May 12 , 2022.
Alaska , Edgecumbe :
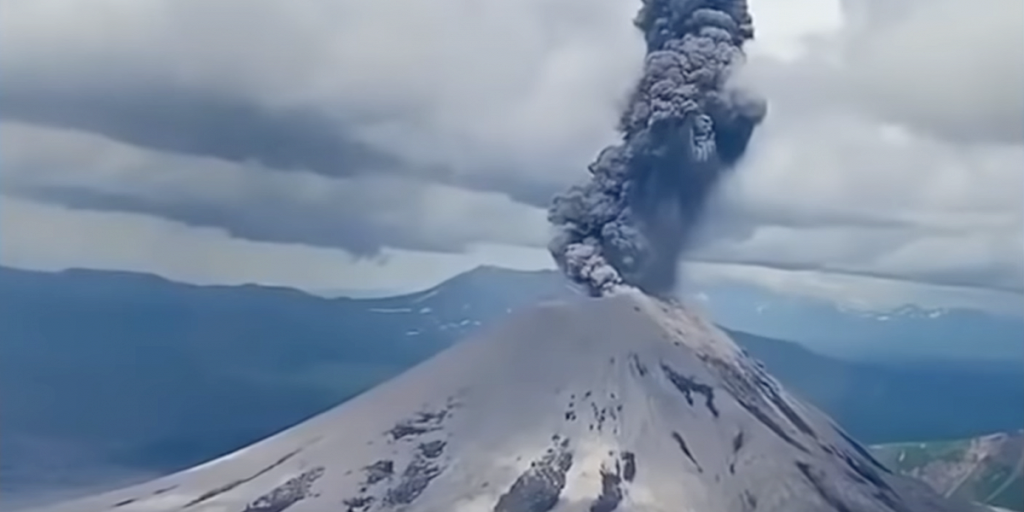
Mount Edgecumbe volcanic field changes from « dormant » to « active » . Posted: May 09, 2022
The Mount Edgecumbe volcanic field (MEVF) is now classed as « historically active » by the standards of the Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO) because it is experiencing deformation related to the presence of magma intruding three miles below the surface.
AVO defines an « active » volcano as a volcanic center that has had a recent eruption or a period of intense deformation, seismic activity, and/or fumarolic activity that likely reflects the accumulation of magma in the crust below the volcano. Note that this definition does not require an actual eruption and instead uses eruptions as well as measurements of magma beneath a volcano. AVO uses the term « historical » to mean within the past 300 years and the beginning of written records in Alaska. It is important to note that the Indigenous oral histories of Alaska cover a far greater period of time. As our geologic understanding of Alaska’s volcanoes improves through additional fieldwork and modern radiometric-dating techniques, our understanding of past activity will continue to evolve.
The Mount Edgecumbe volcanic field (MEVF) has been previously described by people outside of the Alaska Volcano Observatory as a « dormant » volcano. Let’s talk about that word, « dormant ». The American Geosciences Institute Glossary of Geology defines « dormant volcano » as: « A volcano that is not now erupting but is considered likely to do so in the future. There is no precise distinction between a dormant and an active volcano. » The term « dormant volcano » is so little used and undefined in modern volcanology that the Encyclopedia of Volcanoes (2000) does not contain it in the glossaries or index.
The Alaska Volcano Observatory prefers to classify volcanoes as to when they were most recently active, and previously labeled the MEVF as « Holocene », meaning that we thought the most recent activity at Edgecumbe was within the past ~11,700 years. (For more information on divisions of geologic time, see this publication: Divisions of Geologic Time – Major Chronostratigraphic and Geochronologic Units). However, with our recent observation that magma is likely intruding underneath Edgecumbe, the Alaska Volcano Observatory now classifies the MEVF as « historically active. »
The Mount Edgecumbe volcanic field is on Kruzof Island, which is within the Tongass National Forest and managed by the US Forest Service.
Source : AVO
Photo : Jim Riehle (U.S. Geological Survey, Alaska Volcano Observatory).
Colombia , Nevado del Ruiz :
Weekly bulletin of the activity of the Nevado del Ruiz volcano
The activity level continues at the yellow activity level or (III): changes in the behavior of volcanic activity.
