December 15 , 2025.
Hawaii , Kilauea :
HAWAIIAN VOLCANO OBSERVATORY DAILY UPDATE , U.S. Geological Survey
Sunday, December 14, 2025, 8:43 AM HST (Sunday, December 14, 2025, 18:43 UTC)
19°25’16 » N 155°17’13 » W,
Summit Elevation 4091 ft (1247 m)
Current Volcano Alert Level: WATCH
Current Aviation Color Code: ORANGE
Activity Summary:
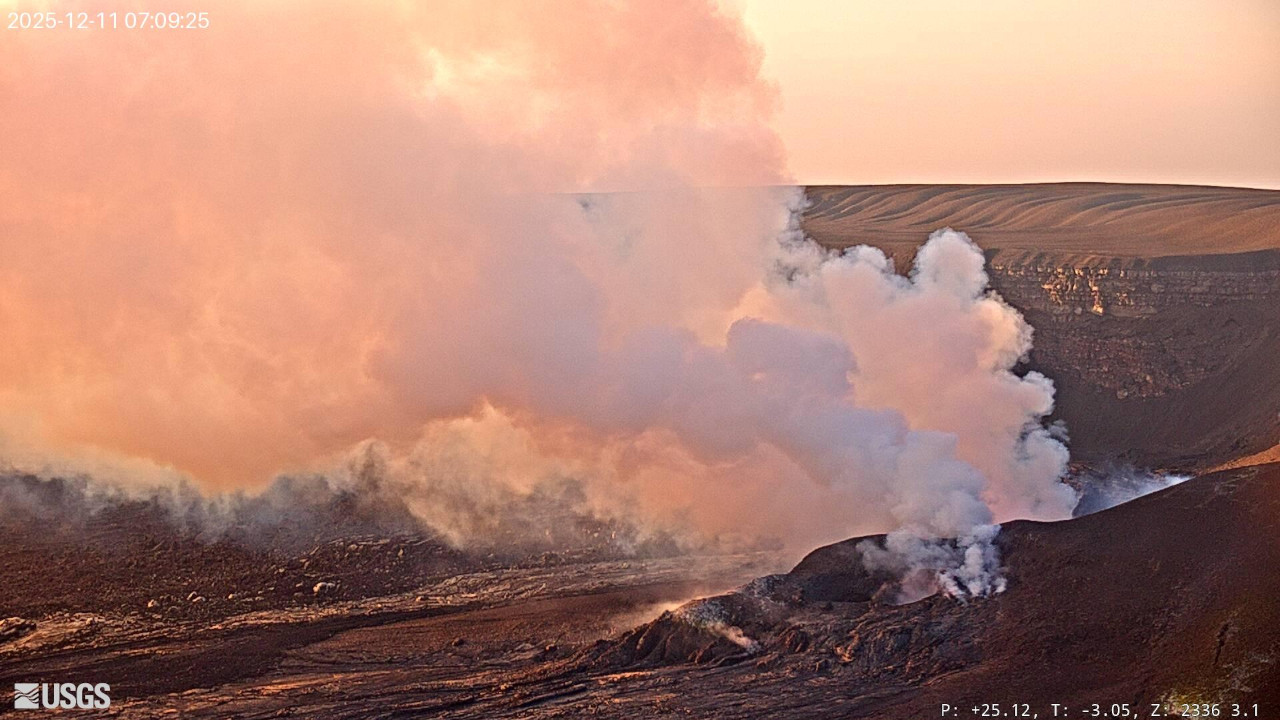
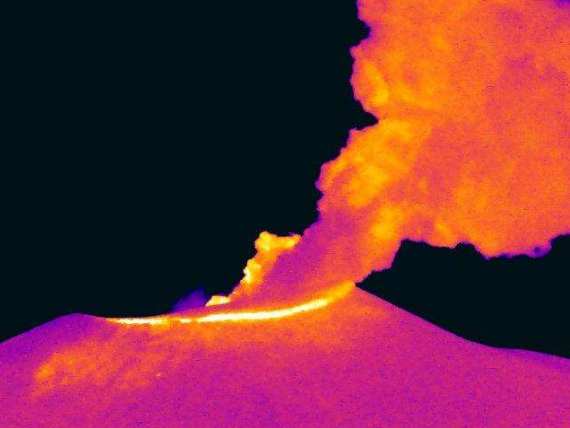
The ongoing summit eruption at Kīlauea is paused. Moderate glow continued overnight in the south vent accompanied by tremor spikes indicative of gas pistoning. The onset of episode 39 is likely to occur between December 22 and 27.
Summit Observations:
Glow continued overnight from the south vent with little to no glow from the north vent. Tremor is punctuated by pronounced spikes related to gas pistoning at regular intervals this morning.
