October 04 , 2023.
Alaska , Shishaldin :
AVO/USGS Volcanic Activity Notice
Current Volcano Alert Level: WATCH
Current Aviation Color Code: ORANGE
Issued: Monday, October 2, 2023, 11:43 PM AKDT
Source: Alaska Volcano Observatory
Notice Number: 2023/A1459
Location: N 54 deg 45 min W 163 deg 58 min
Elevation: 9373 ft (2857 m)
Area: Aleutians
Volcanic Activity Summary:
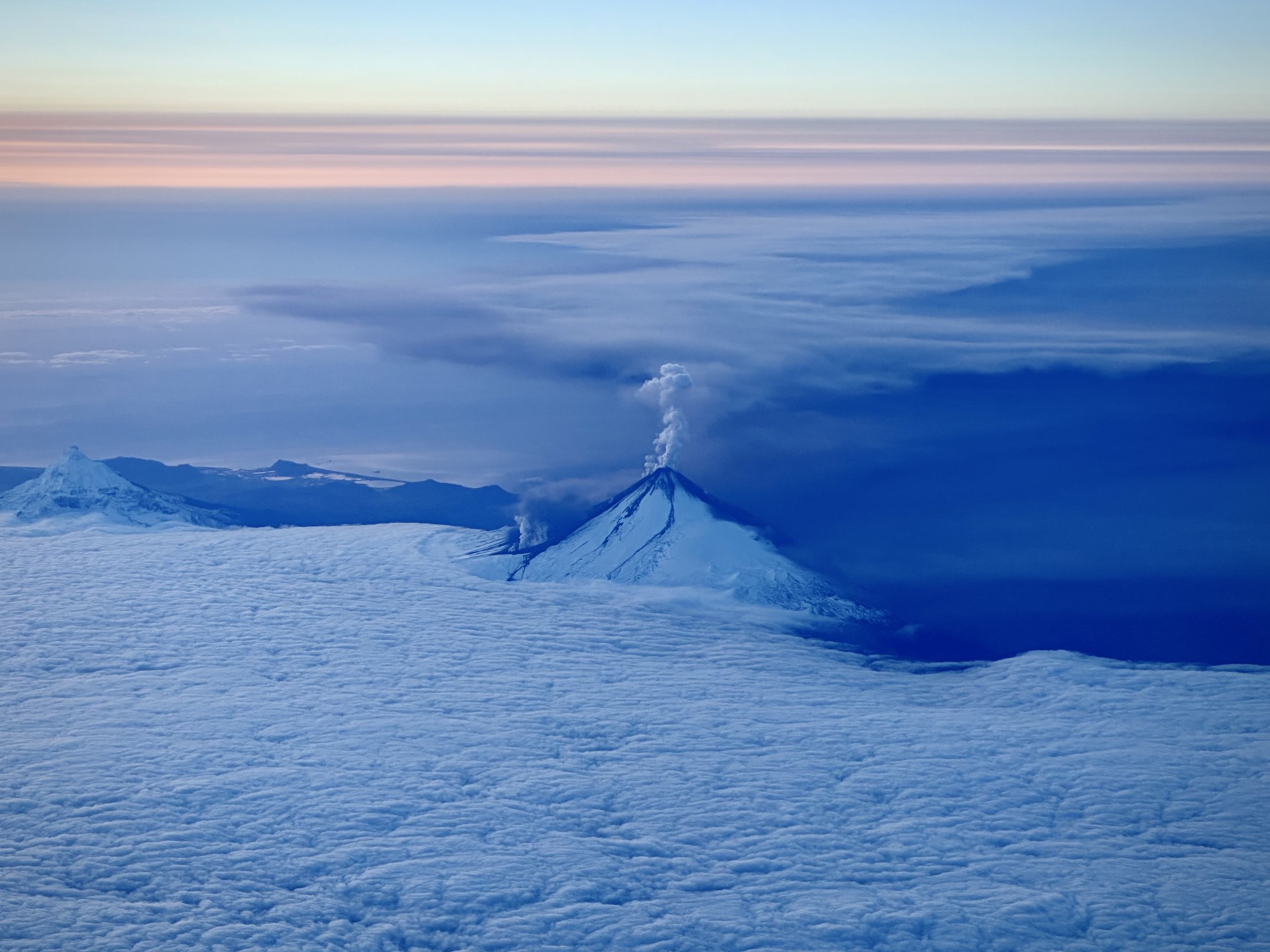
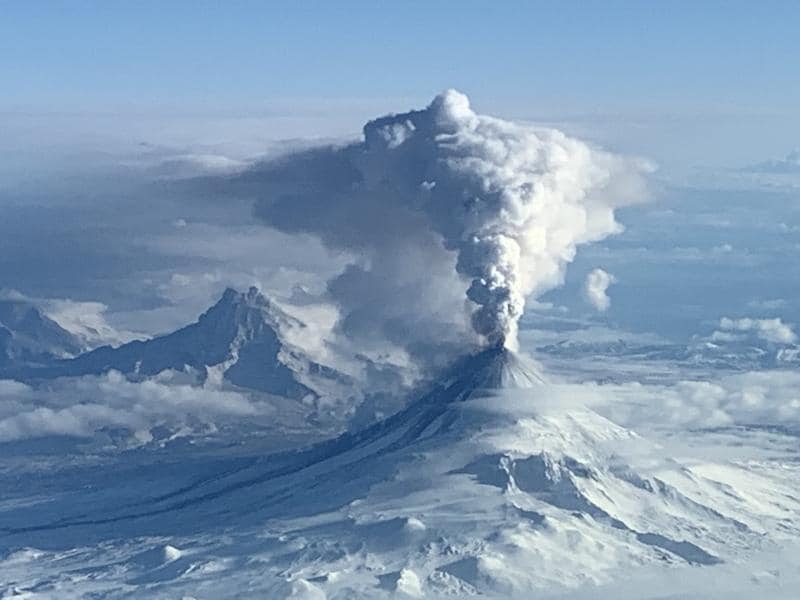
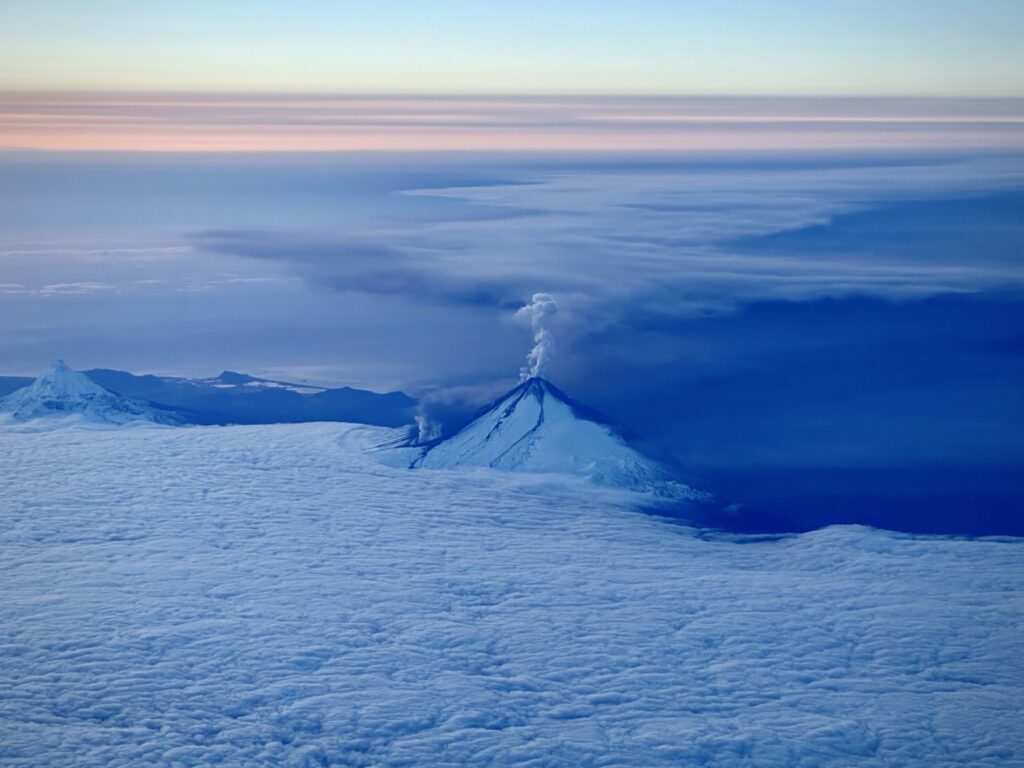
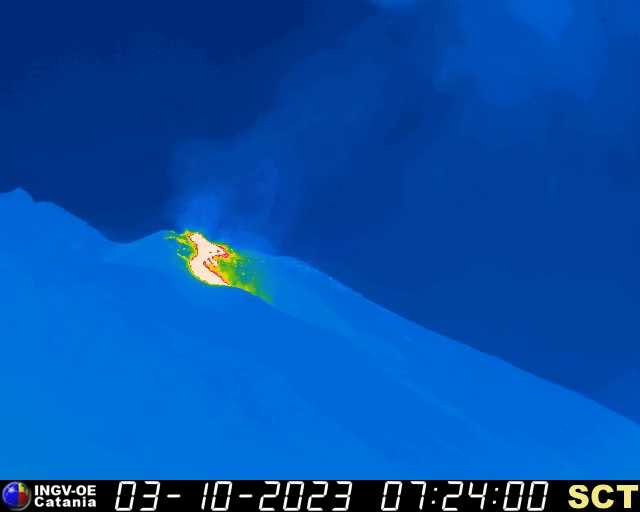
Eruptive activity at Shishaldin has increased in the last 2 hours with lava fountaining observed. Starting at 9:00 pm AKDT (October 3 05:00 UTC) seismic activity at the volcano began to increase significantly. Around the same time, satellite images showed an increase in surface temperature consistent with lava fountaining, which was confirmed in clear web camera images. This fountaining has produced small hot avalanches of rock and lava down the slope of the volcano, and likely is producing minor ash clouds downwind of the volcano but these have not been large enough to detect in satellite images.
