June 30 , 2022 .
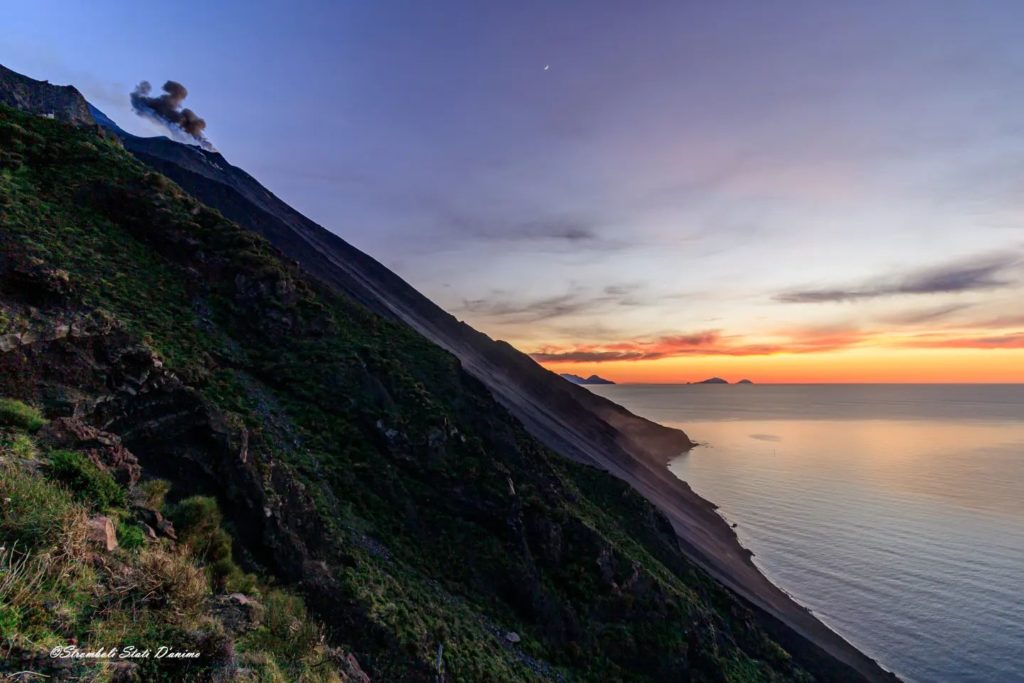
Italy , Stromboli :
Press release on Stromboli’s activity. June 29, 2022, 03:08 (01:08 UTC).
The National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology, Osservatorio Etneo, reports that monitoring networks recorded an anomalous seismic signal at 03:05 (01:05 UTC).
Press release on Stromboli’s activity. June 29, 2022, 03:54 (01:54 UTC).
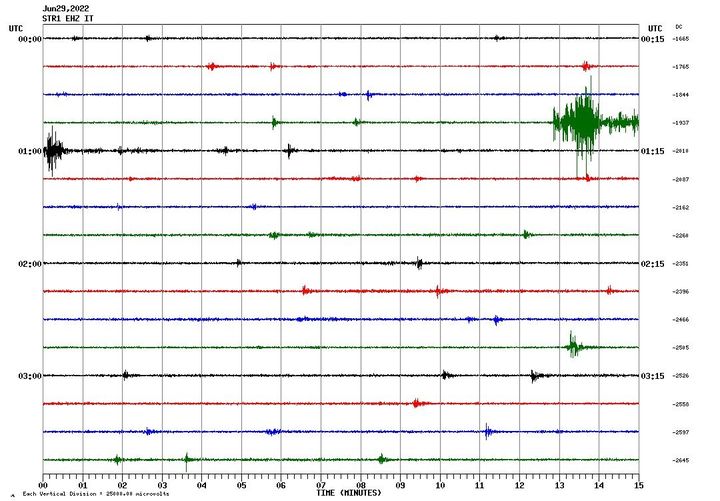
The National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology, Osservatorio Etneo, announces that at 00:57 (UTC) the seismic stations of Stromboli recorded a low frequency signal which in a few seconds evolves showing the characteristics of the waveforms associated with landslides. ground. After about 3 minutes, the phenomenon ends.
The HF GNSS network shows no significant changes. The inclinometer network is not currently available.
Due to cloud cover, it was not possible to observe the phenomenon from surveillance cameras.
At 04:32 (02:32 UTC), the settings return to normal activity.
Further updates will be communicated soon.
WEEKLY BULLETIN, from June 20, 2022 to June 26, 2022. (issue date June 28, 2022)
ACTIVITY STATUS SUMMARY
In the light of the surveillance data, it is highlighted:
1) VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS: In this period a normal explosive activity of Strombolian type was observed. The total hourly frequency of explosions was contained between low values (3 events/h) and medium-low values (9 events/h). The intensity of the explosions was low to medium in the North Crater area and low in the Center-South Crater area.
