June 11 , 2025 .
Italy / Sicily , Etna :
WEEKLY BULLETIN, from June 2, 2025 to June 8, 2025 (publication date: June 10, 2025)
ACTIVITY STATUS SUMMARY
Based on monitoring data, the following points are highlighted:
1) VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS: Lava fountaining activity, effusive activity, and pyroclastic flows originating from the Southeast Crater, and degassing from the Bocca Nuova Crater, the Voragine Crater, and the Northeast Crater.
2) SEISMOLOGICAL: Absence of seismic activity due to fracturing with Ml >=2.0. Medium tremor amplitude; high during the paroxysmal episode at the Southeast Crater.
3) INFRASOUND: Mainly medium infrasound activity; high during the paroxysmal episode at the Southeast Crater.
4) GROUND DEFORMATION: Ground deformation monitoring networks did not record significant variations, except for slight variations in tilt/deformation during the June 2 activity.
5) GEOCHEMISTRY: Average SO2 flux.
Soil CO2 flux (EtnaGas Network): increasing, at average values.
Dissolved CO2 in groundwater (EtnaAcque Network): average to low values, within seasonal variability.
Helium isotope ratio at peripheral sites: no update; the latest data indicated average to high values (May 19).
6) SATELLITE OBSERVATIONS: Thermal activity observed by satellite in the summit area was generally moderate. High to very high levels were observed, corresponding to lava fountains and pyroclastic activity produced by the Southeast Crater on June 2, 2025.
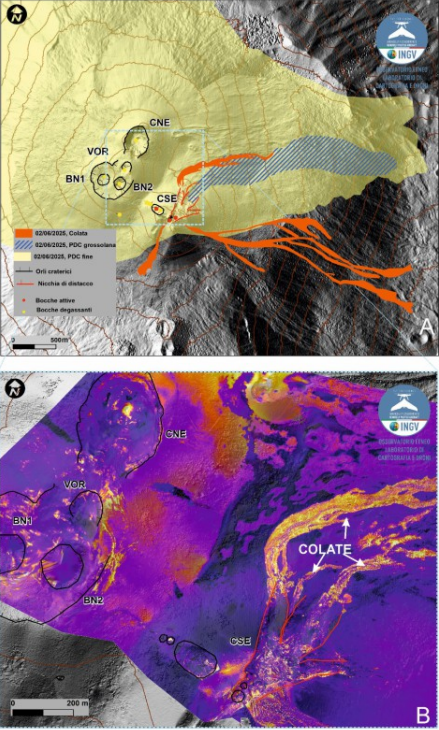
Map of the summit area of Mount Etna superimposed on the shaded relief, obtained by processing drone images acquired on June 4. Geoidic contours are plotted every 100°C. CSE = Southeast Crater, CNE = Northeast Crater, VOR = Voragine, BN = Bocca Nuova. B) Thermal orthomosaic.
VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS
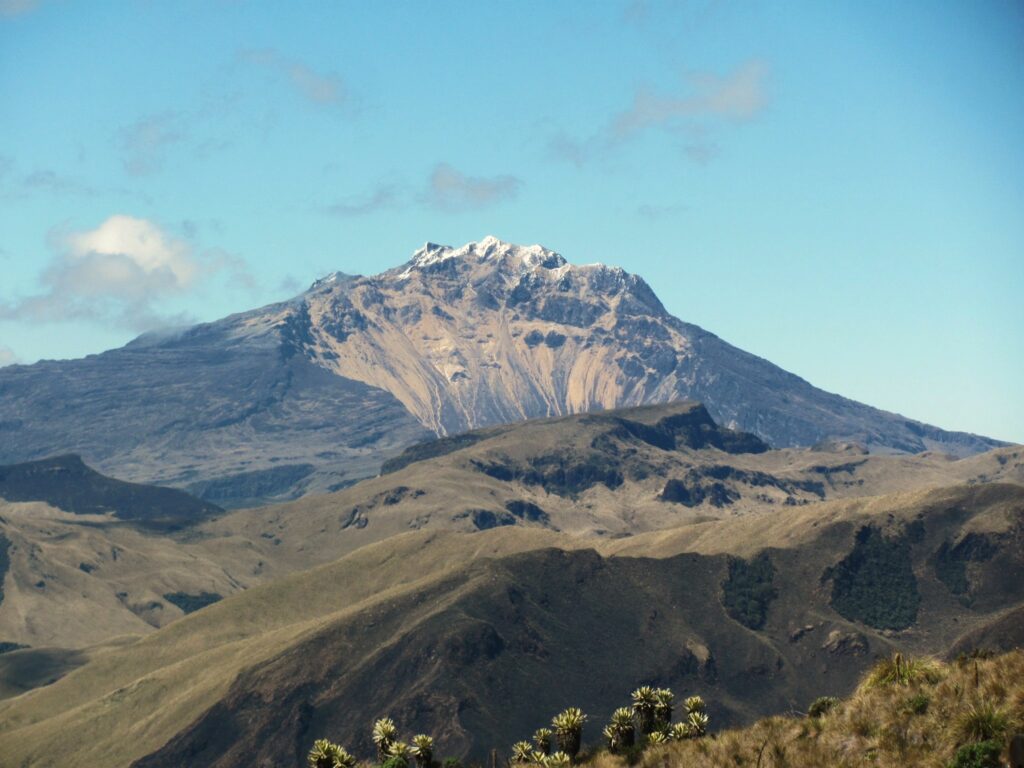
