September 30 , 2022.
Alaska , Trident :
AVO/USGS Volcanic Activity Notice
Current Volcano Alert Level: ADVISORY
Previous Volcano Alert Level: NORMAL
Current Aviation Color Code: YELLOW
Previous Aviation Color Code: GREEN
Issued: Thursday, September 29, 2022, 2:56 PM AKDT
Source: Alaska Volcano Observatory
Notice Number: 2022/A1083
Location: N 58 deg 14 min W 155 deg 6 min
Elevation: 3599 ft (1097 m)
Area: Alaska Peninsula
Volcanic Activity Summary:
The swarm of earthquakes that began on August 24, 2022, beneath Trident volcano continues. In addition, episodes of weak seismic tremor and low frequency earthquakes have been detected since August 28. Together, these observations mean that Trident is exhibiting signs of elevated unrest above known background level. Therefore, we are raising the Aviation Color Code to YELLOW and the Volcano Alert level to ADVISORY.
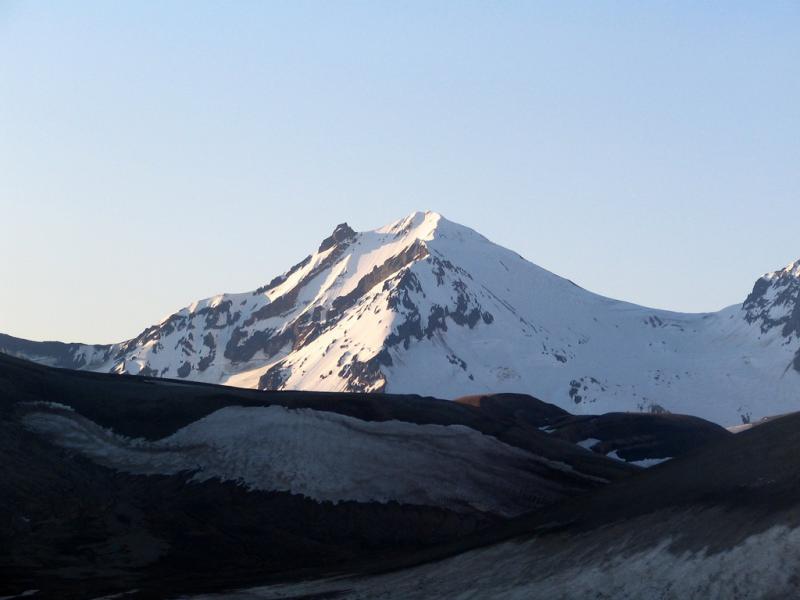
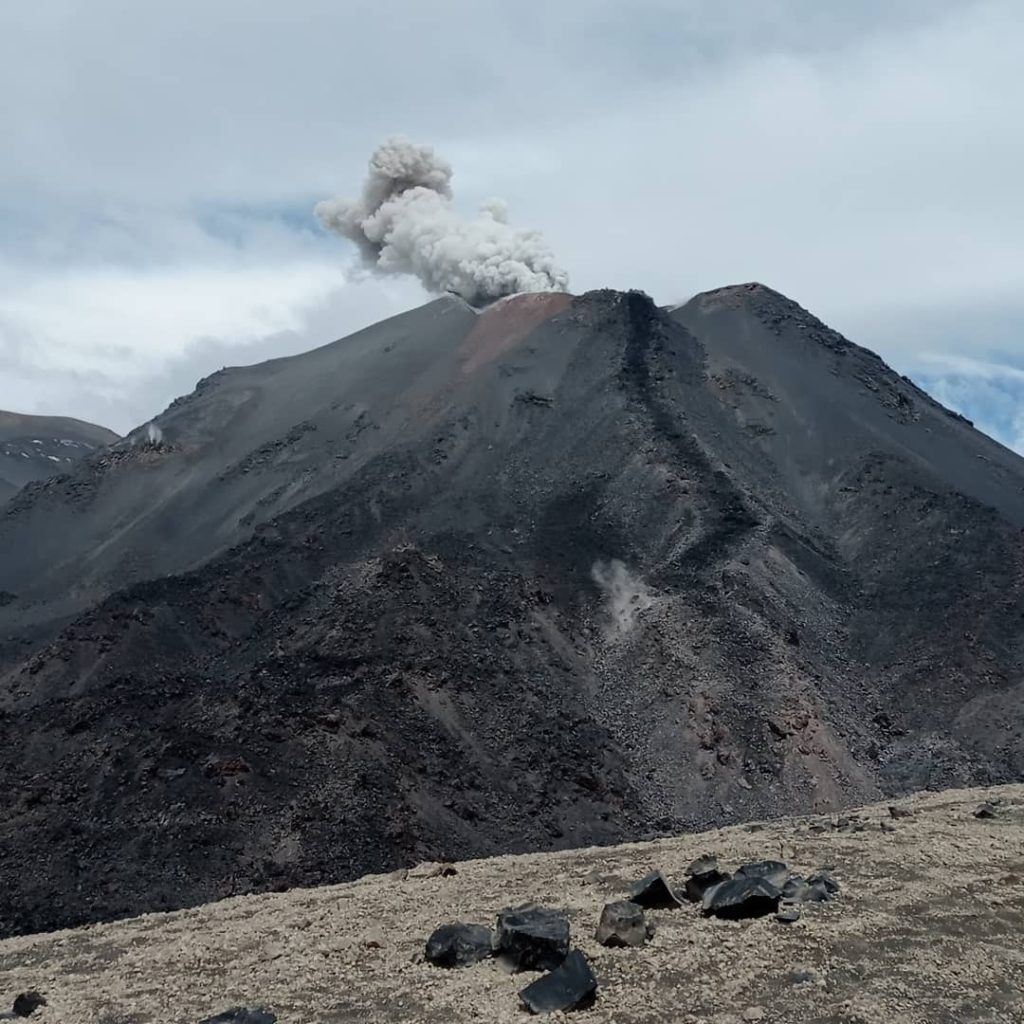
Glaciated remnant of East Trident volcano, as seen near sunrise from the Baked Mountain hut in Katmai National Park and Preserve.
