February 03 , 2024.
United States , Yellowstone :
Thursday, February 1, 2024, 12:15 PM MST (Thursday, February 1, 2024, 19:15 UTC)
44°25’48 » N 110°40’12 » W,
Summit Elevation 9203 ft (2805 m)
Current Volcano Alert Level: NORMAL
Current Aviation Color Code: GREEN
Recent Work and News
There were no eruptions of Steamboat Geyser in January, although minor activity began at the geyser on about January 20 and continued through the end of the month. This suggests that the geyser will erupt soon, possibly in the first half of February.
Seismicity
During January 2024, the University of Utah Seismograph Stations, responsible for the operation and analysis of the Yellowstone Seismic Network, located 226 earthquakes in the Yellowstone National Park region. The largest event of the month was a minor earthquake of magnitude 3.3 located about 10 miles north-northeast of Old Faithful in Yellowstone National Park on January 3 at 5:10 PM MST.
December seismicity in Yellowstone was marked by two swarms:
1. A swarm of 119 earthquakes, located approximately 10 miles north-northeast of Old Faithful, occurred January 1–10. The largest earthquake in the sequence was also the largest of the month (described above).
2. A swarm of 38 earthquakes occurred approximately 9 miles east-northeast of West Yellowstone, MT, during January 6–7. The largest earthquake in the sequence was a magnitude 2.1 event on January 5 at 4:24 PM MST.
Earthquake sequences like these are common and account for roughly 50% of the total seismicity in the Yellowstone region.
Yellowstone earthquake activity is currently at background levels.
Ground Deformation
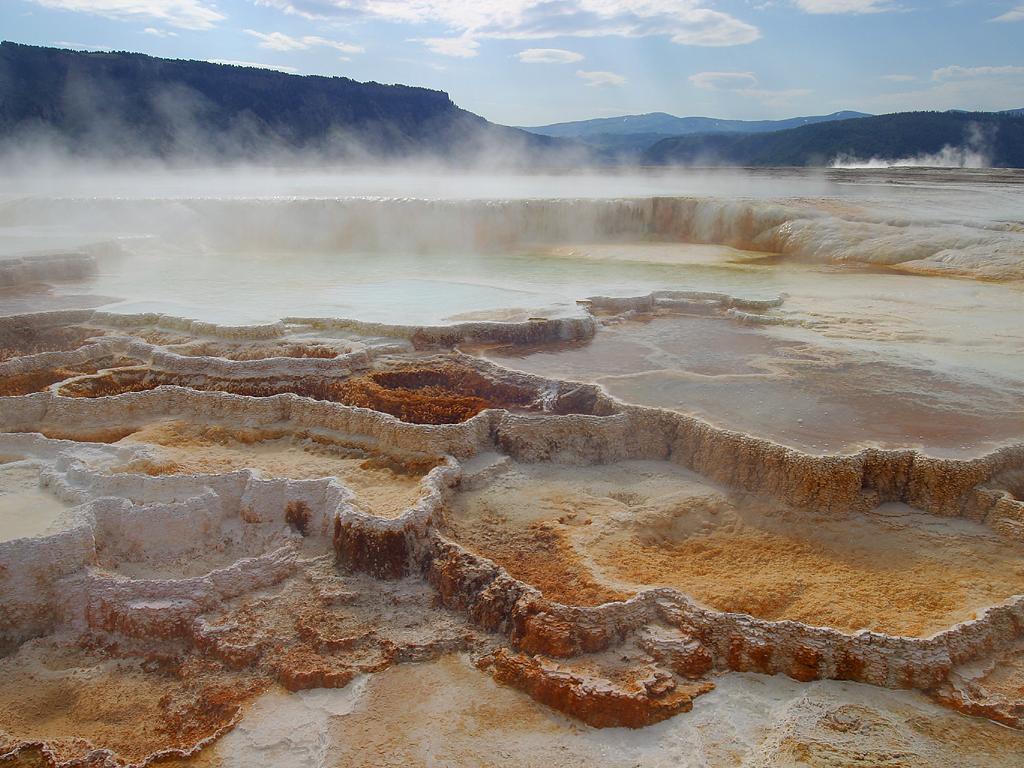
During the month of January, continuous GPS stations in Yellowstone caldera showed subsidence, which has been ongoing since 2015, interrupted in summer months by a pause or slight uplift caused by seasonal changes related to snowmelt and groundwater conditions. The caldera has subsided by slightly more than 2 cm (about 1 in) since the end of September. No significant deformation has occurred at Norris Geyser Basin since the end of summer.
