August 25 , 2025.
Italy / Sicily , Etna :
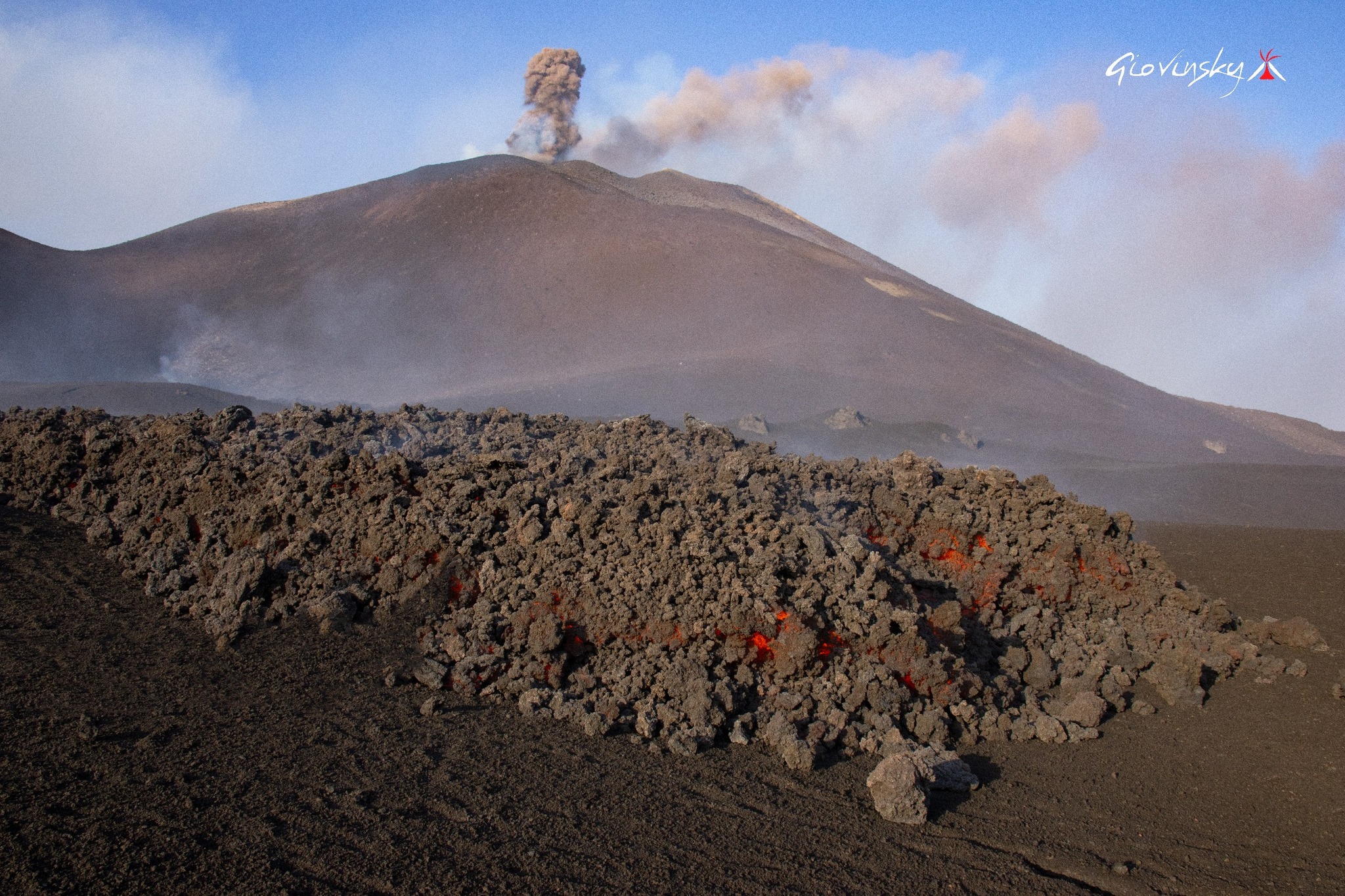
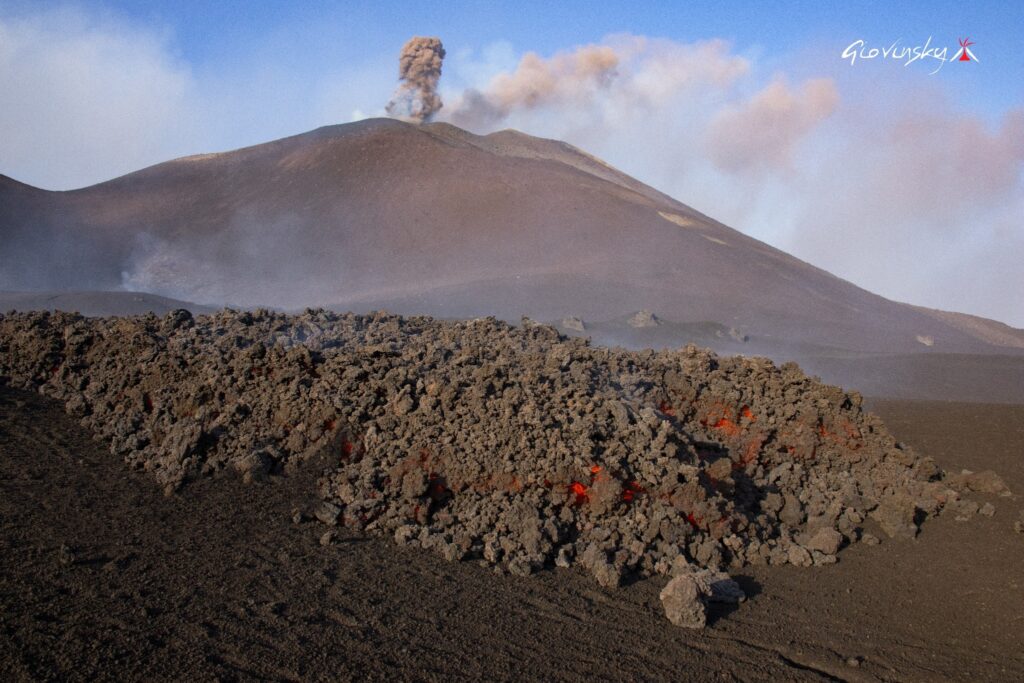
Etna Activity Report, August 24, 2025, 6:45 PM (4:45 PM UTC).
The National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology, Osservatorio Etneo, reports that, according to volcanological observations made by INGV personnel at the summit and analysis of images acquired by the video surveillance network, effusive activity is continuing at the vent located at an altitude of 3,200 m, on the southern flank of the southeast crater, which feeds a lava field divided into several branches propagating southwest and south.
The most advanced front toward the southwest reached an altitude of 2,950 m.
The most advanced front toward the south reached an altitude of 2,980 m.
Furthermore, effusive activity continues at the chimney located at an altitude of 3,100 m, feeding a lava flow directed towards the southwest, the most advanced front of which has reached an altitude of 3,000 m. The lava flow emitted by the chimney located at an altitude of 2,980 m is no longer fed and is cooling. Strombolian activity continues at the southeast crater, characterized by emissions of pyroclastic materials falling beyond the crater rim. Sporadic emissions of volcanic ash have also been observed, rapidly diluted and dispersed by high-altitude winds.