During the week, volcanic activity at Mount Etna was monitored through the analysis of images from the INGV-OE (Etneo Observatory) surveillance cameras, as well as through a field inspection carried out by the INGV-OE team on June 4 using drones and satellite images. Overall, during the observation period, Etna was characterized by a paroxysmal event with pyroclastic flow at the Southeast Crater (SCC) and degassing of varying intensity at the Bocca Nuova (BN), Northeast Crater (CNE), and Voragine (VOR) craters.
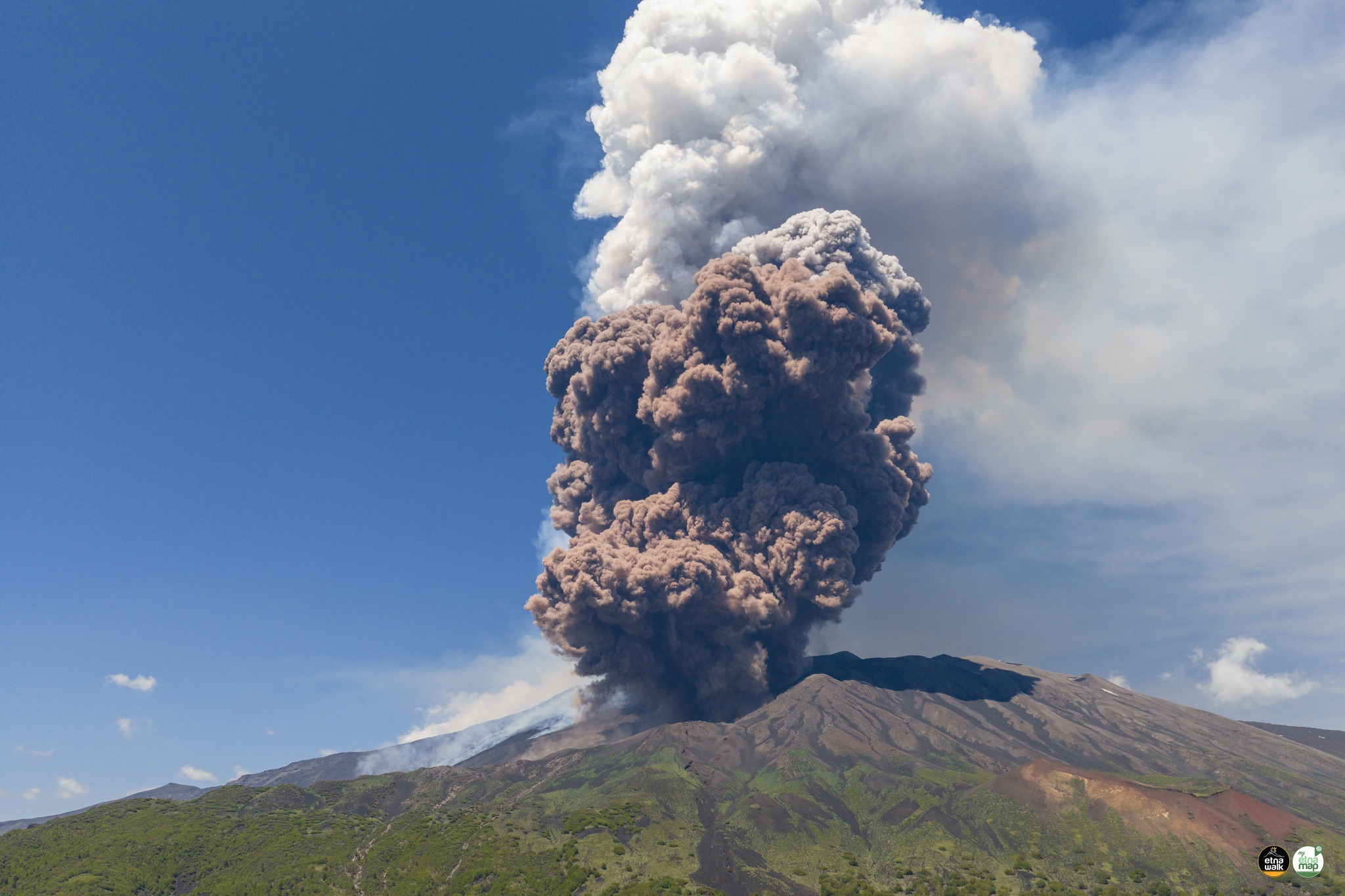
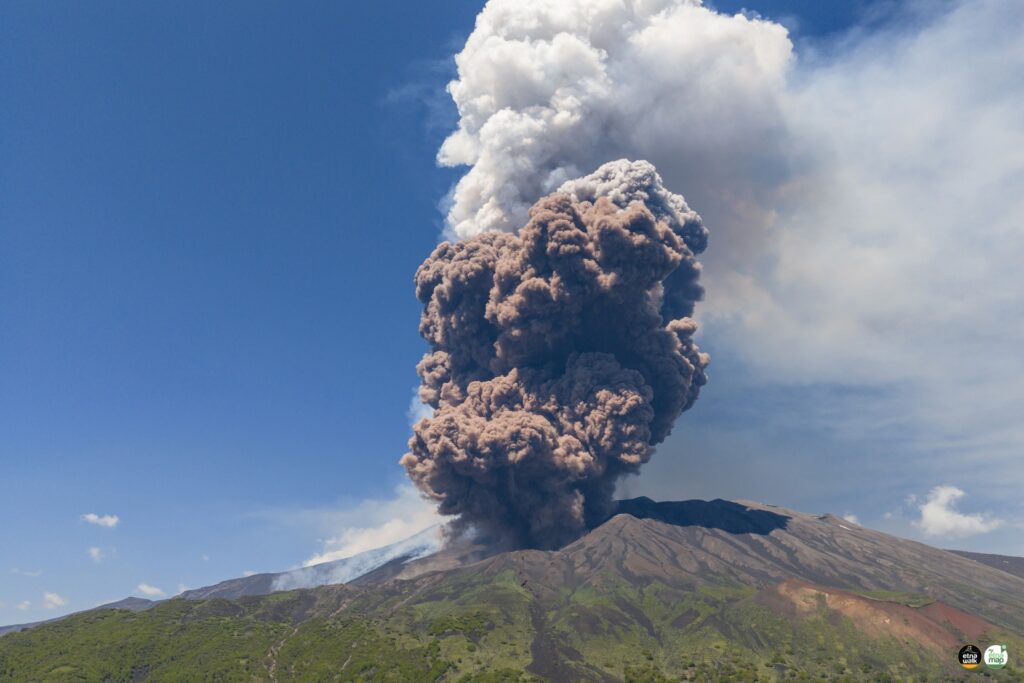
In particular, after the eruptive activity of May 12, characterized by Strombolian activity and lava flows, on June 2, after 20 days, the Southeast Crater (SCC) fueled a new eruptive episode. Strombolian activity began at 01:52 UTC (all times in UTC), although a weak thermal anomaly associated with intracrater activity was observed as early as 23:50 on June 1.
