October 18 , 2025.
Hawaii , Kilauea :
HAWAIIAN VOLCANO OBSERVATORY DAILY UPDATE . U.S. Geological Survey
Friday, October 17, 2025, 9:34 AM HST (Friday, October 17, 2025, 19:34 UTC)
19°25’16 » N 155°17’13 » W,
Summit Elevation 4091 ft (1247 m)
Current Volcano Alert Level: WATCH
Current Aviation Color Code: ORANGE
During the lapse in appropriations, the USGS Hawaiian Volcano Observatory (HVO) continues to maintain monitoring networks and issue updates and notifications of volcanic activity via the Hazard Notification Service. Volcano monitoring data will continue to be available on the HVO website. Static website content will not be updated until further notice and information may become outdated over time.
Activity Summary:
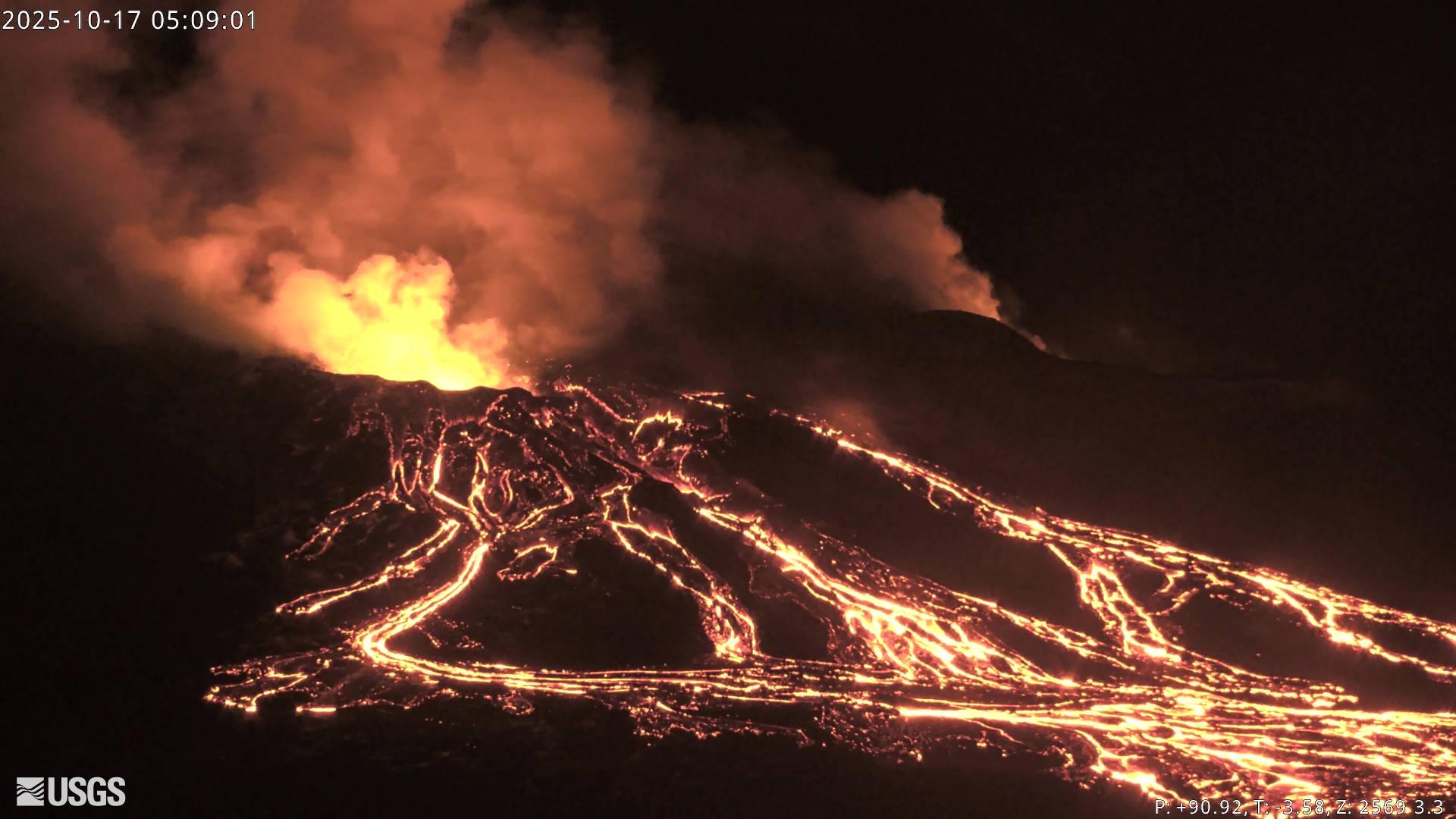
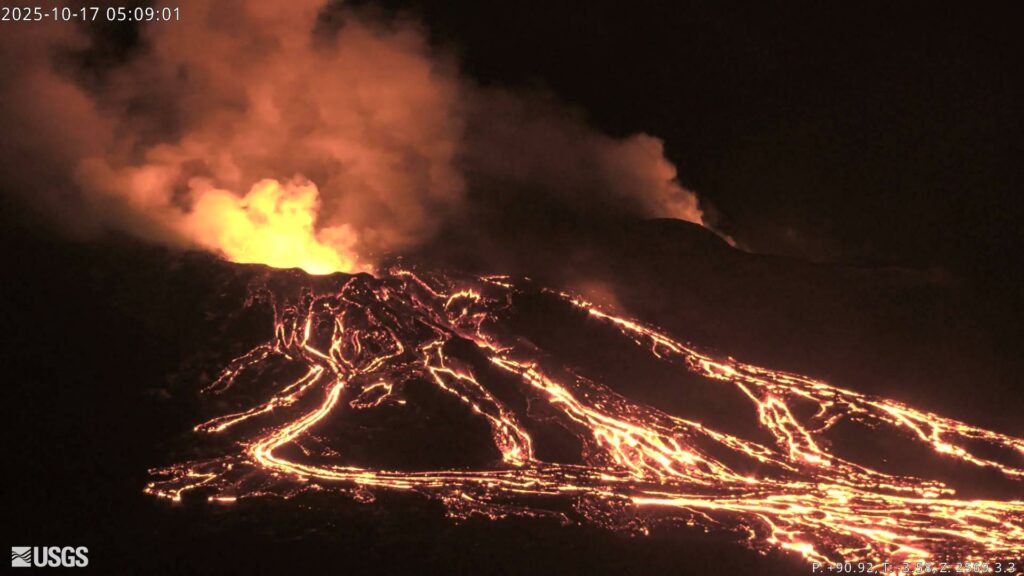
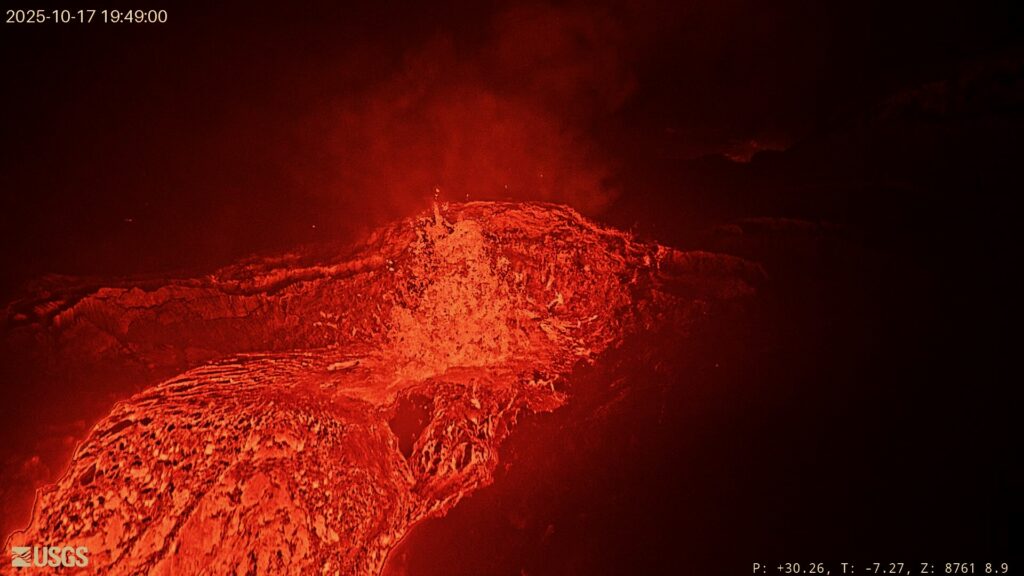
Precursory low-level activity for episode 35 of the ongoing Halemaʻumaʻu eruption increased yesterday, October 16. Twenty-five south vent overflow-drainback events occurred over the past 24 hours. Each overflow produced lava flows that flowed onto the crater floor. Each overflow ended with lava suddenly draining back into the south vent. Similar overflow-drainback events occurred during the lead up to previous fountaining episodes. Vigorous intermittent lava spattering has occurred at the north vent over the past 24 hours. More overflows, drainbacks, spattering and small fountains are expected as we approach the onset of episode 35 sustained fountaining. Seismic tremor and inflationary tilt continued at the summit over the past 24 hours. Forecast models based on the rate of summit inflation indicate that episode 35 lava fountaining is likely to begin between today, October 17, and October 22, with the most likely window between tomorrow and October 20.
