January 16 , 2022 .
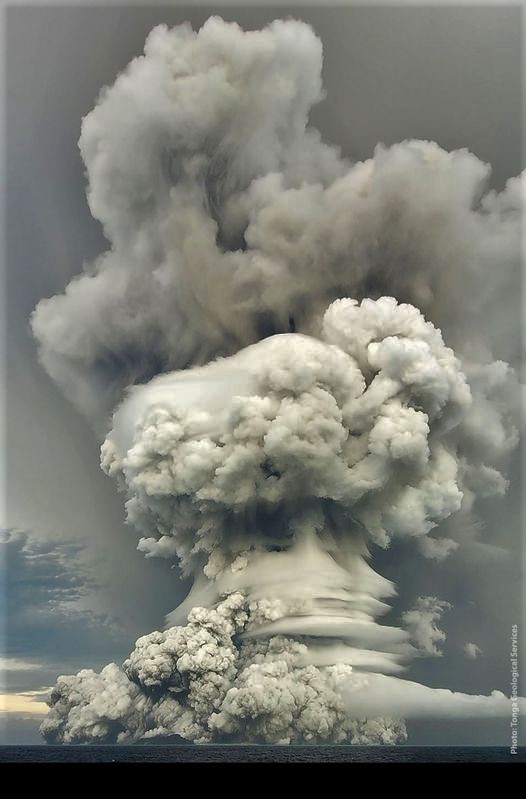
Tonga Islands , Hunga tonga-Hunga Ha’apai :
In an image of the planet SkySat, the HungaTongaHungaHaapai volcano has changed a lot. The entire central part of the island was missing, probably destroyed in the explosions of January 14, 2022.
Observations from satellite images captured between 5:00 a.m. on January 15, 2022 and 12:40 p.m. on January 15, 2022 are as follows.
The volcanic eruption is continuing, with ash emitted and detected at 7:20 a.m. this morning.
This ash plume was due to an eruption that lasted 10-15 minutes and was drifting downwind east of Hunga. No other eruption has been detected since then.
Coastal water turbulence caused by the eruption is expected to have ceased for all shores of Ha’apai and Tongatapu islands. The public is advised to watch the currents before entering the water.
Source : Tonga Geological Services, Government of Tonga.
Photos : Skysat , Taaniela Kula/TGS. Taken from Matangi Tonga Online.
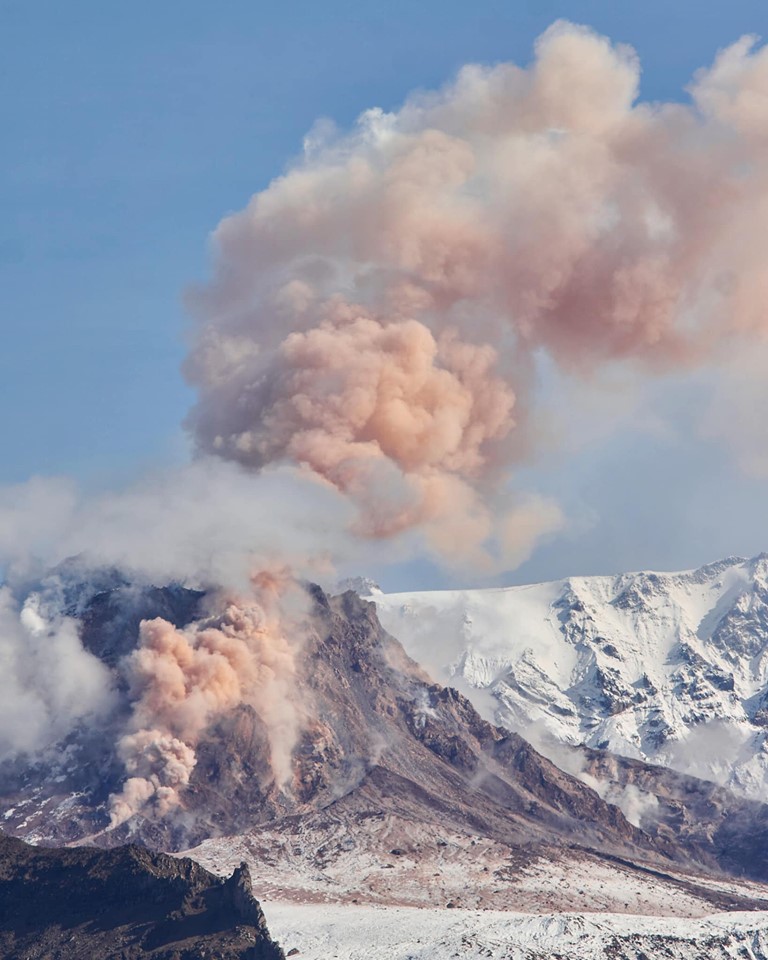
La Réunion Island , Piton de la Fournaise :
Press release of January 16, 2022 – 11:30 a.m.