2) SEISMOLOGY: The seismological parameters monitored do not show any significant variations.
3) GROUND DEFORMATIONS: During the period under review, the island’s ground deformation monitoring networks did not record any significant variations.
4) GEOCHEMISTRY: SO2 flux at an average level
5) SATELLITE OBSERVATIONS: The thermal activity observed by satellite in the summit area was at a low level.
VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS.
The N1 crater, with three emission points, located in the North crater area produced explosions of low intensity (less than 80 m high) to medium (less than 150 m high) emitting fine materials (ash ) mixed with coarse materials (bombs and lapilli). The N2 crater showed almost continuous pulsating degassing and sometimes accompanied by weak projection activity. The average frequency of explosions from the mouths of this area was almost constant with 3-4 events/h.
In the south-central area, craters C and S1 did not show significant explosive activity. The S2 crater, with two emission points, showed explosions of mainly low intensity (less than 80 m high) and sometimes medium (less than 150 m) with emission of coarse material. The frequency of the explosions varied between none and 5 events/h.
Source : INGV.
Photos : INGV , Stromboli stati d’animo.
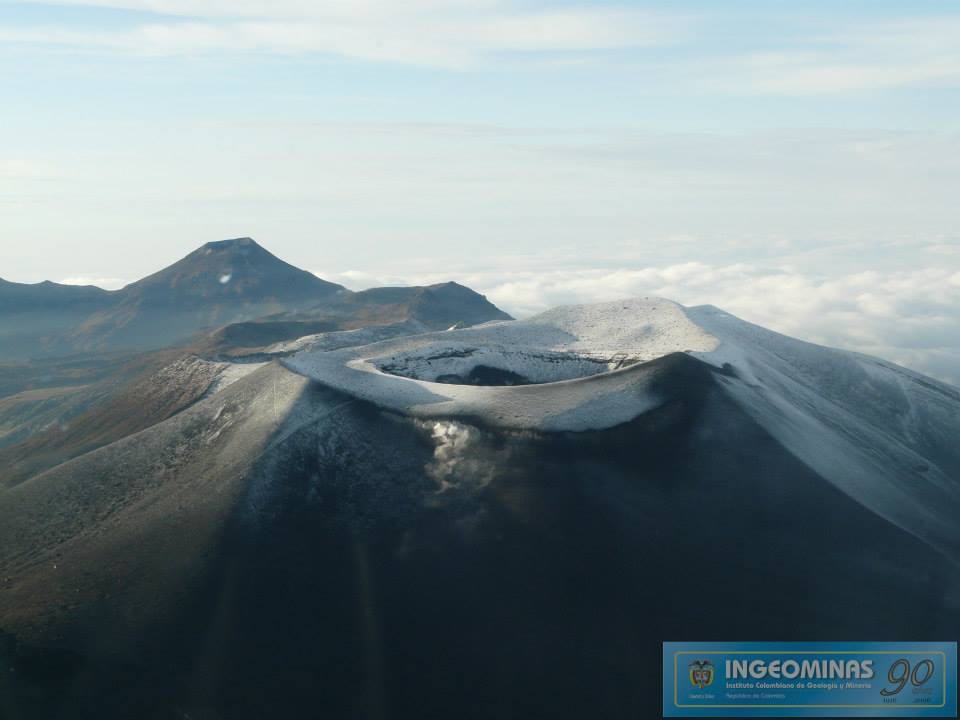
Colombia , Puracé – Los Coconucos Volcanic Range :
Weekly bulletin of the activity of the Puracé volcano – Los Coconucos volcanic chain
The level of activity of the volcano continues at the Yellow activity level or (III): changes in the behavior of volcanic activity.
From the analysis and evaluation of the information obtained through the monitoring network of the Puracé volcano – Los Coconucos volcanic chain, during the week of June 21 to 27, 2022, the COLOMBIAN GEOLOGICAL SERVICE – Volcanological and Seismological Observatory of Popayan reports that:
During this week, the strong occurrence of earthquakes associated with the movement of fluids inside the volcano continues. A total of 698 seismic events were presented, of which 61 were associated with rock fracturing processes (type VT) and 637 with fluid dynamics in volcanic conduits; of these, 534 were classified as long period events (LP type), three (3) events as hybrid (HB type), 16 low frequency events (BF type), six (6) « tornillos » (TO type ) and 78 as low energy tremor pulses (TR type).
• The geodetic network of GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) stations monitoring ground deformation continues to record a process associated with inflation.