Strombolian activity gradually intensified, transforming into a lava fountain at 8:05 AM, with the development of a dense eruptive column starting around 8:37 AM. At the same time, at 2:40 AM, a lava flow began to flow from the south side of the CSE, and at 3:19 AM, a new lava flow flowed from the east side. At 8:48 AM, the opening of an eruptive fissure was also observed on the northeast side of the cone of the Southeast Crater (CSE), from which a third lava flow was generated.
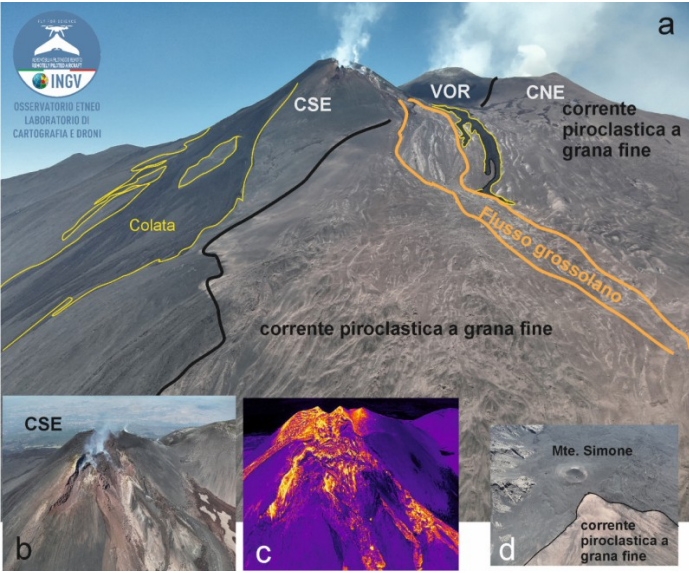
At 9:23 AM, in the same area of the northeast flank of the cone, the development of a fracture was observed, characterized by the emission of dense white vapor, from which a reddish pyroclastic flow rapidly formed, gaining height and spreading rapidly downstream. Locally along the fracture, the presence of dark ash is also observed, probably due to the interaction between snow and hot materials, as highlighted by the strong explosions that occur at two points at the base of the CSE about 47 seconds after the start of the pyroclastic flow. The flow traveled a distance of about 3 km at an average speed estimated at about 140 km/h, stopping just upstream of Monte Simone. From 10:00, the lava flow activity gradually decreases to cease around 10:45; the episode gradually ends around 03:00 on June 3.
Overall, the paroxysmal episode generated an eruptive cloud laden with reddish material, associated with the pyroclastic flow. This cloud reached a maximum altitude of about 11 km above sea level and fed lava flows that propagated in south, southeast, and northeast directions. The most advanced fronts reached a minimum altitude of 1880 m above sea level, for a total volume of 7.6 x 10^5 m^3.
Regarding the pyroclastic flow, the densest, coarse-grained part propagated towards Monte Simone, reaching an altitude of 2150 m above sea level and covering an area of 2.5 x 10^5 m^2. The fine-grained, reddish-colored portion was scattered in a semicircle around the northern sector of the summit area, from east to west, covering an area of 2.5 x 10^7 m^2 and falling on the localities of Cesarò and Bronte.
Furthermore, during the inspection, a detachment niche was detected, formed following the collapse of a part of the upper northeastern flank of the CSE. This niche is approximately 300 m long and 260 m wide. The volume of material detached from this niche is 1.0 x 10^6 m^3 (error 30%).
Drone image of the Valle del Bove and Valle del Leone. The yellow lines delineate the flows, the black lines the fine-grained reddish pyroclastic flow, and the orange lines the coarser pyroclastic flow. (b) and (c) visible and thermal images of the CSE and the detachment niche. (d) the most advanced part of the deposit near Monte Simone.
Regarding the other summit craters, during the week of observation, the Bocca Nuova crater was characterized by degassing from BN-2 and some fumarolic zones. In addition, still from BN-2, weak ash emissions were observed, rapidly dispersing in the summit area. The Voragine crater fueled widespread fumarolic activity, and the Northeast crater experienced degassing, sometimes accompanied by booms, from an active vent on the crater floor.
Source : INGV.
Photos : INGV , Etna Walk /Giuseppe Distefano / Marco Restivo / FB , Guy de Saint Cyr , INGV.