Regarding the monitoring of the activity of the Nevado del Ruiz volcano, the COLOMBIAN GEOLOGICAL SERVICE reports that:
Seismicity associated with rock fracturing increased in number of earthquakes and seismic energy released, compared to the previous week. This seismic activity was located mainly in the northeast, southwest and southeast sectors of the volcano and, to a lesser extent, in the Arenas crater and in the distal northwest sector of the volcano. The depth of the earthquakes varied between 0.6 and 6.5 km. The maximum magnitude recorded during the week was 3.0 ML (Local Magnitude), corresponding to the earthquake that occurred on May 9 at 10:05 a.m. (local time), located 2.0 km northeast of the Arenas crater, at a depth of 4.0 km.
The recording of several episodes of short duration, low energy and « drumbeat » type seismicity associated with the fracturing of the rock on May 5 and 8 stands out. This seismicity has been linked to the processes of ascent, emplacement-growth and evolution of a lava dome at the bottom of the Arenas crater.
Seismicity related to fluid dynamics inside volcanic conduits increased in number of earthquakes and seismic energy released, compared to the previous week. This seismic activity was characterized by the occurrence of continuous volcanic tremors, tremor pulses, long and very long period type earthquakes. These signals exhibited low to moderate energy levels and variable spectral content. Most of these earthquakes were located in the Arenas crater. Some of them were associated with gas and ash emissions that were confirmed by the cameras installed in the volcano area and by reports from Los Nevados National Natural Park officials and residents of the area of influence. of the volcano. The thermographic cameras made it possible to observe the evolution of the relative temperature of the material emitted into the atmosphere.
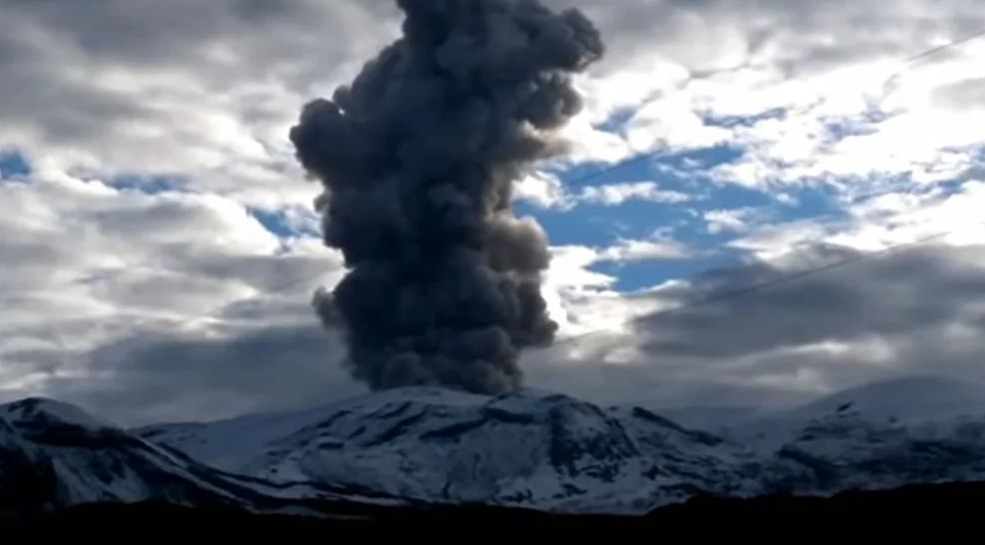
The column of gas and steam reached a maximum height of 2,932 m measured at the top of the volcano on May 9, associated with the emission of ash at 08:57 (local time).
On 10 May Servicio Geológico Colombiano’s (SGC) reported that during the previous week the number of seismic signals indicating both rock fracturing and fluid movement at Nevado del Ruiz had increased compared to the week before. Several episodes of drumbeat seismicity were recorded on 5 and 8 May, indicting growth of the lava dome. Some low-temperature thermal anomalies were also identified at Arenas Crater. Gas-and-ash emissions were periodically visible in webcam images. A small ash emission on 3 May caused minor ashfall in the municipalities of Manizales (25 km N), Dosquebradas (40 km W), Santa Rosa, and Pereira (40 km WSW). At 0857 on 9 May an ash plume drifted NW, W, and SW, causing ashfall in Manizales, Villamaría (28 km NW), and Chinchiná (30 km WNW) in the department of Caldas, and in Pereira, Dosquebradas, and Santa Rosa de Cabal (33 km W) in the department of Risaralda. The Alert Level remained at 3 (Yellow; the second lowest level on a four-color scale).