During the current swarm, earthquake depths were initially mostly deep at around 25 km (16 miles) below sea level but became progressively shallower to around 5 km (3 miles) by August 28. Since then, earthquakes have mostly occurred 3 to 6 km (about 2 to 4 miles) below sea level, although some deeper events have been detected. Earthquake magnitudes (M) have ranged from M –0.7 to M 1.9. At the peak of the swarm, dozens of earthquakes occurred daily beneath the volcano, but earthquake rates have since decreased to just a few per day. No other signs of unrest have been detected in monitoring data.
The increase in seismic activity is likely caused by movement of magma or magmatic fluids. Increases in seismic activity have been detected previously at Trident and other similar volcanoes, with no subsequent eruptions. We expect additional shallow seismicity and other signs of unrest, such as gas emissions, elevated surface temperatures, and surface deformation to precede any future eruption, if one were to occur.
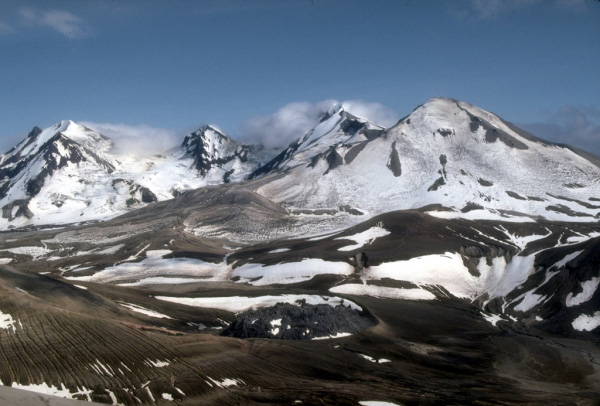
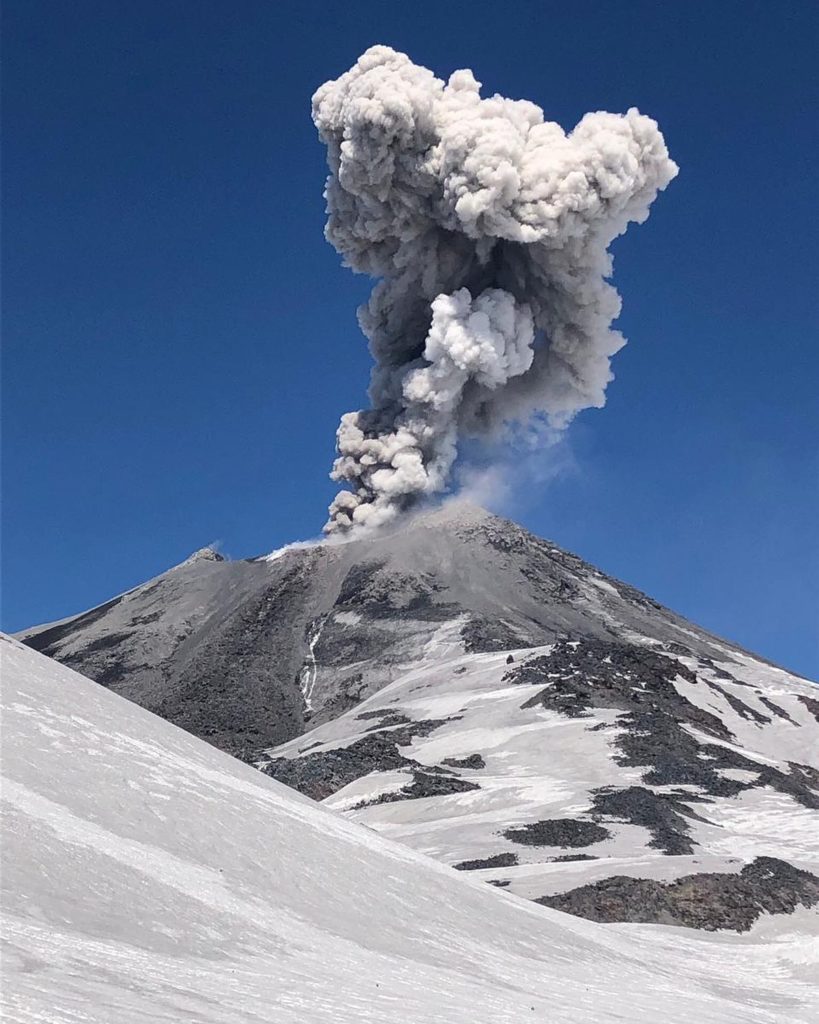
The multiple peaks of Trident Volcano as viewed from the top of Baked Mountain in the Valley of Ten Thousand Smokes, Alaska. Trident Volcano is composed of a cluster of andesite and dacite cones and is the only Katmai group volcano other than Katmai and Novarupta to have had historical activity. The Novarupta lava dome is visible at bottom, center.
Remarks:
Trident is one of the Katmai group of volcanoes located within Katmai National Park and Preserve on the Alaska Peninsula. Trident consists of a complex of four cones and numerous lava domes, all andesite and dacite in composition, that reach as high as 6,115 ft above sea level. An eruption beginning in 1953 constructed the newest cone, Southwest Trident, and four lava flows on the flank of the older complex. This eruption continued through 1974 and produced ash (an initial plume rose to 30,000 ft asl), bombs, and lava at various times. Fumaroles remain active on the summit of Southwest Trident and on the southeast flank of the oldest, central cone. Trident is located 148 km (92 miles) southeast of King Salmon and 440 km (273 miles) southwest of Anchorage.
Source : AVO.
Photos : Tilman, M. R. / Alaska Volcano Observatory / University of Alaska Fairbanks , McGimsey, R. G./ Alaska Volcano Observatory/U.S. Geological Survey .
La Réunion , Piton de la Fournaise :
Press release, Paris Institute of Earth Physics, Piton de la Fournaise Volcanological Observatory, September 29, 2022 – 3:15 p.m. (local time) – 11:15 a.m. (UTC time).
