October 02 , 2018.
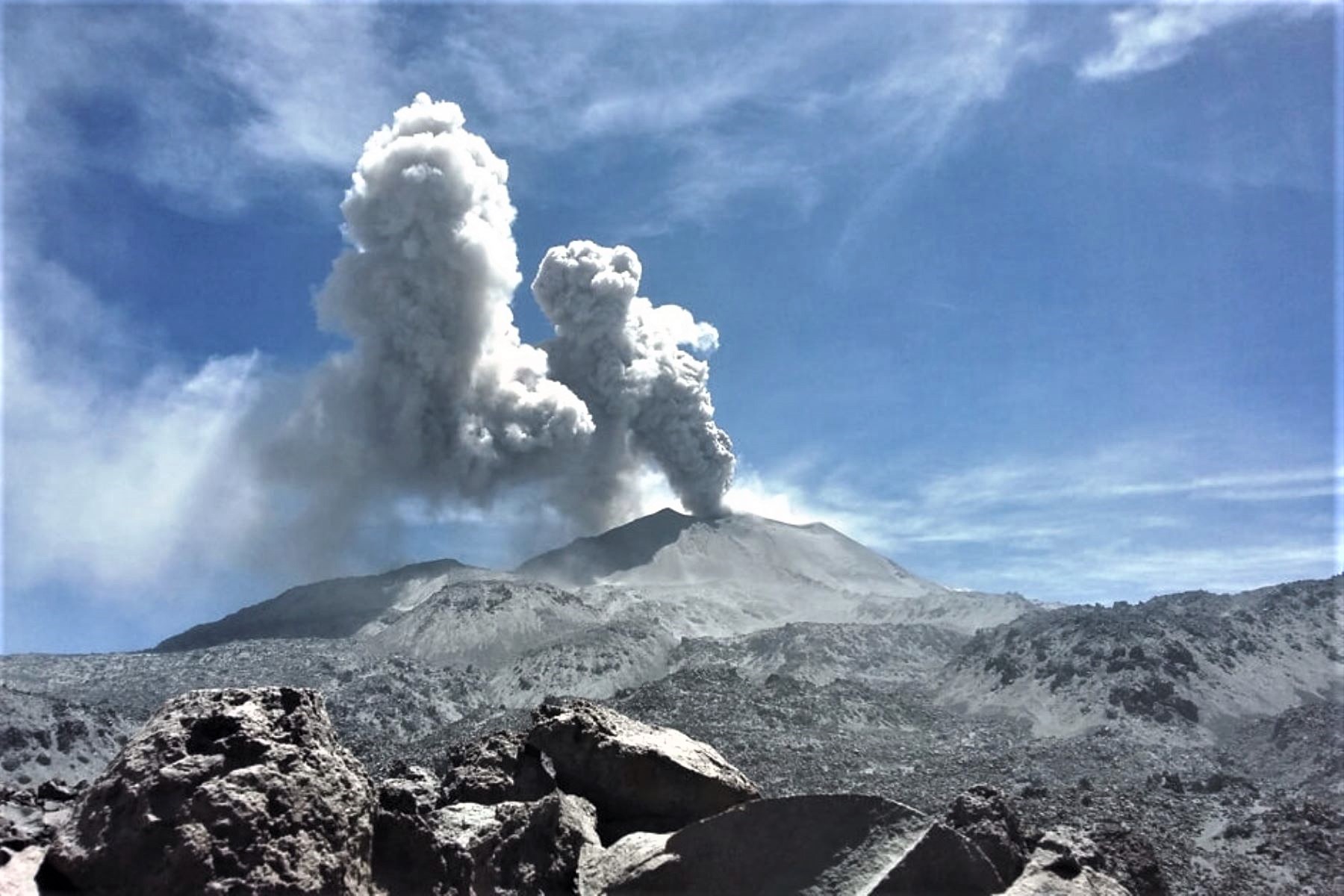
Peru , Sabancaya :
An average of 21 EXP / day was recorded. Earthquakes associated with the rise of magma (hybrid types) remain very few and low energy.
The gas columns and eruptive ash reached a maximum height of 3700 m above the crater. The dispersion of these materials occurred within a radius of about 50 km, mainly to the southwest, southeast and east.
The volcanic gas flow (SO2) recorded on September 29 a maximum value of 3250 tons / day, considered as a significant value.
The deformation of the surface of the volcanic building presented important variations.
The MIROVA satellite system recorded 6 thermal anomalies, with values between 3 MW and 20 MW VRP (Radiated Volcano Power).