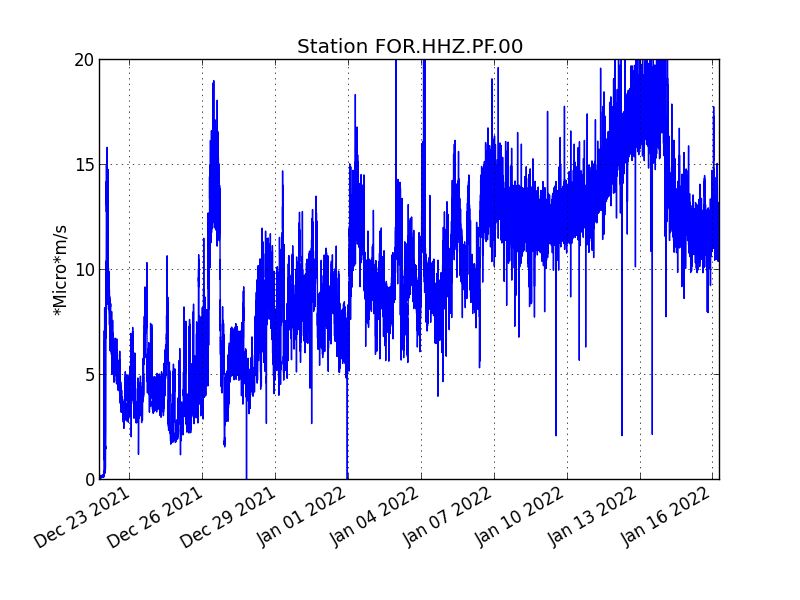
The eruption started on December 22, 2021 around 3:30 a.m. local time continues. After a decrease in its amplitude observed for two days, the tremor is relatively stable over the last 24 hours.
Fluctuations in the amplitude of the tremor are partly related to the level of the lava lake which varies according to the mode of degassing, the erosion of the eruptive conduit and the sporadic openings of the tunnels which allow emptying of the cone. The openings in the tunnels generate a drop in pressure at the level of the cone and within the tunnels, and lead to a drop in the amplitude of the tremor.
Thus, a decrease in the amplitude of the tremor is accompanied by the appearance of numerous resurgences and persistent flows within the lava field, as has been observed since
two days .
The observations of the eruptive site carried out this morning show that the lava projections at the level of the cone are still present, even if they are less frequent than at the beginning of the week, and
occasionally exceed the height of the cone. No overflow from the lava lake has been reported in the past 24 hours.
The front of the last flow arm set up along the southern rampart of the Enclos Fouqué for several days is progressing only very slowly given the relatively low slopes in the sector. A few small fires at the foot of the rampart, heavily vegetated, are observed.
Over the last 24 hours:
– The surface deformations always show a deflation at the level of the summit zone, linked to the emptying of the magma reservoir located under the summit (about 2-2.5 km deep) feeding the eruptive site.