The average amplitude of the seismic tremor, since the early hours of the day, has gradually decreased, while remaining in the high range. The centroid of the tremor sources is still located in the Southeast Crater area, at a depth of approximately 3,000 meters above mean sea level. Infrasound activity is discontinuous, with low-amplitude events located in the Southeast Crater. Ground deformation signals recorded by GNSS (HF) and inclinometer networks currently show no significant variation. The DRUV dilatometer station continues to indicate a slow variation in decompression, accumulating to date, since the beginning of the current effusive activity, a total of approximately -28 nano-deformations.
In particular, consistent with volcanological observations, the dilatometer signal shows a slight variation in slope, accumulating a lower daily variation than that reported in recent days.
Updates will be communicated shortly.
Source : INGV
Photo : Giovinsky Aetnensis
Iceland , Hafrafellslón :
Beginning of a glacial jökulhlaup at Hafrafellslón, west of Langjökull
August 22, 2025
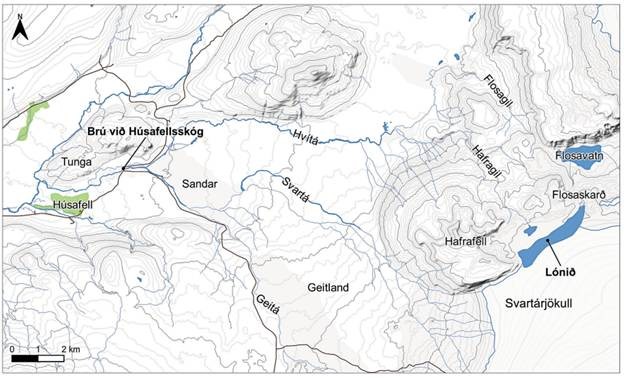
Water flows into the Svartá River, then into Hvítá, in Borgarfjörður.