• With regard to the monitoring of volcanic gases, the fluxes of sulfur dioxide (SO2) emissions recorded by the telemetry stations showed a stable behavior, reaching
throughput values at permanent stations with a maximum output of 1573 t/d for June 23. On June 22, a mobile campaign was carried out to measure the far-field SO2 flux, which recorded a value of 1005 t/d. The other gas analysis instruments in the volcanic influence zone do not show any relevant changes for the evaluated period.
• In the monitoring of surface activity, the images obtained during the week thanks to the Anambío, Mina, Lavas Rojas and Cerro Sombrero web cameras showed degassing of the volcanic system, with a white column oriented preferentially towards the North- West.
• Sensors monitoring magnetic and electric fields and infrasonic waves did not record variations associated with changes in volcanic activity.
Therefore, it is concluded that significant variations in volcanic activity continue to be recorded, in accordance with the behavior expected at activity level III (yellow level), which could evolve towards states of greater activity.
Source : SGC.
Photo : Ingeominas.
Indonesia , Anak Krakatau :
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION – VONA
Issued : June 29 , 2022.
Volcano : Anak Krakatau (262000)
Current Aviation Colour Code : ORANGE
Previous Aviation Colour Code : orange
Source : Anak Krakatau Volcano Observatory
Notice Number : 2022KRA57
Volcano Location : S 06 deg 06 min 07 sec E 105 deg 25 min 23 sec
Area : Lampung, Indonesia
Summit Elevation : 502 FT (157 M)
Volcanic Activity Summary :
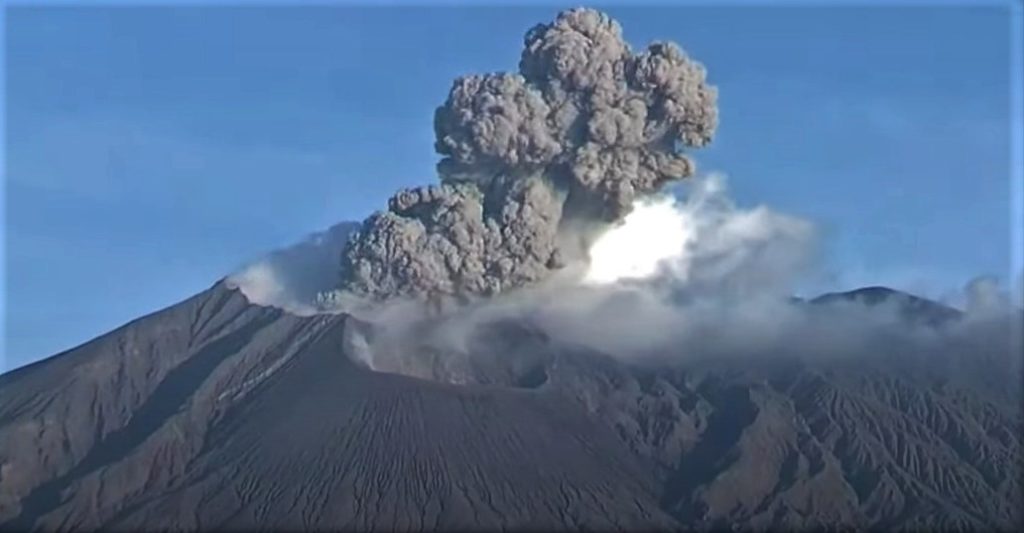
Eruption with ash clouds at 07:51UTC (14:51 local time). The eruption lasted for 116 seconds
Volcanic Cloud Height :
Best estimate of ash-cloud top is around 6902 FT (2157 M) above sea level, may be higher than what can be observed clearly. Source of height data: ground observer.
Other Volcanic Cloud Information :
Visuals directly from the cctv were observed eruptions with the color of the thick black eruption smoke 2000m from the top of the volcano, the wind direction slowly to the north.
Remarks :
Eruption recorded on seismogram with maximum amplitude 60 mm and maximum duration 116 second.
Mount Anak Krakatau erupted on Wednesday, June 29, 2022 at 2:51 p.m. WIB with an ash column height observed at ± 2000 m above the summit (± 2157 m above sea level). The ash column is observed to be black with a moderate to thick intensity oriented towards the North. This eruption was recorded on a seismograph with a maximum amplitude of 60 mm and a duration of 116 seconds
SEISMICITY OBSERVATION
1 continuous tremor with an amplitude of 1-10 mm, dominant value 2 mm.
RECOMMENDATION
People/visitors/tourists/climbers should not approach Mount Anak Krakatau or engage in activities within 5 km of the active crater.
Source et photo : Magma Indonésie.
Japan , Sakurajima :
JMA reported that nighttime incandescence at Minamidake Crater (at Aira Caldera’s Sakurajima volcano) was visible during 20-27 June. At 1221 on 27 June an eruptive event produced an ash plume that rose 1.5 km above the crater rim. The Alert Level remained at 3 (on a 5-level scale), and residents were warned to stay 2 km away from the crater.