Source : YVO
Photo : Mammoth hot spring , Jon Sullivan /wikipedias
Hawaii , Kilauea :
Friday, February 2, 2024, 5:05 PM HST (Saturday, February 3, 2024, 03:05 UTC)
19°25’16 » N 155°17’13 » W,
Summit Elevation 4091 ft (1247 m)
Current Volcano Alert Level: WATCH
Current Aviation Color Code: ORANGE
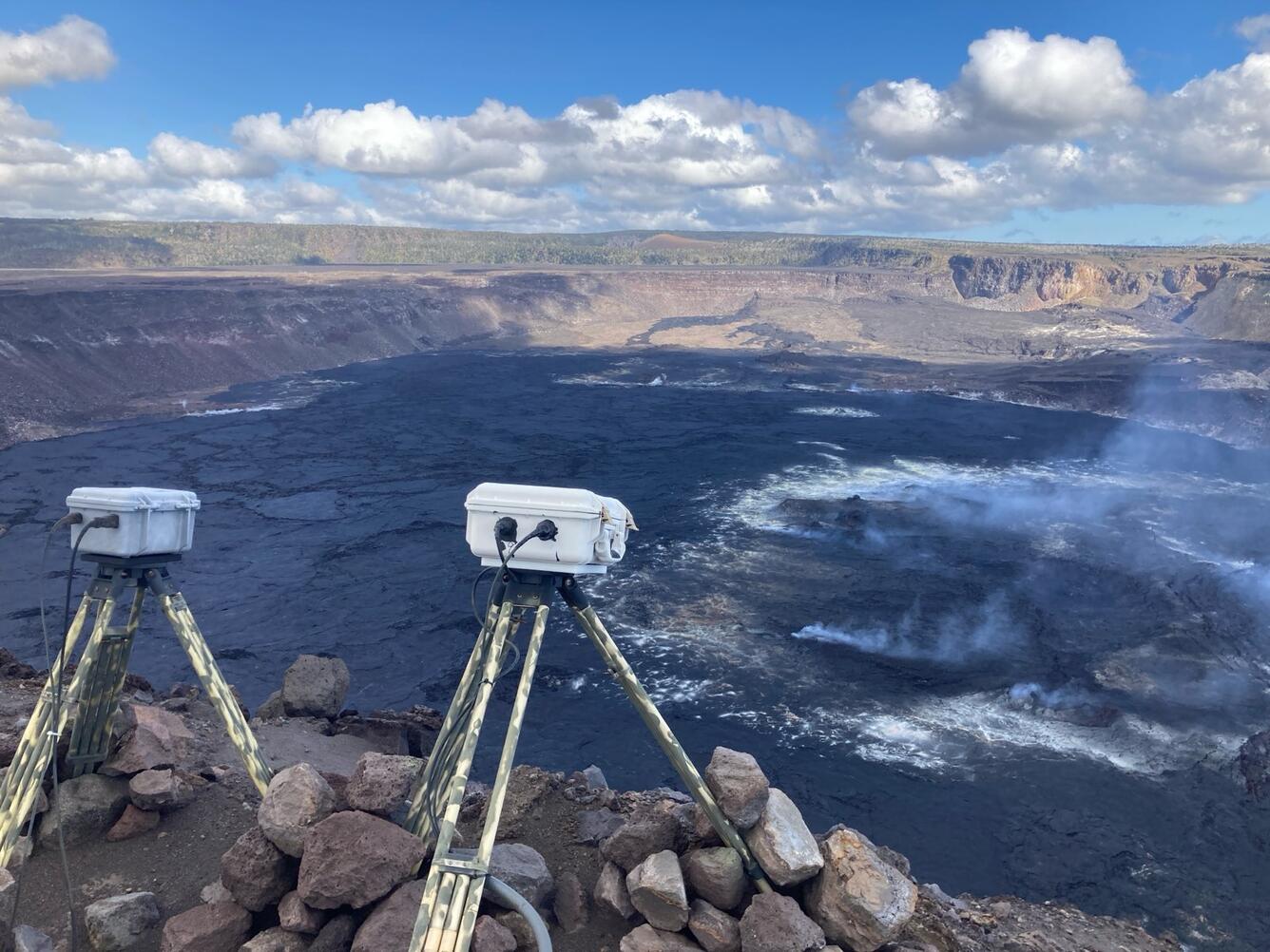
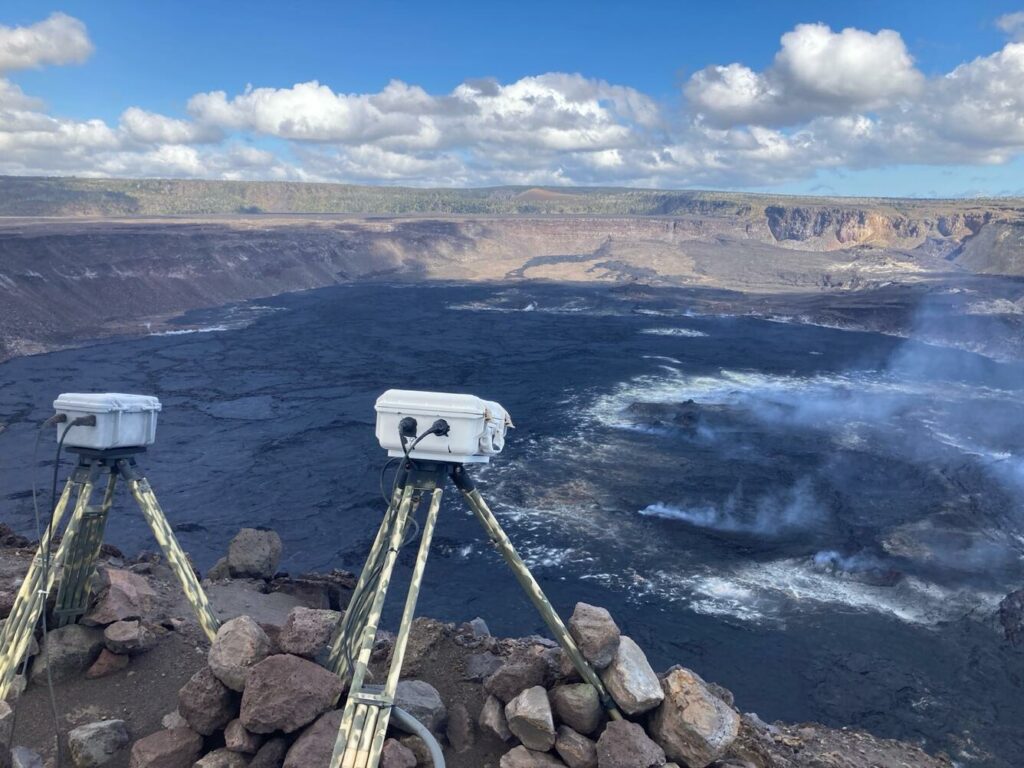
Kīlauea is not erupting. The ongoing seismic swarm continues with most earthquakes occurring beneath the Koaʻe fault zone 5-8 miles (8-12 km) southwest of Kīlauea caldera. There have been roughly 15-20 earthquakes per hour in this region for most of the day. There continue to be a few scattered earthquakes within Kīlauea caldera, but no significant clusters of activity.