The reservoir water level appears higher than ever, and it is possible that the flash flood will be more severe than in 2020.
Local residents are advised to assess the potential impact on property and livestock along the banks of the Hvítá.
The course of the flash flood is highly uncertain, but the speed of the flow increase will largely determine the maximum flow and its spread.
The water level at Hafrafellslón, west of Langjökull, appears higher than ever. In recent weeks, experts from the Icelandic Meteorological Office have been monitoring the reservoir’s development using satellite images. Hafrafellslón is a marginal reservoir where glacier meltwater accumulates in summer. The last major flood caused by a glacier break occurred in August 2020, and another, smaller one occurred in the summer of 2021.
Close-up of the area from Húsafell to Langjökull
Satellite images taken on August 20th showed signs of the reservoir emptying. Yesterday, the Icelandic Meteorological Office received reports from local residents that water had begun flowing from the reservoir over the edge of the glacier, then towards Svartá, which then flows into Hvítá above Húsafell.
Since last night, the water level at Hvítá, upstream of Húsafell, has risen, a clear sign that the flash flood has begun to reach the river. For now, the water level is still within the limits measured during heavy flooding due to rainfall, but it is expected to continue rising in the coming days.
Source : IMO.
Photo : carte : Bureau météorologique islandais et Service topographique islandais. Carte tirée d’un rapport de 2021.
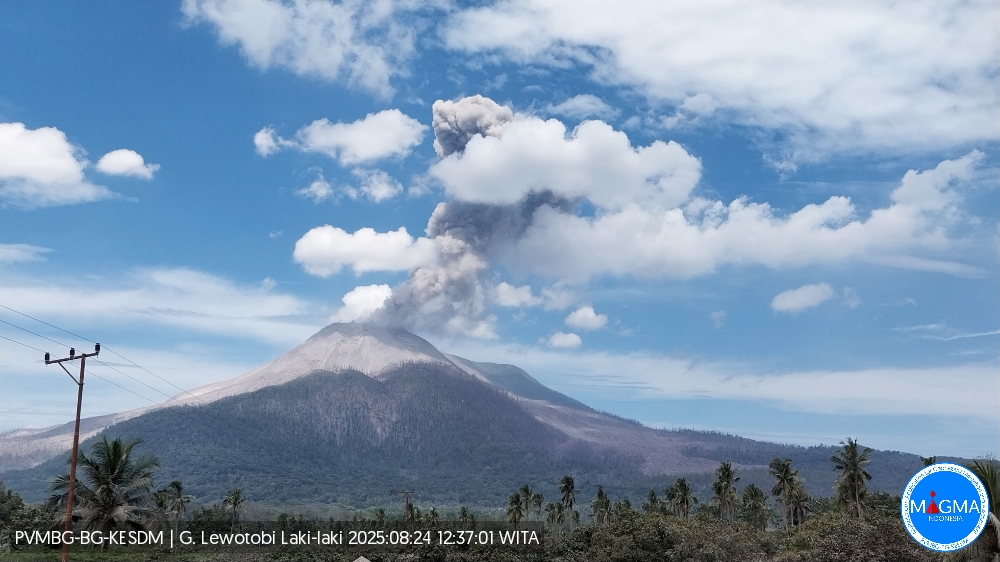
Indonesia , Lewotobi Laki-laki :
An eruption of Mount Lewotobi Laki-laki occurred on Sunday, August 24, 2025, at 12:33 WITA. The observed ash column was ± 2,000 m above the summit (± 3,584 m above sea level). The ash column was gray and of strong intensity, oriented towards the southwest and west. This eruption was recorded by seismograph with a maximum amplitude of 7.4 mm and a duration of 182 seconds.
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION – VONA
Issued : August 24 , 2025 .
Volcano : Lewotobi Laki-laki (264180)
Current Aviation Colour Code : ORANGE
Previous Aviation Colour Code : orange
Source : Lewotobi Laki-laki Volcano Observatory
Notice Number : 2025LWK389
Volcano Location : S 08 deg 32 min 20 sec E 122 deg 46 min 06 sec
Area : East Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia
Summit Elevation : 5069 FT (1584 M)
Volcanic Activity Summary :
Eruption with volcanic ash cloud at 04h33 UTC (12h33 local).