Summit Observations:
Twenty-five south vent overflow-drainback events occurred over the past 24 hours. Overflow durations ranged from 4 to 34 minutes. Each overflow produced lava flows that flowed onto the crater floor. Each overflow ended with lava suddenly draining back into the south vent. Many drainbacks were immediately preceded by a short burst of spattering or small fountaining in the vent.Similar overflow-drainback events occurred during the lead up to previous fountaining episodes. Vigorous intermittent lava spattering has occurred at the north vent over the past 24 hours. Strong glow was visible from both vents overnight between events. Seismic tremor bursts consistent gas pistoning activity continued over the past 24 hours. The UWD tiltmeter showed continued inflationary tilt and has recovered approximately 23 microradians since episode 34 ended.
Elevated degassing continues from the vents largely in bursts related to gas piston events. Overall, average sulfur dioxide (SO2) emission rates during pauses are typically 1,200 to 1,500 t/d, though emission rates can vary on short time scales.
Source et photo : HVO
Chile , Planchón Peteroa :
Special Volcanic Activity Report (REAV)
October 17, 2025, 6:55 p.m. local time (Continental Chile)
The National Geology and Mining Service of Chile (Sernageomin) releases the following preliminary information, obtained using the monitoring equipment of the National Volcanic Monitoring Network (RNVV), processed and analyzed at the Southern Andean Volcanological Observatory (OVDAS):
Today, Friday, October 17, using images from surveillance cameras installed near the Planchón Peteroa volcanic complex, a column of gas and pyroclasts was observed at 8:57 p.m. UTC. It reached 1,440 meters above the crater, dispersing eastward.
Based on the latest volcanic activity reports published by SERNAGEOMIN for this system, and taking into account the above, the occurrence of new episodes of explosions of similar or greater energy, of low to moderate magnitude, likely to affect the immediate vicinity of the active craters, cannot be ruled out.
OBSERVATIONS:
As of the publication date of this report, seismic activity has not shown any other significant changes.
The technical volcanic alert remains in effect at: YELLOW technical volcanic alert.
Source et photo : Sernageomin.
Colombia , Nevado del Ruiz :
Manizales, October 14, 2025, 8:40 p.m.
Regarding the monitoring of the activity of the Nevado del Ruiz volcano, the Colombian Geological Survey (SGC), an entity affiliated with the Ministry of Mines and Energy, reports that:
During the week of October 7 to 13, 2025, the volcano continued to exhibit unstable behavior. The main variations in the monitored parameters compared to the previous week were:
– Seismic activity associated with rock fracturing processes within the volcanic edifice increased, with an increase in the number of recorded earthquakes and the seismic energy released. The events were located mainly on the southeast and west flanks of the volcano and, to a lesser extent, on the east, east-southeast, northeast, and southwest flanks, as well as in the Arenas crater. In general, earthquakes in the Arenas crater occurred at distances of less than 8 km and at depths ranging from less than 2 km (for earthquakes in the crater and some in the southeast sector) to 6 km. The highest magnitude recorded was 1.2, corresponding to the earthquakes that occurred on October 7 at 22:03 (7 km east-southeast of the crater, 3 km deep) and on October 11 at 22:28 (2 km south-southeast of the crater, 4 km deep).
– Seismicity associated with fluid dynamics in volcanic conduits decreased with the number of recorded earthquakes and maintained similar levels of seismic energy release. The energy levels of the seismic events were low to occasionally moderate. Cameras (conventional or thermographic) used to monitor the volcano, as well as reports from Los Nevados National Park (PNN) officials, confirmed several pulsed ash emissions and variations in the apparent temperature of the ejected materials. Furthermore, on October 9, seismic activity related to the lava dome (protuberance or mound) located at the crater floor was recorded. This activity was characterized by this type of seismic signals (related to fluid dynamics) and low energy levels.
– The volcano continues to emit water vapor and volcanic gases, primarily sulfur dioxide (SO₂), into the atmosphere. The estimated values of SO₂ flux associated with degassing processes were similar to those obtained the previous week. This trend was also confirmed by satellite monitoring of this parameter.
– The vertical height of the column of gas, water vapor, or ash reached 600 m, measured above the volcano’s summit. During dispersal, the maximum height reached 1,600 m during the ash emission recorded on October 11 at 9:03 a.m. Regarding the direction of dispersal, the column showed a preferential trend toward the northwest flank of the volcano and, to a lesser extent, toward the other flanks. National Park officials received reports of ashfall from the Azufrado River canyon area.