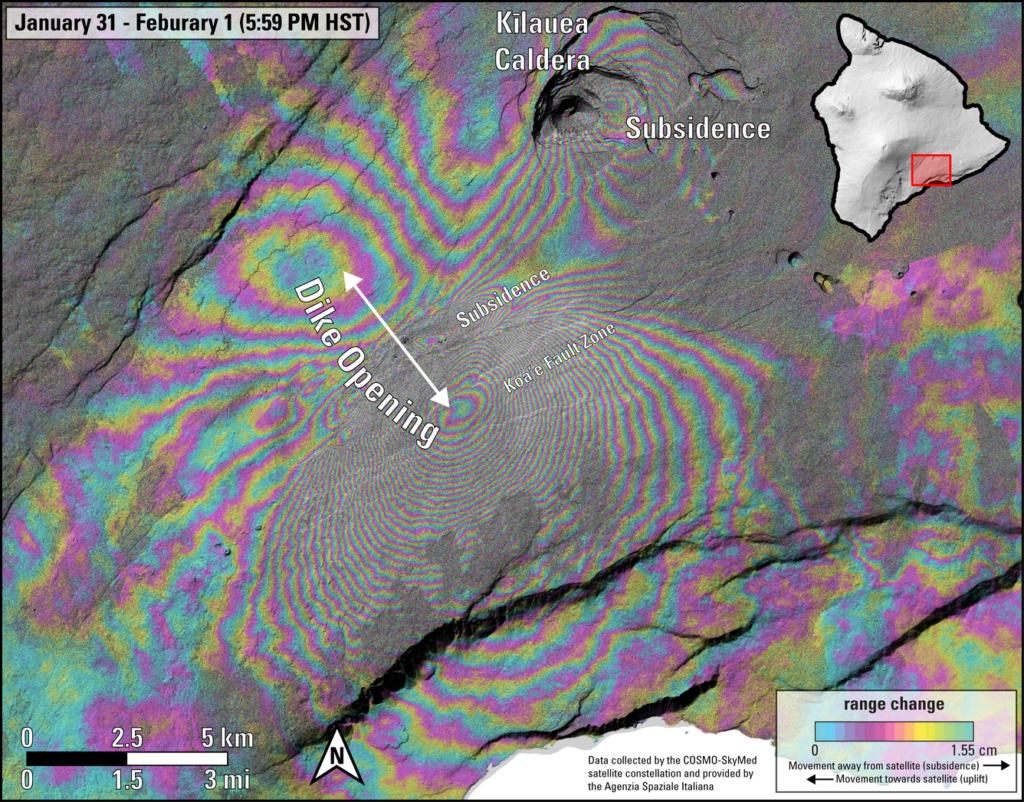
This image shows ground deformation during the recent intrusive activity at Kīlauea volcano. Unlike previous shared interferograms, note that this one is isolated to a one-day timeframe from 6 p.m. HST on January 31 through 6 p.m. HST on February 1, 2024. It therefore highlights the volcanic signals, with reduced interference from sources of data noise. Colored fringes denote areas of ground deformation, with more fringes indicating more deformation. Each color cycle represents 1.5 cm (0.6 in) of ground motion toward or away from the satellite (the direction of motion depends on the sense of color change). The complex patterns indicate overall deflation of the summit area as magma moved underground to the southwest, where the patterns show uplift (up to about 50 centimeters, or 20 inches) and spreading (along with subsidence) due to intrusion of a dike (a vertical sheet of magma). Comparing this to the previous image, which was posted earlier today and that spanned up until January 31 at 6 PM, shows that the dike intrusion moved farther to the SW, consistent with patterns of seismicity. Data are from the COSMO-SkyMed constellation of radar satellites, provided by the Italian Space Agency (Agenzia Spaziale Italiana) through the Hawaiʻi Supersite.
Tiltmeters at Sand Hill and Uēkahuna bluff continue to show ground motion at consistent directions and rates, suggesting that the summit region is deflating as magma moves from this region to the southwest.
A significant amount of lava has been intruded south and southwest of Kīlauea caldera since Saturday, January 27th, 2024. Models suggest an accumulation of as much as 40 million cubic yards (30 million cubic meters) in the region to the southwest of the caldera during this event. As long as the intrusion continues, there is a chance that an eruption could occur within or southwest of the caldera with little advanced warning.
Upgrades to the network may continue to cause intermittent outages that are affecting public access to monitoring data. HVO maintains internal access to volcano monitoring data and will continue to report on volcanic activity. We apologize for any inconvenience during this dynamic time.
Kīlauea volcano alert level and aviation color code remain at WATCH/ORANGE as the situation remains dynamic. HVO will continue to issue daily Kīlauea updates; additional notices will be issued as activity warrants.
Source : HVO
Photos : COSMO-SkyMed , USGS/ M. Patrick.
Colombia , Chiles / Cerro Negro :
Weekly activity bulletin of the Chiles and Cerro Negro Volcanic Complex (CVCCN)
Regarding the monitoring of the activity of the CHILES AND CERRO NEGRO VOLCANOES, the MINISTRY OF MINES AND ENERGY, through the COLOMBIAN GEOLOGICAL SERVICE (SGC), reports that:
Seismic activity, between January 23 and 29, 2024, showed low levels of occurrence and energy released, similar to those recorded during the previous week. The predominant seismicity continues to be linked to the fracturing of the rocks of the volcanic edifice, although the seismicity linked to the processes associated with the movement of fluids inside the conduits increased during this week.
