October 17 , 2025.
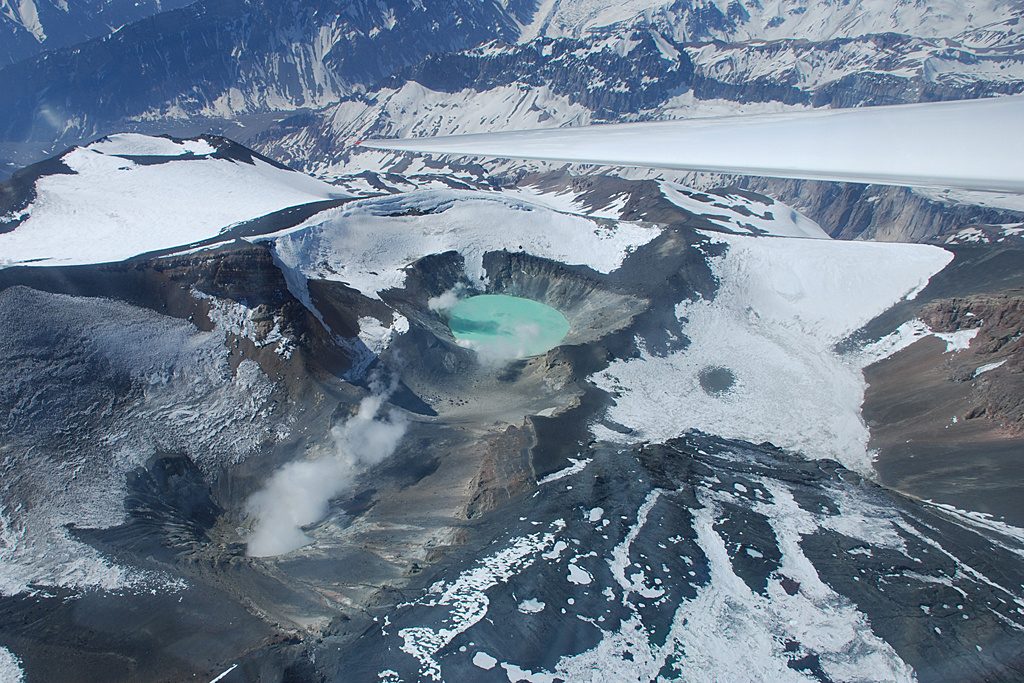
Hawaii , Kilauea :
HAWAIIAN VOLCANO OBSERVATORY STATUS REPORT , U.S. Geological Survey
Thursday, October 16, 2025, 1:14 PM HST (Thursday, October 16, 2025, 23:14 UTC)
19°25’16 » N 155°17’13 » W,
Summit Elevation 4091 ft (1247 m)
Current Volcano Alert Level: WATCH
Current Aviation Color Code: ORANGE
During the lapse in appropriations, the USGS Hawaiian Volcano Observatory (HVO) continues to maintain monitoring networks and issue updates and notifications of volcanic activity via the Hazard Notification Service. Volcano monitoring data will continue to be available on the HVO website. Static website content will not be updated until further notice and information may become outdated over time.