The Aira caldera in the northern half of Kagoshima Bay contains the post-caldera Sakurajima volcano, one of Japan’s most active. Eruption of the voluminous Ito pyroclastic flow accompanied formation of the 17 x 23 km caldera about 22,000 years ago. The smaller Wakamiko caldera was formed during the early Holocene in the NE corner of the Aira caldera, along with several post-caldera cones. The construction of Sakurajima began about 13,000 years ago on the southern rim of Aira caldera and built an island that was finally joined to the Osumi Peninsula during the major explosive and effusive eruption of 1914. Activity at the Kitadake summit cone ended about 4850 years ago, after which eruptions took place at Minamidake. Frequent historical eruptions, recorded since the 8th century, have deposited ash on Kagoshima, one of Kyushu’s largest cities, located across Kagoshima Bay only 8 km from the summit. The largest historical eruption took place during 1471-76.
Source : GVP. Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA)
Photo : Webcam.
Hawaii , Kilauea :
19°25’16 » N 155°17’13 » W,
Summit Elevation 4091 ft (1247 m)
Current Volcano Alert Level: WATCH
Current Aviation Color Code: ORANGE
Activity Summary:
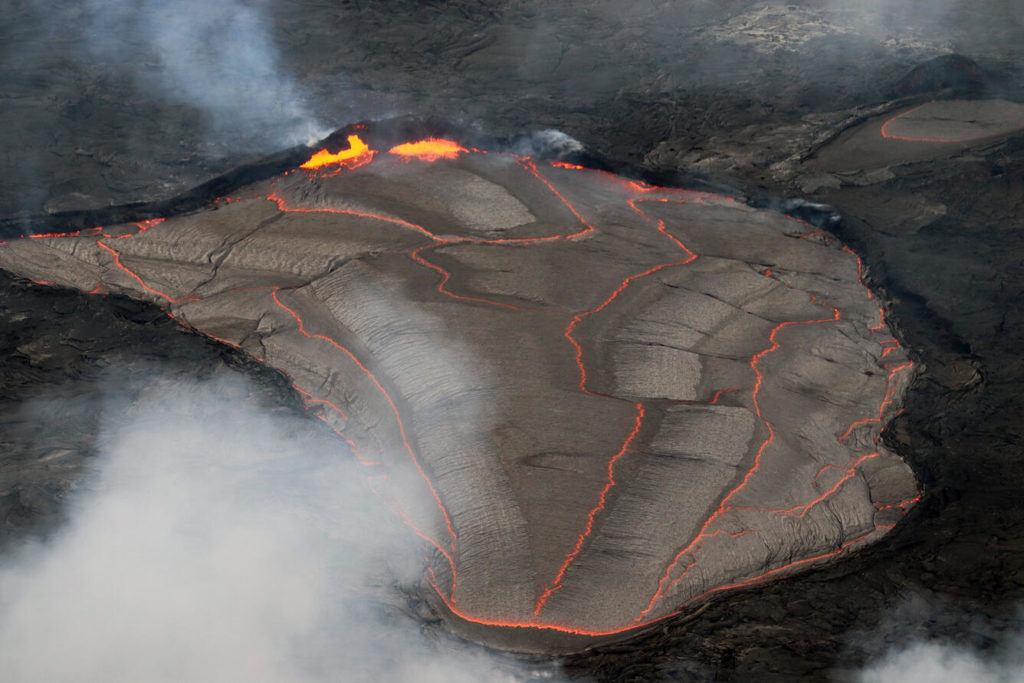
The summit eruption of Kīlauea volcano, within Halemaʻumaʻu crater, continued over the past 24 hours. All recent lava activity has been confined to the crater, and current data indicate that this scenario is likely to continue. No significant changes have been noted at the summit or in either rift zone.
Summit Observations:
Eruption of lava from the Halemaʻumaʻu crater western vent into the active lava lake, and weak ooze-outs along the northern crater floor, have continued over the past 24 hours. Overflight measurements on June 17, 2022, indicated that the crater floor had seen a total rise of about 120 meters (394 feet. No significant change in tilt was recorded by summit tiltmeters over the past 24 hours. A sulfur dioxide (SO2) emission rate of approximately 1,200 tonnes per day (t/d) was measured on June 28, 2022.
Rift Zone Observations:
No unusual activity has been noted along the East Rift Zone or Southwest Rift Zone; steady rates of ground deformation and seismicity continue along both. Measurements from continuous gas monitoring stations downwind of Puʻuʻōʻō in the middle East Rift Zone remain below detection limits for SO2, indicating that SO2 emissions from Puʻuʻōʻō are negligible.
Source : HVO.
Photo : USGS / M. Patrick