July 03 , 2023.
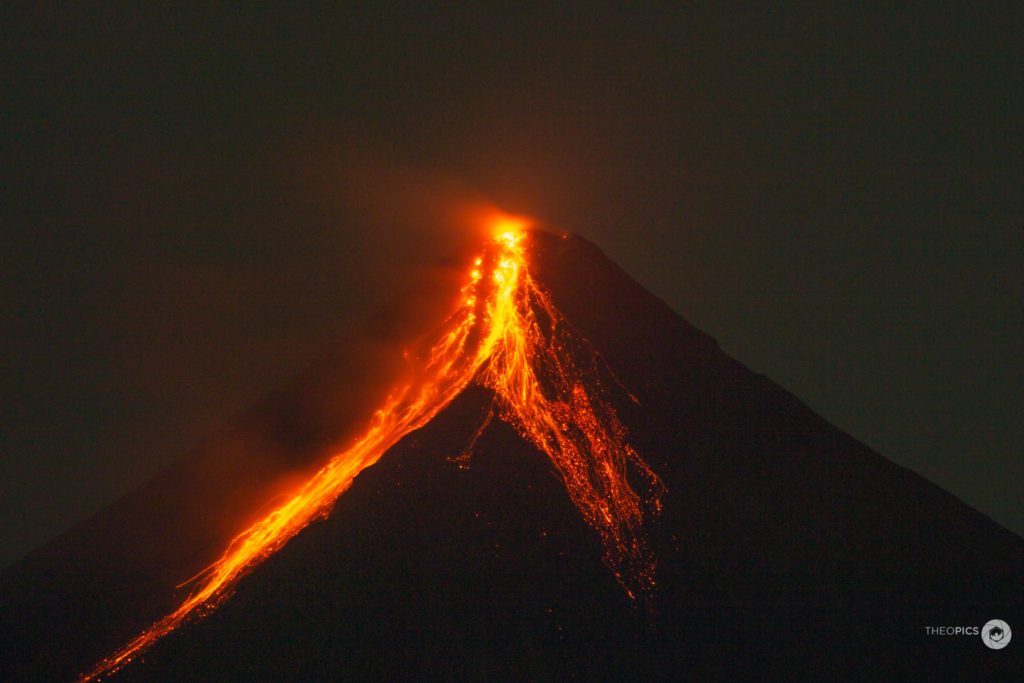
La Réunion , Piton de la Fournaise :
Press release from the Institute of Earth Physics in Paris, Volcanological Observatory of Piton de la Fournaise. July 02, 2023 – 2:00 p.m. – 10:00 a.m. UTC.
Ongoing eruption
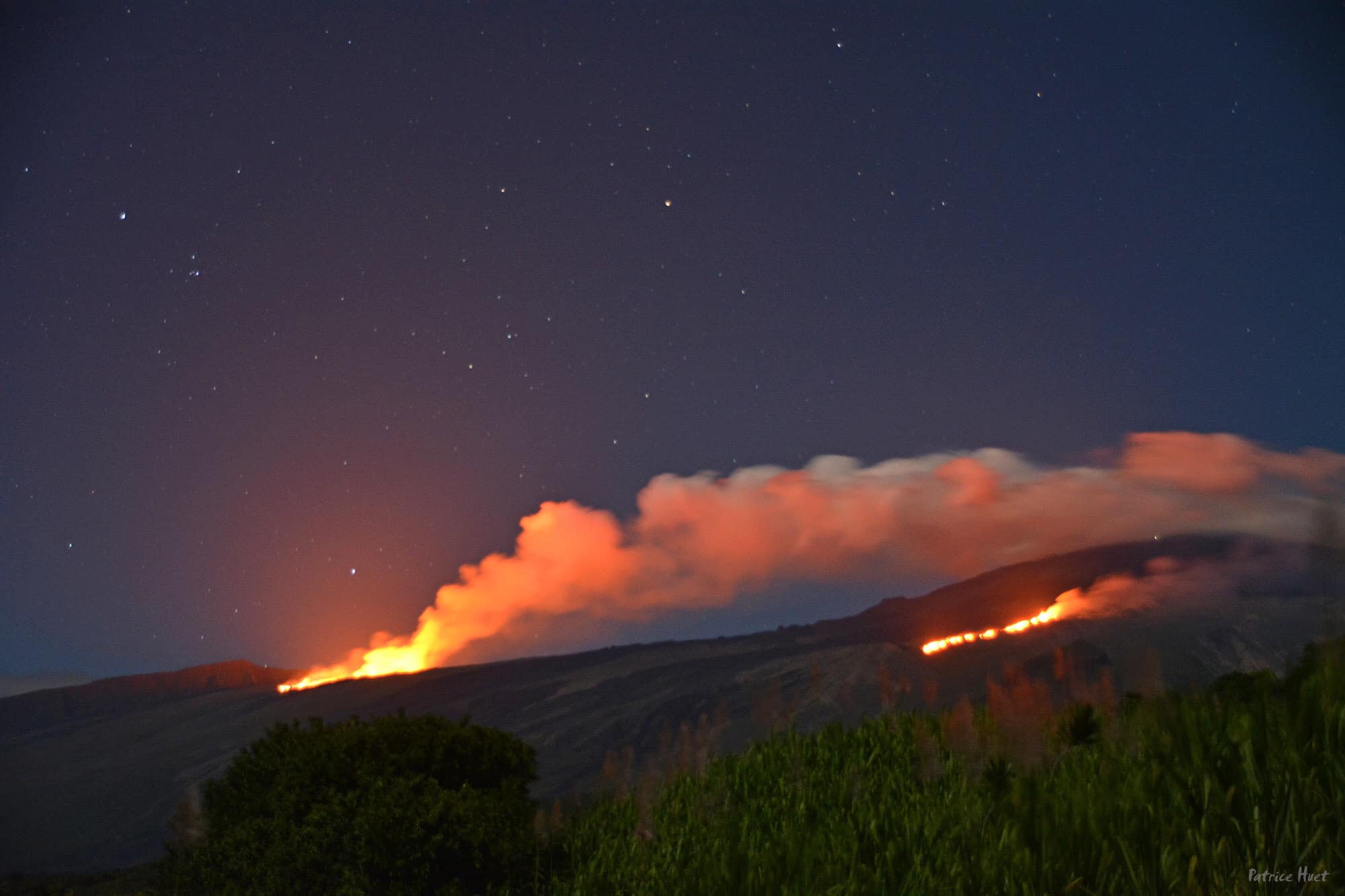
The eruption started today, July 02, 2023, around 08:30 local time continues.
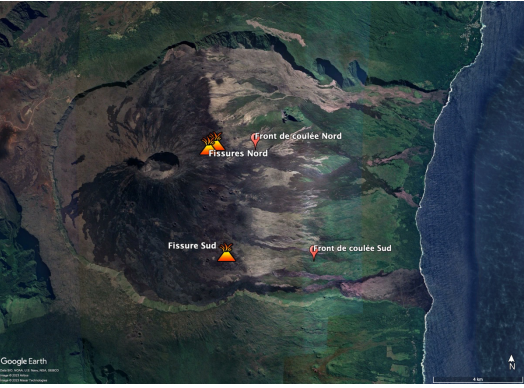
The data from the volcanological observatory, confirmed by an overflight of the SAG, made it possible to locate the eruptive fissure on the eastern flank of the volcano at around 2000 m altitude north of Piton Vouvoul (eruption of April 2020).
After a sharp drop in the intensity of the tremor (indicator of an emission of lava and gas on the surface) and the observation of a residual tremor between 11:45 a.m. (7:45 a.m. UTC) and 12:30 p.m. (8:30 a.m.) – period during which no more surface activity was visible – the tremor is again on the rise with a localized source at lower altitude, around 1500 m altitude.
This increase and this location of the tremor suggests the opening of a second eruptive fissure at the top of the Grandes Pentes. But no visual confirmation could be made at the moment.