Italy , Stromboli :
WEEKLY BULLETIN, from June 2, 2025 to June 8, 2025 (publication date: June 10, 2025)
SUMMARY OF ACTIVITY STATUS
Based on monitoring data, the following points are highlighted:
1) VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS: During this period, ordinary Strombolian eruptive activity was observed. The total hourly frequency ranged between average values (9 to 15 events/h). The intensity of the explosions was low and medium in the North and South-Central crater areas.
2) SEISMOLOGY: The monitored seismological parameters do not show any significant variations.
3) GROUND DEFORMATION: Ground deformation monitoring networks did not show any significant variations.
4) GEOCHEMISTRY: SO2 flux: at an average level. Soil CO2 flux in the Pizzo area (STR02): No update.
C/S ratio in the plume: High to very high values.
Dissolved helium isotope ratio (R/Ra) in the thermal aquifer: No update.
Soil CO2 flux in the San Bartolo area: No update.
Soil CO2 flux in the Scari area: Medium to low values.
5) SATELLITE OBSERVATIONS: Thermal activity observed by satellite in the summit area was generally low.
VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS
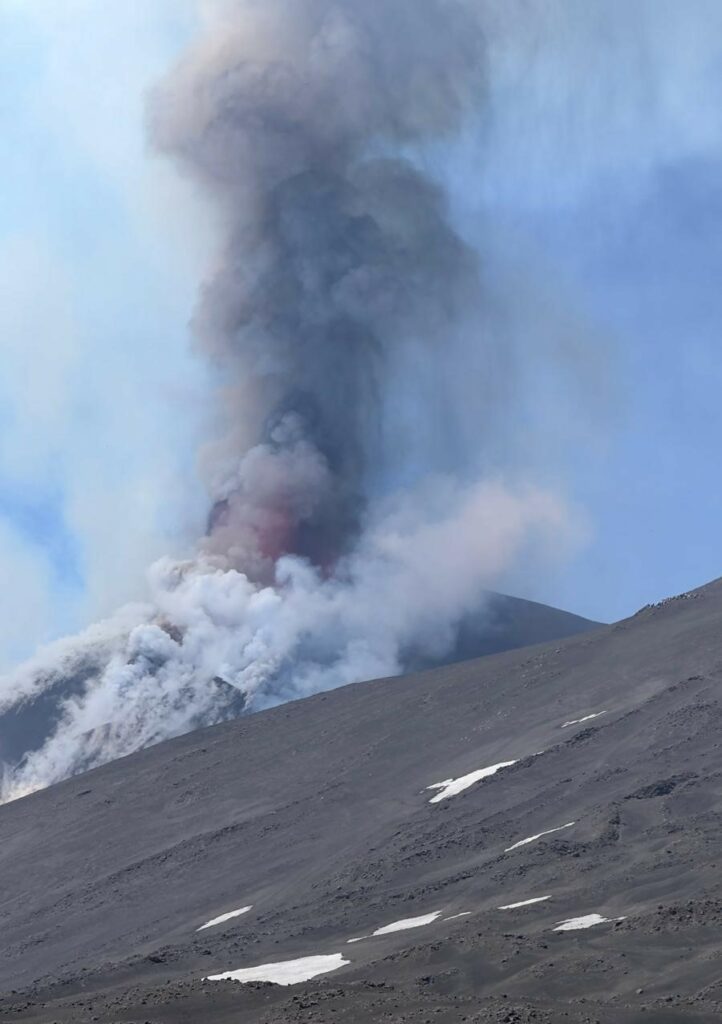
During the observation period, Stromboli’s eruptive activity was characterized by analyzing images recorded by INGV-OE surveillance cameras located at an altitude of 190 m (SCT-SCV) and at Punta dei Corvi (SPCT). Explosive activity was mainly produced by four eruptive vents located in the North Crater area and by at least two vents located in the Central-South area.
Observations of explosive activity recorded by surveillance cameras
In the North Crater (N) area, four active vents were observed, producing low-intensity explosive activity (less than 80 m in height) and sometimes medium-intensity explosive activity (less than 150 m in height). The eruptive products consisted mainly of coarse materials (bombs and lapilli). The average explosion frequency ranged from 6 to 11 events per hour. In the South-Central (SC) area, explosive activity was produced by at least two vents. The explosions were mainly of low and medium intensity, composed of fine materials (ash), sometimes mixed with coarse materials (lapilli and bombs). The average explosion frequency ranged from less than 1 to 6 events/h.