Based on previous eruption cycles, more significant ash emissions are likely to occur, however, the time from initial activity to more significant explosions ranges from hours to over a day.
AVO/USGS Volcanic Activity Notice
Current Volcano Alert Level: WARNING
Previous Volcano Alert Level: WATCH
Current Aviation Color Code: RED
Previous Aviation Color Code: ORANGE
Issued: Tuesday, October 3, 2023, 6:12 AM AKDT
Volcanic Activity Summary:
An ash cloud from Shishaldin Volcano reaching 40,000 ft (12 km) above sea level was observed in satellite data at 5:20 am AKDT (13:50 UTC). This follows a several-hour increase in observed eruptive activity, and a recent sharp increase in infrasound, seismicity, and lighting detections. In response, the Aviation Color Code is being raised to RED and the Volcano Alert Level is being raised to WARNING. The National Weather Service has issued a SIGMET for this ash cloud. Based on previous eruption cycles, significant ash emissions are likely to continue for several hours. Pyroclastic and mudflows are likely on the immediate flanks of the volcano.
AVO/USGS Volcanic Activity Notice
Current Volcano Alert Level: WARNING
Current Aviation Color Code: RED
Issued: Tuesday, October 3, 2023, 9:31 AM AKDT
Volcanic Activity Summary:
Ash emissions from Shishaldin Volcano continue since starting this morning at 5:50 AKDT (13:50 UTC), but at a lower level of 20,000 to 25,000 ft asl after an initial height of ~40,000 ft asl. Seismicity and infrasound have diminished but are still above background.
The Aviation Color Code remains at RED and the Volcano Alert Level at WARNING. The National Weather Service has issued a SIGMET for this ash cloud, and a Special Weather Statement has been issued for possible ashfall on Unimak Island and the lower Alaska Peninsula, including False Pass, Cold Bay, and Sand Point.
Source : AVO
Photos : Matt Brekke , Barnes, Chris .
