October 4 , 2024.
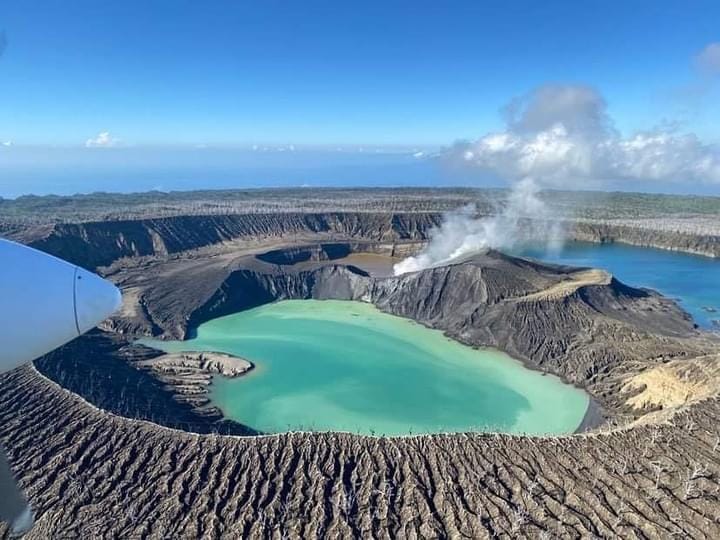
Vanuatu , Ambae :
On 26 September the Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD) reported that steam-and-gas emissions from the active vents at Ambae were ongoing during the previous month; ash content was not confirmed. The observations were based on webcam and satellite images and field observations. Seismic data also confirmed ongoing unrest. The Alert Level remained at 2 (on a scale of 0-5), and the public was warned to stay outside of the Danger Zone, defined as a 2-km radius around the active vents in Lake Voui, and away from drainages during heavy rains.
The island of Ambae, also known as Aoba, is a massive 2,500 km3 basaltic shield that is the most voluminous volcano of the New Hebrides archipelago. A pronounced NE-SW-trending rift zone with numerous scoria cones gives the 16 x 38 km island an elongated form. A broad pyroclastic cone containing three crater lakes (Manaro Ngoru, Voui, and Manaro Lakua) is located at the summit within the youngest of at least two nested calderas, the largest of which is 6 km in diameter. That large central edifice is also called Manaro Voui or Lombenben volcano. Post-caldera explosive eruptions formed the summit craters about 360 years ago. A tuff cone was constructed within Lake Voui (or Vui) about 60 years later. The latest known flank eruption, about 300 years ago, destroyed the population of the Nduindui area near the western coast.
Sources: Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD) , GVP.
Photo : Air taxi Vanuatu ( 11/2022)
Iceland , Grjótárvatn :
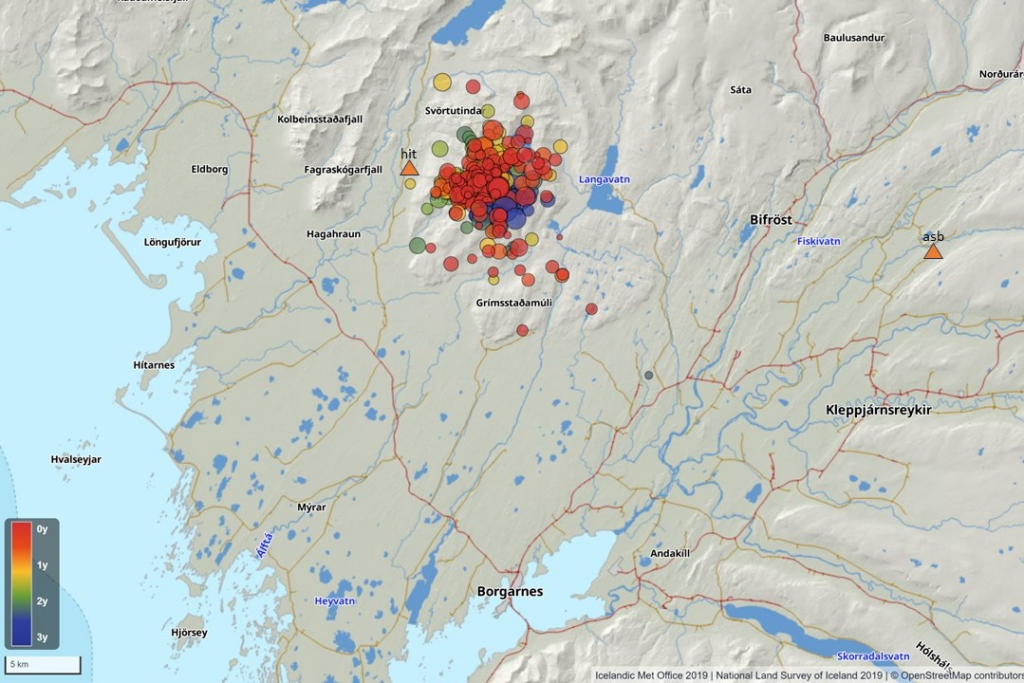
New seismometer installed in Hítárdal . Increased monitoring due to seismic activity in Grjótárvatn
October 3, 2024
More than 360 earthquakes since May 2021, including about 80 in August 2024
The seismic activity in Grjótárvatn is not thought to be caused by magma accumulation.
