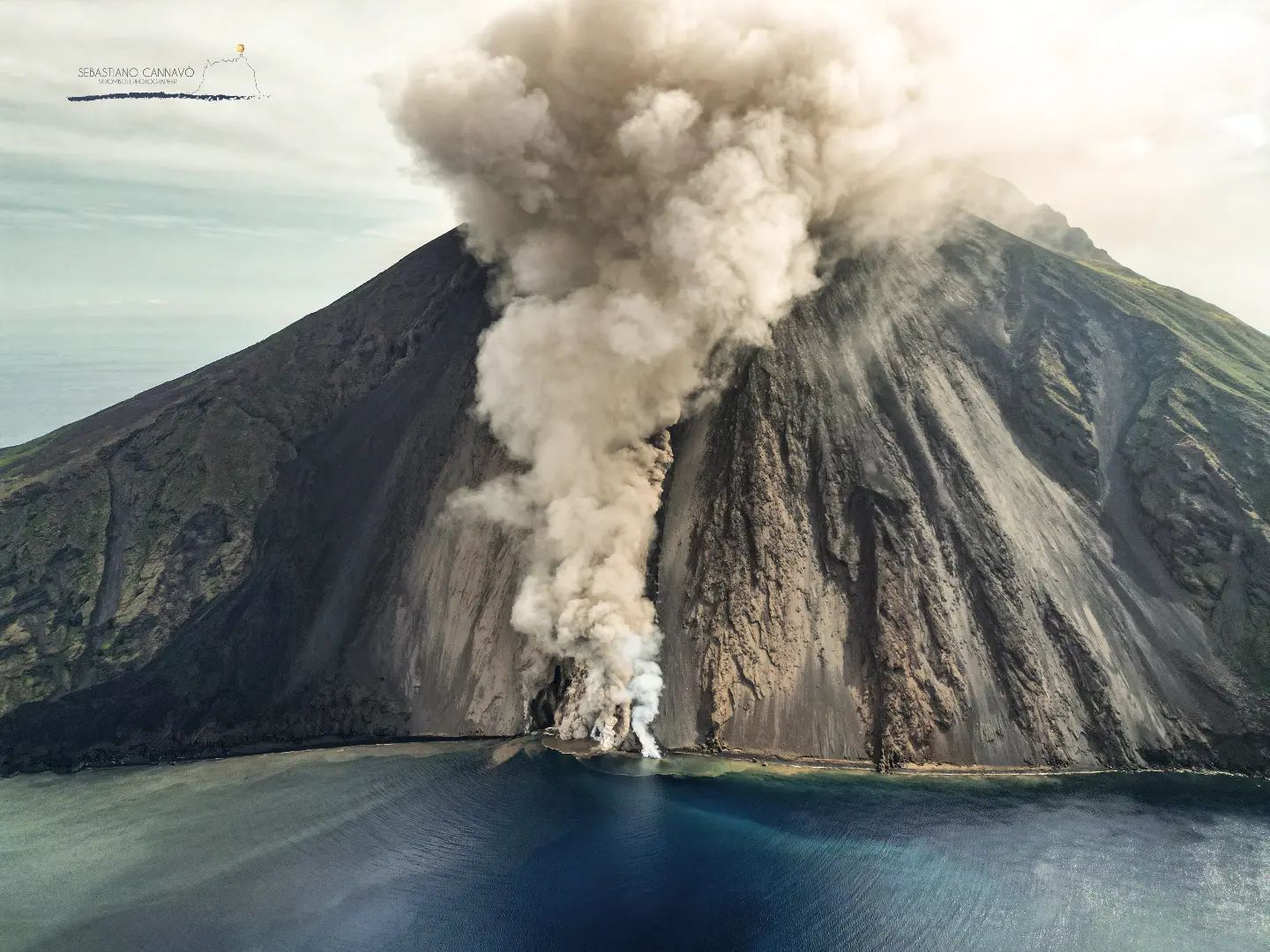
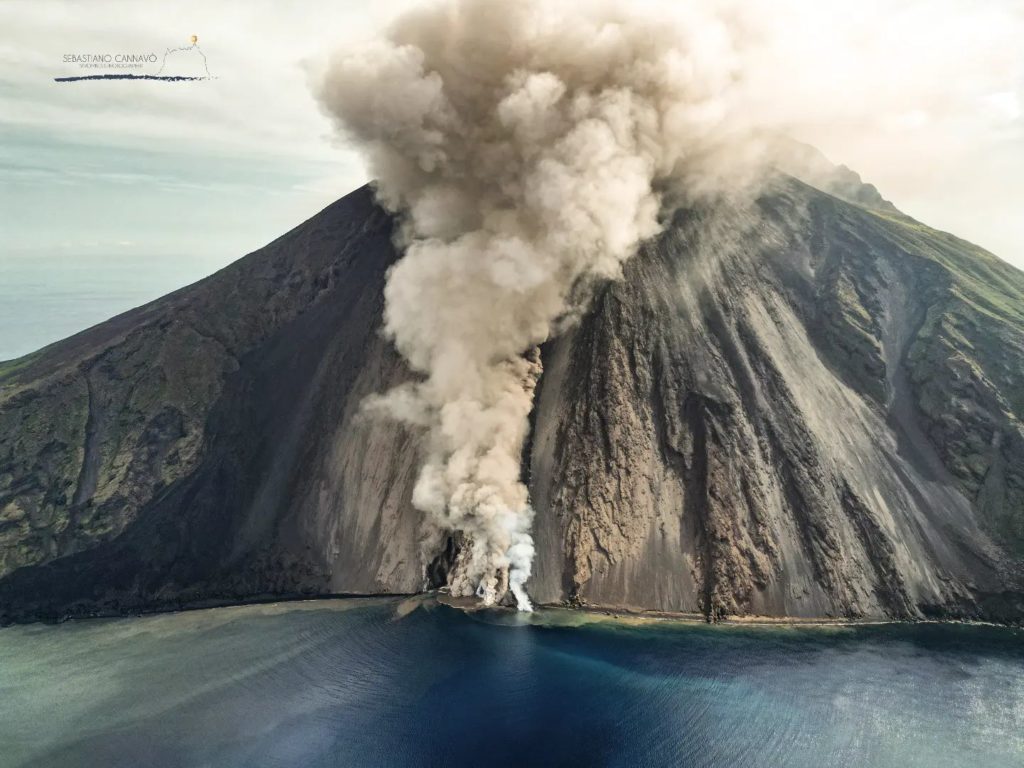
During the observation period, the eruptive activity of Stromboli was characterized by the analysis of the images recorded by the INGV-OE surveillance cameras at an altitude of 190 m (SCT-SCV; the cameras at altitude 400m and Pizzo are currently not available following damage to the optical fiber connecting Punta Labronzo and COA due to the bad weather that hit the island on August 12, 2022). During the period under observation, the explosive activity was mainly produced by three eruptive vents located in the North Crater area. All vents are placed