February 14 , 2019.
Indonesia , Karangetang :
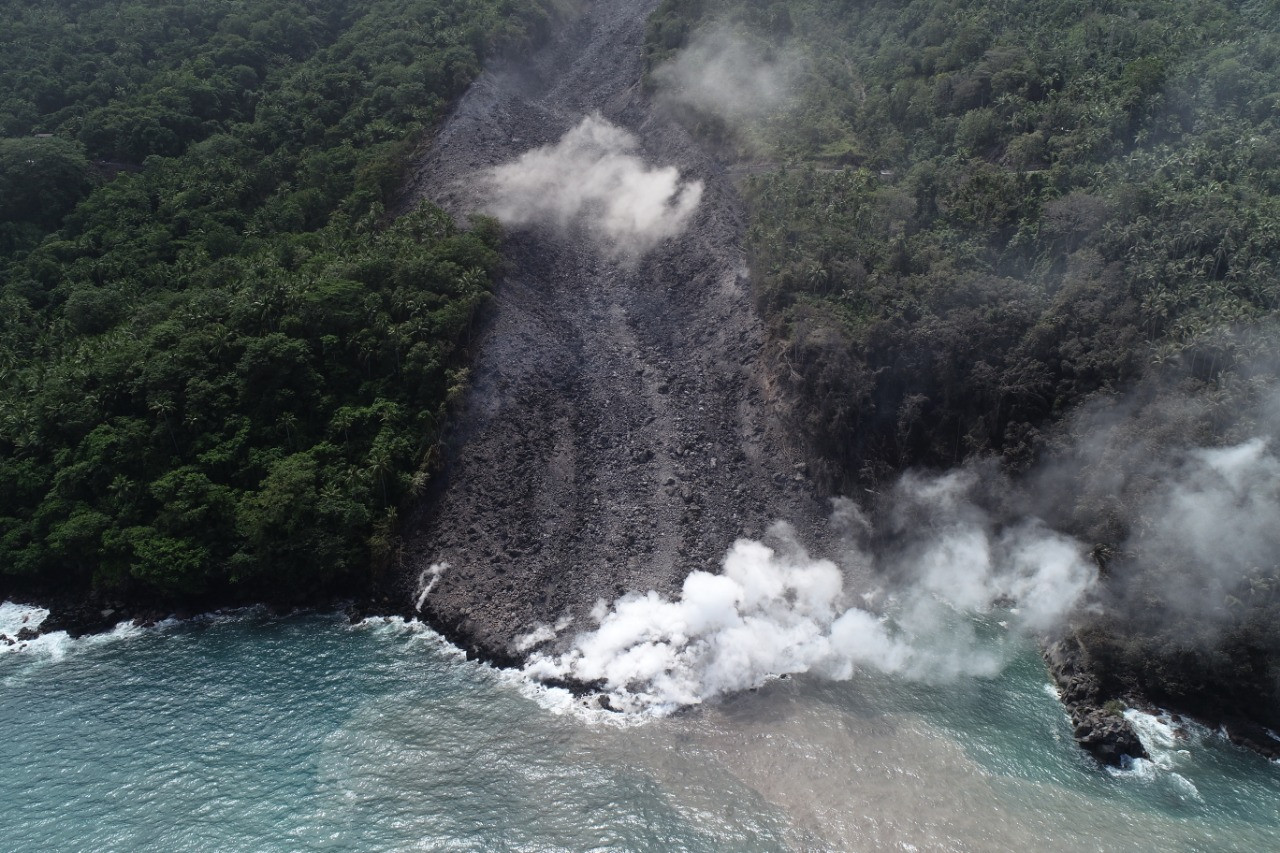
Lava flow from Mount Karangetang on Siau Island, North Sulawesi, has blocked connecting roads between two villages in the area.
As a result,12 junior high school students had to take shelter at a nearby school on account of the blocked road between the villages of Kiawang and Batubulan.
“These students would walk to their school in Kiawang but they now have to take the sea route [to go to school]. But water transportation is dangerous,” Bob Wuaten, Siau Tagulandang Biaro Islands Disaster Mitigation Agency (BPBD Siau Tagulandang Biaro) head, told kompas.com, adding that his team was coordinating with the education agency to resolve the matter.