New seismic monitoring station in Hítárdal .
A new seismometer was installed in late September in Hítárdal, about 5 km northwest of Grjótárvatn. Since May 2021, earthquakes have been occasionally recorded in Grjótárvatn in Vesturland. A total of 360 earthquakes have been recorded since spring 2021, but the highest number has been about 20 earthquakes per month until August 2024, when nearly 80 earthquakes have been recorded in the area. Most earthquakes are magnitude 1 to 2, but the largest measured 3.0 on October 7, 2021 and was felt in many places in Snæfellsnes. There had been little seismic activity in this area before 2021, but occasional earthquakes had been recorded there in recent decades.
With the introduction of the seismometer at Hítárdal, the accuracy of earthquake location in the area will increase. Previously, the nearest station was at Ásbjarnarstaðir in the Borgarfjörður highlands, about 30 km from the source of the earthquakes.
What causes earthquakes?
Grjótárvatn lies in a fissure zone that belongs to the Ljúsfjalla volcanic system in the Snæfellsnes crater belt. The last small eruption took place in the 10th century. More information about the Ljúsfjalla system can be found on the Icelandic Volcano website. At present, the seismic activity at Grjótárvatn is not thought to be caused by magma accumulation. They may be caused by intraplate seismic activity, but the area needs to be studied more closely. There, the new seismometer will shed light on the activity that has been taking place there for more than three years.
Source : vedur is
Photo : Bergur H. Bergsson , IMO .
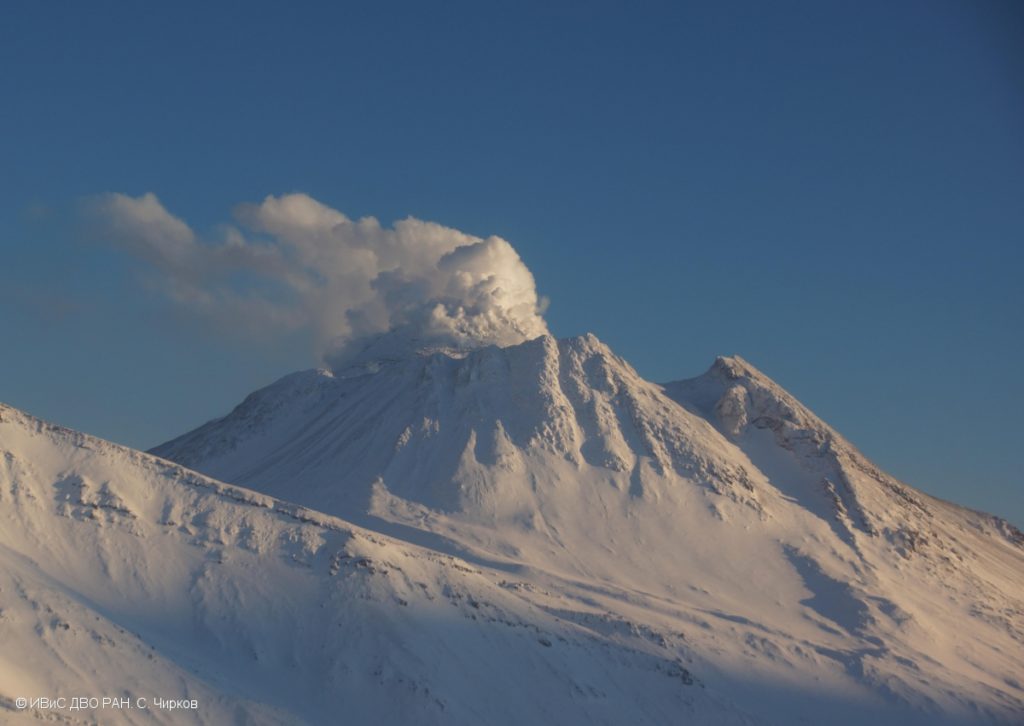
Kamchatka , Bezymianny :
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION (VONA)
Issued: October 04 , 2024
Volcano: Bezymianny (CAVW #300250)
Current aviation colour code: YELLOW
Previous aviation colour code: orange
Source: KVERT
Notice Number: 2024-80
Volcano Location: N 55 deg 58 min E 160 deg 35 min
Area: Kamchatka, Russia
Summit Elevation: 2882 m (9452.96 ft)
Volcanic Activity Summary:
A gas-steam activity of the volcano continues. Currently, there is no movement of resuspended ash from the pyroclastic flow of the volcano near the Bezymianny, but a long cloud of resuspended ash continues to move southeast from the volcano, its edge is at a distance of about 1400 km from the volcano. KVERT continues to monitor of the Bezymianny volcano.