within the depression that occupies the crater terrace. As for the effusive activity which began on October 9, it showed a slow and gradual decrease from the 10 to run out on October 14.
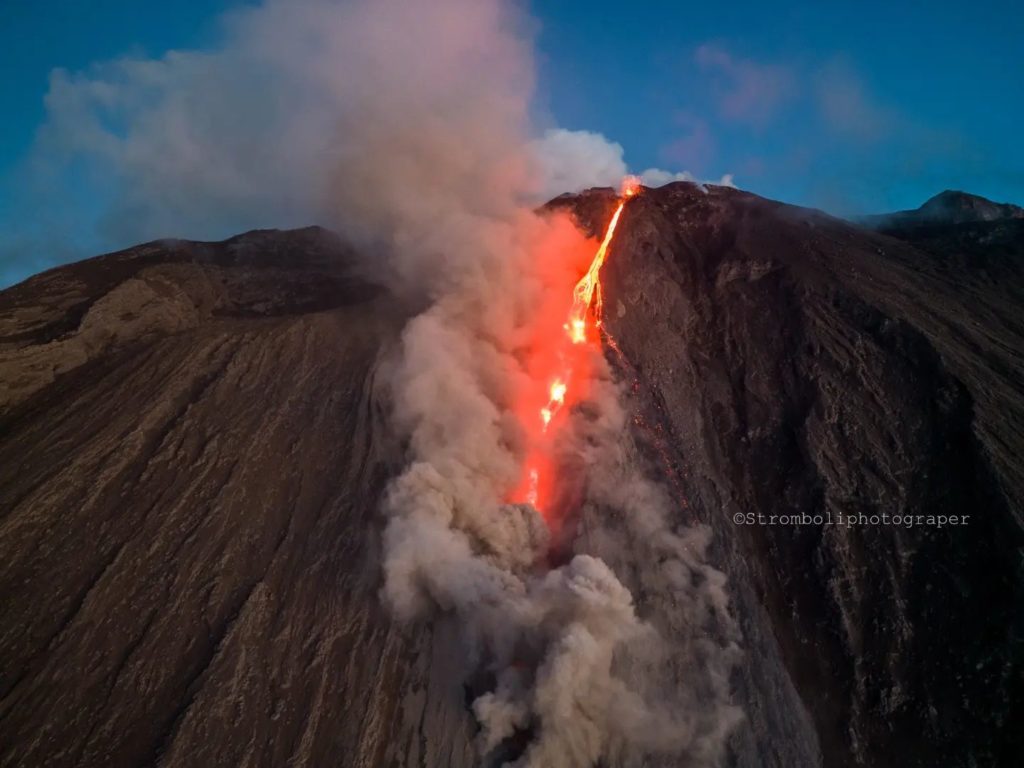
Effusive activity of October 9, 2022
Between October 10 and 16, INGV personnel carried out various remote inspections and observations of the Sciara del Fuoco (SdF) from an altitude of 190 m, 290 m and 400 m and of Roccette. This activity was carried out within the framework of the DPC-INGV All.A convention and the UN departmental project. The evolution of the activity during the week is presented below.