Source : SGC. GVP.
Photos : infobae.com , Diana M Bustamante.
Kamchatka , Karymsky :
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION (VONA)
Issued: May 11 , 2022
Volcano: Karymsky (CAVW #300130)
Current aviation colour code: ORANGE
Previous aviation colour code: orange
Source: KVERT
Notice Number: 2022-33
Volcano Location: N 54 deg 2 min E 159 deg 26 min
Area: Kamchatka, Russia
Summit Elevation: 1486 m (4874.08 ft)
Volcanic Activity Summary:
A moderate eruptive activity of the volcano continues. The explosions sent ash up to 6 km a.s.l., the ash cloud 7×10 km in size is moving for 25 km to the west-northwest of the volcano.
A moderate activity of the volcano continues. Ash explosions up to 12 km (39,400 ft) a.s.l. could occur at any time. Ongoing activity could affect international and low-flying aircraft.
Volcanic cloud height:
6000 m (19680 ft) AMSL Time and method of ash plume/cloud height determination: 20220511/2320Z – Himawari-8
Other volcanic cloud information:
Distance of ash plume/cloud of the volcano: 25 km (16 mi)
Direction of drift of ash plume/cloud of the volcano: WNW / azimuth 283 deg
Time and method of ash plume/cloud determination: 20220511/2320Z – Himawari-8
Source : Kvert.
Photo : Daily Afisha. Ru.
Chile , Nevados de Chillan :
VOLCANIC COMPLEX OF NEVADOS DE CHILLÁN
Seismology
Volcano-tectonic (VT) seismicity added a total of 47 events caused by brittle fracture processes; the most energetic had a local magnitude (ML) equal to 2.1, located 3.9 km east (E) of the volcanic edifice, with a depth of 4.3 km from the summit. This seismicity, which was spatially and temporally linked in the previous phases of this eruptive cycle with changes in the deformation of the volcanic edifice, remains at low levels compared to periods of greater activity.
Long period (LP), explosion (EX) and tremor (TR) seismicity continues to be recorded, associated with fluid dynamics within the volcanic system. 682 LP-type earthquakes were classified, including 175 linked to explosions at surface level, due to the presence of acoustic waves and/or gaseous emissions, often with the addition of particulate matter. The size of the largest LP-type earthquake estimated from the reduced displacement parameter (DR) reached a value equal to 481 cm2 and was associated with an explosion that caused an acoustic wave that obtained a reduced pressure of 40 Pa Km.
Regarding TR type seismicity, 260 episodes were identified, the most important of which reached a DR of 83 cm2. The daily energy levels observed for earthquakes associated with fluid movement remained at a level considered low compared to periods of greatest eruptive activity.
Fluid Geochemistry
Data on sulfur dioxide (SO2) emissions obtained by optical differential absorption spectroscopy (DOAS) equipment, corresponding to the Philippi and Chillán stations, installed 1.5 km to the South-South-East (SSE) and 2.7 km east-southeast (ESE) of the active crater, respectively, showed an average value of 551 ± 68 t/d, with a maximum daily value of 849 t/d, recorded on 18 april. An increase in SO2 levels is observed, consistent with the presence of a new effusive body inside the active Nicanor crater.
No anomalies were reported in sulfur dioxide (SO2) emissions into the atmosphere in the area near the volcanic complex, according to data published by Tropospheric Monitoring.
Satellite thermal anomalies
A thermal alert was recorded in the area associated with the volcanic complex during the period, with a maximum Volcanic Radiative Power (VRP) of 1 MW on April 17, a value considered low according to data processed by the Middle Infrared of Observation of Volcanic Activity. (MIROVA, http://www.mirovaweb.it/).
At the same time, according to the analytical processing of satellite images (Sentinel 2-L2A in combination of false color bands), luminance anomalies were observed on April 18, 20, 28 and 30.
In general, the volcanic complex of Nevados de Chillán continues its activity in a context of moderate eruption with a low explosive level, prevailing with a state of low seismic energy. Surface activity during this period was characterized by predominantly gaseous explosions with little or no pyroclastic content; In addition, a small volume of extruded material (effusive body) continues to be observed. According to the analysis of data from geodetic stations, the volcanic system remains in a deflationary process without significant variations.