The seismicity associated with the fracturing of the rocks of the volcanic system was located mainly towards the southern sector of the Chiles volcano, at distances of up to 4 km, depths of up to 6 km from its summit (4,700 m d altitude) and a maximum magnitude of 2.5. None of these earthquakes were reported as felt.
Volcanic deformation processes are maintained, according to recordings from ground-mounted sensors and remote satellite sensors.
The evolution of activity in the CVCCN continues, due to internal processes derived from the complex interaction between the magmatic, hydrothermal system and the geological faults of the area, such that the probability of occurrence of energetic earthquakes that may be felt by residents of the CVCCN area of influence.
Volcanic activity remains on YELLOW ALERT Status: Active volcano with changes in baseline behavior of monitored parameters and other manifestations
Source et photo : SGC
Ecuador , Sangay :
DAILY REPORT ON THE STATE OF THE SANGAY VOLCANO, Friday February 2, 2024.
Information Geophysical Institute – EPN.
Surface activity level: High, Surface trend: No change
Internal activity level: High, Internal trend: No change
Seismicity: From February 1, 2024, 11:00 a.m. to February 2, 2024, 11:00 a.m.:
The number of seismic events recorded at the reference station over the past 24 hours is shown below. The level of seismic activity of the volcano remains high.
Explosion Event (EXP): 126
Precipitation/Lahars:
Rains were recorded in the volcano area without generating mudslides or debris. **In the event of heavy rains, these could remobilize the accumulated materials, generating mud and debris flows which would descend the sides of the volcano and flow into adjacent rivers.**
Emissions/ash column:
Due to weather conditions, no gas or ash emissions were observed using surveillance cameras. No ash emissions were also observed via the GOES-16 satellite system and no reports were received from the VAAC in Washington.