Between October 10 and 16, the lava flow infeed showed a gradual decrease from what was observed on October 9. The lava field developed gradually over the days, with many overlaps of smaller flows. The lava front also showed a slow retreat from 400 m a.s.l. until Oct. 11 to 600 m a.s.l. on Oct. 16. Due to the pulsating regime of the lava flow, frequent collapses and detachments of material were triggered from the lava channel eroded by the flows and from the front of the flow itself which, rolling along the Sciara del Fuoco, quickly reached the coast and spilled into the sea, forming a delta of debris. Upon contact with water, the material dispersed forming lobes, while clouds of steam and ash formed which rose into the air. Regarding the explosive activity, it was maintained at a low level with intense splashing activity of variable regime at the level of the N2 crater (North zone) and with phases which sometimes resulted in lava fountains . On October 14, the eruptive activity appeared in clear decrease compared to what had been observed the previous days. The projection activity at the level of the N2 crater (North zone) was more contained and the thermal anomaly associated with the apical parts of the lava flow seemed to attenuate. The frequency and magnitude of material collapses had markedly decreased on the 15th from the analysis of surveillance camera images and field observations, it was observed that the flow along the Sciara del Fuoco did not was more fed, while modest spattering activity at the N2 vent persisted in the North Crater area on October 16.
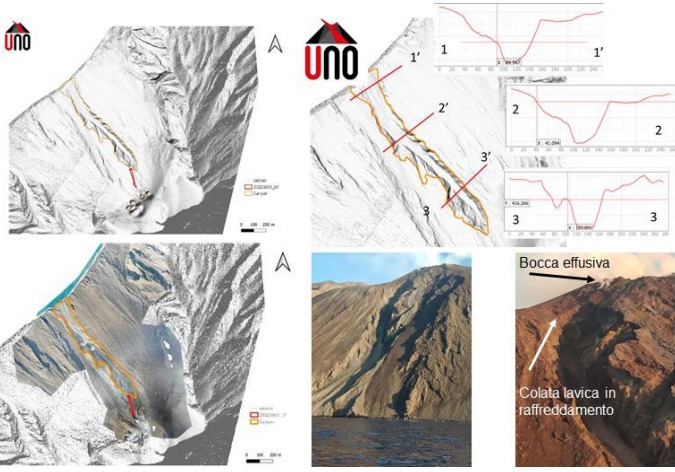
On October 16, drone overflights were carried out to highlight the morphological changes in the crater area. The soundings highlighted the presence of fractures with obvious thermal anomalies between N1 and N2, not observed in the soundings prior to the current eruptive crisis. These fractures cross N1 with an approximate North-North-East/South-South-West direction. Topographic profiles were located along three sections of the slope: at the base, approximately in the middle and near the highest point of the incision. The depth of the incision varies from a few tens of meters at sea level to a maximum of about 70 m and has a maximum width of 120 m.
Shaded terrain model and orthomosaic. The orange line delimits the incision, the red line the cooling flow of October 15, 2022. The topographic profiles were drawn according to three sections located at the base, in the middle and near the highest point of the incision. Images of the Sciara del fuoco taken on October 15 at 5:30 p.m. local time, from a coastguard boat.
