June 03 , 2021.
Italy / Sicily , Etna :
Press release on ETNA activity, 02 June 2021, 09:44 (07:44 UTC).
The National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology, Osservatorio Etneo, reports that from surveillance cameras, it is possible to observe the resumption of weak Strombolian activity at the level of the Southeast Crater. This activity produces discontinuous and light emissions of dilute ash which disperse rapidly near the summit area of the volcano.
At the same time, occasional ash emissions from the Bocca Nuova crater are observed, which are also quickly dispersed near the summit area.
From the seismic point of view, from 06:00 UTC, a gradual increase in the average amplitude of the volcanic tremor is observed, which has now reached average values.
The location of the centroid of volcanic tremor sources is in the Southeast Crater region at an altitude of about 2800-2900 m above sea level. A slight increase in the rate of occurrence of infrasonic events is observed which are located in the area of the Southeast Crater.
There are no significant changes in the time series of tilt and GNSS stations.
Press release on ETNA activity, 02 June 2021, 10:45 (08:45 UTC).
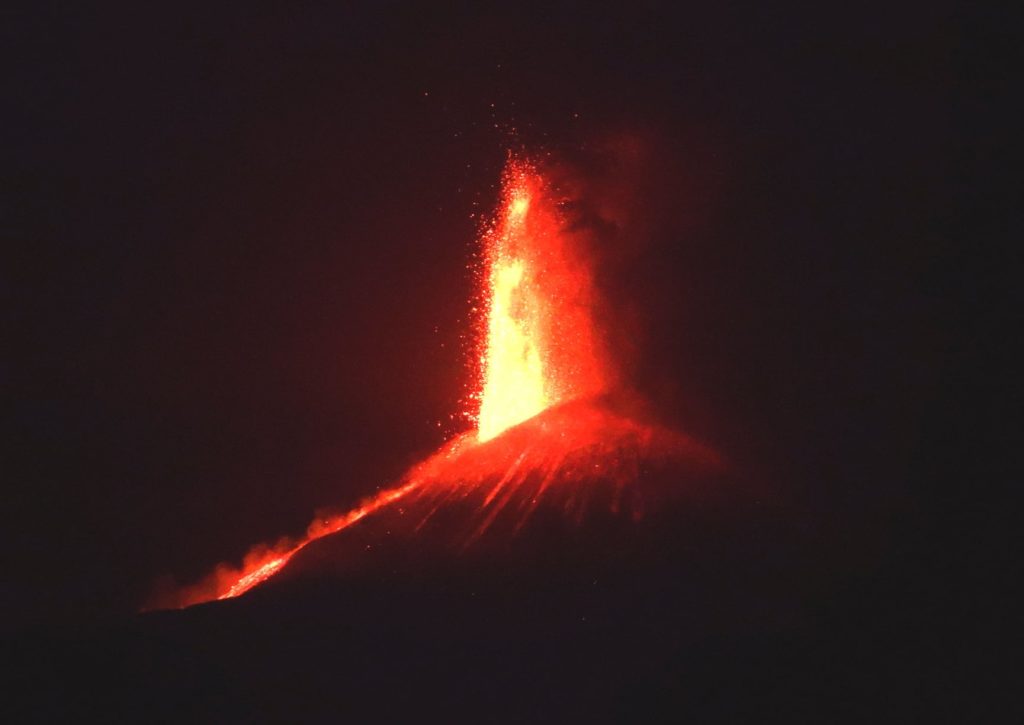
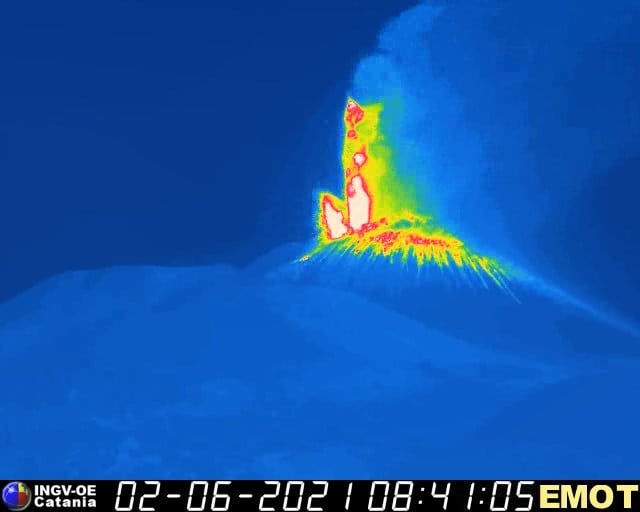
The National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology, Osservatorio Etneo, announces that from around 08:30 UTC, the transition of Strombolian activity from the Southeast Crater to the lava fountain stage is observed from surveillance cameras . Based on the predicted model, the eruptive cloud disperses eastward.
