April 20 , 2019 .
Japan , Asosan :
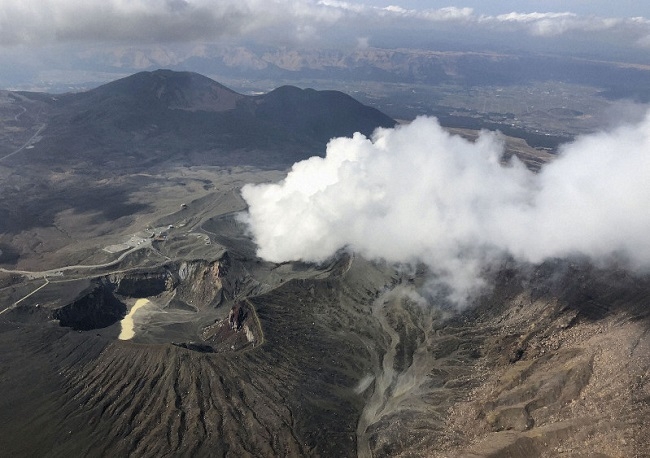
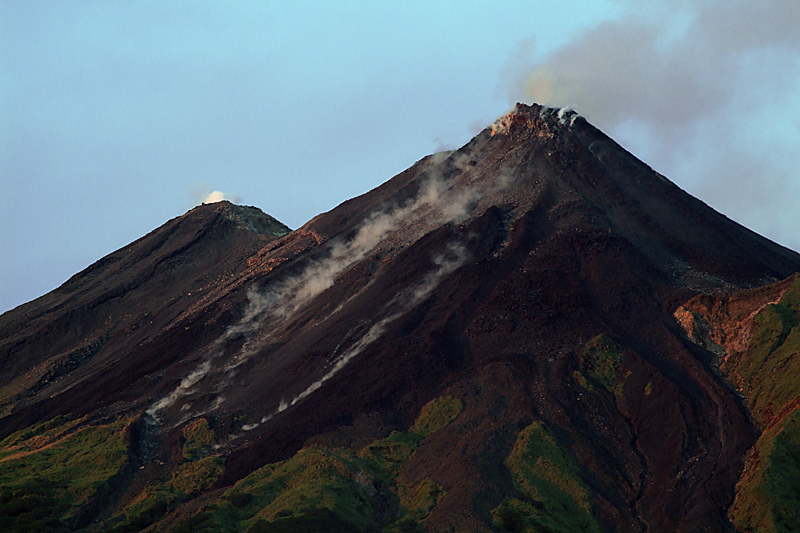
Mt Aso in southwestern Japan erupts again
Apr. 19 01:23 pm .
Mt Aso in Kumamoto Prefecture had a minor eruption Friday following a similar event observed earlier this week, the weather agency said.
The eruption occurred at 8:24 a.m. at the No. 1 Nakadake crater, the same area as Tuesday’s eruption, spewing smoke as high as 400 meters, according to the Japan Meteorological Agency.
There were no immediate reports of injuries, according to local police.
The agency maintained Mt Aso’s volcanic alert level at 2 on a scale of 5. This restricts entry to areas around the crater as even a small volcanic eruption can be dangerous, possibly spewing large flying rocks and causing pyroclastic flows.
The eruption on Tuesday was the first at the volcano since October 2016. Local municipalities have restricted entry to areas within one kilometer of the crater.
« As eruptions continue ahead of a big holiday, it is regrettable that tourists cannot visit the crater on the mountain, » said an official of the city of Aso.
Source : Japantoday.
Photo : kyodo
Chile , Copahue :
During this period, 159 seismic events classified as volcano-tectonic (VT) type were recorded, associated with fracturing processes of rigid materials. The event with the greatest energy obtained a local magnitude equal to M 2.6 and was located 2.6 km north (N) of the active crater El Agrio, 800m deep.
Similarly, 2 earthquakes associated with fluid dynamics were recorded under the volcanic building, classified as long period type (LP) events, with a maximum reduced displacement value (DRC) of 1.2 cm2. During this period, very long period earthquakes (VLPs, for their acronym in English Very Long Period) were not recorded.
The continuous tremor signal showed oscillations in its amplitude between the values of 0.8 and 1.2 μm / s with dominant frequencies between 1.0 and 3.0 Hz mainly.