In this context, the technical alert is maintained at the level:
YELLOW TECHNICAL ALERT: Changes in volcanic activity behavior
Observation:
The area likely to be affected by volcanic processes such as lava flows, pyroclastic density currents and ballistic projection pyroclasts, includes a radius of 2 km around the active crater
Source : Sernageomin.
Read the article : https://rnvv.sernageomin.cl/rnvv/TI_Santiago_prod/reportes_LB/2022/RAV_20220509_%C3%91uble_v8.pdf
Photos : Sernageomin , 24 horas .
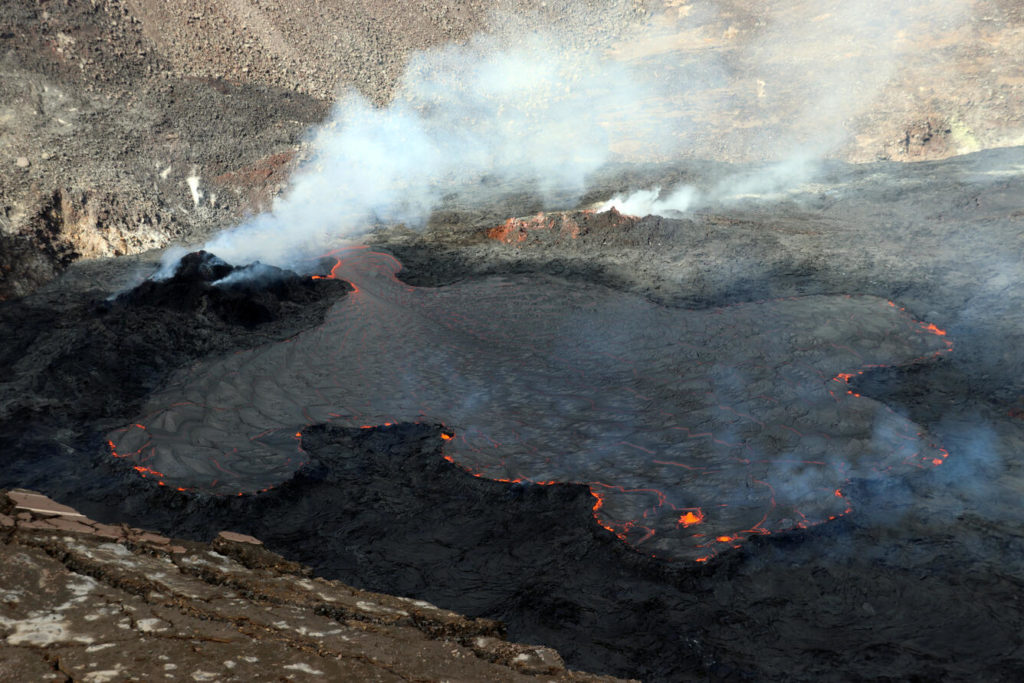
Hawaii , Kilauea :
19°25’16 » N 155°17’13 » W,
Summit Elevation 4091 ft (1247 m)
Current Volcano Alert Level: WATCH
Current Aviation Color Code: ORANGE
Activity Summary:
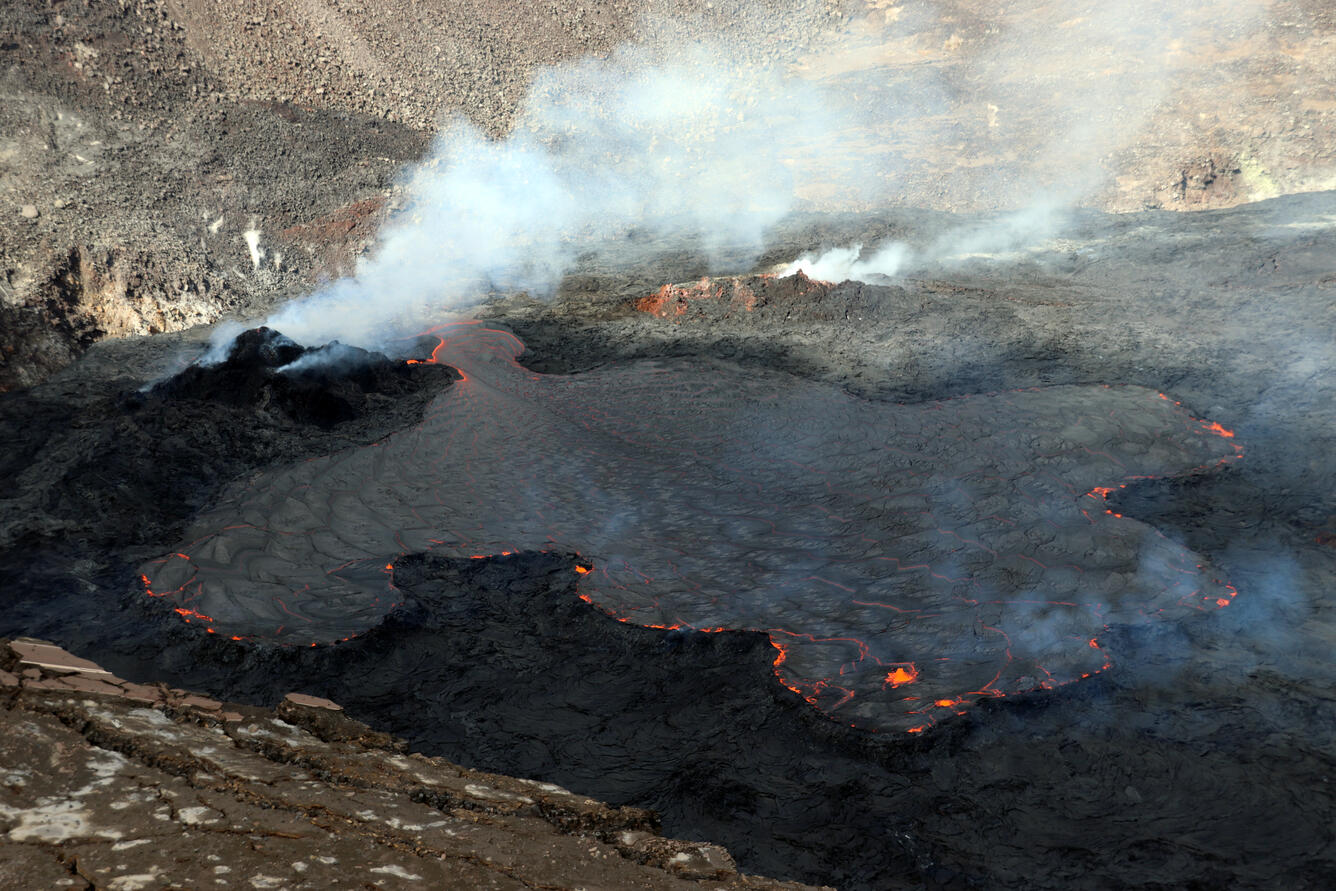
The summit eruption of Kīlauea Volcano, within Halemaʻumaʻu crater, has continued over the past 24 hours. All recent lava activity has been confined to the crater, and current data indicate that this scenario is likely to continue. No significant changes have been noted in the summit or East Rift Zone.
Halemaʻumaʻu crater Lava Lake Observations:
Eruption of lava from the Halemaʻumaʻu western vent into the active lava lake and onto the crater floor has continued over the past 24 hours. The active lava lake has shown continuous surface activity, with lake level increasing slightly around 8pm last night. Lava ooze-out activity yesterday was very weak, and mostly restricted to the northeast margin of the lake. Larger ooze-out activity on the northwest margin of the lake resumed around 2am today. Overflight measurements on April 6, 2022 indicated that the crater floor had seen a total rise of about 99 meters (325 feet) .
Summit Observations:
Summit tiltmeters indicated inflation through yesterday morning, which leveled off yesterday afternoon; tilt has remained flat since then. A sulfur dioxide (SO2) emission rate of approximately 2,700 tonnes per day (t/d) was measured yesterday (May 10, 2022).
Source : HVO.
Photo : USGS / M. Patrick ( archive).
Italy , Vulcano :
WEEKLY BULLETIN. from 02 May 2022 to 08 May 2022. (issue date 10 May 2022)
ACTIVITY STATUS SUMMARY
In the light of the surveillance data, it is highlighted:
1) Temperature of the crater fumaroles: The fumarole field has equivalent emission temperatures along the entire summit fracture line, confirming a thermal anomaly always maintained by a constant vapor flow.