– When monitoring thermal anomalies at the floor of the Arenas Crater using satellite monitoring platforms, detection was limited by atmospheric conditions of high cloud cover in the volcanic area. However, some low energy anomalies have been reported.
Source et photo : SGC.
La Martinique , Mount Pelée :
Weekly Report, Paris Institute of Earth Physics, Martinique Volcanological and Seismological Observatory
Saint-Pierre, October 17, 2025 at 4:30 p.m. local time (GMT-4)
Volcanic activity decreased this week, with 408 earthquakes of volcanic origin observed.
Between October 10, 2025 at 4:00 p.m. (UT) and October 17, 2025 at 4:00 p.m. (UT), the OVSM recorded:
• 382 shallow volcano-tectonic earthquakes. Of these, 23 had a magnitude (duration magnitude Md or local magnitude Mlv) greater than 0.5, and two had a magnitude greater than 1. The largest had a magnitude Mlv = 2.53. The others were of lower energy. These earthquakes are located at depths between 0.5 and 4.0 km below the volcano’s summit, as was the case the previous week. A significant number of them originate from the well-known seismically active zones at Mount Pelée, located between 1.0 and 1.4 km below the volcano’s summit. The shallow volcano-tectonic seismicity is associated with microfracturing in the volcanic edifice, linked to the overall reactivation of the volcano observed since 2019.
• 11 shallow hybrid earthquakes and 15 long-period low-energy earthquakes. Their signals indicate that they are likely located in the same areas as the shallow volcano-tectonic earthquakes. The seismic signals from these types of earthquakes are enriched in (or contain only) low frequencies and are associated with the circulation of fluids (gas, hydrothermal fluids) within the volcanic edifice.
No earthquakes have been confirmed as having been felt by the population. However, a volcanic earthquake has a magnitude close to that of earthquakes likely to be slightly felt by hikers on Mount Pelée and residents of the communities closest to the volcano.
The previous week, the OVSM had recorded 2,666 earthquakes of volcanic origin. As of October 17, 2025, and over the past four weeks, the OVSM has therefore observed a total of 7,926 volcanic earthquakes, an average of 1,981 to 1,982 earthquakes per week.
During phases of volcanic reactivation of volcanoes similar to Mount Pelée, it is common to observe seismic activity of varying intensity and frequency, which can evolve rapidly but also cease quickly without any major changes to the system. The deformations of the edifice are very slight, and to date, there is no evidence of marked inflation of the summit area or evidence of deformation associated with deeper sources. There is currently no indication of fumarolic activity on Mount Pelée.
The probability of short-term eruptive activity remains low. However, given all the observations collected since the end of 2018 and their nature, and based on recent observations from the OVSM-IPGP, we cannot rule out a change in the situation in the medium term (weeks, months).
The volcanic alert level, in accordance with the measures planned by the authorities, is currently YELLOW: vigilance.
The alert level is currently YELLOW: vigilance.
Source : OVSM.
Photo : IPGP.
Costa Rica , Poas :
OVSICORI-UNA Weekly Volcano Monitoring Bulletin, October 17, 2025
Latitude: 10.20°N;
Longitude: 84.23°W;
Altitude: 2,687 m
Current Activity Level: Alert
This week, the tremor amplitude decreased compared to the previous week. However, it remains high compared to recent months. The acoustic tremor remains low in intensity and shows little variation. This week, an increase in the number of long-period events was observed, with four proximal volcano-tectonic events and one distal volcano-tectonic event.
The geodetic network records a slight contraction and subsidence of the volcano.
MultiGAS stations measured an average SO₂/CO₂ ratio of 2.3 ± 0.8 this week, slightly higher than last week’s (1.8 ± 0.6). The H₂S/SO₂ ratio has remained very low (< 0.1) in recent weeks. The ExpoGAS station located at the visitor observation point measured a maximum of 4.1 ppm SO₂ this week, representing a moderate concentration. DOAS stations measured an SO₂ flux of 165 ± 131 t/d, similar to the previous week’s (159 ± 91 t/d). Additionally, satellite measurements of atmospheric SO₂ remained detectable, generally exceeding 100 tonnes this week, with a peak of 658 tonnes of SO₂ on October 14.
This week, the lake level fluctuated due to heavy rainfall on some days. It ended the week with a value approximately 0.8 m higher than the previous week.
Source : Ovsicori.
Photo : Archive RSN.