Since the beginning of the eruption, strong seismic activity is still recorded. Thus, 466 superficial volcano-tectonic earthquakes under the summit and 30 deep volcano-tectonic earthquakes under the eastern flank were recorded between 9 a.m. and 1 p.m. local time. This seismic activity is accompanied by the observation of numerous long-period type signals testifying to a magmatic circulation still active at depth.
Given this strong seismicity, especially under the eastern flank of the volcano, it is not excluded that other eruptive cracks will open, especially at lower altitudes.
Alert level: Alert 2-1 (eruption in the Enclos without any particular threat to the safety of people, property or the environment).
Press release from the Institute of Earth Physics in Paris, Volcanological Observatory of Piton de la Fournaise. July 02, 2023 – 6:20 p.m. – 2:20 p.m. UTC.
Eruption in progress – new eruptive fissure
The eruption started today, July 02, 2023, around 08:30 local time continues.
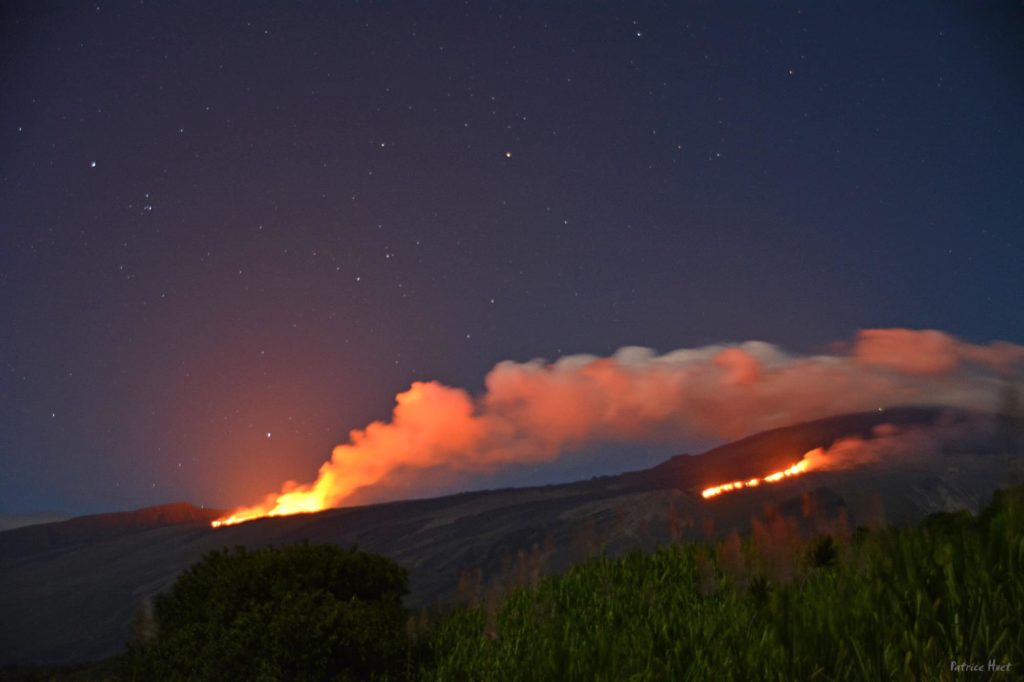
Around 5:50 p.m., a new crack opened on the southeast flank of the volcano inside the Enclos Fouqué. Currently two eruptive sites are active, one at 2000 m altitude on the eastern flank and the other on the south-eastern flank on the heights of the Grandes Pentes.
Even if the eruptive flows on the surface remain low (<5m3/sec), the activity at depth is maintained. Since the beginning of the eruption, strong seismic activity is still recorded. Thus, 1156 superficial volcano-tectonic earthquakes under the summit and 38 deep volcano-tectonic earthquakes under the eastern flank were recorded between 9 a.m. and 6 p.m. local time. This seismic activity is accompanied by the observation of numerous long-period type signals testifying to a magmatic circulation still active at depth.
Given this strong seismicity, especially under the eastern flank of the volcano, it is not excluded that other eruptive cracks will open, especially at lower altitudes, and/or outside the Enclos .