Since the end of episode 38, Kīlauea has inflated 17.8 microradians as recorded on the UWD tiltmeter this morning with an increase of 2.4 microradians over yesterday.
Volcanic gas emissions have greatly decreased with the end of the eruption and are back in the normal range of 1200 to 1500 tonnes per day of SO2.
Rift Zone Observations:
Rates of seismicity and ground deformation remain very low in the East Rift Zone and Southwest Rift Zone. SO2 emissions from the East Rift Zone remain below the detection limit.
Analysis:
The rapid rebound of inflationary tilt, continued tremor indicative of gas pistoning, and moderate glow from the south overnight all indicate another fountain episode will occur. There are some discrepancies between the inflation models, but the onset of episode 39 is most likely between December 22 and 27. The forecast interval may change if the inflation rate varies.
Kīlauea has been erupting episodically since December 23, 2024, primarily from two vents (north and south) in Halema‘uma‘u. Eruptive episodes, which can last up to 12 hours, are separated by pauses that can be as long as two weeks.
HVO continues to closely monitor Kīlauea and is in contact with Hawai‘i Volcanoes National Park and the Hawai‘i County Civil Defense Agency about eruptive hazards.
Source et photo : USGS.
Colombia , Puracé – Los Coconucos volcanic chain :
Popayán, December 14, 2025, 8:45 a.m.
Regarding the monitoring of activity in the Los Coconucos volcanic chain, the Colombian Geological Survey (SGC), an agency under the Ministry of Mines and Energy, reports the following:
Since the publication of yesterday’s extraordinary bulletin and up to the date of this announcement, earthquakes related to fluid movements within the volcanic edifice continue to occur. These include long-period (LP) earthquakes, seismic pulses (TR), and continuous tremor. This seismicity is primarily located beneath the Puracé volcano crater, at depths of less than 1 km, and is linked to the internal dynamics of gases and their emission into the atmosphere. In addition, low-magnitude seismic signals, associated with rock fracturing, were recorded within a radius of less than 2 km around the crater of the Purace volcano, at depths of less than 2 km.
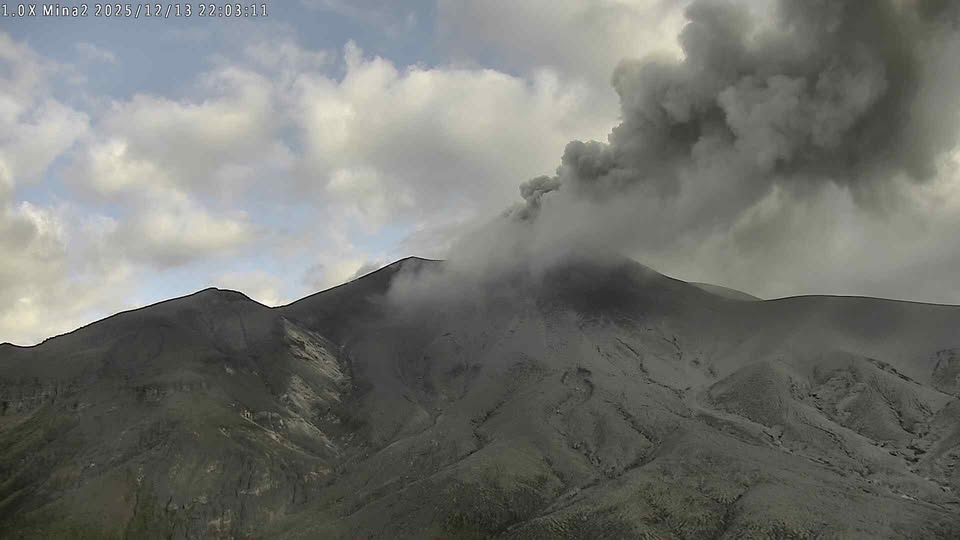
Some seismic signals were associated with ash emissions dispersed mainly to the northwest, following the wind direction, and reached altitudes of up to 700 meters above the volcano’s summit. A total of 10 ash emissions were recorded and alerted the Civil Aviation Authority.
Significant levels of sulfur dioxide (SO2) emissions into the atmosphere continue to be detected by satellite, dispersing primarily to the northwest within a 150-kilometer radius of the volcano. Similarly, temperatures comparable to those observed in previous days continue to be recorded in the crater area, possibly linked to the emission of hot gases from within the volcano.
While the orange alert remains in effect, temporary fluctuations in volcanic activity are possible, meaning that it may occasionally decrease compared to previous days or weeks. However, this does not necessarily mean that the volcano has returned to a stable level of activity. To return to the yellow alert level (increased stability), a reasonable period of time is needed to assess all monitored parameters and detect any trend indicating a return to normal.