The lava flow of one of Mount Karangetang’s craters on the island of Siau in northern Sulawesi reaches the seashore.
(National Disaster Mitigation Agency (BNPB) / File)
The volcano is located on the small island on the north eastern part of Sulawesi and a part of Siau Tagulandang Biaro Islands regency.
Aditya Gurasali, a monitoring official at the mountain, said the volcano had been given the siaga (alert) status, the second-highest level on the four-tiered volcano alert system.
He suggested that nearby residents and visitors avoid activities within a 2.5 to 4 kilometer radius of the crater.
Aditya also recommended the usage of masks to anticipate respiratory problems owing to possible ash rain.
BPBD Siau Tagulandang Biaro officials are moving people living in Niambangeng, Beba and Batubulan to outside the danger zone.
For people living near the river banks, the agency urges them to be on alert for lava-induced rain and flash floods.
On 8 February PVMBG reported that lava from Karangetang’s Kawah Dua (North Crater) continued to advance over 3.5 km down the Malebuhe River drainage on the NW flank into the ocean. Levees had formed at the margins channeling the lava down the middle of the flow. Avalanches from the edges of the flow generated brown and gray plumes. A lava delta was building out into the ocean and generating a dense steam plume. Drone footage acquired on 9 February showed that the flow was about 160 m wide where it crossed a road (about 210 m from the coast) and about 140 m wide at the coast. Seismicity remained high. The Alert Level remained at 3 (on a scale of 1-4), and residents were warned to remain outside of the 2.5-km exclusion zone around the N and S craters, and not enter within 3 km WNW and 4 km NW.
Source : The Jakarta Post , GVP.
Photo : BNPB.
Video : Suaradot.com
Colombia , Nevado del Ruiz :
Weekly activity bulletin of the Nevado del Ruiz volcano
The level of activity continues at the level: activity level Yellow or (III): Modifications of the behavior of the volcanic activity.
With regard to monitoring the activity of the Nevado del Ruiz volcano, the COLOMBIAN GEOLOGICAL SERVICE announces that:
The Nevado del Ruiz volcano over the past week continued to show instability in its behavior. The recorded seismicity was mainly associated with the fracturing of rocks near the volcano (volcano-tectonic seismicity). This seismic activity showed a slight increase in the number of earthquakes and released seismic energy compared to the previous week. The earthquakes were located in the Arenas crater, in the North-East, South-South-East and North-North-West parts of the volcano, at depths between 0.4 and 8.4 km. The higher energy earthquake was recorded on February 10th at 15:07 (local time), had a magnitude of 1.0 ML (local magnitude) and was located 2.7 km south of Arenas crater and at a depth of 3 ,7 km. The occurrence of short-lived, low-energy volcano-tectonic earthquakes was recorded between 23:13 (local time) on 12 February and 00:20 (local time) on 13 This type of seismicity is related to the processes of ascension and evolution of lava domes on the surface of a volcano.
Regarding the seismicity related to the fluid dynamics inside the ducts of the volcanic structure, there was a slight decrease in the number of earthquakes and a slight increase in seismic energy released compared to the previous week. This seismic activity was characterized by the appearance of slight pulses of volcanic tremor and earthquakes for a very long time. The earthquakes occurred mainly in the crater Arenas and its surroundings.
Volcanic deformation measured from electronic inclinometers, as well as GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) stations, showed stability during the week without recording significant deformation processes of the volcanic structure.
The volcano continues to emit water vapor and gases into the atmosphere, among which is the sulfur dioxide (SO2), as evidenced by the values obtained by the SCANDOAS stations installed in the region of the volcano. satellite image analysis. During the week, the NASA FIRMS and MIROVA portals reported several low-energy thermal anomalies.
The column of gas and steam reached a maximum height of 1500 m, measured at the top of the volcano on 6 February. The direction of dispersion of the column was governed by the direction of the wind in the region, which prevailed towards the northwest of the volcano.
The Nevado del Ruiz volcano continues at the level of yellow activity.
Source : SGC.
Photo : SGC.
La Réunion , Piton de la Fournaise :
Activity Bulletin of Wednesday, February 13, 2019
Alert level: Vigilance.