Activity Summary:
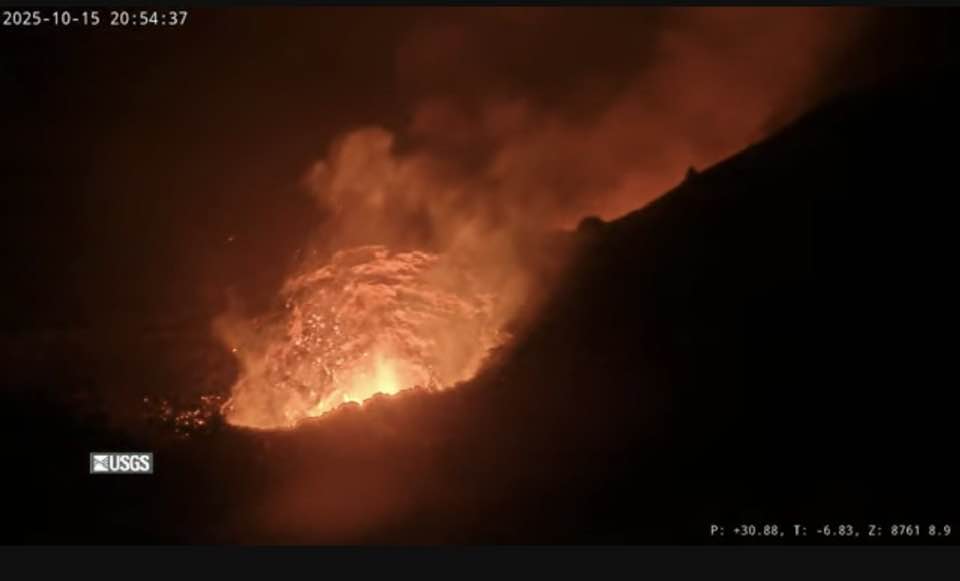
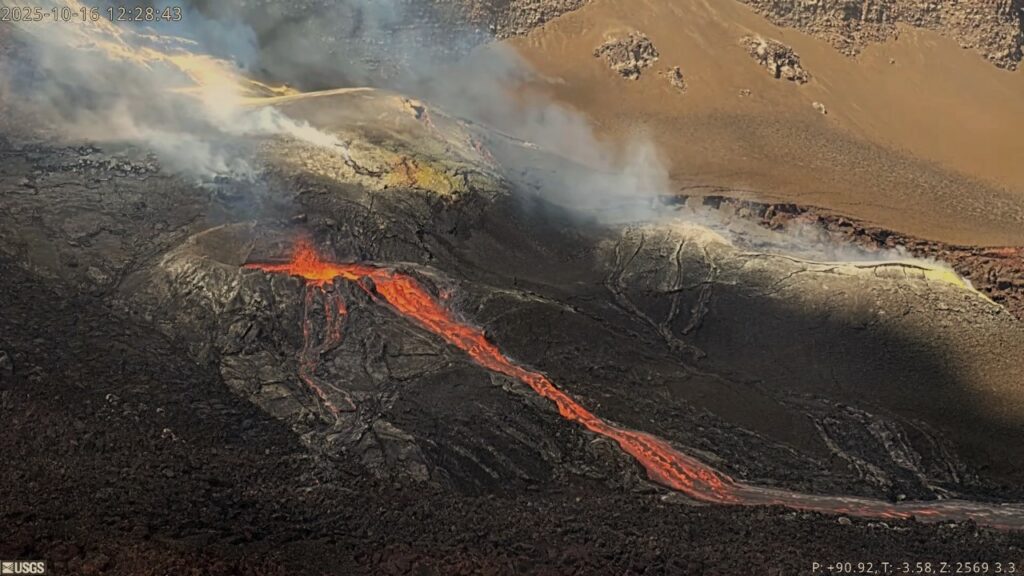
Precursory low-level activity for episode 35 of the ongoing Halemaʻumaʻu eruption increased this morning, October 16, 2025, with a series of lava overflows and drainbacks occurring from the south vent.
Seven lava overflow-drainback events occurred between 7:47 AM and 1:00 PM HST. A table of event times and durations is provided below. Each overflow produced short, channelized lava flows that flowed onto the crater floor. Each overflow event ended with lava suddenly draining back into the south vent. The drainbacks were immediately preceded by a short burst of spattering or small fountaining in the vent.
Additional overflow-drainback events are expected in the coming hours and days, possibly with increased frequency and/or duration. Similar events occurred during the days leading up to the onset of previous episodes. Approximately 100 overflow-drainback events were observed prior to episode 34 fountaining. Precursory activity prior to previous fountaining episodes has lasted from a few hours to a few days and has included eruptive vent spattering, small dome fountains, lava overflows, and lava drainbacks. Current activity therefore suggests that episode 35 fountaining is likely to begin within the next few days.
Forecast models based on the rate of summit inflation indicate that episode 35 lava fountaining is likely to begin between October 17 and 22, 2025, with the most likely dates being between October 18 and 20. The onset of episode 35 lava fountaining may occur sooner if rates of inflation and precursory activity increase.