The average amplitude of the volcanic tremor, after a first increase around 06:00 UTC, around 08:00, showed a sudden increase reaching high levels. The location of the center of gravity of the sources of the volcanic tremor is located near the Southeast Crater at an altitude of about 3000 m above sea level.
No significant change is observed in the time series of soil deformation monitoring data.
Press release on ETNA activity, 02 June 2021, 13:29 (11:29 UTC).
The National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology, Osservatorio Etneo, reports that as of approximately 10:45 UTC, the lava fountain of the Southeast Crater has ceased. In accordance with the forecast model, the dispersion concerned the eastern sector of the volcano. INGV staff in the field reported the impact of the products in the north of Zafferana, in the town of Petrulli and in Santa Venerina. Due to the cloud cover, it was not possible to determine the height of the eruptive cloud, but according to information received from INGV personnel in the field, the cloud reached a height of around 5 to 6 km altitude.
In addition, the lava fountain produced an overflow of lava from the southern slope of the Southeast Crater, which spread in a southwest direction.
From around 10:20 UTC a rapid decrease in the mean amplitude values of the volcanic tremor is observed, which always remain at a high level, with a clear tendency to decrease. The centroid of the volcanic tremor sources remains located in the area of the Southeast Crater at an altitude of about 3000 m s.l.m. The infrasound activity, which continues to be localized in the Southeast Crater area, shows a clear decrease in the number of events and their amplitude.
Stations at the top of the Etna tilt network have small variations on both signal components. No significant change observed in GNSS network data.
Press release on ETNA activity, 02 June 2021, 21:55 (19:55 UTC).
The National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology, Osservatorio Etneo, reports that from approximately 18:50 UTC, from surveillance cameras, the resumption of weak Strombolian activity at the level of the Southeast Crater is observed.
From the seismic point of view, the average amplitude values of the volcanic tremor are always at an average level showing weak fluctuations. The centroid of the volcanic tremor sources remains located in the area of the Southeast Crater at an altitude of about 3000 m s.l.m. The infrasound activity remains at low levels and the sources are located near the crater of Bocca Nuova.
There are no significant changes in the time series of tilt and GNSS networks.
Further updates will be communicated shortly.
Source : INGV.
Photos : INGV ( 02/06 , 31/05)
Democratic Republic of Congo , Nyiragongo :
01 June 2021:
Although there are still recorded earthquakes, their energy is generally lower. However, we observe an activity of earthquakes, mostly not felt, which manifests itself towards the South, under Lake Kivu. The GPS network always indicates a decrease in the travel speeds measured at the stations. The physical impossibility of installing seismic or GPS stations in the lake does not allow precise detection of a possible rise of magma under the lake. This decrease in energy released by earthquakes, as well as in GPS speeds, cannot yet be interpreted as indicating the cessation of volcanic activity. During phases of volcanic activity, periods of higher activity often alternate with phases of lower activity.
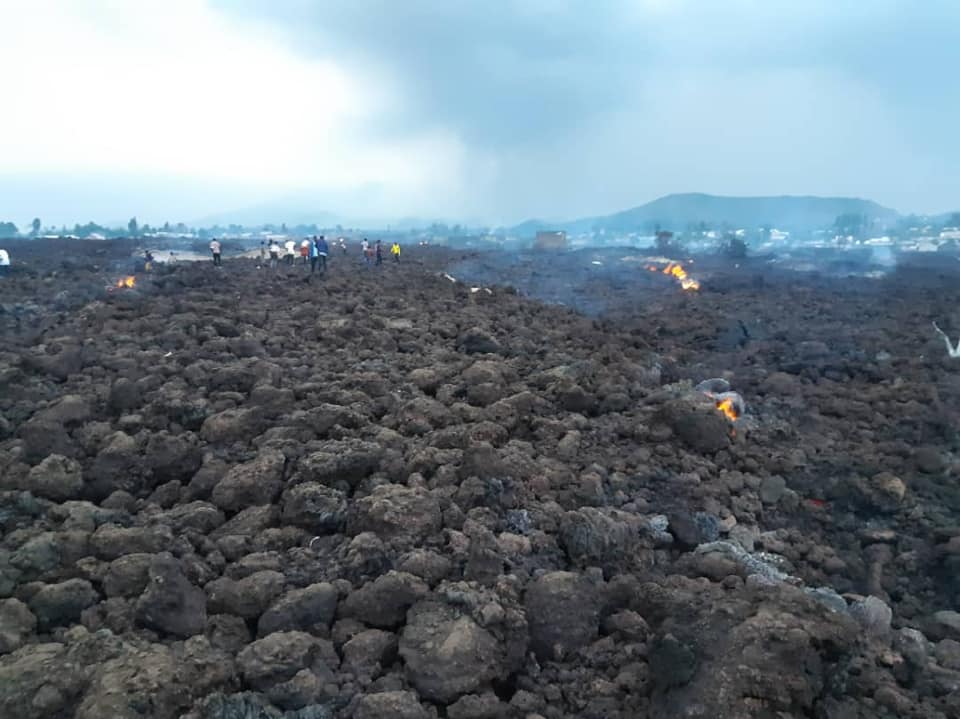
Satellite data and analysis indicated that the lava flows at Nyiragongo during 22-23 May were the result of a N-S trending dike that had intruded beneath the volcano and Goma, and likely extended beneath Lake Kivu. Though lava effusion ceased, intense seismicity continued afterwards and indicated the dike continued to be active, according to GeoRiskA. Ground cracking in the city and damage to buildings from earthquakes continued to be reported. On 27 May authorities mandated an evacuation of the at least 400,000 residents in higher risk areas (about 10 districts) according to news organizations. The total population of Goma is an estimated 670,000 people. Photos in news articles showed masses of people and cars jammed for kilometers on roads leading out of the city. During 28-29 May GeoRiskA reported that seismicity began to decrease and continued a downward trend at least through 1 June; both the seismic data and GPS data indicated that the dike was no longer propagating. A news article noted that residents had begun returning to their homes within a few days.