Increased vigilance is required in the sectors bordering the North and South Enclos . Indeed, given the high probability of the emission of degassed magma, it could be that the OVPF stations located in the sector do not record a volcanic tremor if a crack were to open at low altitude. and/or outside the Enclos .
Alert level: Alert 2-1 (eruption in the Enclos without any particular threat to the safety of people, property or the environment).
Press release from the Institute of Earth Physics in Paris, Volcanological Observatory of Piton de la Fournaise. July 03, 2023 – 04:30 – 00:30 UTC.
Eruption in progress.
The eruption started on 02/07/2023, around 08:30 local time continues. Following the opening of a crack on the southeast flank of the volcano (inside the Enclos ) yesterday around 5:50 p.m., a slight increase in the amplitude of the tremor was observed until 8 p.m. local time ( 4:00 p.m. UTC) yesterday, followed by a stabilization and then a slight decline since around 02:30 local time (22:30 UTC).
The two eruptive sites, one at 2000 m altitude on the eastern flank and the other on the south-eastern flank on the heights of the Grandes Pentes are still active.
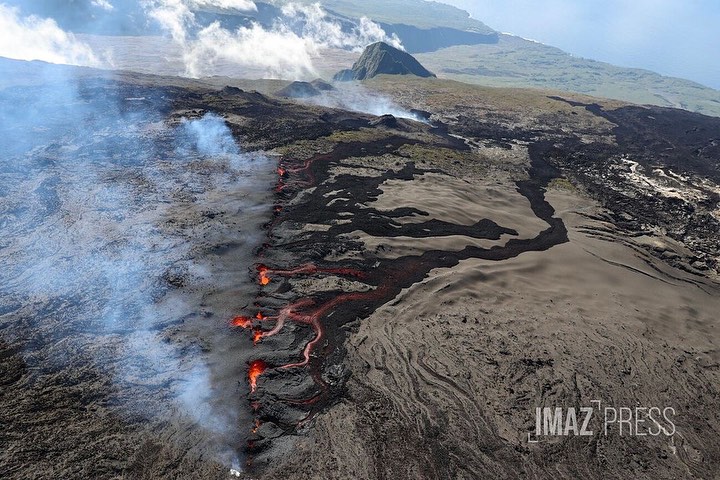
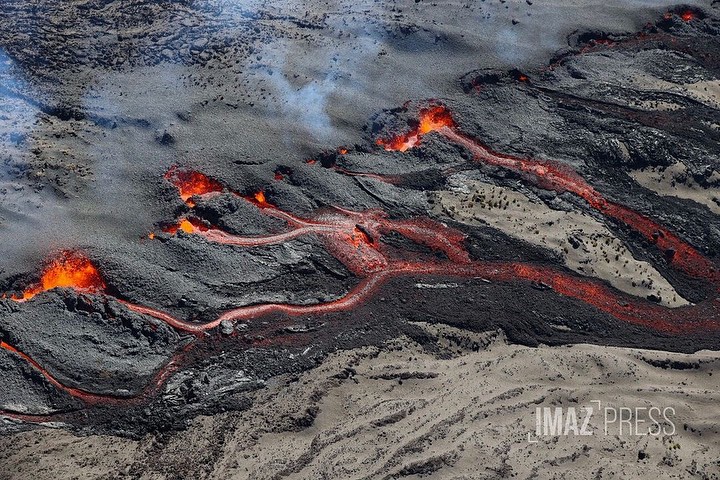
Currently the most active eruptive site in the South East with a lava flow that is spreading in the Grandes Pentes.
If conditions allow, an aerial reconnaissance of the OVPF-IPGP is planned this morning on the ground in particular to refine the position of the fronts of the flows.
Lava flow estimates established by satellite method on the HOTVOLC platform (OPGC – Clermont Auvergne University) indicate an average flow of around 12 m3/s (fluctuation between 7 and 27 m3/s). These flows estimated by satellite method from thermal radiance data include the two eruptive sites.
Deep activity still continues. Since the beginning of the eruption, strong seismic activity is still recorded. Thus, 1367 superficial volcano-tectonic earthquakes under the summit and 38 deep volcano-tectonic earthquakes under the eastern flank have been recorded since the start of the eruption. This seismic activity is accompanied by the observation of long-period type signals testifying to a magmatic circulation still active at depth.