Observations during the inspection on June 5, 2025.
On the morning of June 5, INGV personnel, as part of a UN departmental project, conducted an inspection in the summit area (Pizzo sopra la Fossa) to characterize the morphostructural changes of the crater terrace, observe explosive activity, and install instruments.
During the inspection, it was observed that the fracture field around the SW crater had widened compared to the observations on April 10, 2025. Furthermore, the two fractures, oriented approximately east-west, were associated with a minor thermal anomaly.
The explosive activity produced by the South-Central zone was not intense (1 to 3 events/h); it was characterized by strong explosions of rising gas producing modest projections of lava fragments associated with fine materials (ash). Regarding the North Crater area, in sector N1, explosions of coarse materials mixed with fine materials were observed on average every 3 to 4 events/h, reaching heights of 100 to 150 m, while in sector N2, sporadic and modest jets of gas and coarse materials were observed.
Source : INGV.
Photo : Stromboli stati d’animo / Sebastiano Cannavo
Hawaii , Kilauea :
Tuesday, June 10, 2025, 9:59 AM HST (Tuesday, June 10, 2025, 19:59 UTC)
19°25’16 » N 155°17’13 » W,
Summit Elevation 4091 ft (1247 m)
Current Volcano Alert Level: WATCH
Current Aviation Color Code: ORANGE
Activity Summary:
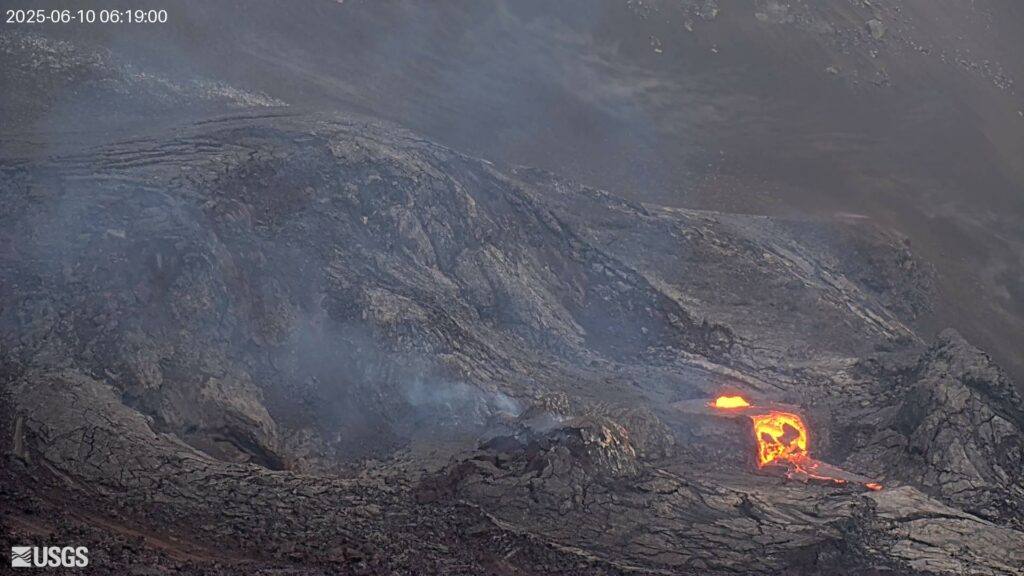
Episode 25 precursory activity has begun in Halema‘uma‘u. Sustained lava fountaining is forecast to begin between tomorrow (Wednesday) and Thursday. However, there is a chance that activity could proceed to high fountaining today. Precursory activity started within Halemaʻumaʻu this morning, June 10. Glow and intermittent lava spattering in the north vent changed to more continuous spattering in the early morning hours. At about 5:54 AM HST, lava overflowed the north vent cone and is currently flowing onto the crater floor. Current activity includes gas pistoning from the north vent and a lava flow onto the crater floor. Summit inflation continues since the end of episode 24 on June 5, 2025.