Summary of south vent lava overflow/drainback events recorded between 7:47 a.m. and 1:00 p.m. HST, October 16:
Overflow Start time Overflow End time Duration (hr:mm)
10/16/25 7:35 AM 10/16/25 7:47 AM 0:12
10/16/25 8:50 AM 10/16/25 9:03 AM 0:13
10/16/25 9:29 AM 10/16/25 9:34 AM 0:05
10/16/25 10:47 AM 10/16/25 10:51 AM 0:04
10/16/25 11:12 AM 10/16/25 11:26 AM 0:14
10/16/25 11:54 AM 10/16/25 12:28 PM 0:34
10/16/25 12:41 AM 10/16/25 12:54 PM 0:13
As reported in this morning’s Kīlauea Daily Update, nearly continuous strong glow was visible from both the north and south vents last night, indicating that magma within the conduits is close to the surface. Intermittent spattering in the north vent became visible just after dark last night. Infrequent spattering also occurred from the south vent after 10:00 p.m. HST. Seismic tremor changed from continuous to irregular gas pistoning last night. Kīlauea’s summit region continued to inflate over the past 24 hours. The UWD tiltmeter shows continued inflationary tilt and has recovered more than 22 microradians since episode 34 ended. Inflation rates increased on October 15 to approximately 2 microradians per day.
At the start of previous episodes, precursory activity has rapidly escalated into sustained high fountaining over minutes to tens of minutes. During previous episodes, fountains reached heights of more than 1,000 feet (300 meters) and the eruptive plume reached heights of up to 20,000 feet (6,000 meters) above ground level soon after sustained high fountaining began.
Source et photos : HVO.
Indonesia , Lewotobi Laki-laki :
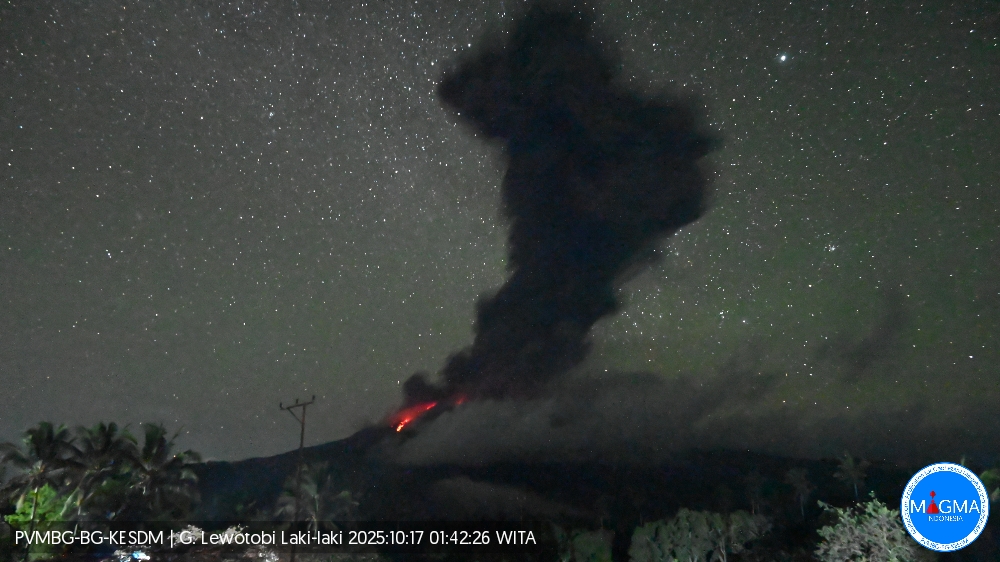
An eruption occurred at Mount Lewotobi Laki-laki on Friday, October 17, 2025, at 1:41 a.m. (local time). An ash column was observed about 4,000 m above the summit (about 5,584 m above sea level). The ash column was gray and dense toward the southwest, west, and northwest. At the time of writing, the eruption was still ongoing.
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION – VONA
Issued : October 17 , 2025
Volcano : Lewotobi Laki-laki (264180)
Current Aviation Colour Code : ORANGE
Previous Aviation Colour Code : red
Source : Lewotobi Laki-laki Volcano Observatory
Notice Number : 2025LWK488
Volcano Location : S 08 deg 32 min 20 sec E 122 deg 46 min 06 sec
Area : East Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia
Summit Elevation : 5069 FT (1584 M)
Volcanic Activity Summary :
Eruption with volcanic ash cloud at 17h41 UTC (01h41 local).