An effusive eruption of the volcano continues. Ongoing activity could affect low-flying aircraft.
Volcanic cloud height: NO ASH CLOUD PRODUSED
Other volcanic cloud information: NO ASH CLOUD PRODUSED
Source : Kvert
Photo : S. Chirkov, IVS FEB RAS.
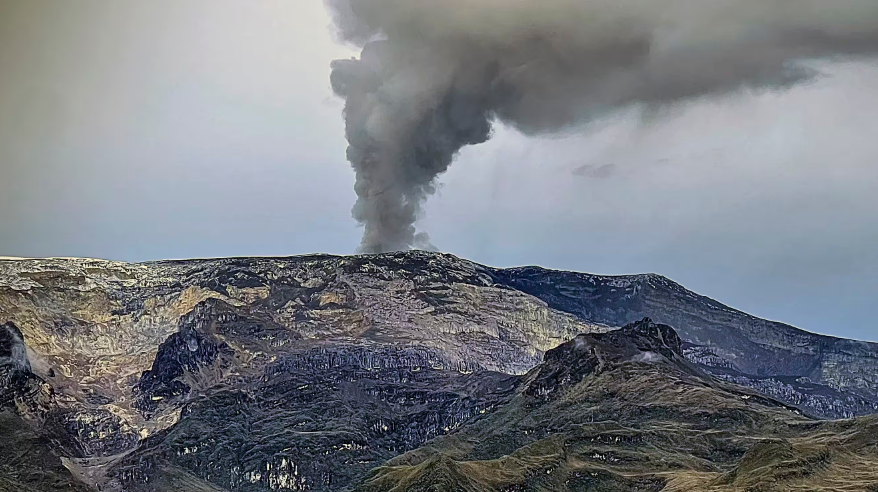
Colombia , Nevado del Ruiz :
Manizales, October 1, 2024, 7:00 p.m.
From the monitoring of the activity of the Nevado del Ruiz volcano, the Colombian Geological Survey (SGC), an entity attached to the Ministry of Mines and Energy, reports that:
During the week of September 24 to 30, 2024, the volcano continued with unstable behavior. Compared to the previous week, the main variations in the monitored parameters were:
– Seismicity related to the activity of fluids inside volcanic conduits increased in the number of earthquakes recorded and in the seismic energy released, especially from seismic signals related to pulsatile ash emissions. The energy levels of this seismicity were variable with values ranging from low to moderate. Thanks to the cameras used to monitor the volcano and the reports received from those responsible for the Los Nevados National Natural Park, it was possible to confirm some ash emissions. Using FLIR (thermographic) cameras, several changes in the temperature of the emitted material were detected. Both phenomena were associated with some of the recorded seismic events.
– Seismic activity associated with the fracturing of rocks inside the volcanic edifice increased in the number of recorded earthquakes and maintained similar levels in the released seismic energy. The earthquakes were located mainly in the Arenas crater and on the south-southwest, south-southeast and northeastern flanks, at distances less than 4 km from the crater. The depths of the events varied between less than 1 km and 8 km from the summit of the volcano. The highest magnitude of the week was 1.0, corresponding to the earthquake recorded on September 28 at 21:31, located 2 km south-southeast of the Arenas crater, at a depth of 4 km. On September 29 and 30, seismic activity related to the activity of the lava dome located at the bottom of the crater was recorded with low energy levels.
– On the volcano, the emission of water vapor and gas into the atmosphere from the Arenas crater continued. The sulfur dioxide (SO2) degassing rates were variable and their estimation was affected by the wind direction, which did not favor the location of the measuring stations. However, from the satellite monitoring platforms, it was observed that the SO2 degassing rates increased, reaching a notable value on September 29, a value that had not been recorded since February 2023.