Given the persistence of strong seismicity, especially under the eastern flank of the volcano, it is not excluded that other eruptive cracks will open, especially at lower altitudes, and/or outside the Enclos .
Increased vigilance is required in the sectors bordering the North and South Enclosure. Indeed, given the high probability of the emission of degassed magma, it could be that the OVPF stations located in the sector do not record a volcanic tremor if a crack were to open at low altitude. and/or outside the Enclos .
Alert level: Alert 2-1 (eruption in the Enclos without any particular threat to the safety of people, property or the environment)
Source : OVPF
Photos : IMAZ Press, Cité du volcan.
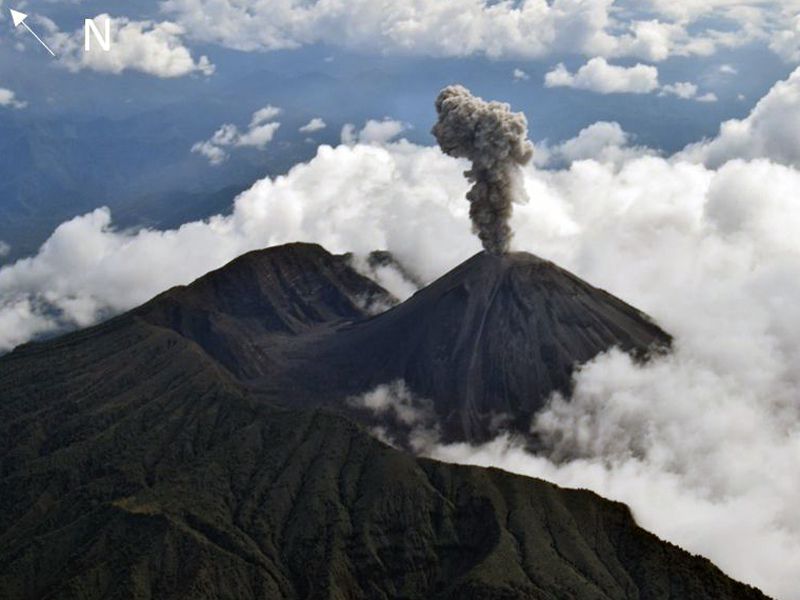
Philippines , Mayon :
MAYON VOLCANO BULLETIN 03 July 2023 8:00 AM
In the past 24-hour period, very slow effusion of lava from the summit crater of Mayon Volcano continued to feed lava flows and collapse debris on the Mi-isi (south) and Bonga (southeastern) gullies as well as rockfall and PDCs on these and the Basud (eastern) Gullies. The lava flows have advanced to approximate lengths of two thousand seven hundred (2700) meters and one thousand three hundred (1300) meters along Mi-isi and Bonga gullies, respectively, from the summit crater while collapse debris have deposited to four thousand (4000) meters from the crater. Two (2) dome-collapse pyroclastic density currents (PDC) that lasted two (2) minutes, two (2) lava front collapse pyroclastic density currents (PDC) that generated 200 meters high light-brown plume, two hundred ninety-five (295) rockfall events, and three (3) volcanic earthquakes were recorded by the Mayon Volcano Network.
Continuous moderate degassing from the summit crater produced steam-laden plumes that rose 500 meters before drifting to the west and west-northwest direction. Sulfur dioxide (SO2) emission averaged 962 tonnes/day on 02 July 2023. Short-term observations from EDM and electronic tiltmeter monitoring show the upper slopes to be inflating since February 2023. Longer-term ground deformation parameters based on EDM, precise leveling, continuous GPS, and electronic tilt monitoring indicate that Mayon is still inflated, especially on the northwest and southeast.
Alert Level 3 is maintained over Mayon Volcano, which means that it is currently in a relatively high level of unrest as magma is at the crater and hazardous eruption within weeks or even days is possible.