Volcanic Cloud Height :
Best estimate of ash-cloud top is around 17869 FT (5584 M) above sea level or 12800 FT (4000 M) above summit. May be higher than what can be observed clearly. Source of height data: ground observer.
Other Volcanic Cloud Information :
Ash cloud moving from southwest, west to northwest. Volcanic ash is observed to be gray. The intensity of volcanic ash is observed to be thick.
Remarks :
Eruption recorded on seismogram with maximum amplitude 47.3 mm and maximum duration 179 second.
Source et photo : Magma Indonésie.
Colombia , Puracé – Los Coconucos volcanic chain:
Popayán, October 14, 2025, 3:00 p.m.
Regarding the monitoring of the activity of the Puracé Volcano – Los Coconucos Volcanic Range, the Colombian Geological Survey (SGC), an entity affiliated with the Ministry of Mines and Energy, reports that:
During the week of October 7 to 13, 2025, a continuous volcanic tremor signal continued to be recorded persistently, associated with increased degassing from the crater of the Puracé Volcano. The earthquakes, related to fluid movements, were characterized by low energy input and were mainly located beneath the western flank of the crater of the Puracé Volcano, at a depth of less than 1 km. Compared to previous weeks, the number of fracture earthquakes remained stable, mainly located between the Puracé, Piocollo, and Curiquinga volcanoes, at depths ranging from 1 to 3 km, with magnitudes up to 1.4. Satellite and field instrument measurements showed that sulfur dioxide (SO2) emissions remained stable, with values similar to those of previous weeks.
Furthermore, the slow deformation process detected after the eruption of the Curiquinga volcano on January 20, 2025, persists.
Images captured by satellite sensors and visible and infrared webcams continued to observe degassing processes, with a maximum column height of 2 km, measured from the summit of Puracé Volcano, and thermal anomalies in the crater and fumarole field on the outer rim.
In conclusion, the variations observed at Puracé Volcano (Los Coconucos volcanic chain) indicate that the system remains active and that monitoring parameters remain above their reference levels. Therefore, the community is advised to avoid any ascent to the upper part of the volcanic chain. At yellow alert status, phenomena such as sporadic ash emissions (minor eruptions of limited magnitude and impact, whose dispersion depends on wind direction), the presence of incandescent light, small explosions in the crater, low-energy thermal anomalies, noise, felt earthquakes, odors, precipitation of elemental sulfur near the crater, in hot springs and fumaroles, as well as degassing outside the crater, may occur. Fissure formation and the formation of minor lahars, among other things, may also occur.
The alert status for volcanic activity remains yellow: an active volcano exhibiting changes in the baseline behavior of monitored parameters and other manifestations.
Source et photo : SGC.
Chile , Tupungatito :
Seismology
Seismological activity during this period was characterized by:
319 VT-type earthquakes, associated with rock fracturing (volcano-tectonics).
102 LP-type earthquakes, associated with fluid dynamics within the volcanic system (long period). The magnitude of the largest earthquake, assessed by the reduced displacement (RD) parameter, was 6 cm².
One TR-type earthquake, associated with sustained fluid dynamics within the volcanic system (TRemor). The magnitude of the earthquake, assessed by the reduced displacement (RD) parameter, was 1 cm².
Eight VLP-type earthquakes, associated with the dynamics of large volumes of fluid within the volcanic system (very long period). The size of the largest earthquake, assessed by the reduced displacement (RD) parameter, was 99 cm².
The previous report indicated a significant change in the volcano’s seismic activity, with a notable episode on August 28. This episode combined VT earthquakes with fluid-related seismicity, including for the first time VLP earthquakes at this volcano. Since this event, the volcanic system has not returned to its usual level; rather, it has maintained slightly increased activity, with the occurrence of new VLP earthquakes, suggesting changes in the volcano’s internal dynamics.
Fluid Geochemistry
No anomalies in sulfur dioxide (SO₂) emissions into the atmosphere were reported in the area near the volcano, according to data published by the Tropospheric Monitoring Instrument (TROPOMI) and the Sulfur Dioxide Group of the Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI).