Observations of explosive activity captured by surveillance cameras
Sector N1 located in the North crater area produced low intensity explosions (less than 80 m high) emitting coarse materials (bombs and lapilli). Sector N2, with two emission points, showed intense continuous projection activity that fed the lava flows that followed one another along the Sciara del Fuoco for most of the period before building the edge of the crater and to remain confined within sector N2. On the morning of October 16 in the N2 sector, when the projection activity ceased, numerous series of low intensity volcanic ash impulsive events were observed. The average frequency of explosions varied between 2 and 4 events/h. In the Center-South zone, it was not possible to discriminate between the different sectors due to the close framing of the cameras at an altitude of 190 m towards the CS crater zone. In this crater area during the period under observation no activity was shown.
Source : INGV.
Photos : Sebastiano Cannavo / Stromboli Stati d’animo , INGV.
Philippines , Mayon :
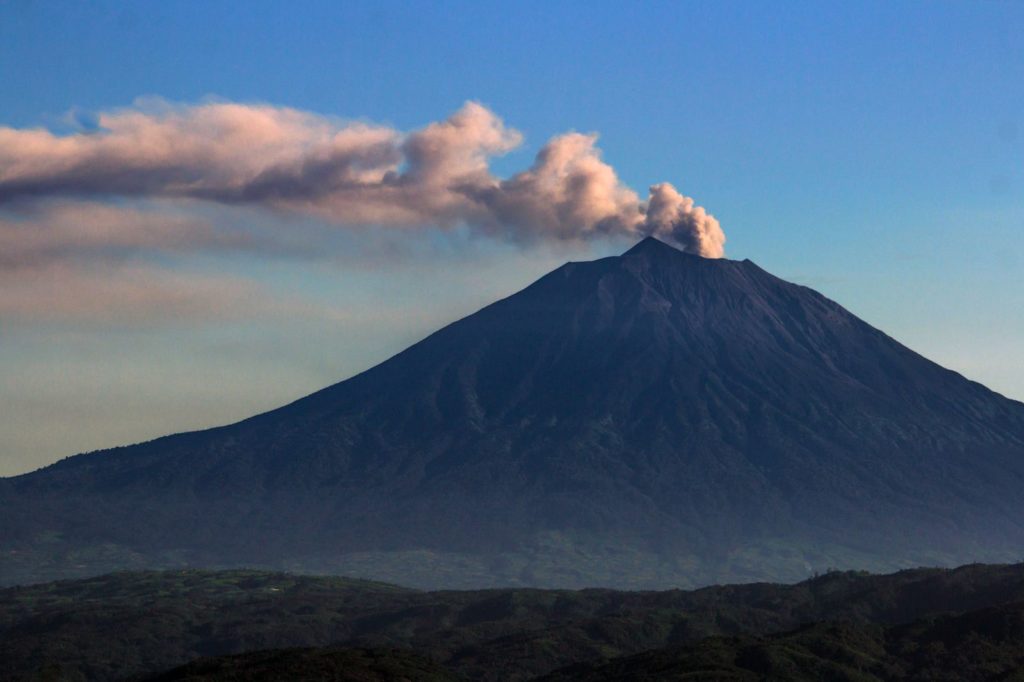
MAYON VOLCANO BULLETIN 19 October 2022 8:00 AM
In the past 24-hour period, the Mayon Volcano Network recorded two (2) volcanic earthquakes and one (1) rockfall event. Moderate emission of white steam-laden plumes that crept downslope before drifting to the general east was observed. Faint crater glow from the summit could be observed at night. Sulfur dioxide (SO2) emission was last measured at an average of 260 tonnes/day on 13 October 2022. Based on ground deformation parameters from EDM, Precise Leveling, electronic tilt and continuous GPS monitoring, Mayon Volcano has been slightly inflated since 2020.

Alert Level 2 (Increased Unrest) prevails over Mayon Volcano. The public is reminded that there is current unrest driven by shallow magmatic processes that could eventually lead to phreatic eruptions or even precede hazardous magmatic eruption. Entry into the six (6) kilometer-radius Permanent Danger Zone (PDZ) is strictly prohibited to minimize risks from sudden explosions, rockfall and landslides. In case of ash fall events that may affect communities downwind of Mayon’s crater, people should cover their nose and mouth with damp, clean cloth, or dust mask. Civil aviation authorities must also advise pilots to avoid flying close to the volcano’s summit as ash from any sudden eruption can be hazardous to aircraft.