Source : Phivolcs
Photo : Teopics
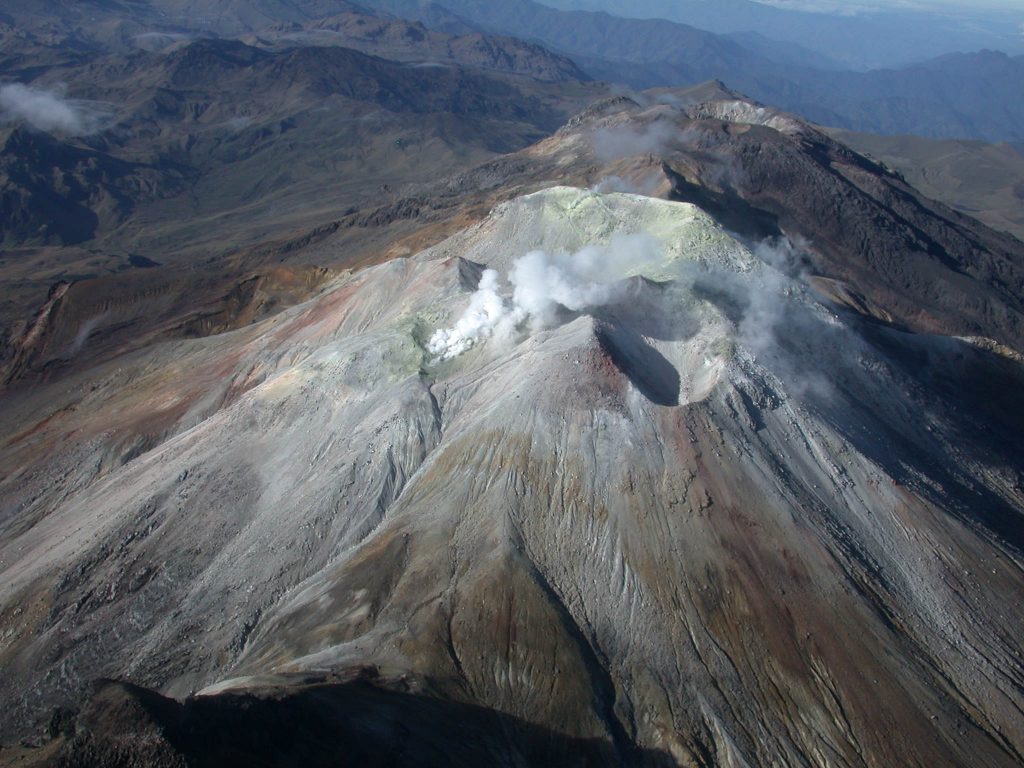
Colombia , Cumbal :
Cumbal Volcanic Complex Weekly Activity Bulletin
Regarding the monitoring of the activity of the CUMBAL VOLCANIC COMPLEX (CVC), the MINISTRY OF MINES AND ENERGY through the COLOMBIAN GEOLOGICAL SERVICE (SGC) informs that:
For the period between June 20 and 26, 2023, a slight increase in seismic activity was observed compared to the previous week, both in occurrence and in energy released. The predominant seismic events were mainly associated with the fracture of the rock inside the volcanic edifice, some of them being located towards the northern sector of the volcanic complex with shallow depths and a maximum local magnitude of 0, 5.
There were records of gas emissions from the « El Verde » fumarolic field located northeast of the volcanic complex and the « Rastrojos » and « Boca Vieja » fumarolic fields southwest of the Complex, with white columns that disperse following the direction of the wind.
No significant variation was observed in the other geophysical parameters of volcanic monitoring.
The activity level of the volcano remains at the YELLOW LEVEL ■ (III): CHANGES IN THE BEHAVIOR OF VOLCANIC ACTIVITY
Source et photo : SGC
Ecuador , Reventador :
DAILY REPORT OF THE STATE OF THE REVENTADOR VOLCANO, Sunday July 02, 2023.
Information Geophysical Institute – EPN.
Surface Activity Level: High, Surface Trend: Unchanged
Internal activity level: Moderate, Internal trend: No change
Seismicity: From June 24, 2023, 11:00 a.m. to June 25, 2023, 11:00 a.m.:
The following table shows the number of seismic events from the reference station over the past 24 hours.