Humanitarian organizations noted that within five days after lava flow stopped nearly 700 children had been re-united with their families, and more than 200 were in foster care or other transitional facilities. More than 170 families continued to search for missing children. The eruption had destroyed 3,629 homes, 12 schools, and 3 health facilities. More than 20,000 people were displaced and 31 had died. Goma’s international airport remained closed, though one across the border in Rwanda was operating.
Sources : georiska.africamuseum.be , GVP .
Photos : Nyiragongo volcano Virunga ,
Indonesia , Anak Krakatau :
The Darwin VAAC reported that a diffuse ash plume from Anak Krakatau was visible in satellite images drifting SW at an altitude of 1.8 km (6,000 ft) a.s.l.
Level of activity level II (WASPADA) since March 25, 2019. The Anak Krakatau volcano (157 m above sea level) has experienced increased volcanic activity since June 18, 2018, which was followed by a series of eruptions during the period from September 2018 to February 2019.
The volcano is clearly visible until it is covered in fog. The observable smoke emitted from the crater is white with low to medium intensity, rising about 25-100 meters above the summit. The weather is sunny to cloudy, the wind is weak in the northeast. The air temperature is around 26-31.5 ° C.
CCTV visuals are clear, weak to medium white smoke is observed at 25-100m altitude. Calm sea waves.
According to the seismographs of June 1, 2021, it was recorded:
7 low frequency earthquakes
1 shallow volcanic earthquake
1 continuous Tremor type signal with an amplitude of 1 to 35 mm (dominant value 2 mm)
Recommendation:
The public / tourists are not allowed to approach the crater within a radius of 2 km around the crater
Source : GVP , PVMBG.
Photo : Arief/detikcom.
La Réunion Island , Piton de la Fournaise :
Seismicity
In May 2021, the OVPF recorded in the Piton de la Fournaise massif in total:
• 105 superficial volcano-tectonic earthquakes (0 to 2.5 km above sea level) below the summit craters;
• 0 deep earthquake (below sea level);
• 261 collapses (in the Crater Dolomieu, the ramparts of the Enclos Fouqué and Piton de Crac, and the Rivière de l’Est).
Following the start of the eruption on April 9, 2021, a gradual drop in seismicity was recorded, dropping from 89 surface earthquakes on April 11 to less than 5 surface earthquakes per day over the period from April 26-30. For the month of May 2021, an average of 3 superficial earthquakes per day was recorded.
After the eruption ended on May 24, 2021 (2:00 a.m. local time, May 23, 10:00 p.m. UTC), weak seismicity was still recorded with an average of 2 shallow volcano-tectonic earthquakes per day.
Deformation
Following the start of the eruption on April 9, 2021, a slight deflation of the edifice was recorded linked to the transfer of magma from the magmatic storage area under the summit area to the eruptive site.
At the end of April, slight inflation set in and continued throughout May, including after the eruption ended on May 24, 2021 (2:00 a.m. local time, May 23, 10:00 p.m. UTC). This inflation showed a pressurization of the superficial magmatic reservoir located around 2 km deep.
Balance sheet
The building’s inflation and the CO2 levels in the soil, which remained high in May 2021, witnessed magmatic transfers from deep areas to the superficial magmatic reservoir. This recharge explains the continuation of the eruption from April 9 until May 24, 2021 (2:00 a.m. local time, May 23, 10:00 p.m. UTC). Since the end of the eruption, the inflation (swelling) of the volcanic edifice has continued, testifying to a still persistent superficial magmatic reservoir pressurization.
Source : OVPF.
Read the article : https://www.ipgp.fr/sites/default/files/ovpf_20210602_bullmensu.pdf
Photo : Imaz Press