DOST-PHIVOLCS maintains close monitoring of Mayon Volcano and any new development will be communicated to all concerned stakeholders.
Source et photo : Phivolcs.
Indonesia , Kerinci :
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION – VONA
Issued : October 19 , 2022.
Volcano : Kerinci (261170)
Current Aviation Colour Code : ORANGE
Previous Aviation Colour Code : yellow
Source : Kerinci Volcano Observatory
Notice Number : 2022KER03
Volcano Location : S 01 deg 41 min 49 sec E 101 deg 15 min 50 sec
Area : Jambi, West Sumatra, Indonesia
Summit Elevation : 12176 FT (3805 M)
Volcanic Activity Summary :
Ash cloud at 01h15 UTC (08h15 local). Ash emission is continuing.
Volcanic Cloud Height :
Best estimate of ash-cloud top is around 14416 FT (4505 M) above sea level, may be higher than what can be observed clearly. Source of height data: ground observer.
Other Volcanic Cloud Information :
Ash cloud moving to Northwest
Remarks :
Seismic activity is characterized by contiuous volcanic tremor.
Source : Magma Indonésie.
Photo : gvp-luke-mackin-f
Hawaii , Mauna Loa :
19°28’30 » N 155°36’29 » W,
Summit Elevation 13681 ft (4170 m)
Current Volcano Alert Level: ADVISORY
Current Aviation Color Code: YELLOW
Activity Summary:
Mauna Loa is not erupting and there are no signs of an imminent eruption at this time. However, Mauna Loa continues to be in a state of heightened unrest as indicated by increased earthquake activity and inflation of the summit. The current unrest is most likely being driven by renewed input of magma 2-5 miles (3-8 km) beneath Mauna Loa’s summit. Monitoring data show no significant changes in the past day.
Observations:
During the past 24 hours, HVO detected 29small-magnitude (below M3.0) earthquakes 2-3 miles (3-5 km) below Mokuāʻweoweo caldera and 4-5 miles (6-8 km) beneath the upper-elevation northwest flank of Mauna Loa. Both of these regions have historically been seismically active during periods of unrest on Mauna Loa.
Global Positioning System (GPS) instruments at the summit and on the flanks of Mauna Loa continue to measure inflation at rates elevated since mid-September. However, tiltmeters at the summit are not showing significant surface deformation over the past week.
Concentrations of sulfur dioxide (SO2), hydrogen sulfide (H2S), and carbon dioxide (CO2), as well as fumarole temperatures, remain stable at the summit and at Sulphur Cone on the upper Southwest Rift Zone. Webcam and thermal camera views have shown no changes to the volcanic landscape on Mauna Loa over the past week.
Source et photo : HVO
Chile , Nevados de Chillan :
Special Report on Volcanic Activity (REAV), De Nuble region, Nevados de Chillan volcanic complex, October 17, 2022, 09:40 a.m. local time (mainland Chile).
The National Service of Geology and Mines of Chile (Sernageomin) publishes the following PRELIMINARY information, obtained through the monitoring equipment of the National Volcanic Monitoring Network (RNVV), processed and analyzed at the Volcanological Observatory of the Southern Andes ( Ovdas):
Monday, October 17, 2022, at 09:10 local time (12:10 UTC), monitoring stations installed near the Nevados de Chillan volcanic complex recorded an earthquake associated with fluid dynamics (long period type), inside the volcanic system .
The characteristics of earthquakes after their analysis are as follows:
ORIGINAL TIME: 09:10 local time (12:10 UTC)
LATITUDE: 36.874°S
LONGITUDE: 71.384° W
DEPTH: 0.1km
REDUCED DISPLACEMENT: 961 (cm*cm)
ACOUSTIC SIGNAL: 171 Pascals (Pa) reduced to 1 km
The characteristics of surface activity are as follows:
MAXIMUM HEIGHT OF THE COLUMN: 2700 m above the point of emission
DIRECTION OF DISPERSION: Southwest (SW)
COMMENTS:
An explosion was observed with a high content of black/grey colored pyroclasts, with an emission column height of 2700 m above the emission point. In addition, an important pyroclastic flow was recorded in a preferential direction towards the North-North-East, with a distance greater than 500m from the active crater.
Because of the cloudiness in the area, it was not possible to determine the height of the emission column. But from the Andarivel camera, it could be evaluated at more than 400m, in the direction of dispersion towards the South-East (SE).
The volcanic technical alert remains at the Yellow level.
Sources et photo: Sernageomin.