Volcanic Cloud Height :
Best estimate of ash-cloud top is around 11469 FT (3584 M) above sea level or 6400 FT (2000 M) above summit. May be higher than what can be observed clearly. Source of height data: ground observer.
Other Volcanic Cloud Information :
Ash cloud moving from southwest to west. Volcanic ash is observed to be gray. The intensity of volcanic ash is observed to be thick.
Remarks :
Eruption recorded on seismogram with maximum amplitude 7.4 mm and maximum duration 182 second.
Source et photo : Magma Indonesia .
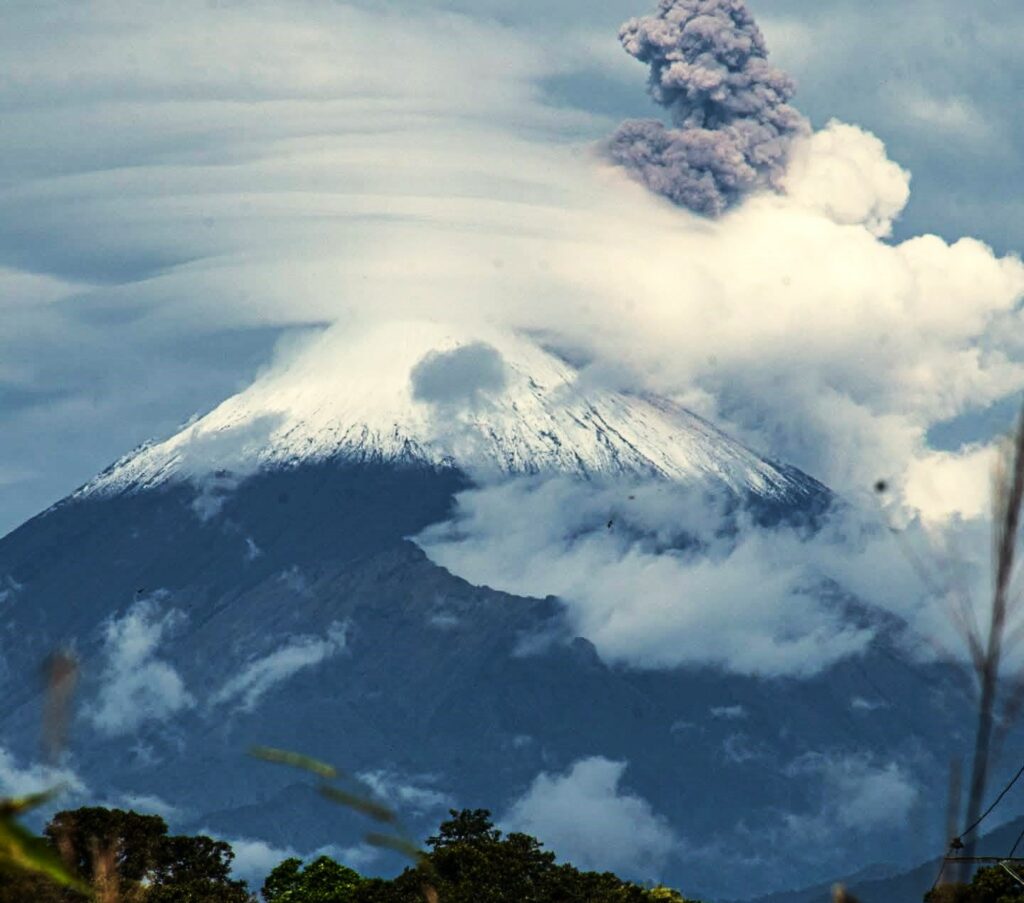
Ecuador , Sangay :
DAILY STATUS REPORT OF SANGAY VOLCANO, Sunday, August 24, 2025.
Information Geophysical Institute – EPN.
Surface Activity Level: High, Surface Trend: Descending
Internal Activity Level: Moderate, Internal Trend: No Change
Seismicity: From August 23, 2025, 11:00 a.m. to August 24, 2025, 11:00 a.m.:
Seismicity:
Below is the count of seismic events recorded at the reference station.
Explosion (EXP): 46
Precipitation/Lahars:
No rainfall has been recorded in the volcanic area. **Heavy rainfall could remobilize accumulated material, generating mud and debris flows that would cascade down the volcano’s flanks and flow into adjacent rivers.**
Emission/Ash Column:
Due to cloud cover near the volcano, no gas and/or ash emissions were observed by the surveillance camera network or the GOES-19 satellite system. Additionally, the Venezuelan Meteorological Agency (VAAC) in Washington reported an altitude of 850 m NSC in a westerly direction.