The IP cameras installed near the volcano made it possible to determine the absence of emission, simply noting a degassing column on 04 April 2019 from the edge of the active crater (El Agrio) at a maximum height of 80 m, white color .
According to the analysis of the data obtained by four geodetic monitoring stations, small amplitude variations are observed which do not suggest a destabilization of the volcanic system.
Sulfur Dioxide (SO2) emissions recorded by DAS equipment for Mellizas, located 5 km east-northeast of the active crater, had an average value of 434 +. – 105 t / day for the month of March, with a maximum value of 753 t / day reported on April 12th. SO2 emissions are considered moderate if we look at the current state of the volcano.
No thermal warnings were reported in the area associated with the volcanic building during the reporting period, according to the data processed by the mean infrared observation of volcanic activity (MIROVA) (http://www.mirovaweb.it/) and near-real-time thermal monitoring of global hot spots (MODVOLC) (http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/) .
The seismological parameters showed a decrease in comparison with the previous period, mainly the LP and VLP type seismicity. The volcano-tectonic type seismicity continues despite a decrease in the amount of events and the calculated energy. In relation to the superficial activity, we note the absence of nocturnal incandescence. The satellite images observed on the portal www.planet.com shows that the lake, located in the crater El Agrio continues to drop. The volcanic seismicity recorded during the previous weeks as the variation of the water level of the crater lake could be related to a feed of the magmatic system which would allow the hydrothermal system to be gradually depleted.
According to the characteristics shown during the previous and recent volcanic process by the volcano, it does not rule out the occurrence of an imbalance of the volcanic system, implying the possibility of occurrence of minor explosions that would affect the vicinity of the crater and a increase in surface activity.
Therefore, the alert level is maintained at the level:
YELLOW LEVEL: Changes in the behavior of volcanic activity – Probable time for an eruption: WEEKS / MONTH.
Observation: Est considérée comme zone d’affectation un rayon de 500m autour du cratère .
Source : Sernageomin .
Colombia , Nevado del Ruiz :
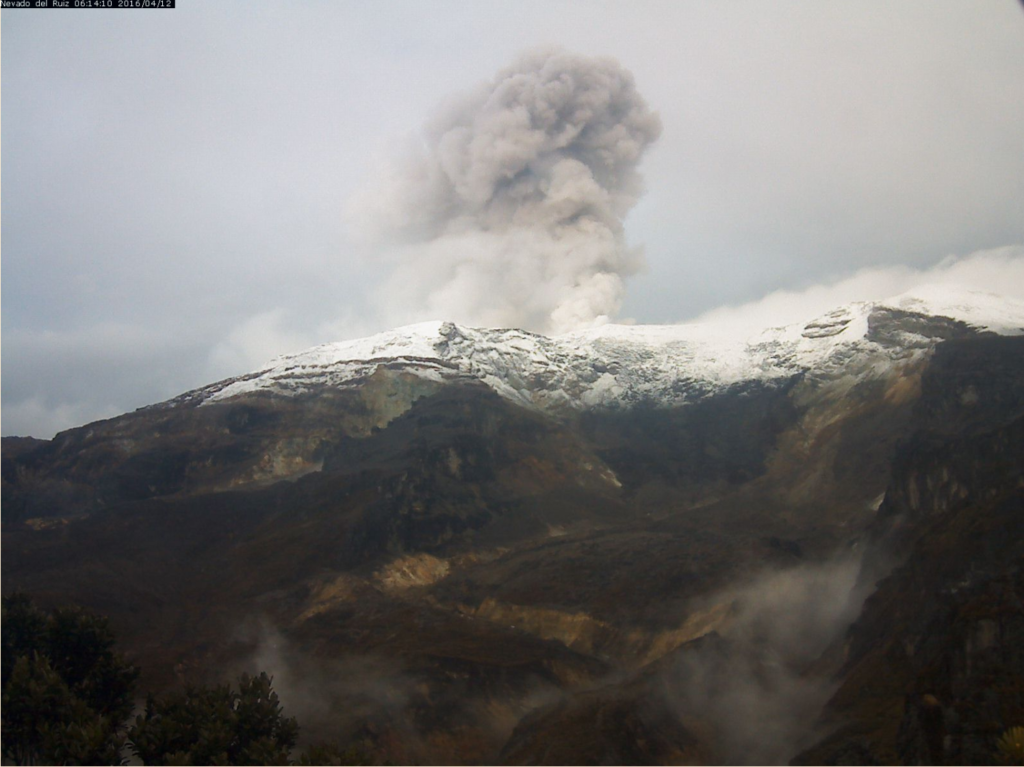
Activity of the Nevado del Ruiz volcano, April 18, 2019.