In general, eruptive activity maintains moderate levels. No significant changes are expected in the following days.
Source : IGP.
Photo : Andina
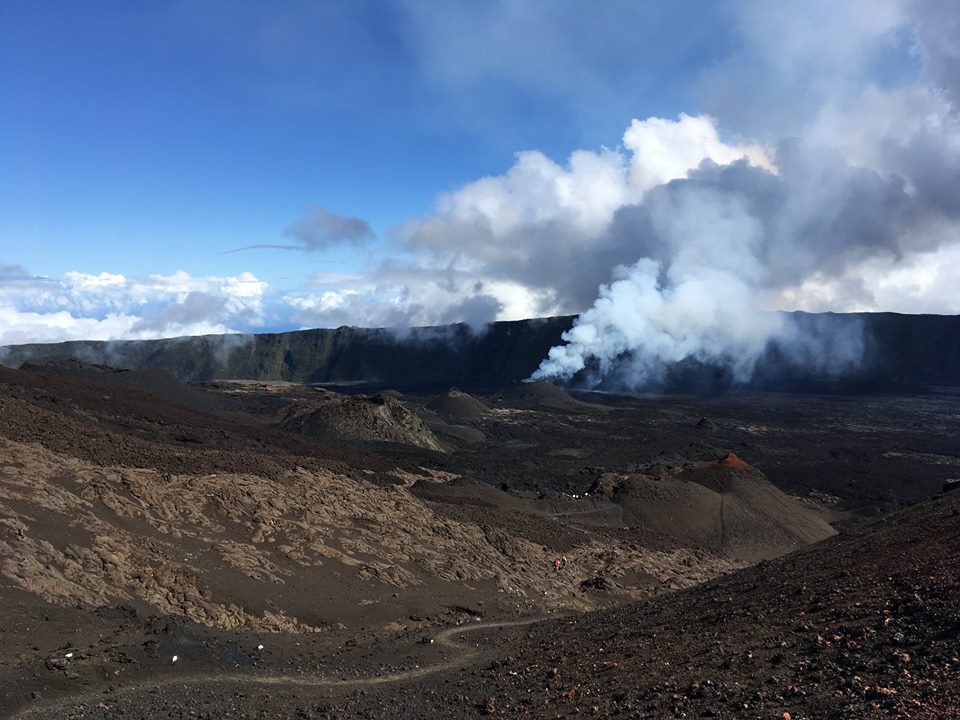
La Réunion , Piton de la Fournaise :
Activity Bulletin from Monday 1st October 2018 at 15:30 (local time).
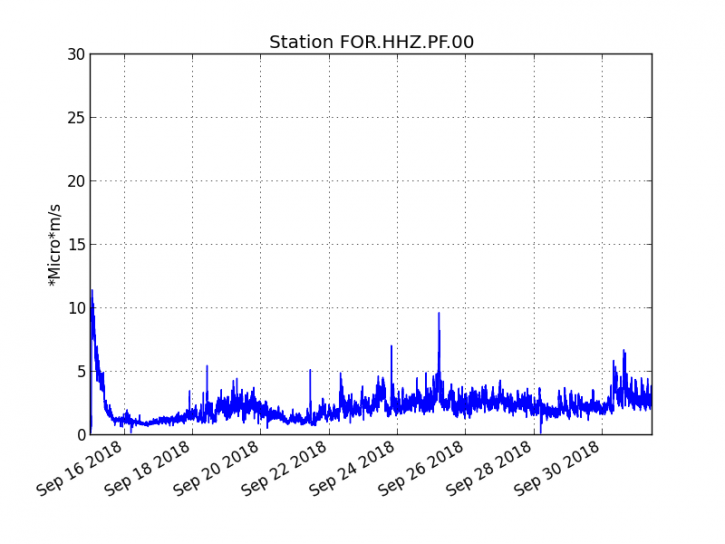
The eruption started on September 15th at 4:25 am local time continues. The intensity of the volcanic tremor (indicator of surface eruptive intensity) has remained relatively stable over the last 24 hours (Figure 1).
Figure 1: Evolution of the RSAM (indicator of the volcanic tremor and the intensity of the eruption) between 04h00 (00h UTC) on September 15th and 15h00 (11h00 UTC) on October 1st on the FOR seismic station, located near the crater Chateau Fort (2000 m altitude on the southeast flank of the terminal cone).
– Two superficial volcano-tectonic earthquakes and a deep volcano-tectonic earthquake were recorded during the day of 30 September. A deep volcano-tectonic earthquake was also recorded during the current day.