Fountaining episodes have occurred approximately once per week since the start of the eruption on December 23, 2024. All eruptive activity remains within Hawaiʻi Volcanoes National Park. No significant activity has been noted along Kīlauea’s East Rift Zone or Southwest Rift Zone. Current hazards include volcanic gas emissions and windblown volcanic glass (Pele’s hair) and tephra that have impacted Hawaiʻi Volcanoes National Park and nearby communities.
Summit Observations:
Summit webcams showed glow and scattered spattering at the north vent through yesterday. This changed to more continuous spattering and gas pistoning in the early morning hours. At about 5:54 AM HST, lava overflowed the north vent cone. The north vent continues to generate a lava flow onto the crater floor during high stands of the gas pistoning events.
Vigorous degassing is visible from both the north and south vents. The average sulfur dioxide (SO2) emission rate during inter-episode pauses is typically around 1,200 tonnes per day (t/d). Once high fountaining begins, SO2 emission rates are likely to increase to about 50,000 tonnes/day.
Tiltmeter UWD, near Uēkahuna, has recovered about 13 microradians of inflationary tilt since the end of episode 24 and a tiltmeter near Sandhill (SDH) has recovered 9.5 microradians, since episode 24 ended on June 5.
Source et photo : HVO.
Colombia , Chiles / Cerro Negro :
San Juan de Pasto, June 10, 2025, 5:30 p.m.
Regarding the monitoring of the activity of the Chiles-Cerro Negro Volcanic Complex (CVCCN), the Colombian Geological Survey (SGC), an entity affiliated with the Ministry of Mines and Energy, reports that:
From June 3 to 9, 2025, the main variations in the monitored parameters compared to the previous week were:
● The decline continued, both in terms of occurrence and seismic energy released, following the increase recorded in early May 2025. During the week under review, 659 earthquakes occurred, representing 48% of the seismic activity recorded the previous week, when 1,364 earthquakes were recorded.
● The localized earthquakes were located primarily beneath the Chiles Volcano collapse zone, at depths between 2.8 and 4.7 km from the summit of Chiles Volcano (approximately 4,700 m above sea level), with a maximum magnitude of 1. The other earthquakes were located to the west, southwest, and south of the summit of Chiles Volcano, at distances between 1.3 and 3 km and at depths between 2 and 7.6 km from the summit. The maximum magnitude of these events was 1.5. In addition, a few events were located at distances between 4.4 and 8 km southeast of Chiles Volcano, at depths between 6.7 and 9.6 km from the summit. The largest earthquake, measuring 1.7, was located in this area.
● Analysis of information obtained from satellite sensors and ground stations continues to indicate variations related to deformation processes in the volcanic area.
Based on the assessment and correlation of monitored parameters, the SGC recommends closely monitoring their development through weekly bulletins and other information published through our official channels, as well as instructions from local and departmental authorities and the National Disaster Risk Management Unit (UNGRD).
Volcanic activity remains on yellow alert: active volcano with changes in the baseline behavior of monitored parameters and other manifestations.
Source et photo : SGC
Indonesia , Raung :
Mount Raung erupted on Wednesday, June 11, 2025, at 9:18 WIB. The observed ash column was ± 750 m above the summit (± 4,082 m above sea level). The ash column was white to gray, with moderate to thick intensity, oriented northeast and east. At the time of this report, the eruption was still ongoing.
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION – VONA
Issued : June 11 , 2025
Volcano : Raung (263340)
Current Aviation Colour Code : ORANGE
Previous Aviation Colour Code : orange
Source : Raung Volcano Observatory
Notice Number : 2025RAU008
Volcano Location : S 08 deg 07 min 30 sec E 114 deg 02 min 31 sec
Area : East java, Indonesia
Summit Elevation : 10662 FT (3332 M)
Volcanic Activity Summary :
Eruption with volcanic ash cloud at 02h18 UTC (09h18 local).
Volcanic Cloud Height :
Best estimate of ash-cloud top is around 13062 FT (4082 M) above sea level or 2400 FT (750 M) above summit. May be higher than what can be observed clearly. Source of height data: ground observer.
Other Volcanic Cloud Information :
Ash cloud moving from northeast to east. Volcanic ash is observed to be white to gray. The intensity of volcanic ash is observed from medium to thick.
Remarks :
Tremor recorded on seismogram with maximum amplitude 3 mm. Seismic activity is characterized by continuous tremor
Source : Magma Indonésie .
Photo : Istimewa