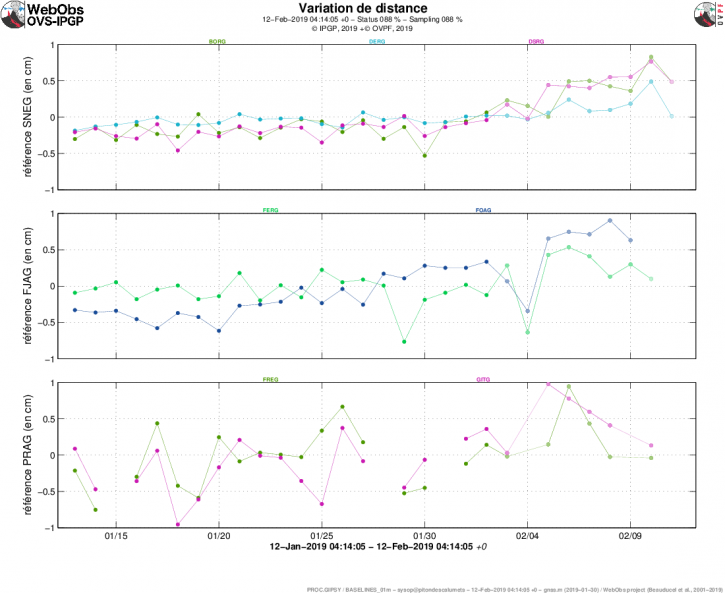
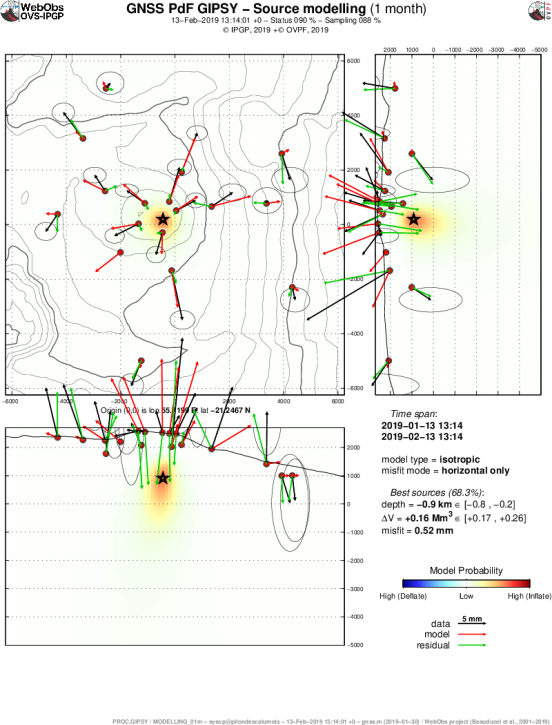
Since the end of January 2019, inflation (swelling) of the base and top of the Piton de la Fournaise building has been observed again by the OVPF deformation network (Figure 1). This recovery in the building’s inflation is synonymous with a pressurization of the superficial magmatic reservoir (Figure 2).
Figure 1: Illustration of the deformation over the last month. Bases are shown here (variation in distance between two GPS receivers) crossing the Piton de la Fournaise building, at the top (at the top), at the base of the terminal cone (in the middle) and in the far field (at the bottom ). A rise is synonymous with elongation and therefore swelling of the volcano; conversely, a decrease is synonymous with contraction and therefore deflation of the volcano. (© OVPF-IPGP
Figure 2: Location of the source (best model resulting from a « Mogi » type of modeling) at the origin of the displacements recorded during the last month on the GPS stations of the base and the summit of the terminal cone of the Piton de la Searing. (© OVPF-IPGP, © F. Beauducel IPGP / IRD).
This recovery in inflation is accompanied by an increase in CO2 concentrations in the far-field soil (Plaine des Cafres and Plaine des Palmistes sectors) since the end of January. Near-field CO2 concentrations in the volcano deposit area have also been increasing since December 2018. These CO2 concentrations are in agreement with a deep rise of magma towards the superficial reservoir.
Note that this process of recharging the superficial reservoir can last several days to several weeks before the roof of the tank becomes brittle and breaks, thus giving rise to an injection of magma towards the surface and an eruption, and can also stop without giving rise to an eruption in the short term.
Source : OVPF
Photo : Wikipedia , B.navez
Indonesia , Anak Krakarau :
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION – VONA.