– 29 volcano-tectonic earthquakes, of low magnitude (<1), were recorded under the summit. This seismicity is linked to the emptying of the magma reservoir located under the summit, weakening its roof.
– Lava flows could be estimated by satellite method with the HOTVOLC platform (OPGC – Clermont Auvergne University). They were between 6 and 26 m3/sec. These variations are explained by the method, which is based on the infrared radiation of the flow, the perception of which by the satellites can be largely influenced by the meteorological conditions above the flows as well as the flow conditions of the lava ( on the surface or in the tunnel).
The main orientation of the eruptive plume towards the south and the failure of the « NOVAC » BERT station at the start of the eruption, did not make it possible to estimate the gas flows at the start of the eruption. On the other hand, since the beginning of January 2022, the SO2 fluxes emitted by the eruption and measured by the DOAS « NOVAC » network have shown 1) a gradual increase in high temperature gas fluxes after January 7, 2022, and therefore an increase in average flows of magma arriving at the surface, then a decreasing trend since January 12, 2022; with values
between 5 and 15 m3/sec over the last two days.
Alert level: Alert 2-1 (eruption in the Enclos )
Source : OVPF
Alaska , Semisopochnoi :
51°55’44 » N 179°35’52 » E,
Summit Elevation 2625 ft (800 m)
Current Volcano Alert Level: WATCH
Current Aviation Color Code: ORANGE
The eruption at Semisopochnoi volcano continues. Small explosions producing low-level ash clouds from the north crater of Mount Cerberus on Semisopochnoi Island occurred intermittently throughout the last week. These explosions were detected by local seismic and infrasound sensors. When weather conditions allowed, small ash emissions were observed in web camera images. Throughout most of the week, these low-level emissions could not be seen in satellite views. However, an ash plume drifting to the south could be seen in satellite views on Thursday, January 13 at an altitude of approximately 5,000 ft above sea level.
Small explosions that produce minor ash deposits within the vicinity of the active north crater of Mount Cerberus, and ash clouds typically under 10,000 ft above sea level have characterized the recent activity and show no signs of abating.
Semisopochnoi is monitored by local seismic and infrasound sensors, satellite data, web cameras, and remote infrasound and lightning networks.
Remote Semisopochnoi volcano occupies the largest, young volcanic island in the western Aleutians. The volcano is dominated by a 5-mile (8 km) diameter caldera that contains a small lake and several post-caldera cones and craters. The age of the caldera is not known with certainty but is likely early Holocene. Prior to 2018, the previous known historical eruption of Semisopochnoi occurred in 1987, probably from Sugarloaf Peak on the south coast of the island, but details are lacking. Another prominent, young post-caldera landform is Mount Cerberus, a three-peaked cone cluster in the southwest part of the caldera. The island is uninhabited and part of the Alaska Maritime National Wildlife Refuge. It is located 40 miles (65 km) northeast of Amchitka Island and 130 miles (200 km) west of Adak.
Source : AVO .
Photo : AVO/USGS / Alaska Volcano Observatory / U.S. Geological Survey.