Information:
The COLOMBIAN GEOLOGICAL SERVICE informs the authorities and the community that in recent days, on the Nevado del Ruiz volcano, we continue to record seismic signals (pulses of volcanic tremors and long-period type earthquakes) of low energy. associated with small ash emissions, as reported since last Tuesday in the weekly bulletin. Some of these shows have been seen through the webcams installed in the volcano area (see photographs). In general, the height of the column was variable, between 230 and 1300 m, measured at the top of the volcano, the direction of dispersion being governed by the direction of the wind at the time of emission. It has been highlighted major trends towards North West and South of the volcano.
It is not excluded the possibility of an ash fall on populations located in the direction of the wind regime, nor the recording of new seismic signals associated with emissions of gas and ash.
The level of activity continues in yellow or (III): Changes in the behavior of volcanic activity. The Colombian geological service continues to pay attention to any change of activity and invites to consult the official information that will be provided by the Colombian geological service.
Source : SGC.
Photo : Archive SGC , 12-04-2016.
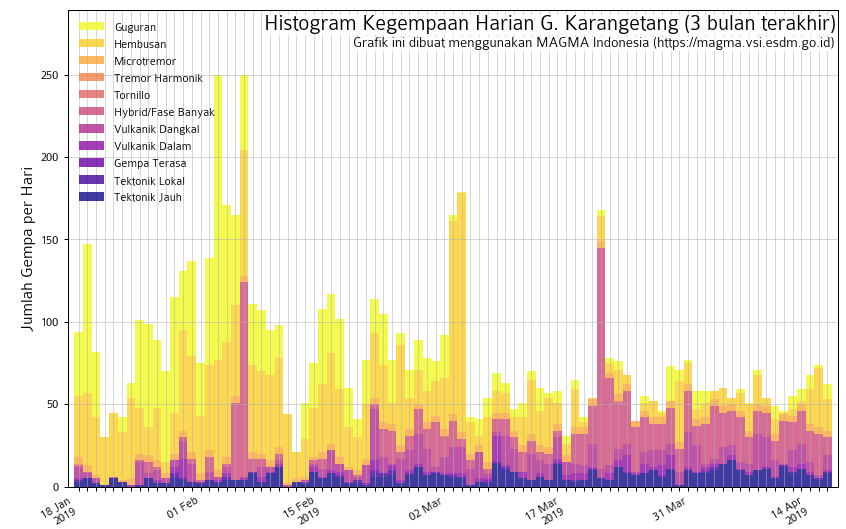
Indonesia , Karangetang :
Level of activity at Level III (SIAGA). Mount Karangetang (1784 m) has been erupting since 25 November 2018.
Since yesterday and until this morning, the volcano was clearly visible until it was covered with fog. Smoke from the main crater was observed at a maximum height of 200 meters above the crater, with a white color and strong intensity.
The seismographs, on April 19, 2019, recorded:
2 avalanche earthquakes.
5 explosion earthquake.
6 hybrid earthquakes
7 shallow volcanic earthquakes
4 deep volcanic earthquakes
11 distant tectonic earthquakes
Continuous tremor with a dominant amplitude of 0.25 mm.
Recommendation: As of March 26, 2019 at 12:00 WITA, the technical recommendations were as follows:
The public and visitors / tourists should not approach, climb or move in the hazard forecast area which is 2.5 km from the Kawah Dua (North crater) and the main crater (South) peaks. in the sectoral expansion zone of the Dua Crater at West-Sea, in the North, up to 4 km, an area between Kali Batuare and Kali Saboang.
People living around rivers from the summit of Mount Karangetang must be prepared for the potential threat of lahars and sudden floods that can spread to the coast.
VONA: The latest VONA code sent the YELLOW color code, published November 25, 2018 at 13:32 WITA, for volcanic ash emission at an altitude of approximately 2284 m above sea level or approximately 500 m above the summit, the wind blowing in the East.
Source : PVMBG.
Photo : Unknown author.