Italy , Stromboli :
WEEKLY BULLETIN, from September 25, 2023 to October 1, 2023 (publication date October 3, 2023)
SUMMARY STATEMENT OF ACTIVITY
In light of the monitoring data, it appears:
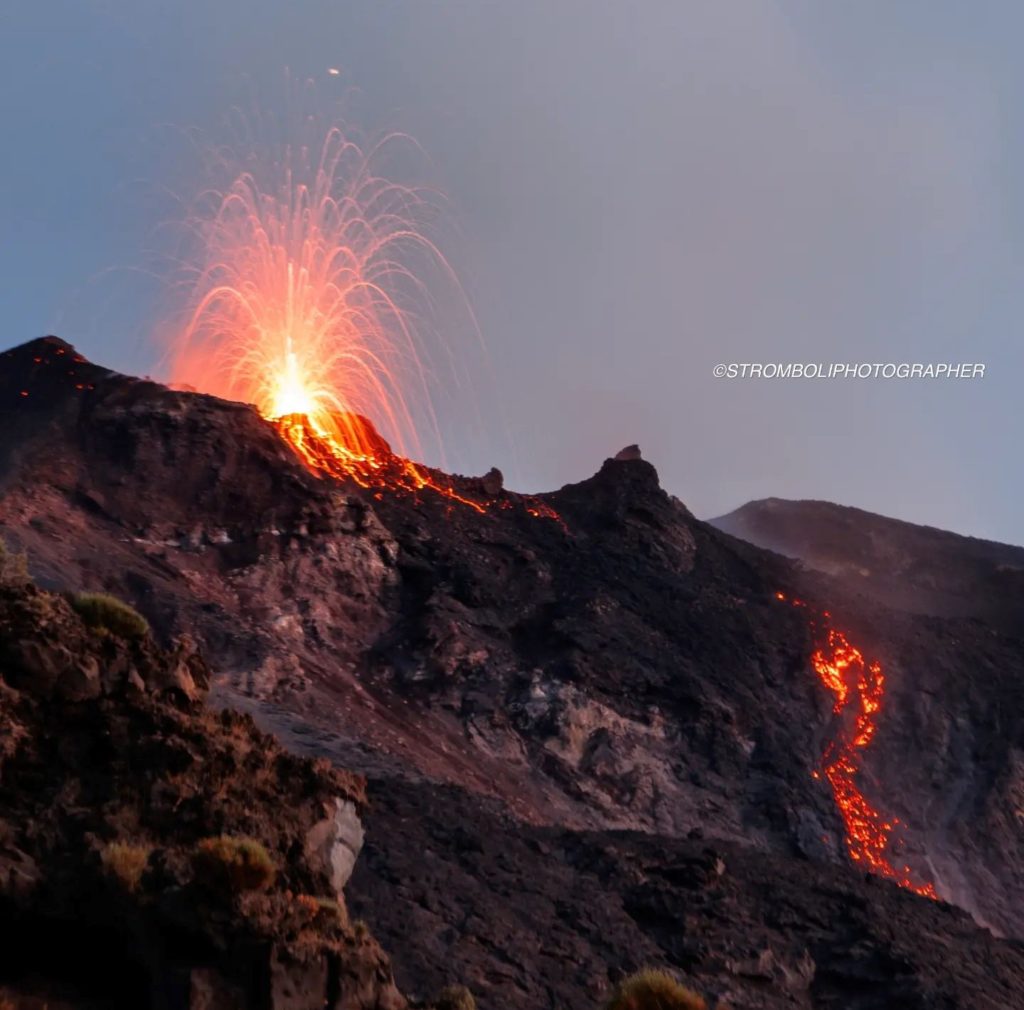
1) VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS: During this period, normal Strombolian activity was observed with splashing activity in the North and South Central crater areas. Additionally, a lava flow was produced from the North Crater area. The total hourly frequency fluctuated between medium values (13 events/h) and high values (20 events/h). The intensity of the explosions varied from low to medium in the North Crater area and high in the South-Central area.
2) SISMOLOGY: The monitored seismological parameters do not show significant variations.
3) GROUND DEFORMATIONS: The island’s ground deformation monitoring networks did not show significant variations during the period considered.
4) GEOCHEMISTRY: SO2 flux at an average level and increasing since August. The CO2 flux in the Pizzo area shows values at medium-high levels.
There are no updates for the C/S ratio.
The isotopic ratio of Helium dissolved in thermal wells shows a further increase, reaching high values.
5) SATELLITE OBSERVATIONS: Thermal activity observed by satellite has generally been at a moderate to high level.