Thermal imaging from the Mina camera, located 2.2 km north of the Puracé volcano. Gas and ash plume recorded at 1:19 a.m. on December 14, 2025.
Given the above, the Geological Survey of Colombia (SGC) recommends staying away from the volcano’s crater and surrounding areas, closely monitoring the situation through special bulletins and information published on our official channels, and following the instructions of local and departmental authorities and the National Unit for Disaster Risk Management (UNGRD).
The volcanic activity level remains at ORANGE alert: Volcano exhibiting significant variations in monitored parameters.
Source et photos : SGC.
Indonesia , Marapi :
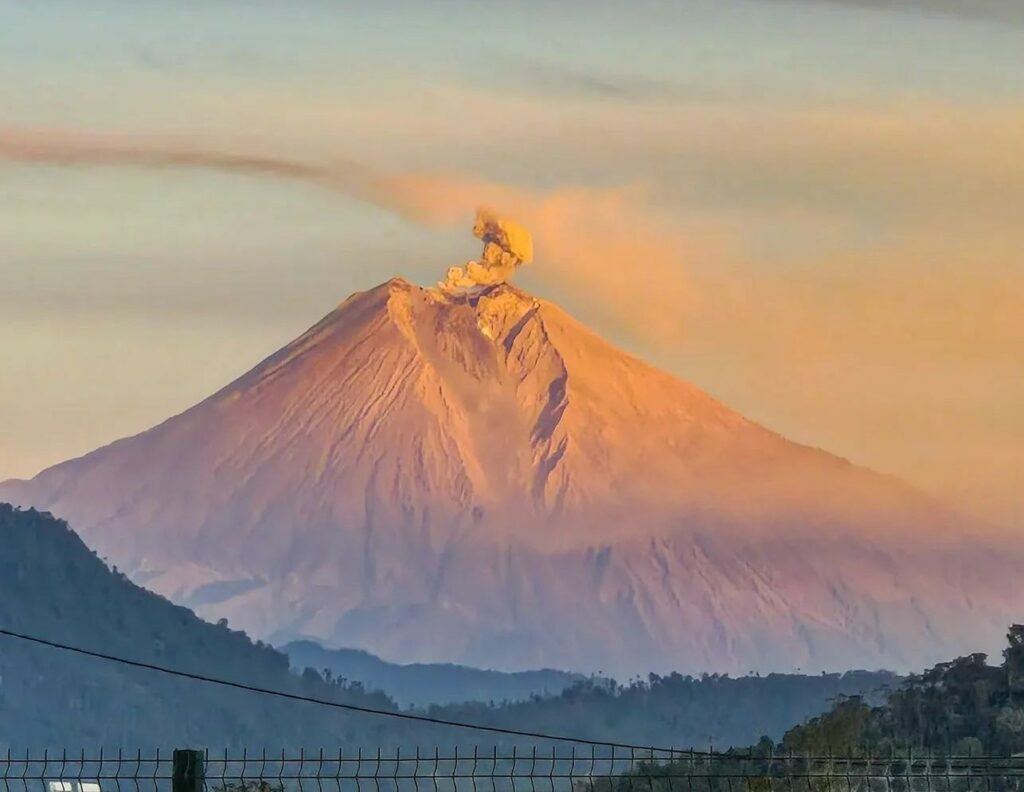
An eruption of Mount Marapi occurred on Sunday, December 14, 2025, at 4:37 PM (Jakarta time). The observed ash column rose approximately 1,200 meters above the summit (at an altitude of about 4,091 meters). Gray in color and of moderate intensity, it drifted northward. This eruption was recorded by a seismograph, with a maximum amplitude of 9.8 mm and a duration of 61 seconds.
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION – VONA
Issued : December 14 , 2025
Volcano : Marapi (261140)
Current Aviation Colour Code : YELLOW
Previous Aviation Colour Code : orange
Source : Marapi Volcano Observatory
Notice Number : 2025MAR086
Volcano Location : S 0 deg 22 min 52 sec E 100 deg 28 min 23 sec
Area : West Sumatra, Indonesia
Summit Elevation : 9251 FT (2891 M)
Volcanic Activity Summary :
Increasing in volcanic activity.
Volcanic Cloud Height :
Best estimate of ash-cloud top is around 13091 FT (4091 M) above sea level or 3840 FT (1200 M) above summit. May be higher than what can be observed clearly. Source of height data: ground observer.
Other Volcanic Cloud Information :
Ash cloud moving to north. Volcanic ash is observed to be gray. The intensity of volcanic ash is observed to be medium.