– The height of the gas column reached 1800 m and 2000 m respectively in vertical and dispersion. These values were estimated at the summit of the volcano during the ash emission recorded on September 30 at 22:44. The direction of dispersion of the column was variable with a preferential tendency towards the northwest and west-northwest flanks during the first half of the month. In the second half, the direction varied between the northern, eastern and southeastern flanks of the volcano. According to the different directions of dispersion, ashfall reports were received from Cabaña de Brisas, northwest of the volcano, and from sectors of the Lagunilla River, east of the volcano.
– By monitoring thermal anomalies at the bottom of the Arenas crater, from satellite monitoring platforms, several reports of low to moderate energy level anomalies were obtained.
Source : SGC.
Photo : COLOMBIAN AIR FORCE ( 5/2024).
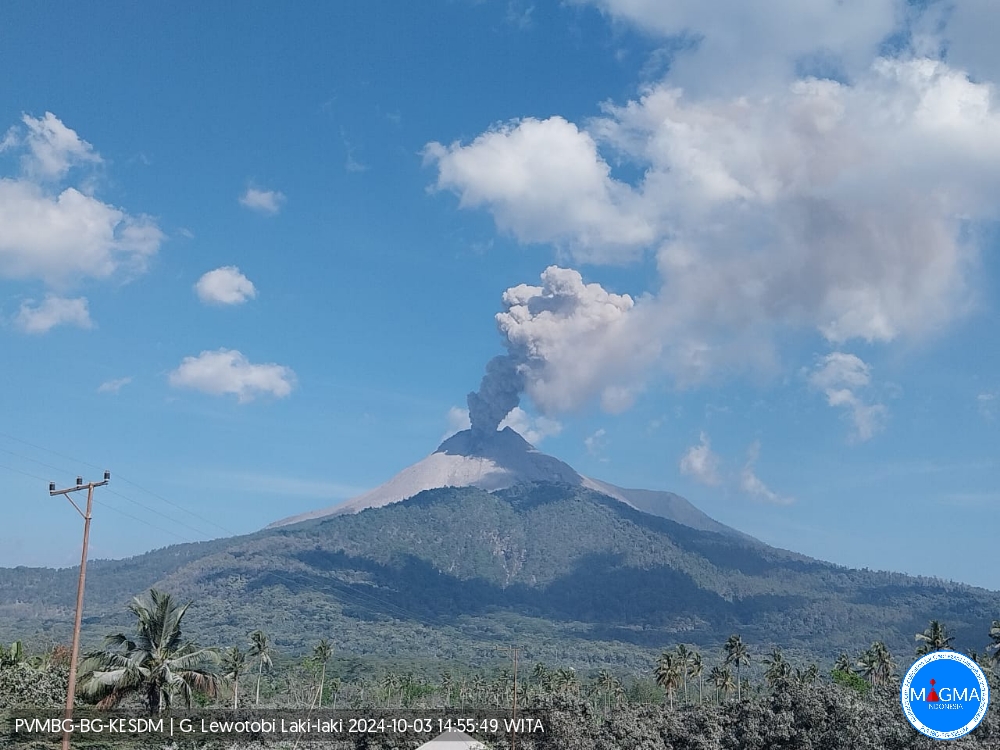
Indonesia , Lewotobi Laki-laki :
An eruption of Lewotobi Laki Laki occurred on Thursday, October 3, 2024 at 14:43 WITA with the height of the ash column observed at ± 800 m above the summit (± 2384 m above sea level). The ash column was observed to be gray with a thick intensity, oriented towards the southwest and west. This eruption was recorded on a seismograph with a maximum amplitude of 7.4 mm and a duration of 582 seconds.
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION – VONA
Issued : October 03 , 2024
Volcano : Lewotobi Laki-laki (264180)
Current Aviation Colour Code : ORANGE
Previous Aviation Colour Code : orange
Source : Lewotobi Laki-laki Volcano Observatory
Notice Number : 2024LWK589
Volcano Location : S 08 deg 32 min 20 sec E 122 deg 46 min 06 sec
Area : East Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia
Summit Elevation : 5069 FT (1584 M)
Volcanic Activity Summary :
Eruption with volcanic ash cloud at 06h43 UTC (14h43 local).
Volcanic Cloud Height :
Best estimate of ash-cloud top is around 7309 FT (2284 M) above sea level or 2240 FT (700 M) above summit. May be higher than what can be observed clearly. Source of height data: ground observer.
Other Volcanic Cloud Information :
Ash cloud moving to west. Volcanic ash is observed to be gray. The intensity of volcanic ash is observed to be thick.
Remarks :
Eruption recorded on seismogram with maximum amplitude 7.4 mm and maximum duration 582 second.
Source et photo : Magma Indonésie .