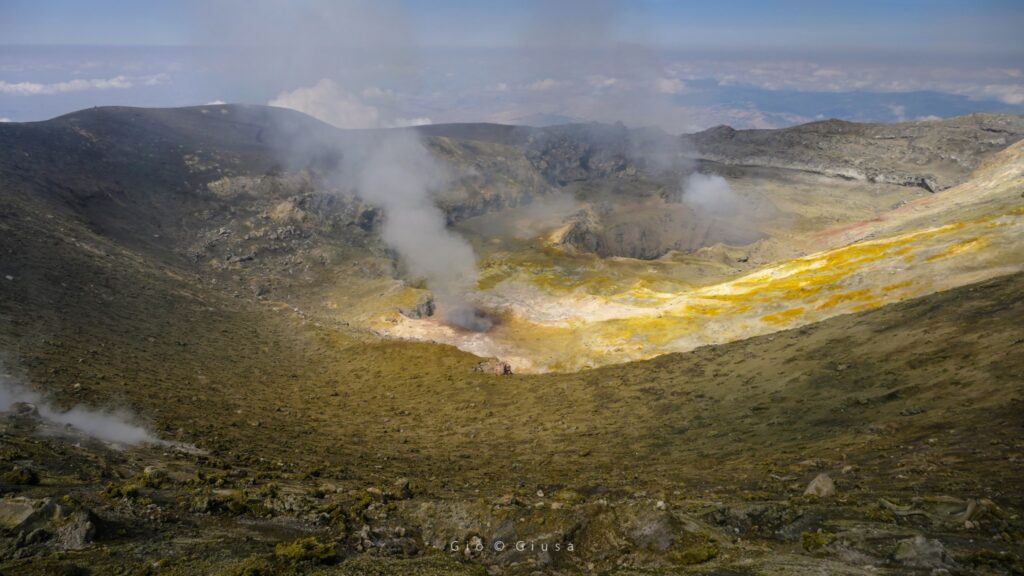
VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS
In the observed period, the eruptive activity of Stromboli was characterized through the analysis of images recorded by the INGV-OE surveillance cameras at altitude 190m (SCT-SCV), from
Pizzo and Punta dei Corvi. The explosive activity was mainly produced by 3 (three) eruptive vents located in the North area of the crater and by 3 (three) vents located in the South Central area.
In the area of the North crater (N), with two vents located in sector N1 and one in sector N2, explosive activity of varying intensity from low (less than 80 m high) to medium (less than 150 m high). top) was observed. The products emitted in the eruption were mainly coarse materials (bombs and lapilli) sometimes mixed with fine materials (ashes). In addition, continuous projection activity was observed in sector N1 which was intense on September 27 and 28 coinciding with the emission of the lava flow. The average frequency of explosions oscillated between 7 and 13 events/h.
In the South-Central (CS) zone, sectors S1 and C did not show significant activity while sector S2, with three active chimneys also active at the same time, mainly showed high intensity explosive activity ( more than 150 m in height). ) emitting coarse material widely distributed along the outer slopes of the crater terrace. Additionally, intense splashing activity was observed on September 26. The average frequency of explosions fluctuated between 6 and 8 events/h.
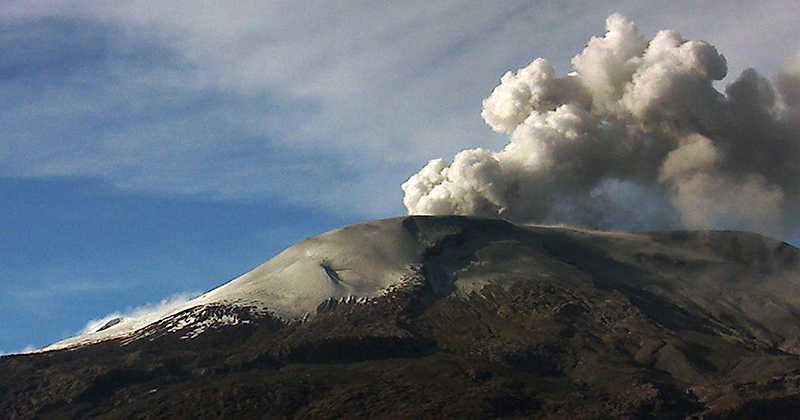
Press release on Stromboli activity, October 3, 2023, 09:00 (07:00 UTC).
The National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology, Osservatorio Etneo, communicates that from approximately 06:33 UTC, a lava overflow fueled by the splashing activity present in the North Crater area is visible. For the moment, the overflow remains confined to the upper part of the Sciara del Fuoco.
From a seismic point of view, during the last 24 hours the average amplitude of the volcanic tremor has fluctuated between medium and high values and is currently at a high level. Furthermore, no significant changes were reported in the frequency of occurrence and amplitude of explosion earthquakes.