Other monitoring parameters:
The FIRMS satellite system recorded 4 thermal anomalies and the MIROVA-MODIS satellite system recorded 1 thermal anomaly, over the last 24 hours.
Observation:
Since yesterday afternoon, thanks to the camera system, it has been observed that the volcano has remained cloudy most of the time. During the night of yesterday and early today, several descents of incandescent material could be observed between 500 and 1000 meters below the level of the crater. At the time of this report, the volcano is completely cloudy.
Alert level: yellow
Source : IGEPN.
Photo : Eqphos_fotografía
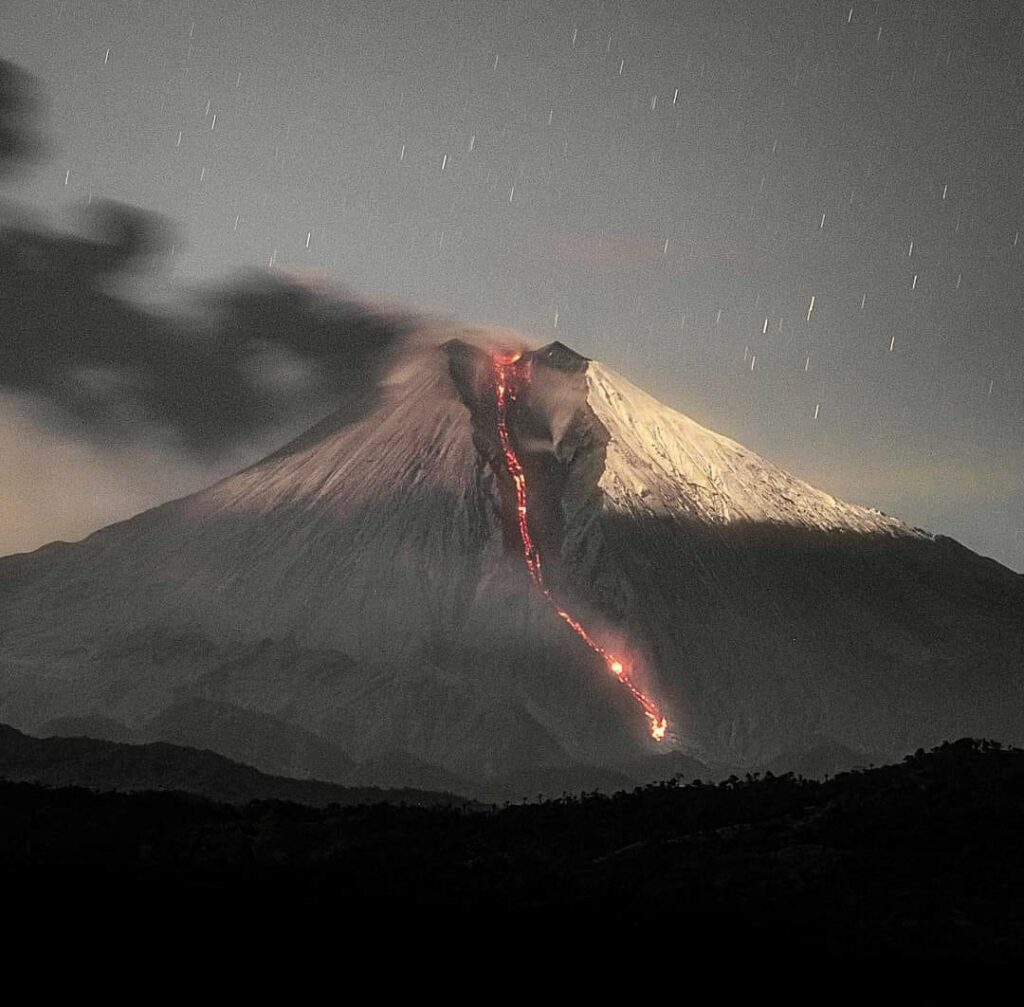
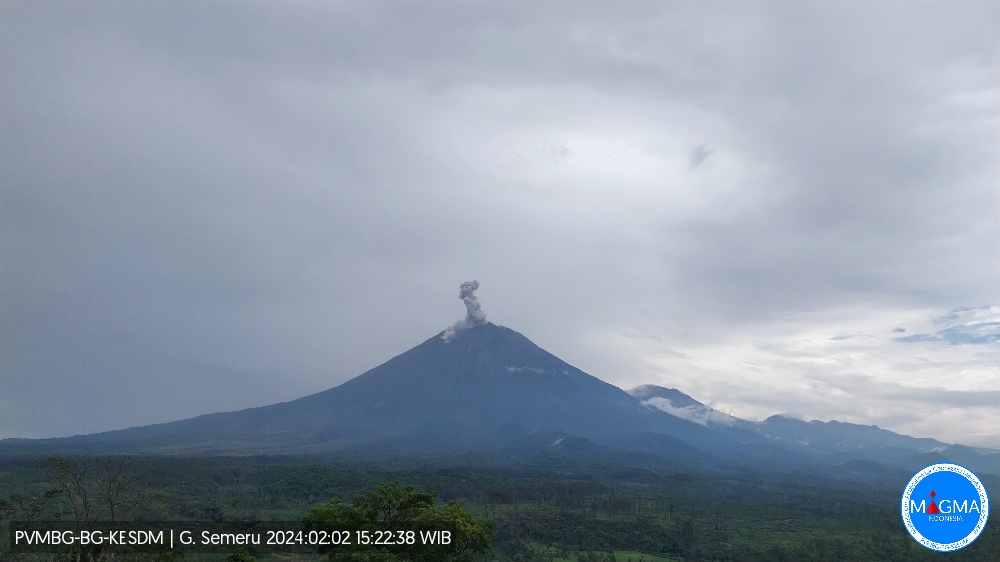
Indonesia , Semeru :
Mount Semeru exhibited an eruption on Friday, February 2, 2024 at 3:21 p.m. WIB with the height of the ash column observed at ± 1300 m above the summit (± 4976 m above sea level). The ash column was gray in color with thick intensity, oriented towards the northeast. This eruption was recorded on a seismograph with a maximum amplitude of 23 mm and a duration of 124 seconds.
SEISMICITY OBSERVATIONS
32 eruption/explosion earthquakes with an amplitude of 10 to 22 mm and a seismic duration of 61 to 165 seconds.
1 lahar earthquake with an amplitude of 24 mm and an earthquake duration of 2330 seconds.
RECOMMENDATION
1. Do not carry out any activities in the South-East sector along Besuk Kobokan, 13 km from the summit (center of the eruption). Apart from this distance, people do not carry out activities within 500 meters of the river bank (river boundary) along Besuk Kobokan as they may be affected by the expansion of warm clouds and lahar flows up to a distance of 17 km from the summit.
2. Do not practice activities within a 5 km radius around the crater/summit of the Mount Semeru volcano as it is subject to the risk of stone projection.
Source et photo : Magma Indonésie.