Gas:
The Mounts satellite system did not detect any SO2 emissions over Sangay in the past 24 hours.
Observation:
From yesterday afternoon until the closing of this report, the volcano remained completely cloudy.
Alert level: yellow
Source : IGEPN
Photo : Cristopher Cárdenas , 11/07/2025
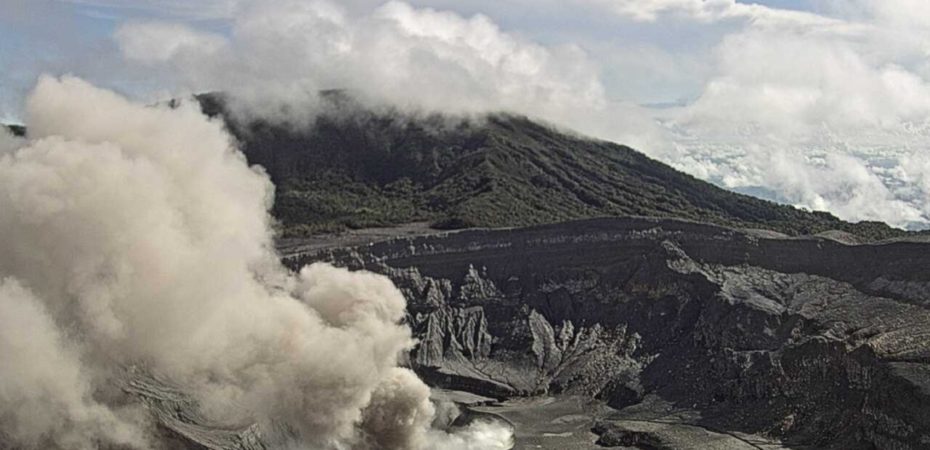
Costa Rica , Poas :
Latitude: 10.20°N;
Longitude: 84.23°W;
Altitude: 2,687 m
Current Activity Level: Alert
This week, a slight continuous ash emission was recorded at Boca A. It began on August 20 at 8:00 a.m. and lasted for several hours.
The seismic amplitude of the tremor remained low over the past week. It sometimes becomes harmonic with a frequency of approximately 3 Hz. From August 18 to 21, banded tremor was observed. A continuous acoustic tremor of moderate amplitude was also recorded. Additionally, distal VT-type volcanotectonic earthquakes were recorded on August 19 at 11:52 and 13:05, on August 20 at 3:51 and 4:55, and on August 21 at 21:14. Proximal volcanotectonic earthquakes also occurred on August 19 at 22:58 and on August 20 at 6:14. The number of long-period events remains similar to that of the previous week.
In recent weeks, no significant deformation of the volcano has been detected.
MultiGAS stations measured an average SO2/CO2 ratio of 1.5 ± 0.4 this week, similar to last week. The H2S/SO2 ratio has remained very low (< 0.1) in recent weeks. Based on observed ratios, the gases are interpreted to be originating from a surface magmatic source. DOAS stations measured an SO2 flux of 297 ± 48 t/d. Satellite measurements of atmospheric SO2 show a slight increase compared to July. A peak value of approximately 600 tons was recorded on August 16. Sentinel 2’s SWIR satellite sensor has detected several significant thermal anomalies since early June in Poás Crater, the most recent on August 12 and the highest on August 7. Webcam observations and remote field measurements demonstrate a variability of several hundred degrees Celsius in the temperature of the gas emitted by Boca A from one day to the next.
For example, on August 6, a maximum temperature of 600°C was measured near the rim of Boca A, and on August 7, a maximum temperature of over 800°C was measured from a drone at a distance of 80 meters.
(CNE information).
This week, a temperature above 520°C was measured 600 meters from El Mirador, a high value, and pulses of incandescent gas were observed at night. The volcanic plume remains rich in water vapor, sulfur dioxide, and aerosols (which give it a bluish color) and is dispersed by the prevailing winds toward the west-southwest of the volcano. The level of the new hyperacid lake at Boca C remained stable this week.
Given the significant gas and heat flux persisting at Boca A, as well as the recent phreatomagmatic activity, a large and sudden eruption cannot be ruled out, even in the absence of precursor signals, and could affect the visited areas of the National Park (e.g., ballistic projections projected towards the Mirador). Level 2 (Caution) does not rule out ballistic events in the visited areas. Any phase of activity carries a potential risk.
Source et photo : Ovsicori .