The deformation data from the inclinometer and GNSS networks do not highlight any significant associated variations.
Further updates will be communicated shortly.
Source : INGV
Photos : stromboli stati d’animo / Sebastiano Cannavo , INGV.
Italy / Sicily , Etna :
WEEKLY BULLETIN, from September 25, 2023 to October 1, 2023 (publication date October 3, 2023)
SUMMARY STATEMENT OF ACTIVITY
In light of the monitoring data, it appears:
1) VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS: Degassing activity at the summit craters, particularly at the Bocca Nuova crater (BN) and the South-East crater (CSE).
2) SEISMOLOGY: Very low seismic activity due to fracturing; average amplitude of the volcanic tremor at the intermediate level.
3) INFRASOUND: Moderate infrasound activity, increasing compared to the previous week.
4) GROUND DEFORMATIONS: Over the past week, ground deformation monitoring networks have recorded a slight upward trend in areal expansion.
5) GEOCHEMISTRY: Medium-level SO2 flux.
The soil CO2 flux presents average values.
The partial pressure of CO2 dissolved in groundwater presents values included in seasonal variability.
There is no update on the helium isotope ratio.
6) SATELLITE OBSERVATIONS: Thermal activity observed by satellite was generally weak.
7) OTHER OBSERVATIONS: Inspections were carried out in the summit area with RTKs and thermal drones to update the CSE topography and monitor craters.
VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS
During the week, the monitoring of the volcanic activity of Etna was carried out through the analysis of images from the surveillance cameras of the INGV, Etneo Observatory (INGV-OE) and through various inspections in the summit area carried out by INGV OE staff. The week was characterized by degassing activity from the Bocca Nuova crater (BN) and the Southeast crater (CSE).
During the week under review, numerous inspections were carried out with drones equipped with visible and thermal sensors in collaboration with T. R. Walter and Benjamin De Jarret (GFZ Potsdam). The various inspections and analysis of images from INGV-OE surveillance cameras have highlighted that the activity at the summit craters remains unchanged compared to what was described in the previous bulletin (Rep. N. 39/ 2023 ETNA).
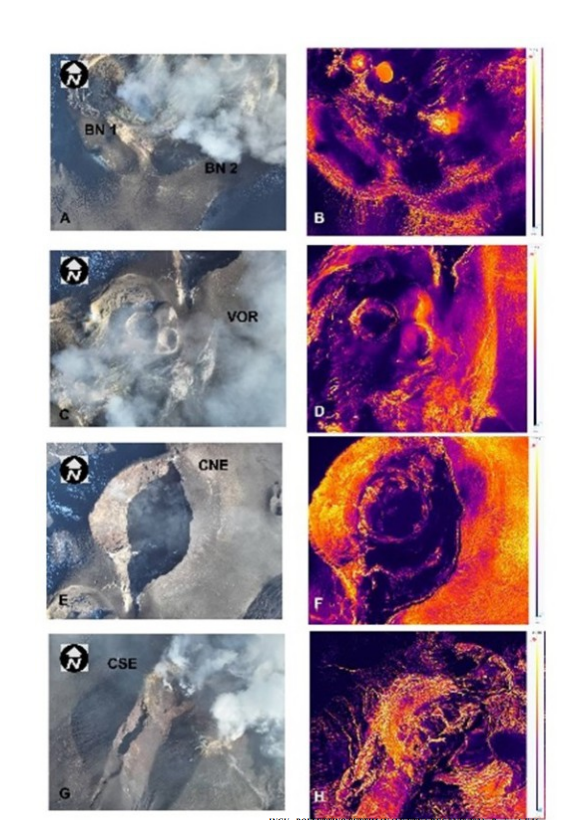
Visible and thermal images of the summit craters taken by drone on September 29, 2023
Figure 3.2 shows the most significant images obtained during the flybys. The BN crater presents intense degassing, almost continuous at the BN-1 vent and pulsating at the BN-2 vent (Fig.3.2). The CSE shows degassing activity in the summit zone and the fracture present on its southwest flank (Fig.3.2). Finally, the North-East Crater (CNE) and the Voragine crater (VOR) still remain obstructed and present weak fumarolic activity.
Source : INGV.