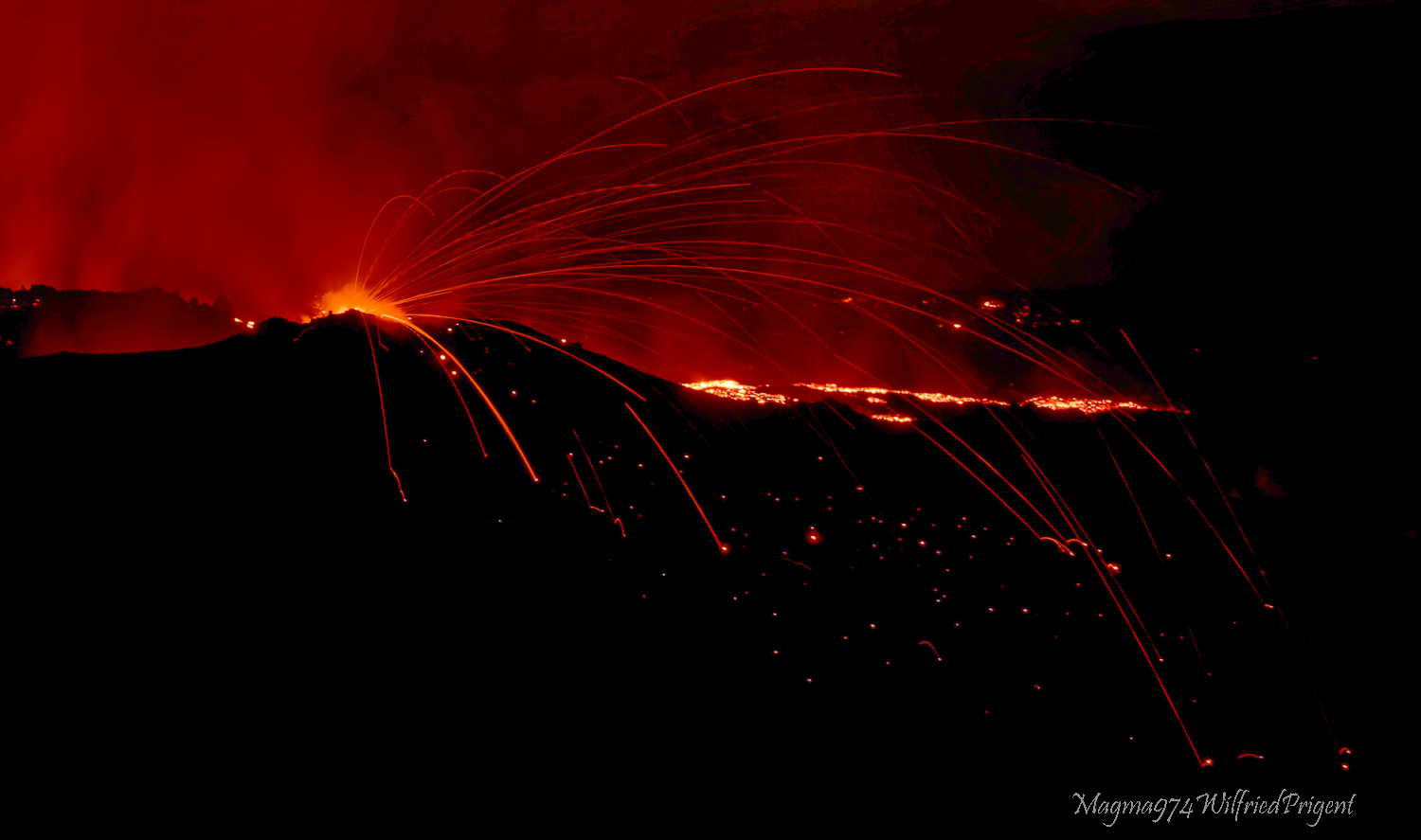
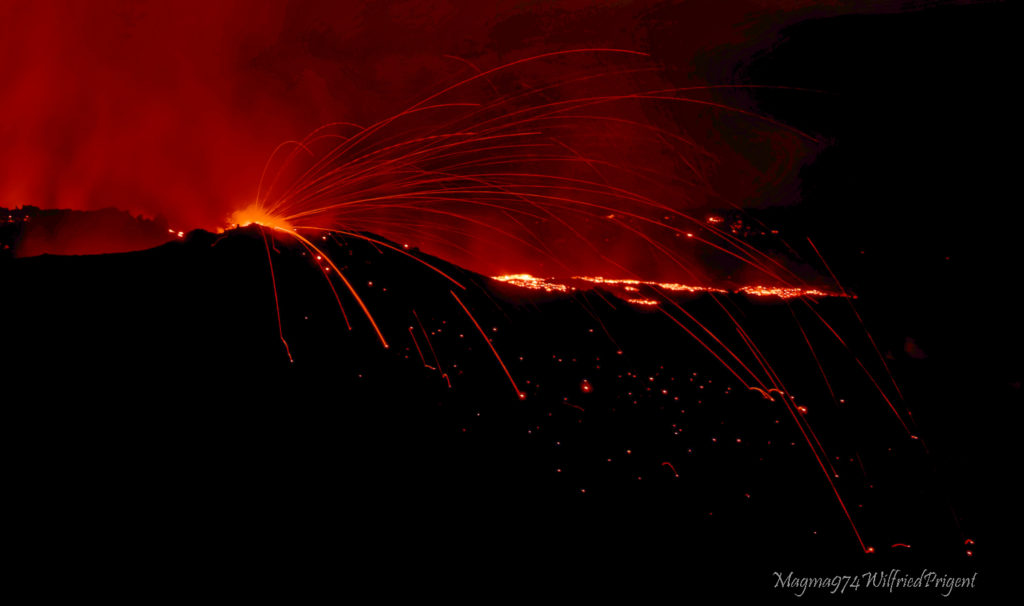
Ongoing eruption
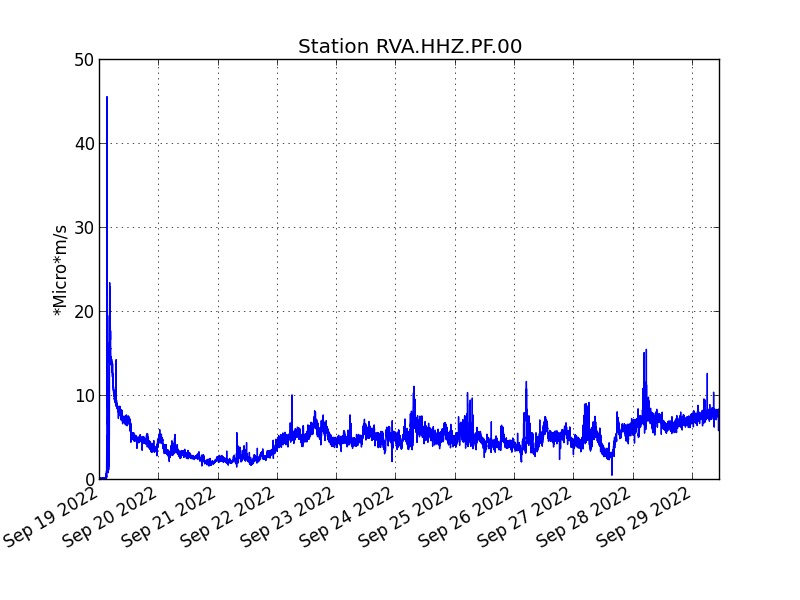
The eruption started on 09/19/2022 around 07:48 local time continues. The amplitude of the eruptive tremor (indicator of surface lava emission) has remained generally stable over the past 24 hours (Figure 1).
Evolution of the RSAM (indicator of a surface lava emission) since 09/19/2022 00:00 UTC time (04:00 local time) on the RVA seismological station located at the Rivals crater (© OVPF / IPGP).
– No volcano-tectonic earthquake has been recorded directly above the summit area over the past 24 hours.
– The resumption of a slight inflation (swelling) on the whole volcano (summit and enclosure) is confirmed but remains of low intensity for the moment (< 1 cm).
The lava flow estimates established by satellite method on the HOTVOLC (OPGC – Clermont Auvergne University) and MIROVA (University of Turin) platforms indicate an average flow over the last 24 hours relatively stable and low around 2 m3/s. As lava flow activity now takes place mainly in tunnels, these estimates are values
minimal.
The acquisitions of the COPERNICUS program developed by the European Commission provide images of the TROPOMI instrument intended for the observation of the composition of the atmosphere, and in particular the concentrations of SO2. The September 28 (10:40 UTC) image indicated a weak gas plume still trending west. The integrated mass of SO2
visible is estimated between 0.2 kton (treatment at 7 km altitude) and 0.9 kton (treatment at 1 km altitude).