Explosion(EXP):19
Long Period (LP):27
Transmit Tremor (TREM):9
Rains / Lahars:
There is no rain report. “In the event of heavy rains, these could remobilize the accumulated materials, generating mudslides and debris that would descend the flanks of the volcano and pour into the adjacent rivers.
Emission / Ash Column:
Yesterday afternoon and today several emissions of gas and ash were observed with heights of 400 and 500 meters above the level of the crater in a northeast and northwest direction.
Other Monitoring Parameters:
There have been no thermal alerts on the satellite systems in the past 24 hours.
Observation:
During the night, an incandescence was observed at the level of the crater.
Alert level: Orange.
Source : IGEPN.
Photo : F-Naranjo , GVP.
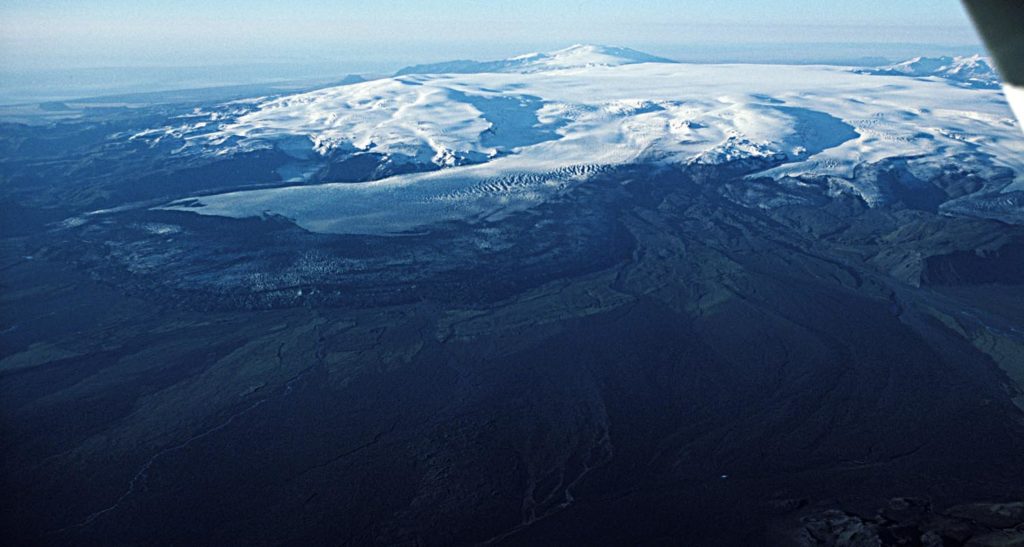
Iceland , Mýrdalsjökull :
A small seismic swarm began yesterday in Vífilsfell area, a total of 600 earthquakes have been detected. The largest earthquake was a M2 at on the 1st of July. Swarms like this are common in the area and occurred last in 2021.
Hikers and other travelers are encouraged to show caution as possible rockfall might occur due to earthquakes.
On June 30th at 01:18 an earthquake swarm started in Mýrdalsjökull. Nine earthquakes were over M3, the largest M4.4 at 02:46. The earthquake activity decreased around noon on Friday but at 22:57 on Sunday there was a small earthquake swarm were the largest earthquake measured 3.1M.
Katla central volcano has a 100 km² caldera. The upper parts are covered by the 600 km² Mýrdalsjökull ice cap (400-700 m thick). Geothermal fields in the caldera are expressed as cauldrons in the surface of the ice.
The partly ice covered Katla volcanic system has been highly active in the Holocene with at least 21 eruption in the last 11 centuries. The last eruption to break through the ice took place in 1918 CE.
The Katla system lies on the Eastern Volcanic Zone and is about 80 km long, consisting of a central volcano rising to 1490 m a.s.l. and an active fissure swarm extending towards northeast. The central volcano is partly covered by up to 700 m thick ice and has an 9×14 km ice-filled caldera.
Source : IMO.
Photo : Oddur Sigurðsson / IMO