– A subtle rebound in inflation (swelling) of the building, witnessing the influence of a source of pressure at the base of the volcano still seems to be emerging, this parameter will follow these days.
– The surface flows estimated from the satellite data, via the HOTVOLC platform (OPGC – Clermont Auvergne University) were <2 m3 / s over the last 24 hours. Note that the eruptive activity now taking place mainly in lava tunnels, detection of anomalous hot spots are increasingly difficult and therefore these values of underrated flows. In the same way the cloud cover this day on the volcano disrupts the acquisition of these data.
– Due to the bad weather conditions on the volcano, no recognition could be made today.
Alert level: Alert 2-2 – Eruption in the Enclos.
Source : OVPF
Iceland , Bárðarbunga :
Earthquake under the Bárðarbunga volcano early Monday morning.
A violent swarm of earthquakes was detected in the Bárðarbunga caldera early Monday morning. An earthquake of magnitude M3.0, with an epicenter 7.6 km east of Bárðarbunga, at the eastern edge of the central volcano caldera, at a depth of 3.4 km (2.1 miles), was detected at 6:09 in the morning. . Half a dozen smaller replicas were detected.
Signs of activity of one of the cauldrons in the Vatnajökull ice cap above the Bárðarbunga volcano. Photo / Tómas Guðbjartsson.
The Bárðarbunga volcanic system has shown increasing levels of activity over the past year, following the Holuhraun eruption in 2014-2015 at the northern limit of the system.
The Bárðarbunga Caldera is the center of a larger volcanic system, the largest in Iceland and one of the largest in the world. In the last 10,000 years, it has produced more lava than any other volcano on Earth. It is composed of a group of fissures 200 km long and 25 km wide that extends from the central highlands north of the Vatnajökull glacier to the Veiðivötn region to the west of the glacier.
A second central volcano is located in the Bárðarbunga system, Hamarinn, also known as Loki or Fögrufjöll. Hamarinn is hidden under the Vatnajökull, southwest of Bárðarbunga.
Eruptions in the Bárðarbunga system have frequently occurred in the fissures north and west of Vatnajökull. The last eruption took place in 2014-2015 along a crack in the Holuhraun lava field in the central highlands north of the glacier.
Source : icelandmag.is
Costa Rica , Turrialba :
Report on the activity of Turrialba volcano, October 01, 2018.
On 01 – 10 – 2018 at 06:00 local time, there is an eruption on the volcano Turrialba, with a column of ash that rose 500 meters above the height of the crater and at 3840 m. (meters above sea level) (12595.2 feet).
Duration of the activity: In progress.
The winds blow towards the North-West.
Ash fall reported in: No reported ash drop
Sulfur odor reported in: No sulfur odor reported