Issued: February 14 , 2019
Volcano: Anak Krakatau (262000)
Current Aviation Colour Code: ORANGE
Previous Aviation Colour Code: orange
Source: Anak Krakatau Volcano Observatory
Notice Number: 2019KRA28
Volcano Location: S 06 deg 06 min 07 sec E 105 deg 25 min 23 sec
Area: Lampung, Indonesia
Summit Elevation: 352 FT (110 M)
Volcanic Activity Summary:
Eruption with ash clouds at 06:26 UTC (00:26 local time). The eruption lasted for 146 seconds.
Volcanic Cloud Height:
No Ash Cloud observed.
Other Volcanic Cloud Information:
Ash cloud is moving to east
Remarks:
Eruption recorded on seismogram with maximum amplitude 26 mm and maximum duration 146 second.
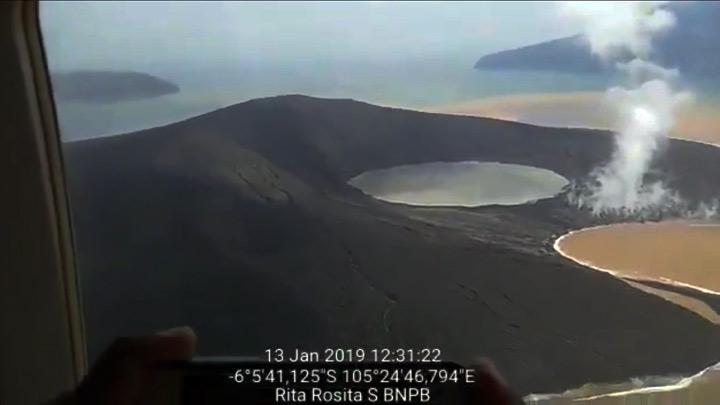
Information on the eruption of Mount Anak Krakatau, February 14, 2019.
Anak Krakatau, Lampung, was erupted on February 14, 2019 at 00:26 WIB, but the height of the ash column was not observed. This eruption is recorded on a seismogram of maximum amplitude of 26 mm and a duration of ± 2 minutes 26 seconds.
Currently, G. Anak Krakatau is at level III (SIAGA) with the recommendations: people / tourists are not allowed to approach the crater within a radius of 5 km.
Source : Magma Indonesia , PVMBG.
Photo : Rita Rosita / BNPB.
Vanuatu , Ambrym :
AMBRYM VOLCANO ALERT BULLETIN No2 issued by the Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department on 14th February 2019 at 15:05 PM:
Ambrym volcano is in the major unrest state. The Volcanic Alert Level is lowered from Level 3 to Level 2.
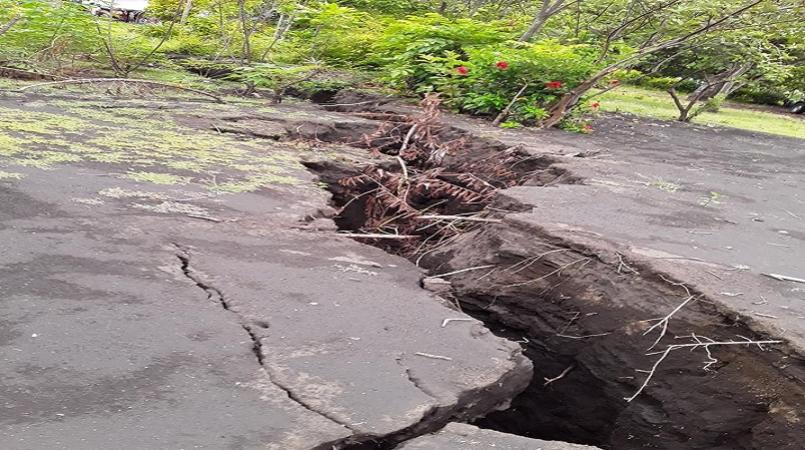
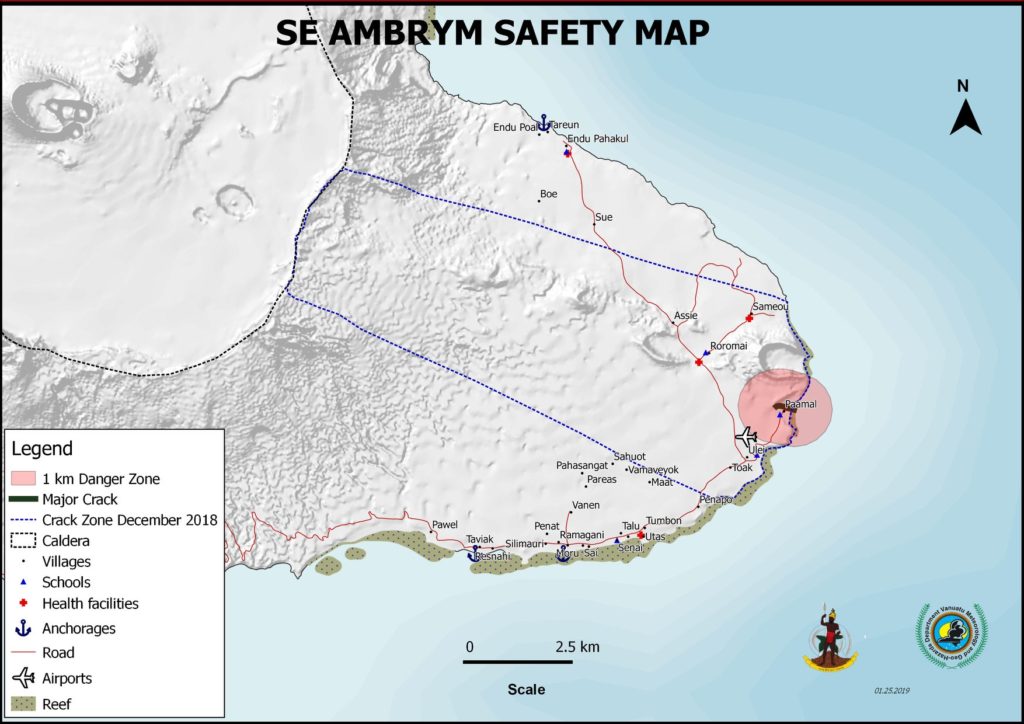
The current volcanic activity is consistent with the volcanic alert Level 2. This declined activity and the presence of active faults in the South-Eastern part of Ambrym contribute in the change of current danger zones of Ambrym volcano. The danger zones at the caldera is now reduced to 1 km around Benbow and 2 km around Marum craters including Maben-Mbwelesu, Niri-Mbwelesu and Mbwelesu) . The Danger Zone for life safety is now limited at the Permanent Exclusion Zone at Benbow and Danger Zone A at Marum. An additional area of risk at the South-East of Ambrym is now identified within 1 km from major cracks (See Safety Map ).