2) Flux of CO2 in the crater area: The flux of CO2 from the ground in the summit area confirms stabilization at high values around 12,000 g m-2 day-1.
3) SO2 flux in the crater area: SO2 flux at a medium-high and stable level
4) Geochemistry of fumarolic gases: No update is available.
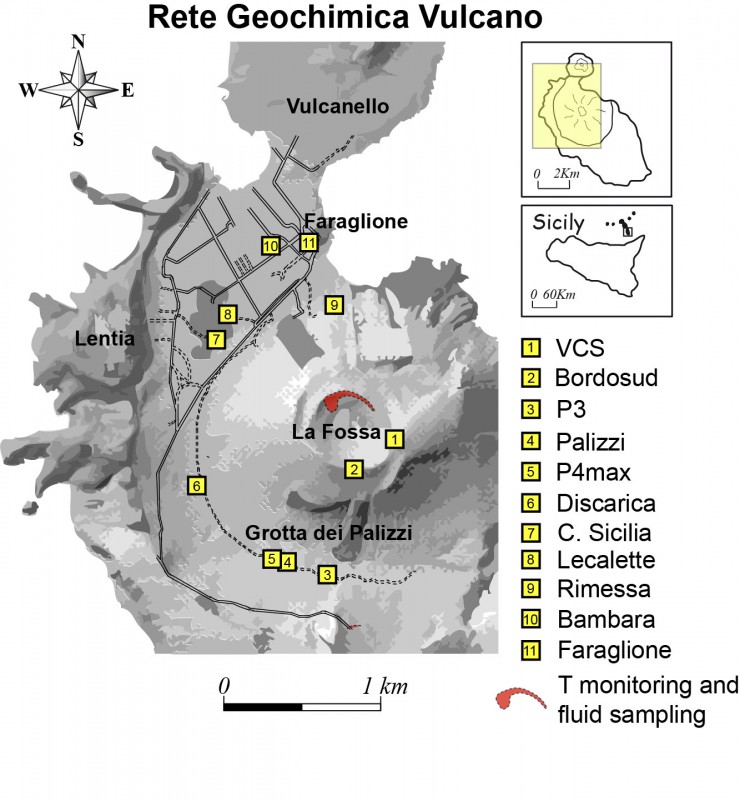
5) CO2 fluxes at the base of the La Fossa cone and in the Vulcano Porto area: The CO2 fluxes recorded in the sites of C. Sicilia, Rimessa and P4max continue to show a slight downward trend, but remain at medium-high values; in the Faraglione site, there are values close to the background level.
6) Geochemistry of thermal aquifers: The temperature measured in the Camping Sicilia well is at high and stable values. The electrical conductivity shows low values, although slightly increasing.
The level values measured in the Bambara well show a moderate upward trend. Conductivity values continue to show a gradual decrease even though they remain at medium-high levels.
7) Local seismicity: Local low level seismic activity
8) Regional seismicity: No fracturing event with Ml greater than 1 was recorded.
9) Deformations – GNSS: The network of permanent GNSS stations has not recorded any significant changes.
10) Deformations – Inclinometry: The inclinometric network has not recorded any significant changes.
11) Other observations: Gravimetry: No significant variation was recorded.
CRATER FUMEROLES TEMPERATURE:
Along the upper edge, the maximum emission temperature has very stable values (T1: 377-383°C), with a weekly average of 381°C. The thermal signal from the sensor located on the interior side was interrupted on May 5, due to a power supply problem, but the site already showed obvious disturbances of an exogenous nature.
It is necessary to completely replace 2 measurement lines and their respective probes (F5 – T3; FA) and reconsider the position of T0_Fa, but the intervention will only take place when the working conditions improve.
CO2 FLOW AT THE BASE OF LA FOSSA CONE AND IN THE PORTO VULCANO AREA:
The CO2 fluxes at the base of the crater in the C. Sicilia site show average to high values, above the background level, although in sharp decrease compared to the period November-December 2021; the Rimessa site recorded average values, stable compared to last week; the P4max site displays medium-high values, which fluctuate cyclically; in the Faraglione site, there are values close to the background level.
Source : INGV.
Photos : INGV.