Remarks :
Eruption recorded on seismogram with maximum amplitude 9.8 mm and maximum duration 61 second.
Source et photo : PVMBG .
Ecuador , Sangay :
DAILY REPORT ON THE STATE OF SANGAY VOLCANO, Sunday, December 14, 2025.
Geophysical Information Institute – EPN.
Surface Activity Level: Moderate, Surface Trend: No Change
Internal Activity Level: Moderate, Internal Trend: No Change
Seismicity: From December 13, 2025, 11:00 AM to December 14, 2025, 11:00 AM:
Seismicity:
Below is the count of seismic events recorded at the reference station:
Explosion (EXP): 165
Rainfall/Lahars:
No rain has been recorded in the volcanic zone. **Heavy rainfall could remobilize accumulated material, generating mudflows and debris flows that would cascade down the volcano’s flanks and flow into adjacent rivers.**
Emission Column/Ash:
Due to cloud cover over the volcano, it was not possible to observe gas and/or ash emissions using surveillance cameras or the GOES-19 satellite system. However, the Washington VAAC agency issued two reports of ash clouds reaching 300 meters in altitude above the crater, drifting northwest and west-southwest.
Other monitoring parameters:
The MIROVA MODIS satellite system recorded two thermal anomalies, the MIROVA VIIRS 375 satellite system also recorded two, and the FIRMS satellite system recorded one in the last 24 hours.
Observations:
From yesterday afternoon until the writing of this report, the volcano remains completely obscured by clouds.
Alert level: Yellow
Source : IGEPN
Photo : Cristopher Cardenas / volcan Sangay / FB.
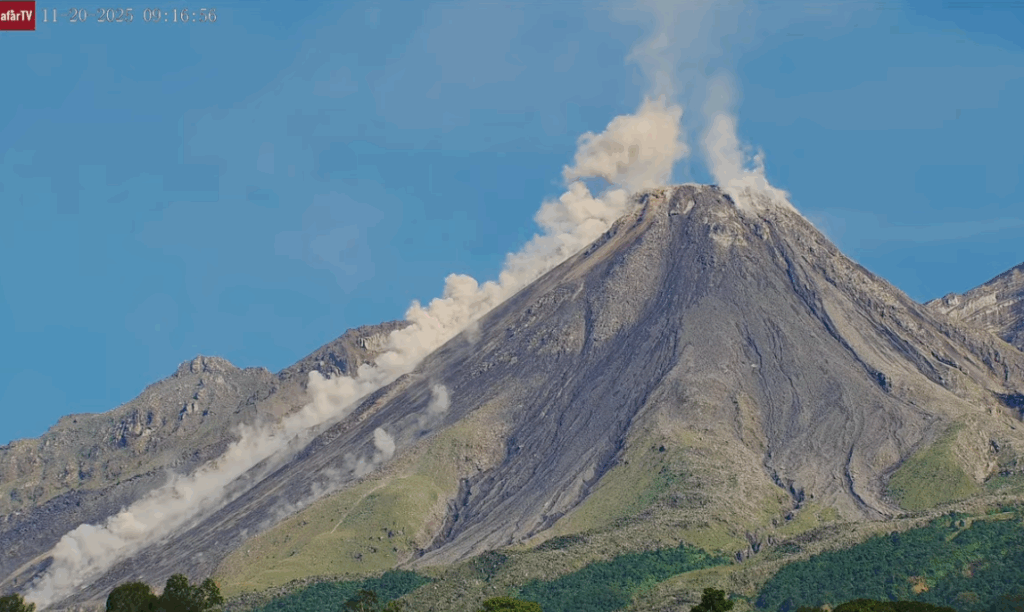
Guatemala , Santiaguito :
Atmospheric conditions: Partly cloudy
Wind: Northeast
Rainfall: 4.60 mm
Activity
The Santiaguito Volcanological Observatory reports unfavorable conditions for observing the dome due to cloud cover. Weak white degassing fumaroles are observed 600 meters above the dome of Doma Caliente, along with weak to moderate explosions at a rate of 3 to 4 per hour, which project columns of gas and ash up to 900 meters in altitude.
These columns are drifting southwest under the influence of the wind. Incandescence may be visible on the dome, as well as the detachment of incandescent rock blocks on the west and southwest flanks. Light ashfall may occur on La Tranquilidad, San Marcos Palajunoj, and the surrounding area due to the wind direction. Because of the significant accumulation of rock material, the Caliente dome and the promontory overlooking the lava flow could collapse and generate long-range pyroclastic flows to the southwest, south, southeast, and northeast. It is therefore imperative to follow the recommendations of Special Bulletin BESAN-063-2025.
Source : Insivumeh .
Photo : AFAR TV ( capture d’écran ).