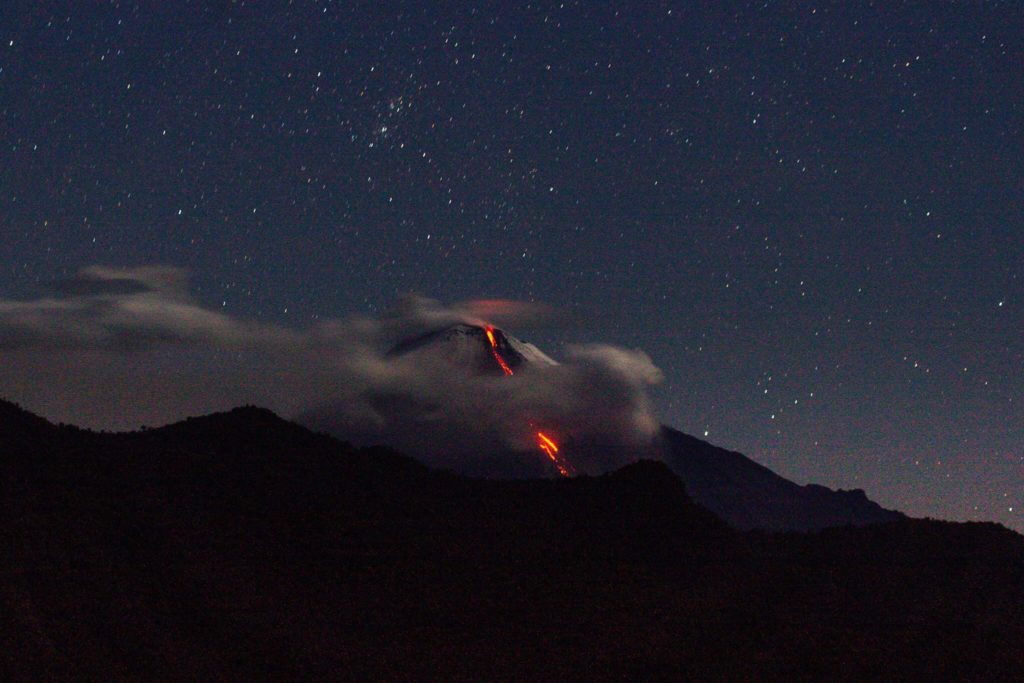
Kamchatka , Sheveluch :
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION (VONA)
Issued: January 16 , 2022
Volcano: Sheveluch (CAVW #300270)
Current aviation colour code: ORANGE
Previous aviation colour code: orange
Source: KVERT
Notice Number: 2022-08
Volcano Location: N 56 deg 38 min E 161 deg 18 min
Area: Kamchatka, Russia
Summit Elevation: 3283 m (10768.24 ft), the dome elevation ~2500 m (8200 ft)
Volcanic Activity Summary:
A growth of the lava dome continues, a strong fumarolic activity, and an incandescence of the lava dome and hot avalanches accompanies this process. Satellite data by KVERT show explosions sent ash up to 6.5 km a.s.l., and ash plume extend for 20 km to the west-southwest of the volcano.
The extrusive eruption of the volcano continues. Ash explosions up to 10-15 km (32,800-49,200 ft) a.s.l. could occur at any time. Ongoing activity could affect international and low-flying aircraft.
Volcanic cloud height:
6000-6500 m (19680-21320 ft) AMSL Time and method of ash plume/cloud height determination: 20220115/2320Z – Himawari-8
Other volcanic cloud information:
Distance of ash plume/cloud of the volcano: 20 km (12 mi)
Direction of drift of ash plume/cloud of the volcano: WSW / azimuth 258 deg
Time and method of ash plume/cloud determination: 20220115/2350Z – Himawari-8
Source : Kvert.