Satellite Thermal Anomalies
During the period under review, no thermal alerts were recorded in the area associated with the volcano, according to analytical processing of Sentinel 2-L2A satellite images, using a combination of false-color bands.
Satellite Geomorphological Analysis
Processing of Planet Scope Scene and Sentinel 2-L2A satellite images revealed no morphological changes in the volcanic system. Degassing was observed in active craters, which is typical of the volcanic system.
Activity remained at levels considered low, suggesting the volcano’s stability. The Volcanic Technical Alert remains in effect:
GREEN TECHNICAL ALERT: Active volcano with stable behavior – No immediate risk
Source et photo : Sernageomin .
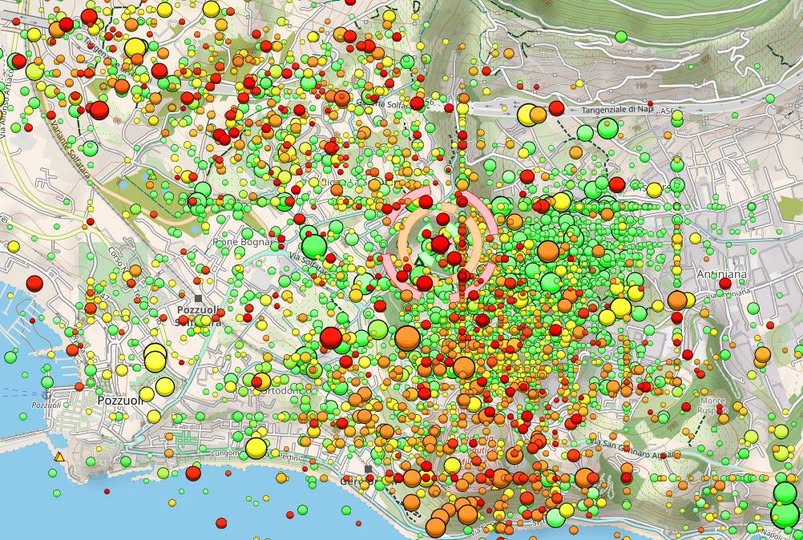
Italy , Campi Flegrei :
Weekly Bulletin, from October 6, 2025 to October 12, 2025. (Publication date: October 14, 2025)
SUMMARY OF ACTIVITY STATUS
Based on monitoring data, the following points should be noted:
1) SEISMOLOGY: During the week of October 6 to 12, 2025, 166 earthquakes with magnitude Md ≥ 0.0 (Mdmax = 2.5 ± 0.3) were recorded in the Phlegraean Fields region.
2) DEFORMATION: Since the beginning of April 2025, ground uplift has continued to be recorded, with a monthly average value of approximately 15 ± 3 mm/month. 3) GEOCHEMISTRY: During the reporting week, the geochemical parameters monitored confirmed the long-term trend of warming of the hydrothermal system and the increase in flow rates already known (see Monthly Bulletins).
SEISMOLOGY
From October 6 to 12, 2025, 166 earthquakes with a magnitude Md ≥ 0.0 (Mdmax = 2.5 ± 0.3) were recorded in the Phlegraean Fields region.
81 earthquakes were recorded during five seismic swarms:
1. On October 6, 2025, at 06:05 UTC, seven earthquakes with a magnitude Md ≤ 1.5 (± 0.3) occurred in the Solfatara region;
2. On October 8, 2025, at 11:46 UTC, five earthquakes with a magnitude Md ≤ 1.7 (± 0.3) occurred in the Pozzuoli-Solfatara region. 3. On 10/11/2025 at 02:05 UTC: 17 earthquakes with magnitude ≤ Md ≤ 1.8 (± 0.3) occurred in the Pozzuoli-Solfatare region.
4. On 10/11/2025 at 14:33 UTC: 26 earthquakes with magnitude ≤ Md ≤ 1.7 (± 0.3) occurred in the Pozzuoli-Solfatare region.
5. On 10/12/2025 at 15:01 UTC: 26 earthquakes with magnitude ≤ Md ≤ 2.5 (± 0.3) occurred in the Solfatara region.
Source : INGV Vulcani .
Photo : INGV via Marc Szeglat / FB