The images from the OVPF-IPGP webcam located at Piton de Bert show for today an activity similar to the previous days, namely:
– still significant degassing at the eruptive site and low-amplitude lava projections;
– field observations yesterday showed that a second small mouth had opened on the southern flank of the eruptive cone, this second mouth was still visible this morning (Figure 3, left)
– a gas plume still directed towards the West;
– a lava flow activity still mainly through lava tunnels;
– resurgences of lava visible at the level of the tunnels
Alert level: Alert 2-1 (Access to the Enclos prohibited; eruption in the Enclos without any particular threat to the safety of persons, property or the environment)
Source : Direction OVPF / IPGP.
Read the full article : http://www.ipgp.fr/sites/default/files/ovpf_20220929_15h15_communique_eruption.pdf
Photos : OVPF , Magma974/Wilfried Prigent ( https://www.facebook.com/profile.php?id=100013589102172
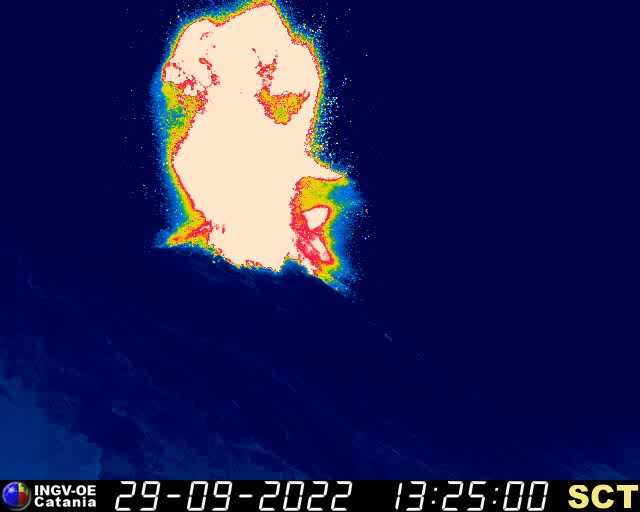
Italy , Stromboli :
Statement on Stromboli activity, September 29, 2022, 15:30 (13:30 UTC).
The National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology, Osservatorio Etneo, reports that monitoring networks recorded a high-intensity explosion at 3:26 p.m. (1:26 p.m. UTC).
Further updates will be communicated soon.
Statement on the activity of Stromboli, September 29, 2022, 16:15 (14:15 UTC).
The National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology, Osservatorio Etneo, announces that the monitoring networks recorded at 4:02 p.m. (14:02 UTC), with the analysis of the CCTV cameras, recorded a major explosion of the North crater area, at 13:24:59 UTC. The material produced fell abundantly along the entire Sciara del Fuoco, while there was no significant fallout of coarse material in the Pizzo area.
At 13:24:30 (UTC) a seismic signal of greater than normal amplitude was recorded. The amplitude of the volcanic tremor remained at high levels for about 6-7 minutes. There were no significant changes in the other parameters.
There are no significant changes in the strain signals.
Further updates will be communicated promptly and in any case within 3 hours of this press release.
Statement on Stromboli activity, September 29, 2022, 21:37 (19:37 UTC).
The National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology, Osservatorio Etneo, announces that the monitoring networks recorded the return of the parameters to normal activity at 21:36 (19:36 UTC).
Source : INGV.
Photos : INGV , LGS
Chile , Nevados de Chillan :
Seismology
The seismological activity of the period was characterized by the recording of:
55 volcanotectonic earthquakes (VT) associated with brittle rupture processes; the most energetic earthquake had a local magnitude (ML) equal to 1.3, whose location was estimated at a depth of 3.6 km and at an epicentral distance of 5.6 km to the East-North-East of the active crater.
Long period (LP), explosion (EX) and tremor (TR) seismicity continued to be recorded, associated with fluid dynamics within the volcanic system. 571 LP-type earthquakes were classified, of which 171 were related to explosions at surface level, due to the presence of acoustic waves and/or gaseous emissions, specifying that the recording of the two characteristics mentioned is difficult due to adverse weather conditions, which may lead to a decrease from the ideal count for this type of event. The size of the largest LP earthquake, estimated from the reduced displacement parameter (DR), reached a value equal to 158 cm2. With regard to TR type seismicity, 200 episodes were identified, the most important of which reached a DR of 46 cm2 accompanied by an acoustic wave of 0.4 Pa Km.