Comments: Passive ash eruption.
https://www.facebook.com/OVSICORI/videos/1747489312045756/
Since 30 September 2018, a continuous eruption has occurred on the Turrialba volcano, with a column rising 500 meters above the crater and 3840 meters above sea level (12595.2 feet).
The seismic activity is similar to that of yesterday.
At the time of this report, the winds are blowing towards the Northeast.
The ash emission probably started in the afternoon of yesterday.
Source : Ovsicori
United – States , Yellowstone :
44°25’48 » N 110°40’12 » W,
Summit Elevation 9203 ft (2805 m)
Current Volcano Alert Level: NORMAL
Current Aviation Color Code: GREEN
Recent work and news
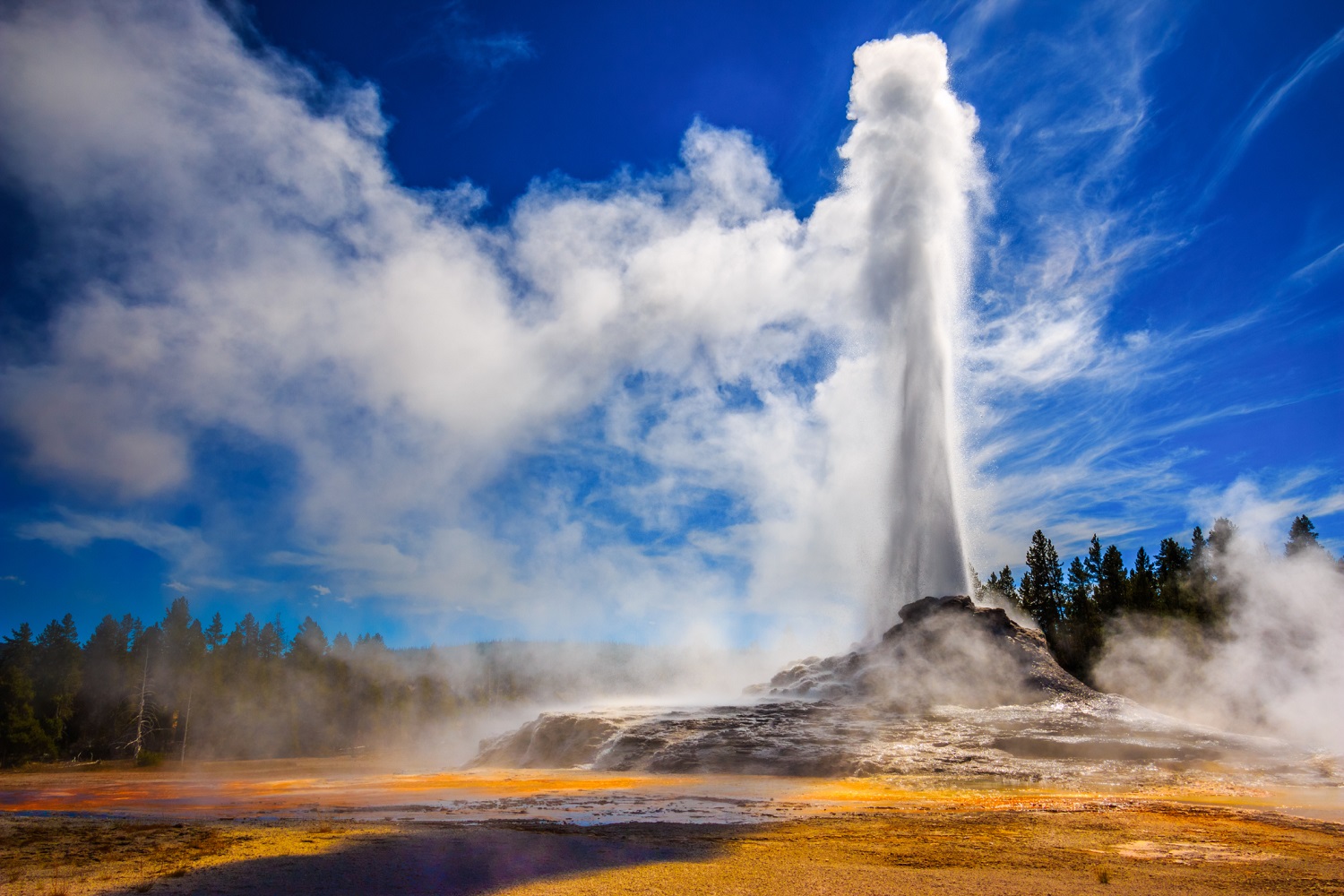
September was a month of hydrothermal activity at Yellowstone. Steamboat geyser experienced water eruptions on September 1, 7, 12, 17, 24, and 30. This brings the total number of Steamboat eruptions in 2018 to 21. In addition, a rare eruption of Ear Spring in the Upper Geyser Basin, not far from Old Faithful, occurred on September 15 and was accompanied by changes to springs and geysers in the Geyser Hill area. A new thermal feature also formed at that time nearby, spouting scalding water that necessitated the closure of the boardwalk through the area. Scientists from Yellowstone National Park deployed temperature sensors and cameras in the area to monitor the activity, and the University of Utah deployed 29 seismic sensors around the region to measure whether or not significant changes in the subsurface plumbing system occurred relative to data collected from the area in November 2017.
Seismicity
During September 2018, the University of Utah Seismograph Stations, responsible for the operation and analysis of the Yellowstone Seismic Network, located 57 earthquakes in the Yellowstone National Park region. The largest event was a micro earthquake of magnitude 2.9 located about 16 miles east-southeast of Mammoth, WY, on September 11 at 07:30 AM MDT.
No swarm activity occurred during the month of September.
Yellowstone earthquake activity remains at background levels.
Ground deformation
Surface deformation recorded by GPS stations in Yellowstone showed little change over the month of September, reflecting the low rates of ground motion in the region. Overall trends since 2015 are of uplift near the Norris Geyser Basin and subsidence of the caldera, all at rates of a few centimeters per year.
The Yellowstone Volcano Observatory (YVO) provides long-term monitoring of volcanic and earthquake activity in the Yellowstone National Park region. Yellowstone is the site of the largest and most diverse collection of natural thermal features in the world and the first National Park. YVO is one of the five USGS Volcano Observatories that monitor volcanoes within the United States for science and public safety.
Source : YVO