Latest satellite imagery and observations in the field from 03rd to 09th February 2019 confirm the presence of open cracks and active faults in Paamal village and its vicinity and the uplift at the coastal area of South-East Ambrym. These fractures are oriented in the WSW-ENE direction. Observations of the crack surfaces confirm that there is no steam, no lava flows, not even any smell of volcanic gases in the cracks. A small seashore activity at the edge of one of the major faults ejected small light volcanic stones (pumice) that were washed ashore at Paamal village. Cracks and uplift in South-East Ambrym may be due to the presence of a possible dyke that may form from the drainage of the main craters of Benbow and Marum at the summit and migrating beneath to the eastern part of the island in December 2018. This activity has reshaped the form of the island and may influence the Potential future volcanic hazards impact areas.
These observations also indicate that the volcano activity at the caldera remains with emissions of steam and other gases from the active craters with obvious collapse in areas around the active craters. Lava lakes that used to appear in Benbow and Marum craters have disappeared since 16th December 2018. People from Ambrym and neighbouring islands may no longer see the volcanic glow at night for the next few weeks/months. These observations confirm that the small –scale eruption in the caldera has now ceased.
Though people are not feeling strong earthquakes compare to the past few days in December 2018, current observations and analysis of seismic data recorded from the monitoring network confirm an ongoing seismicity. This is related to the current volcano eruption. This seismicity may continue to affect the existing cracks, especially in the South-East Ambrym area. Latest satellite imagery analysis confirm that there is no continuing land deformation on Ambrym island.
The possibility that the Ambrym volcano activity escalate to the level of minor eruption (Level 3) and/or lowered to the lower unrest state (Level 1) is low for now.
Source : Geohazard Vanuatu.
Photo : Loop Vanuatu