After the evaluated period, an explosive event was recorded which reached a DR equal to 740 cm2 at the PTZ station, whose seismic energy is one of the highest detected during this entire eruption. This earthquake occurred during an increase in explosive activity on September 17 and 19, which included 2 additional notable events to the one mentioned, all with a significant release of seismic energy as well as acoustic energy, the most important of them with a sound pressure reduced to 1 Km from 165 Pa Km. After the explosive period, a decrease in the daily seismic energy of the fluids is observed similar to what happened after the explosion of 9/29, therefore, future explosive episodes are not excluded.
Satellite thermal anomalies
1 thermal alert was recorded in the area associated with the volcanic complex during the period, with a Volcanic Radiative Power (VRP) of less than 1 MW on September 10, a value considered low according to the data processed by the Middle Infrared Observation of Active Volcanoes (MIROVA). A decrease in the potency of these anomalies was observed during the reference period.
At the same time, according to the analytical processing of satellite images (Sentinel 2-L2A in combination of false color bands), luminance anomalies were observed during September 2, 5, 10, 12 and 15.
Satellite geomorphological analysis
From the geomorphological observations made by the images of the Planet Scope and Sentinel 2 L2A satellites, we observe the partial destruction of Dome 4 after the explosion of August 29. However, the emplacement of a new morphology associated with lava extrusion, spatially coinciding with the thermal radiance anomaly seen on Sentinel 2 L2A false-color images, is gradually observed. Photo-interpretation of a SkySat Collect image from September 13, 2022 shows the presence of a nested dome in the crater, reduced to 35% of the area identified in August (current area: 1037 m2). The set of cracks identified inside the crater also varies from the previous month. The current distribution shows a preferential orientation North-West-South-East, and in the dome orthogonal cracks North-West-South-East, South-North-East. The prominence related to the mechanical disturbance of the rock due to the rise of material characterized the previous fortnight has ceased to rise after the explosion of August 29, and a rock of a different texture, with a fresh appearance, is currently being exposed. bare and maintained at a higher temperature than the surrounding rock.
Source : Sernageomin.
Read the full article : https://rnvv.sernageomin.cl/rnvv/TI_Santiago_prod/reportes_LB/2022/RAV_20220927_%C3%91uble_v17.pdf
Photos : @nluengov , Sernageomin
Philippines , Taal :
TAAL VOLCANO ADVISORY , 29 September 2022 ,07:00 PM
This is a notice of increased volcanic SO2 gas emission from Taal Volcano.
A total of 10,718 tonnes/day of volcanic sulfur dioxide or SO2 gas emission from the Taal Main Crater was recorded today that produced significant volcanic smog or vog over Taal Caldera. Airborne volcanic gas is expected to be drifted to the general west of Taal Volcano Island or TVI based on air parcel trajectory data from PAGASA. SO2 flux averaged 6,612 tonnes/day for the month of September 2022, in a continued trend of elevated emission since 15 July 2022. Since the beginning of August 2022, there was also an increase in degassing activity in the form of visible upwelling of volcanic fluids in the Main Crater Lake and emission of voluminous steam-rich plumes of up to 2,500 meters rise above TVI. Vog was reported this morning by residents of the Municipalities of Laurel, Agoncillo and Sta. Teresita, Batangas.
As a reminder, vog consists of fine droplets containing volcanic gas such as SO2 which is acidic and can cause irritation of the eyes, throat and respiratory tract with severities depending on the gas concentrations and durations of exposure. People who may be particularly sensitive to vog are those with health conditions such as asthma, lung disease and heart disease, the elderly, pregnant women and children. For communities that can be affected by vog, please be mindful of the following.
Limit your exposure. Avoid outdoor activities, stay indoors and shut doors and windows to block out vog.
Protect yourself. Cover your nose, ideally with an N95 facemask. Drink plenty of water to reduce any throat irritation or constriction. If belonging to the particularly sensitive group of people above, watch over yourself and seek help from a doctor or the barangay health unit if needed, especially If serious effects are experienced.
In addition, acid rain can be generated during periods of rainfall and volcanic gas emission over areas where the plume disperses, causing damage to crops and affecting metal roofs of houses and buildings.
Source : Phivolcs.
Photo : EDWIN BACASMAS