Photo : Nickita Batischev
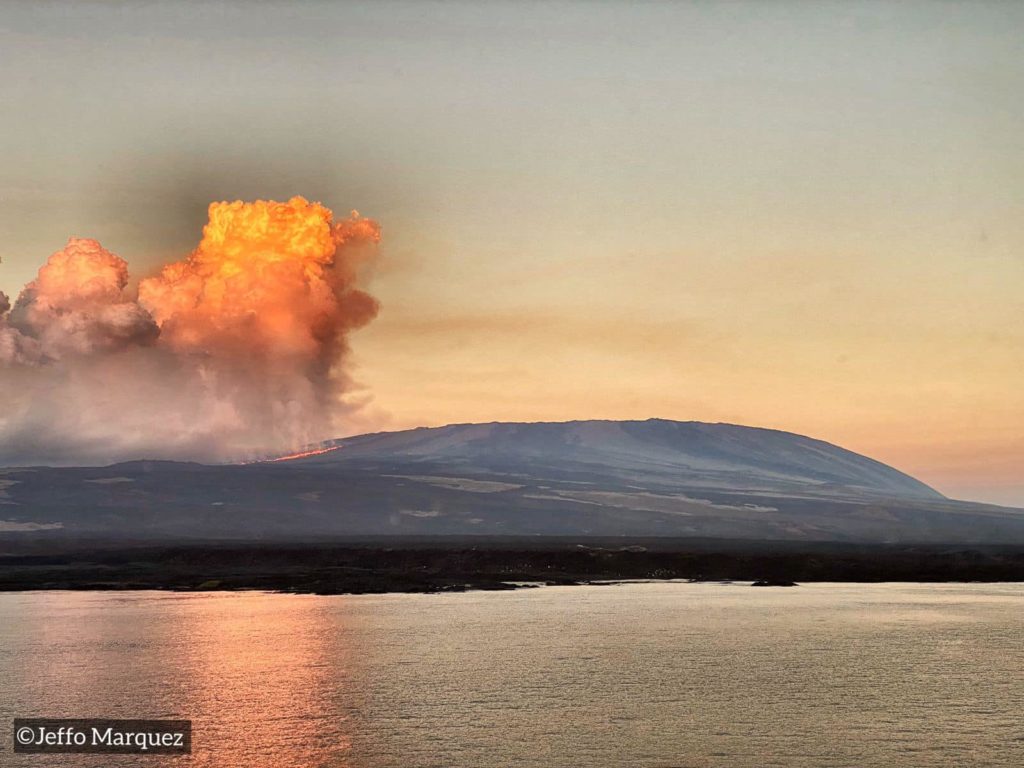
Ecuador , Sangay / Wolf :
DAILY REPORT OF THE STATE OF SANGAY VOLCANO. January 15, 2022.
Surface activity level: High, Surface trend: No change.
Internal activity level: High, Internal trend: No change.
Seismicity: From January 14, 2022, 11:00 a.m. to January 15, 2022, 11:00 a.m.:
Explosions (EXP) 95
Emission Tremors (TREMI) 60
Rains / Lahars:
No rain was recorded. **In the event of heavy rains, these could remobilize the material accumulated in the gullies, generating mudslides and debris that would descend through the drains of the volcano and flow into the adjacent rivers.**
Emission / ash column:
Thanks to images observed on satellite, the Washington VAAC reported several ash emissions from 570 m to 1170 m, the direction of these was towards the West, the South-West, the North-East and the East. .
Other Monitoring Parameters:
FIRMS reports 1 thermal alert and MIROVA reports 1 moderate high thermal alert on the Sangay in the last 24 hours
Information VOLCÁN SANGAY, Saturday January 15, 2022
From around 5:00 p.m. TL, the SAGA seismic station recorded a tremor signal linked to the eruptive activity of the Sangay volcano. The signal amplitude is relatively low compared to the most active pulses of the current eruptive period. Therefore, there is a possibility of light to moderate ash fall in the areas surrounding the volcano located west-northwest of it in the province of Chimborazo. The IG-EPN is monitoring the event and will report on the development of this event. The Geophysical Institute is monitoring and any news will be reported.
Alert level: yellow.
DAILY REPORT OF THE STATE OF WOlF VOLCANO. January 15, 2022.
Surface Activity Level: High, Surface Trend: Downward
Internal activity level: High, Internal trend: Downward
Seismicity: From January 14, 2022, 11:00 a.m. to January 15, 2022, 11:00 a.m.:
Volcano-Tectonics ( VT): 1
Emission / ash column:
Yesterday, according to satellite images (GOES-16), a continuous emission of gas was observed, with a direction towards the South-West.
Other Monitoring Parameters:
FIRMS reports hundreds of thermal alerts and MIROVA reports 1 moderate thermal alert and 3 extremes (15537, 18275 and 17300 MW) on Wolf Volcano in the last 24 hours.
Comments
According to satellite monitoring, it is observed that thermal anomalies are maintained
Source : IGEPN
Photos : TopMotor Storee , Jeffo Marquez .