Photos : Gio Giusa , INGV.
Indonesia , Inielika :
PRESS RELEASE on increasing activity levels of G. Inielika, October 4, 2023.
Mount Inielika is administratively located in Ngada Regency, East Nusa Tenggara. Geographically, it is located at 8.73° South latitude and 120.98° East longitude with a maximum height of 1559 meters above sea level. Mount Inielika is monitored visually and instrumentally from the monitoring station. volcano observation (PPGA) located in Ngelapadhi hamlet, East Nusa Tenggara. The activity level of Mount Inielika has been level I (normal) since 2001.
Volcanic activity at Mount Inielika in 2023 is generally dominated by low-frequency earthquakes and deep volcanic earthquakes that fluctuate at low levels. The daily occurrence of deep volcanic earthquakes is only 0-1 times per day. Smoke coming from the crater was not observed. The latest developments in Mount Inielika activities until October 4, 2023 08:00 WIB are as follows:
- There has been an increase in seismicity, particularly deep volcanic (VA) earthquakes since September 29, 2023. The average occurrence of VA earthquakes has increased to 9 per day. On October 1, 2023, 17 deep volcanic earthquakes were recorded with a maximum amplitude of 50 mm and a maximum duration of 30 seconds. On October 3, 2023, VA earthquakes increased again to reach 18 incidents. This shows that there is an increase in pressure under the body of Mount Inielika, which can trigger shallow earthquakes and phreatic eruptions.
Monitoring of the temperature and concentration of CO2, SO2, CO and H2S gases on October 2, 2023 in 4 (four) hot springs showed a significant decrease compared to measurements in July 2023. This is believed to be due to the formation of a hydrothermal blanket caused by fluid circulation activity in the shallow hydrothermal system which releases mineral deposits, causing a decrease in permeability levels and an increase in pressure in the body of Mount Inielika.
- The potential danger linked to the increase in VA type earthquakes is the appearance of phreatic eruptions and the release of gases dangerous to health in high concentrations.
Based on visual and instrumental monitoring, the Geological Agency declared that the activity level of Mount Inielika was increased from level I (normal) to level II (WASPADA) from October 4, 2023 at 10:00 a.m. WIT .
Source : PVMBG
Photo : http://www.amazonie.ch/
Colombia , Nevado del Ruiz :
Weekly bulletin on the activity of the Nevado del Ruiz volcano
From the monitoring of the activity of the NEVADO DEL RUIZ VOLCANO, the MINISTRY OF MINES AND ENERGY through the COLOMBIAN GEOLOGICAL SERVICE (SGC) reports that:
In the week of September 26 to October 2, 2023, the volcano continued to exhibit instability in its behavior, with low to moderate activity levels. Compared to the previous week, the main variations in the parameters monitored were:
– Seismic activity associated with the fracturing of rocks within the volcanic edifice showed a significant increase in the number of earthquakes recorded and the seismic energy released. This increase was recorded from September 28 to 29 in the South to South-South-East sector of the volcanic structure, between 1 and 4 km from the Arenas crater and at depths between 2 and 5 km. The seismic events at 05:12 (magnitude 3.5) and 06:14 stand out. (magnitude 3.8) on September 28, which were reported to be felt by residents in the volcano’s area of influence. It is important to mention that on other days of the week this type of seismic activity maintained low levels.
– Seismicity related to fluid dynamics within volcanic conduits showed similar levels in the number of earthquakes recorded and a decrease in seismic energy released. Overall, the seismic signals showed low to slightly moderate energy levels. Some of these signals were associated with pulsatile emissions of ash and gas into the atmosphere or changes in the relative temperature of the emitted material. Both phenomena were confirmed by conventional or thermographic cameras used to monitor the volcano.
– At the volcano, the emission of water vapor and gases into the atmosphere continued with low rates of sulfur dioxide (SO2) outgassing which showed a slight increase in recent days. The maximum height of the gas and ash column was 1,400 m vertically and 2,000 m dispersed; these values were measured at the summit of the volcano on September 30. The direction of dispersion of the column varied between the North-West to West flank and the South-West flank. On Saturday, September 30, ash fell in areas near the volcano and in the town of Manizales.
– Several satellite monitoring platforms have reported thermal anomalies detected at the bottom of the crater. These were low to moderate energy levels.
Source et photo : SGC